Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 viewsAuditing: An Overview
Auditing: An Overview
Uploaded by
Abigail ManggasAuditing is a systematic process of objectively obtaining and evaluating evidence to determine if assertions about economic actions and events are accurate according to established criteria. The auditor assesses risks to the fair presentation of financial statements and designs audit procedures to obtain sufficient evidence. The audit has three objectives - to determine if financial statements are fairly presented, transactions are recorded accurately, and disclosures are adequate. The risk-based audit process involves planning, risk assessment, risk response procedures, and reporting conclusions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- GRC Capability Model v3 December 2015 PDFDocument122 pagesGRC Capability Model v3 December 2015 PDFMelissa MorgaNo ratings yet
- SOX Internal Controls ChecklistDocument31 pagesSOX Internal Controls Checklistkamal_bagchi100% (6)
- Acctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlDocument12 pagesAcctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlTrayle HeartNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDocument10 pagesAuditing and Assurance PrinciplesJoannah maeNo ratings yet
- CPA Exam - Aud Flashcards - QuizletDocument16 pagesCPA Exam - Aud Flashcards - QuizletWilliam SusetyoNo ratings yet
- At 02Document5 pagesAt 02Mitch PacienteNo ratings yet
- 4 5850471109056532136Document38 pages4 5850471109056532136Yehualashet MulugetaNo ratings yet
- .Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument39 pages.Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary Activitiespamelajanmea2018No ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of AuditingDocument13 pages1 - Overview of AuditingZooeyNo ratings yet
- Definition and Objective of AuditDocument7 pagesDefinition and Objective of AuditZednem JhenggNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 & 12 - Assurance and Non-Assurance ServicesDocument47 pagesTopic 11 & 12 - Assurance and Non-Assurance Services2022930579No ratings yet
- Aud C11Document46 pagesAud C11FATIN 'AISYAH MASLAN ABDUL HAFIZNo ratings yet
- Summary of Auditing Assurance ServicesDocument3 pagesSummary of Auditing Assurance ServicesMichael BatallaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Overview of The Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument4 pagesLECTURE 2 - Overview of The Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesAlexandra Nicole IsaacNo ratings yet
- Audit DictionayDocument6 pagesAudit DictionayGeraldine PeredillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Gerrelle Cap-atanNo ratings yet
- "Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerDocument4 pages"Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Performing Substantive TestDocument29 pagesUnit VI Performing Substantive TestMark GerwinNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2ADocument10 pagesChapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2AjejelaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing Module GuideDocument230 pagesAdvanced Auditing Module GuideArtwell Zulu100% (1)
- Practical Auditing NotesDocument114 pagesPractical Auditing NotesdevasrisaivNo ratings yet
- Module 1 AUDIT PLANNINGDocument3 pagesModule 1 AUDIT PLANNINGLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Reporting and Materiality Supplement ForDocument29 pagesReporting and Materiality Supplement ForSirak AynalemNo ratings yet
- Audit MethodologyDocument20 pagesAudit MethodologyVikasAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument40 pagesOverview of Audit Process and Preliminary Activitiesgelly studiesNo ratings yet
- Nama:Annisa Wijayanti Npm:185401Document22 pagesNama:Annisa Wijayanti Npm:185401annisa wijayantiNo ratings yet
- Template Presentation - Entrance and Exit MeetingsDocument48 pagesTemplate Presentation - Entrance and Exit MeetingsRheneir MoraNo ratings yet
- Audit Module 1Document13 pagesAudit Module 1Danica GeneralaNo ratings yet
- Audit - Kelompok 1 Financial Statement Audits and Auditor ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesAudit - Kelompok 1 Financial Statement Audits and Auditor Responsibilitiesminuh aNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning StepsDocument42 pagesAudit Planning StepsYismawNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsMaeNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Aue301pDocument168 pagesStudy Notes Aue301pDNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Chapter+5 Audit+PlanningDocument19 pagesChapter+5 Audit+Planningjeff herradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 (Short Notes)Document7 pagesChapter - 1 (Short Notes)Aakansha SinghNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDocument19 pagesAuditing and Assurance Principleskanroji1923No ratings yet
