Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Every Company Is Required To Take Three Main Financial Decisions, They Are
Every Company Is Required To Take Three Main Financial Decisions, They Are
Uploaded by
royette ladicaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Every Company Is Required To Take Three Main Financial Decisions, They Are
Every Company Is Required To Take Three Main Financial Decisions, They Are
Uploaded by
royette ladicaCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem 1
The procedure starts with the planning step that defines the scope and objectives of financial
management and results in the finance management plan. The initiation step is performed once
the work is approved and the resources needed to manage finances are mobilised. The goal of
financial management is to maximize shareholder wealth. For public companies this is the stock
price, and for private companies this is the market value of the owners' equity.
Decision making helps to utilise the available resources for achieving
the objectives of the organization, unless minimum financial
performance levels are achieved, it is impossible for a business
enterprise to survive over time.
Therefore financial management basically provides a conceptual and
analytical framework for financial decision making.
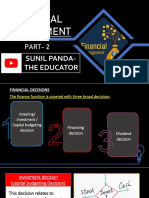
Every company is required to take three main financial
decisions, they are:
1. Investment Decision
2. Financing Decision
3. Dividend Decision
1. Investment Decision:
A financial decision which is concerned with how the firm’s funds are
invested in different assets is known as investment decision.
Investment decision can be long-term or short-term.
A long term investment decision is called capital budgeting decisions
which involve huge amounts of long term investments and are
irreversible except at a huge cost. Short-term investment decisions are
called working capital decisions, which affect day to day working of a
business. It includes the decisions about the levels of cash, inventory
and receivables.
A bad capital budgeting decision normally has the capacity to severely
damage the financial fortune of a business.
A bad working capital decision affects the liquidity and profitability of
a business.
Factors Affecting Investment Decisions / Capital Budgeting
Decisions:
1. Cash flows of the project- The series of cash receipts and payments
over the life of an investment proposal should be considered and
analyzed for selecting the best proposal.
2. Rate of return- The expected returns from each proposal and risk
involved in them should be taken into account to select the best
proposal.
3. Investment criteria involved- The various investment proposals are
evaluated on the basis of capital budgeting techniques. Which involve
calculation regarding investment amount, interest rate, cash flows,
rate of return etc. It is to be considered which technique to use for
evaluation of projects.
2. Financing Decision:
A financial decision which is concerned with the amount of finance to
be raised from various long term sources of funds like, equity shares,
preference shares, debentures, bank loans etc. Is called financing
decision. In other words, it is a decision on the ‘capital structure’ of the
company.
Capital Structure Owner’s Fund + Borrowed Fund
Financial Risk:
The risk of default on payment of periodical interest and repayment of
capital on ‘borrowed funds’ is called financial risk.
Factors Affecting Financing Decision:
1. Cost- The cost of raising funds from different sources is different.
The cost of equity is more than the cost of debts. The cheapest source
should be selected prudently.
2. Risk- The risk associated with different sources is different. More
risk is associated with borrowed funds as compared to owner’s fund as
interest is paid on it and it is also repaid after a fixed period of time or
on expiry of its tenure.
3. Flotation cost- The cost involved in issuing securities such as
broker’s commission, underwriter’s fees, expenses on prospectus etc.
Is called flotation cost. Higher the flotation cost, less attractive is the
source of finance.
4. Cash flow position of the business- In case the cash flow position of
a company is good enough then it can easily use borrowed funds.
5. Control considerations- In case the existing shareholders want to
retain the complete control of business then finance can be raised
through borrowed funds but when they are ready for dilution of
control over business, equity shares can be used for raising finance.
6. State of capital markets- During boom period, finance can easily be
raised by issuing shares but during depression period, raising finance
by means of debt is easy.
3. Dividend Decision:
A financial decision which is concerned with deciding how much of the
profit earned by the company should be distributed among
shareholders (dividend) and how much should be retained for the
future contingencies (retained earnings) is called dividend decision.
Dividend refers to that part of the profit which is distributed to
shareholders. The decision regarding dividend should be taken
keeping in view the overall objective of maximizing shareholder s
wealth.
Factors affecting Dividend Decision:
1. Earnings- Company having high and stable earning could declare
high rate of dividends as dividends are paid out of current and past
earnings.