- A6.4 A UNIT 1 & 2 Auditing PracticesDocument27 pagesA6.4 A UNIT 1 & 2 Auditing PracticesGaurav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Auditing in CIS Environment Review of Auditing ConceptsDocument8 pagesAuditing in CIS Environment Review of Auditing ConceptsSani BautisTaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Advanced Auditing.Document47 pagesCH 1 Advanced Auditing.Ermiyas KebedeNo ratings yet
- Chapt 1Document22 pagesChapt 1Sidra SwatiNo ratings yet
- The Process of Auditing: Auditor Re-Elected at AGM Engagement Letter Signing AuditDocument6 pagesThe Process of Auditing: Auditor Re-Elected at AGM Engagement Letter Signing AuditPhebieon MukwenhaNo ratings yet
- PSA NotesDocument15 pagesPSA NotesHanis MaisarahNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document15 pagesCH 1Harsh DaneNo ratings yet
- Auditing: An IntroductionDocument121 pagesAuditing: An IntroductionKhushbu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Auditing The CPA ProfessionDocument65 pagesOverview of Auditing The CPA ProfessionnabilaqurotaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsKatherine MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Pengertian Internal AuditDocument14 pagesPengertian Internal AuditIqbal SubhanNo ratings yet
- Audit TheoryDocument60 pagesAudit TheoryJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Auditing: Reference: Chapter Two of Audit and Assurance PrincipleDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Auditing: Reference: Chapter Two of Audit and Assurance PrincipleRoyce Maenard EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- Auditing Interview Prepartaion Notes by Alan Biju Palak ACCA PDFDocument15 pagesAuditing Interview Prepartaion Notes by Alan Biju Palak ACCA PDFMeghnaNo ratings yet
- C1 Inter Audit 2024Document16 pagesC1 Inter Audit 2024Aditya JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Nicale JeenNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument18 pagesAuditingonyrulanamNo ratings yet
- Module 1 BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT AUDIT PDFDocument8 pagesModule 1 BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT AUDIT PDFNiño Mendoza Mabato100% (1)
- PEM AuditDocument29 pagesPEM AuditNajib ElNo ratings yet
- Audit: Meaning, External Audit, Internal Audit, Project Audit Mechanism As Per GOB and Donor GuidelinesDocument30 pagesAudit: Meaning, External Audit, Internal Audit, Project Audit Mechanism As Per GOB and Donor GuidelinesNasin BabuNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument13 pagesAuditingRamos JovelNo ratings yet
- At.3207-Considering Materiality and Audit RiskDocument5 pagesAt.3207-Considering Materiality and Audit RiskDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Lessons4 8AuditingandAssurancePrinciplesLecturesDocument55 pagesLessons4 8AuditingandAssurancePrinciplesLecturesHya Althea DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Module #02 - Audits of Historical Financial InformationDocument3 pagesModule #02 - Audits of Historical Financial InformationRhesus UrbanoNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsNo ratings yet
- Awash Bank CSRDocument17 pagesAwash Bank CSRMõ HãzàrdNo ratings yet
- Management Review MOM ODS-QHSE-SF-044 V01: Participants Distribution Name Position Attendance TypeDocument2 pagesManagement Review MOM ODS-QHSE-SF-044 V01: Participants Distribution Name Position Attendance TypeFahmi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Account Project 1Document17 pagesAccount Project 1Roshan SinghNo ratings yet
- 09 Standard CostingDocument5 pages09 Standard CostingabcdefgNo ratings yet
- NoidaDocument23 pagesNoidaAmmar Tambawala100% (1)
- Corporate Governance in Banks: Importance: Highly ImportantDocument16 pagesCorporate Governance in Banks: Importance: Highly ImportantMd NawazishNo ratings yet
- Volume I (Operating Procedures)Document73 pagesVolume I (Operating Procedures)Jay PabloNo ratings yet
- KPCL Notification Aa16 - EnglishDocument5 pagesKPCL Notification Aa16 - EnglishatgsganeshNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6 - Independent Auditor's ReportDocument23 pagesTOPIC 6 - Independent Auditor's ReportLANGITBIRUNo ratings yet
- Trust Deed SampleDocument12 pagesTrust Deed SampleCA Sumanth AshokNo ratings yet
- Transfer of SharesDocument4 pagesTransfer of Shareskjvbhkxcj100% (1)
- Risk Management - Concepts and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesRisk Management - Concepts and ApplicationsStephen EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Stages in Implementing Export TransactionDocument19 pagesStages in Implementing Export TransactionGagan KauraNo ratings yet
- 4040 CD 89981928Document3 pages4040 CD 89981928Sachin N GudimaniNo ratings yet