2. Stability of dividends- Companies generally follow the policy of
stable dividend. The dividend per share is not altered in case earning
changes by small proportion or increase in earnings is temporary in
nature.
3. Growth prospects- In case there are growth prospects for the
company in the near future then, it will retain its earnings and thus, no
or less dividend will be declared.
4. Cash flow positions- Dividends involve an outflow of cash and thus,
availability of adequate cash is foremost requirement for declaration
of dividends.
5. Preference of shareholders- While deciding about dividend the
preference of shareholders is also taken into account. In case
shareholders desire for dividend then company may go for declaring
the same. In such case the amount of dividend depends upon the
degree of expectations of shareholders.
6. Taxation policy- A company is required to pay tax on dividend
declared by it. If tax on dividend is higher, company will prefer to pay
less by way of dividends whereas if tax rates are lower, then more
dividends can be declared by the company.
A finance manager has to find answers to questions such as:
i. What should be the size of firm?
ii. In which assets / projects funds should be invested?
iii. Investments in which assets / projects should be reduced or
discontinued?
Capital budgeting decisions determine the fixed assets composition of
a firm’s Balance Sheet. Capital budgeting decision gives rise to
operating risk or business risk of a firm.
Risk-Return Trade-Off:
Risk and return move in tandem. Higher the risk, higher the return.
Lower the risk, lower the return. This holds true for all investments
(projects & assets).
A finance manager seeks to select projects / assets which:
(a) Minimize the risk for given level of return or
(b) Maximize return for given degree of risk.
Hence there is a risk return trade off in case of capital budgeting
decision. Investment in small plant is less risky than investment in
large plant. But at the same time small plant generates lower return
than a large plant. Hence deciding about the optimal size of the plant
requires a careful analysis of risk and return.
Risk return tradeoff is involved in capital structure decision as well.
Usually Debt is considered cheaper than equity capital because
interest on debt is tax deductible. Also since debt is paid before equity,
risk is lower for investors and so they demand lower return on debt
investments. But excessive debt is riskier than equity capital from the
company’s viewpoint as debt obligations have to be compulsorily met
even if firm incurs losses.
Thus there is a risk-return trade-off in deciding the optimal financing
mix. On one hand, debt has lower cost of capital thus employing more
debt would mean higher returns but is riskier while on the other hand,
equity capital gives lower return due to higher cost of capital but is less
risky.
Dividend decision also involves risk return trade off. Generally
investors expect dividends because dividends resolve future un-
certainty attached with capital gains. So a company should pay
dividends. However when a company, having profitable investment
opportunities pays dividends, it has to raise funds from external
sources which are costlier than retained earnings.
Hence return from the project reduces. A high dividend payout is less
risky but also results in less return while a low dividend payout is
more risky but results in high return in case of growing firms.
Therefore a firm has to strike a balance between dividends and
retained earnings so as to satisfy investors’ expectations.
Working capital management also involves risk-re- turn trade off as it
affects liquidity and profitability of a firm. Liquidity is inversely
related to profitability, i.e., increase in liquidity results in decrease in
profitability and vice versa. Higher liquidity would mean having more
of current assets. This reduces risk of default in meeting short term
obligations.
But current assets provide lower return than fixed assets and hence
reduce profitability as funds that could earn higher return via
investment in fixed assets are blocked in current assets. Thus higher
liquidity would mean lower risk but also lower profits and lower
liquidity would mean more risk but more returns. Therefore the
finance manager should have optimal level of working capital.
You might also like
- About Financial Accounting - Volume 1 by F. Doussy, R.N. Ngcobo, Rehwinkel, D Scheepers, D ScottDocument401 pagesAbout Financial Accounting - Volume 1 by F. Doussy, R.N. Ngcobo, Rehwinkel, D Scheepers, D ScottRegs Accex100% (2)
- Gene Sekur SolutionsDocument11 pagesGene Sekur SolutionsxsnoweyxNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - ACTIVITIESDocument9 pagesChapter 5 - ACTIVITIESSophia De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Financial Analyst Certification ProgramDocument41 pagesFinancial Analyst Certification ProgramChris Opuba88% (8)
- Elements of Corporate FinanceDocument9 pagesElements of Corporate FinanceReiki Channel Anuj Bhargava100% (1)
- Exercise - Accounting - Worksheet - Historia CompanyDocument15 pagesExercise - Accounting - Worksheet - Historia Companytristan ignatiusNo ratings yet
- Financial Management DPSDocument19 pagesFinancial Management DPSYashasviNo ratings yet
- Types of Financial Decisions in Financial ManagementDocument20 pagesTypes of Financial Decisions in Financial ManagementRahul Upadhayaya100% (1)
- DJMD SjdnajkDocument14 pagesDJMD Sjdnajksuhaib shaikhNo ratings yet
- Types of Financial Decisions: Investment Decision, Financing Decision, Dividend Decision and Working Capital Management DecisionDocument4 pagesTypes of Financial Decisions: Investment Decision, Financing Decision, Dividend Decision and Working Capital Management DecisionCjhay MarcosNo ratings yet
- Busines DDocument5 pagesBusines DMadhav SakhujaNo ratings yet
- FM Material UNIT-IIDocument5 pagesFM Material UNIT-IIananthineevs7btsNo ratings yet
- Three (3) Major Decisions The Finance Manager Would TakeDocument11 pagesThree (3) Major Decisions The Finance Manager Would TakeJohn Verlie EMpsNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1: Submitted FromDocument16 pagesAssignment # 1: Submitted FromAbdullah AliNo ratings yet
- A. Investment Decision (Capital Budgeting Decision) :: 1. Cash Flow of The ProjectDocument21 pagesA. Investment Decision (Capital Budgeting Decision) :: 1. Cash Flow of The ProjectRagav AnNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTDocument34 pagesChapter 9 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTLatha VarugheseNo ratings yet
- Ch9 Financial Management XII 2Document33 pagesCh9 Financial Management XII 2Keshvi AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 9Document7 pagesChapter - 9sonal2901No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesFinancial ManagementGaming with AyushNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagmentDocument34 pagesFinancial ManagmentDarsh AroraNo ratings yet
- 12 Business Studies CH 09 Financial ManagementDocument6 pages12 Business Studies CH 09 Financial ManagementMeera TalrejaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document29 pagesChapter 7fifisaffiya05No ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument12 pagesFinancial ManagementnandiniwadhwanwNo ratings yet
- of BST Chapter 9 - (Financial Management)Document38 pagesof BST Chapter 9 - (Financial Management)shreya61062No ratings yet
- Financial Management: Dr. Saurabh Pratap Iiit DM JabalpurDocument40 pagesFinancial Management: Dr. Saurabh Pratap Iiit DM JabalpurPrince SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document22 pagesChapter 1Nabbaale hanifahNo ratings yet
- Financial ManagementDocument16 pagesFinancial ManagementRahul PuriNo ratings yet
- Functions of Financial ManagementDocument5 pagesFunctions of Financial ManagementAthar KhanNo ratings yet
- chp1 Financial ManagementDocument14 pageschp1 Financial ManagementHuda ShahNo ratings yet
- Business FinanceDocument91 pagesBusiness FinanceIStienei B. EdNo ratings yet
- FINANCIAL MANGEMENT - Microsoft OneNote OnlineDocument6 pagesFINANCIAL MANGEMENT - Microsoft OneNote OnlineRajat SharmaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management NotesDocument12 pagesFinancial Management NotesSia AroraNo ratings yet
- Financing DecisionsDocument14 pagesFinancing DecisionsNandita ChouhanNo ratings yet
- FM8 Module 4Document5 pagesFM8 Module 4Kim HeidelynNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Financial DecisionsDocument4 pagesFactors Affecting Financial Decisionsshubham_cool1996No ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 9 Business Studies Revision NotesDocument15 pagesClass 12 Chapter 9 Business Studies Revision NotesFahmida khanamNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Chapter 9 Business Studies Revision NotesDocument15 pagesClass 12 Chapter 9 Business Studies Revision NotesShanel VazNo ratings yet