- Finance Manager, FP&A ManagerDocument3 pagesFinance Manager, FP&A Managerapi-77611892No ratings yet
- QUIZ No. 1Document6 pagesQUIZ No. 1Kathleen FrondozoNo ratings yet
- Verification of Assets and LiabilitiesDocument51 pagesVerification of Assets and Liabilitiessherly joiceNo ratings yet
- ICA Ghana Course Content and RequirementDocument12 pagesICA Ghana Course Content and RequirementRosetta Renner0% (1)
- Accounting For Issunce of Shares Lecture 3Document49 pagesAccounting For Issunce of Shares Lecture 3Huneyn Ali QuadriNo ratings yet
- Huk 3Document2 pagesHuk 3Kharen Mae M. GulfoNo ratings yet
- Guidebook Productivity GainsharingDocument12 pagesGuidebook Productivity GainsharingSujatman SaputraNo ratings yet
- Corp GovernanceDocument37 pagesCorp GovernanceM Navneeth RoyNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Training Course BrochureDocument5 pagesPreparatory Training Course BrochuremuthakkerNo ratings yet
- CFO Chief Financial Officer in Chicago IL Resume Philip GrybasDocument3 pagesCFO Chief Financial Officer in Chicago IL Resume Philip GrybasPhilipGrybasNo ratings yet
- BFIA (Mortgage Finance Regulations)Document24 pagesBFIA (Mortgage Finance Regulations)KELVIN A JOHNNo ratings yet
- Contract Management PlanDocument19 pagesContract Management PlanErnest AlexNo ratings yet
- Thirteen: Reporting For Components Interim Reports Reporting For The SECDocument66 pagesThirteen: Reporting For Components Interim Reports Reporting For The SECFathinus SyafrizalNo ratings yet
- IC Internal Audit Checklist 8624Document3 pagesIC Internal Audit Checklist 8624Tarun KumarNo ratings yet
Auditing: An Overview
Auditing: An Overview
Uploaded by
Abigail Manggas0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views18 pagesAuditing is a systematic process of objectively obtaining and evaluating evidence to determine if assertions about economic actions and events are accurate according to established criteria. The auditor assesses risks to the fair presentation of financial statements and designs audit procedures to obtain sufficient evidence. The audit has three objectives - to determine if financial statements are fairly presented, transactions are recorded accurately, and disclosures are adequate. The risk-based audit process involves planning, risk assessment, risk response procedures, and reporting conclusions.
Original Description:
Auditing overview in Corporate Governance
Original Title
Auditing
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAuditing is a systematic process of objectively obtaining and evaluating evidence to determine if assertions about economic actions and events are accurate according to established criteria. The auditor assesses risks to the fair presentation of financial statements and designs audit procedures to obtain sufficient evidence. The audit has three objectives - to determine if financial statements are fairly presented, transactions are recorded accurately, and disclosures are adequate. The risk-based audit process involves planning, risk assessment, risk response procedures, and reporting conclusions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
21 views18 pagesAuditing: An Overview
Auditing: An Overview
Uploaded by
Abigail ManggasAuditing is a systematic process of objectively obtaining and evaluating evidence to determine if assertions about economic actions and events are accurate according to established criteria. The auditor assesses risks to the fair presentation of financial statements and designs audit procedures to obtain sufficient evidence. The audit has three objectives - to determine if financial statements are fairly presented, transactions are recorded accurately, and disclosures are adequate. The risk-based audit process involves planning, risk assessment, risk response procedures, and reporting conclusions.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 18
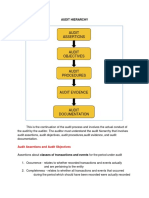
Auditing: An Overview
●A systematic process by which a
competent, independent person
objectively obtaining and evaluating
evidence regarding assertions about
Auditing economic actions and events to ascertain
the degree of correspondence between
these assertions and established criteria,
communicating the results to interested
users.
●Are representations by
management, explicit or
Assertions otherwise, that are embodied in
the Financial Statement.
●Classes of transactions and events -
refer primarily to income statement
accounts.
Categories of
●Account Balances – refer to balance
Assertions
sheet accounts.
●Presentation and Disclosure – refer to
entire Financial Statement.
● Occurrence – transactions and events that have been
recorded have occurred and pertain to the entity.
● Completeness – all transactions and events that should
have been recorded have been recorded.
Classes of ● Accuracy – amounts and other data relating to recorded
transactions transactions and events have been recorded
appropriately.
and events
● Cutoff – transaction and events have been recorded in
the correct accounting period.
● Classification – transactions and events have been
recorded in the proper accounts.
● Existence – assets, liabilities, and equity interest exist.
● Rights and obligations – the entity holds or controls the
right to assets, and liabilities are the obligations of the
entity.
Account ● Completeness – all assets, liabilities and equity interest
Balance that should have been recorded have been recorded.
● Valuation and Allocation – assets, liabilities, and equity
interests are included in the Financial Statements at
appropriate amounts and any resulting valuation or
allocation adjustments are appropriately recorded.
● Occurrence and rights and obligations – disclosed
events, transactions, and other matters have occurred
and pertain to the entity.
● Completeness – all disclosures that should have been
Presentation included in the Financial Statements have been included.
and Disclosure ● Classification and Understandability – financial
information is appropriately presented and described,
and disclosures are clearly expressed.
● Accuracy and valuation – financial and other
information are disclosed fairly and appropriate amount.
●Financial Statement Audit
Types of Audit ●Operations Audit
●Compliance Audit
●This is conducted to determine whether
Financial Statements present fairly the
Financial financial position, performance, and cash
flows of an entity in accordance with the
Statement AFRF (the criteria). The AFRF may be
Audit the full PFRS, PFRS for SMEs, other
acceptable basis of accounting, or the U.S.
GAAP.
●This is a study of an entity’s specific unit for
purposes of measuring whether that unit
conducted its operations efficiently and
Operational effectively.
Audit ●Effectiveness is a measure of whether an entity
(Performance achieves its goals and objectives. (program
result audit)
Audit)
●Efficiency shows how well an entity uses its
resources to achieve its goals. (management
audit)
●This is an evaluation to determine
Compliance whether an entity is following
Audit specific policies, rules, or regulations
set out by higher authority.
External ●These are audits performed by
professional accountant in public practice
Independent who are independent of the entities whose
Audits assertions are the audit subject matter.
●An independent, objective assurance and
Internal Audits consulting activity designed to add value
and improve an organization’s operation.
●Involves determination whether
government funds are being handled
properly in compliance with the
Government
applicable laws and regulations,
Audit government programs are conducted
effectively and efficiently, and Financial
Statements are fairly presented.
●To obtain reasonable assurance whether
the financial statements are free from
material misstatement, whether due to
fraud or error, to enable the auditor to
Auditor’s express an opinion on whether the
overall financial statements are prepared, in all
objectives material respects, in accordance with
AFRF, and;
●To report on the financial statements and
communicate the auditor’s findings.
●Audit risk is the risk (or likelihood) that
the auditor gives an appropriate audit
opinion when the financial statements are
materially misstated (beta risk). Audit
Audit Risk risk does not include the risk that the
auditor might express an opinion that the
financial statement are materially
misstated when they are not (alpha risk).
●Phase 1 – Risk Assessment – the auditor decides
whether to accept an audit engagement.
●Phase 2 – Risk Response – The assessed
ROMM serves as a basis for the auditor’s
Risk – Based responses to obtain sufficient appropriate audit
evidence.
Audit Process
●Phase 3 Conclusion and Reporting – The auditor
evaluates the results of the audit from the audit
evidence obtained and form an opinion on the
financial statements and express clearly that
opinion through a written report.