- Unit 5 Financial Management Complete NotesDocument17 pagesUnit 5 Financial Management Complete Notesvaibhav shuklaNo ratings yet
- Meaning of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesMeaning of Financial ManagementMar JinitaNo ratings yet
- 3.intro To Financial Institution and MarketDocument28 pages3.intro To Financial Institution and MarketKimberly FloresNo ratings yet
- CAIIB-Financial Management-Module B Study of Financial StatementsDocument91 pagesCAIIB-Financial Management-Module B Study of Financial StatementsDeepak RathoreNo ratings yet
- Caiib Fmmodbacs Nov08Document91 pagesCaiib Fmmodbacs Nov08monirba48No ratings yet
- FM1.1 IntroductionDocument4 pagesFM1.1 IntroductionnehaasinghhNo ratings yet
- Entreprenurship & Management-Module 4 - WatermarkDocument11 pagesEntreprenurship & Management-Module 4 - Watermark81 SYBCOM A SHREYA SHINDENo ratings yet
- Buss Finance-IDocument14 pagesBuss Finance-IMuscle mindNo ratings yet
- Financial Management Full Chapter Part 2Document15 pagesFinancial Management Full Chapter Part 2DIVEY KocharNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 FMDocument7 pagesUnit 1 FMpurvang selaniNo ratings yet
- Topic OneDocument15 pagesTopic OnechelseaNo ratings yet
- Financial Management NotesDocument10 pagesFinancial Management NotesMubarak Basha100% (1)
- 1.financial ManagementDocument86 pages1.financial ManagementKiran MohanNo ratings yet
- Financial Management - Meaning, Objectives and Functions Meaning of Financial ManagementDocument6 pagesFinancial Management - Meaning, Objectives and Functions Meaning of Financial ManagementsupriyaswainNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow of The Project: Whenever A Company Is Investing Huge Funds in An InvestmentDocument4 pagesCash Flow of The Project: Whenever A Company Is Investing Huge Funds in An InvestmentkeshavNo ratings yet
- MBA in Financial ManagementDocument14 pagesMBA in Financial Managementedmosdigitex1485No ratings yet
- BS Chap 9Document7 pagesBS Chap 9Shan ShanNo ratings yet
- Functions of FinANCEDocument39 pagesFunctions of FinANCEPalak WadhwaNo ratings yet
- FM ExamDocument13 pagesFM Examtigist abebeNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii-1Document13 pagesUnit Iii-1Archi VarshneyNo ratings yet
- Business Finance NotesDocument42 pagesBusiness Finance Noteskaiephrahim663No ratings yet
- CFMADocument36 pagesCFMAArlan Joseph LopezNo ratings yet
- Port City International University: Assignment OnDocument9 pagesPort City International University: Assignment OnRACHELNo ratings yet
- Port City International University: Assignment OnDocument9 pagesPort City International University: Assignment OnRACHELNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Financial ManagementDocument29 pagesChapter 9 Financial ManagementAjay pandeyNo ratings yet
- Financial Management: Financial Management Refers To That Part of TheDocument19 pagesFinancial Management: Financial Management Refers To That Part of TheMayuraa ShekatkarNo ratings yet
- Dividend PolicyDocument18 pagesDividend Policybishnu paudelNo ratings yet
- 7-Training and Assessment CalendarDocument3 pages7-Training and Assessment Calendarroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Trainees ProfileDocument6 pagesTrainees Profileroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Training Delivery PlanDocument21 pagesTraining Delivery Planroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- TESDA Circular No. 045-A-2021Document1 pageTESDA Circular No. 045-A-2021royette ladicaNo ratings yet
- FINANCE REPORT - Need To ReleaseDocument2 pagesFINANCE REPORT - Need To Releaseroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- FUHS Secretary CertificateDocument1 pageFUHS Secretary Certificateroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Annex "D": Submission of E-Mail Addresses and Mobile Numbers (For Corporations)Document2 pagesAnnex "D": Submission of E-Mail Addresses and Mobile Numbers (For Corporations)royette ladica100% (1)
- How To Open A BarDocument27 pagesHow To Open A Barroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Math10 - Q1 - Mod4 - Finding-The-SumOf Week 4Document19 pagesMath10 - Q1 - Mod4 - Finding-The-SumOf Week 4royette ladica100% (1)
- Math10 - Q1 - Mod5 - Illustrating - Geometric - Sequence - Week 4Document16 pagesMath10 - Q1 - Mod5 - Illustrating - Geometric - Sequence - Week 4royette ladica100% (4)