Phase 3 –
Phase 1 – Risk Assessment Phase 2 – Risk Response Conclusion and
Reporting
Preliminary Planning the Responding to Determining the Completing the
Engagement Audit Assessed Risks Extent of Audit and
Activities Testing Considering
Post Audit
Responsibilities
The Determining Understanding Considering Considering Forming the
Risk-Based Materiality the Entity and its Fraud, Error and Work of Other
Environment NOCLAR Practitioner
Auditor’s
Opinion and
Audit Report Contents
Understanding Identifying and Considering Considering Performing and
Approach the Entity’s Assessing Effect of IT Certain Specific Reporting on
Internal Control ROMM Items Specialized
Roadmap Audit
Engagement
Professional Judgement and Professional Skepticism
Audit Evidence and Documentation
Audit Quality
You might also like
- CIS ReportDocument10 pagesCIS ReportMarieNo ratings yet
- GRC Capability Model v3 December 2015 PDFDocument122 pagesGRC Capability Model v3 December 2015 PDFMelissa MorgaNo ratings yet
- SOX Internal Controls ChecklistDocument31 pagesSOX Internal Controls Checklistkamal_bagchi100% (6)
- Acctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlDocument12 pagesAcctg. Major 6 - Auditing and Internal ControlTrayle HeartNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDocument10 pagesAuditing and Assurance PrinciplesJoannah maeNo ratings yet
- CPA Exam - Aud Flashcards - QuizletDocument16 pagesCPA Exam - Aud Flashcards - QuizletWilliam SusetyoNo ratings yet
- At 02Document5 pagesAt 02Mitch PacienteNo ratings yet
- 4 5850471109056532136Document38 pages4 5850471109056532136Yehualashet MulugetaNo ratings yet
- .Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument39 pages.Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary Activitiespamelajanmea2018No ratings yet
- 1 - Overview of AuditingDocument13 pages1 - Overview of AuditingZooeyNo ratings yet
- Definition and Objective of AuditDocument7 pagesDefinition and Objective of AuditZednem JhenggNo ratings yet
- Topic 11 & 12 - Assurance and Non-Assurance ServicesDocument47 pagesTopic 11 & 12 - Assurance and Non-Assurance Services2022930579No ratings yet
- Aud C11Document46 pagesAud C11FATIN 'AISYAH MASLAN ABDUL HAFIZNo ratings yet
- Summary of Auditing Assurance ServicesDocument3 pagesSummary of Auditing Assurance ServicesMichael BatallaNo ratings yet
- LECTURE 2 - Overview of The Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument4 pagesLECTURE 2 - Overview of The Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesAlexandra Nicole IsaacNo ratings yet
- Audit DictionayDocument6 pagesAudit DictionayGeraldine PeredillaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document3 pagesChapter 4Gerrelle Cap-atanNo ratings yet
- "Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerDocument4 pages"Plans Are Worthless But Planning Is Everything." - Dwight D. EisenhowerLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Unit VI Performing Substantive TestDocument29 pagesUnit VI Performing Substantive TestMark GerwinNo ratings yet
- Chapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2ADocument10 pagesChapter14 - Auditing IT Controls Part 1 - BSA2AjejelaNo ratings yet
- Advanced Auditing Module GuideDocument230 pagesAdvanced Auditing Module GuideArtwell Zulu100% (1)
- Practical Auditing NotesDocument114 pagesPractical Auditing NotesdevasrisaivNo ratings yet
- Module 1 AUDIT PLANNINGDocument3 pagesModule 1 AUDIT PLANNINGLady BirdNo ratings yet
- Reporting and Materiality Supplement ForDocument29 pagesReporting and Materiality Supplement ForSirak AynalemNo ratings yet
- Audit MethodologyDocument20 pagesAudit MethodologyVikasAgarwalNo ratings yet
- Overview of Audit Process and Preliminary ActivitiesDocument40 pagesOverview of Audit Process and Preliminary Activitiesgelly studiesNo ratings yet
- Nama:Annisa Wijayanti Npm:185401Document22 pagesNama:Annisa Wijayanti Npm:185401annisa wijayantiNo ratings yet
- Template Presentation - Entrance and Exit MeetingsDocument48 pagesTemplate Presentation - Entrance and Exit MeetingsRheneir MoraNo ratings yet
- Audit Module 1Document13 pagesAudit Module 1Danica GeneralaNo ratings yet
- Audit - Kelompok 1 Financial Statement Audits and Auditor ResponsibilitiesDocument12 pagesAudit - Kelompok 1 Financial Statement Audits and Auditor Responsibilitiesminuh aNo ratings yet
- Audit Planning StepsDocument42 pagesAudit Planning StepsYismawNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Auditing Theory AT.0104-Introduction To Audit of Financial StatementsMaeNo ratings yet