- Rvey/research Project Content: Goal of Survey or Project Excellent Good Fair Poor GradeDocument3 pagesRvey/research Project Content: Goal of Survey or Project Excellent Good Fair Poor Graderoyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Chap - Test - CH4 - Financial Ratio Analysis and Their Implications To ManagementDocument10 pagesChap - Test - CH4 - Financial Ratio Analysis and Their Implications To Managementroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. DateDocument5 pagesSubject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. Dateroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 ActivitiesDocument3 pagesChapter 4 Activitiesroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Flexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP)Document8 pagesFlexible Instructional Delivery Plan (FIDP)royette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Mt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. DateDocument9 pagesMt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. Dateroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Supplies 2019-2020Document43 pagesSupplies 2019-2020royette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Mt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. DateDocument8 pagesMt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. Dateroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Mt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. DateDocument7 pagesMt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. Dateroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- Mt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. DateDocument5 pagesMt. Carmel College: Subject Quarter No. Grade Level Section Module No. Chapter No. Lesson No. Dateroyette ladicaNo ratings yet
- C. The Carrying Amount of Property, Plant and Equipment : Financial Accounting Theory Preweek Summary IiDocument56 pagesC. The Carrying Amount of Property, Plant and Equipment : Financial Accounting Theory Preweek Summary Iibobo kaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Accounting Testbank For Final 6eDocument35 pagesAdvanced Accounting Testbank For Final 6etoto100% (1)
- C18 - Defined Benefit Plan PDFDocument23 pagesC18 - Defined Benefit Plan PDFKristine Diane CABAnASNo ratings yet
- ACC Multiple Choice Flashcards - QuizletDocument1 pageACC Multiple Choice Flashcards - QuizletIslam SamirNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Classification of CostDocument13 pagesMeaning and Classification of Costpooja456No ratings yet
- 648235Document5 pages648235mohitgaba19No ratings yet
- Quiz 1 Cost AccountingDocument3 pagesQuiz 1 Cost AccountingKryss Clyde TabliganNo ratings yet
- ACC 106 SAS 2 NOTES - Review of The Accounting ProcessDocument5 pagesACC 106 SAS 2 NOTES - Review of The Accounting ProcessbakdbdkNo ratings yet
- Preparation of Financial Statements 081112 RevisedDocument89 pagesPreparation of Financial Statements 081112 RevisedNorhian AlmeronNo ratings yet
- Intacc 3 HWDocument7 pagesIntacc 3 HWMelissa Kayla ManiulitNo ratings yet
- Akuntansi Tugas 4Document2 pagesAkuntansi Tugas 4Biyan ArdanaNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting and Reporting: Page 1 of 4Document4 pagesFinancial Accounting and Reporting: Page 1 of 4ebshuvoNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement Analysis UnileverDocument19 pagesFinancial Statement Analysis UnileverGelay MagatNo ratings yet
- Pre-Feasibility Study: Bangle Making WorkshopDocument15 pagesPre-Feasibility Study: Bangle Making WorkshopRohs VantageNo ratings yet
- Pas 1Document7 pagesPas 1BUQUIRAN, MARY JOYNo ratings yet
- Month Day Month Day: 526-1212, Extension 2403 / 8231-10-73 (Temporary)Document209 pagesMonth Day Month Day: 526-1212, Extension 2403 / 8231-10-73 (Temporary)Ivan ChiuNo ratings yet
- Managerial AccountingDocument4 pagesManagerial AccountingMitch Tokong MinglanaNo ratings yet
- 8 Keys Ratios To Look at Before Buying A ShareDocument10 pages8 Keys Ratios To Look at Before Buying A ShareSiva SubrahmanyamNo ratings yet
- Tally Ledgers and GroupsDocument7 pagesTally Ledgers and Groupshrkumar440No ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document6 pagesTutorial 4Amirul Noris0% (1)
- Double Entry Illustrative ProblemDocument7 pagesDouble Entry Illustrative ProblemYana JaureguiNo ratings yet
- SaadDocument6 pagesSaadSaadUllah MohmandNo ratings yet
- Course Folder Fall 2022Document26 pagesCourse Folder Fall 2022Areeba QureshiNo ratings yet
- Daniel Dobbins PDFDocument1 pageDaniel Dobbins PDFAbhishek MishraNo ratings yet
- Soneri Bank Ltd. Company Profile: Key PeoplesDocument4 pagesSoneri Bank Ltd. Company Profile: Key PeoplesAhmed ShazadNo ratings yet