- Study Notes Aue301pDocument168 pagesStudy Notes Aue301pDNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDocument8 pagesLecture Notes: Manila Cavite Laguna Cebu Cagayan de Oro DavaoDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Chapter+5 Audit+PlanningDocument19 pagesChapter+5 Audit+Planningjeff herradaNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 1 (Short Notes)Document7 pagesChapter - 1 (Short Notes)Aakansha SinghNo ratings yet
- Auditing and Assurance PrinciplesDocument19 pagesAuditing and Assurance Principleskanroji1923No ratings yet
- A6.4 A UNIT 1 & 2 Auditing PracticesDocument27 pagesA6.4 A UNIT 1 & 2 Auditing PracticesGaurav MahajanNo ratings yet
- Auditing in CIS Environment Review of Auditing ConceptsDocument8 pagesAuditing in CIS Environment Review of Auditing ConceptsSani BautisTaNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Advanced Auditing.Document47 pagesCH 1 Advanced Auditing.Ermiyas KebedeNo ratings yet
- Chapt 1Document22 pagesChapt 1Sidra SwatiNo ratings yet
- The Process of Auditing: Auditor Re-Elected at AGM Engagement Letter Signing AuditDocument6 pagesThe Process of Auditing: Auditor Re-Elected at AGM Engagement Letter Signing AuditPhebieon MukwenhaNo ratings yet
- PSA NotesDocument15 pagesPSA NotesHanis MaisarahNo ratings yet
- CH 1Document15 pagesCH 1Harsh DaneNo ratings yet
- Auditing: An IntroductionDocument121 pagesAuditing: An IntroductionKhushbu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Overview of Auditing The CPA ProfessionDocument65 pagesOverview of Auditing The CPA ProfessionnabilaqurotaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsDocument6 pagesChapter 2 - The Professional-StandardsKatherine MagpantayNo ratings yet
- Pengertian Internal AuditDocument14 pagesPengertian Internal AuditIqbal SubhanNo ratings yet
- Audit TheoryDocument60 pagesAudit TheoryJNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Auditing: Reference: Chapter Two of Audit and Assurance PrincipleDocument25 pagesIntroduction To Auditing: Reference: Chapter Two of Audit and Assurance PrincipleRoyce Maenard EstanislaoNo ratings yet
- Auditing Interview Prepartaion Notes by Alan Biju Palak ACCA PDFDocument15 pagesAuditing Interview Prepartaion Notes by Alan Biju Palak ACCA PDFMeghnaNo ratings yet
- C1 Inter Audit 2024Document16 pagesC1 Inter Audit 2024Aditya JhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document9 pagesChapter 1Nicale JeenNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument18 pagesAuditingonyrulanamNo ratings yet
- Module 1 BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT AUDIT PDFDocument8 pagesModule 1 BASIC CONCEPTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT AUDIT PDFNiño Mendoza Mabato100% (1)
- PEM AuditDocument29 pagesPEM AuditNajib ElNo ratings yet
- Audit: Meaning, External Audit, Internal Audit, Project Audit Mechanism As Per GOB and Donor GuidelinesDocument30 pagesAudit: Meaning, External Audit, Internal Audit, Project Audit Mechanism As Per GOB and Donor GuidelinesNasin BabuNo ratings yet
- AuditingDocument13 pagesAuditingRamos JovelNo ratings yet
- At.3207-Considering Materiality and Audit RiskDocument5 pagesAt.3207-Considering Materiality and Audit RiskDenny June CraususNo ratings yet
- Lessons4 8AuditingandAssurancePrinciplesLecturesDocument55 pagesLessons4 8AuditingandAssurancePrinciplesLecturesHya Althea DiamanteNo ratings yet
- Module #02 - Audits of Historical Financial InformationDocument3 pagesModule #02 - Audits of Historical Financial InformationRhesus UrbanoNo ratings yet
- The Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsFrom EverandThe Art and Science of Auditing: Principles, Practices, and InsightsNo ratings yet
- Awash Bank CSRDocument17 pagesAwash Bank CSRMõ HãzàrdNo ratings yet
- Management Review MOM ODS-QHSE-SF-044 V01: Participants Distribution Name Position Attendance TypeDocument2 pagesManagement Review MOM ODS-QHSE-SF-044 V01: Participants Distribution Name Position Attendance TypeFahmi AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Account Project 1Document17 pagesAccount Project 1Roshan SinghNo ratings yet
- 09 Standard CostingDocument5 pages09 Standard CostingabcdefgNo ratings yet
- NoidaDocument23 pagesNoidaAmmar Tambawala100% (1)
- Corporate Governance in Banks: Importance: Highly ImportantDocument16 pagesCorporate Governance in Banks: Importance: Highly ImportantMd NawazishNo ratings yet
- Volume I (Operating Procedures)Document73 pagesVolume I (Operating Procedures)Jay PabloNo ratings yet
- KPCL Notification Aa16 - EnglishDocument5 pagesKPCL Notification Aa16 - EnglishatgsganeshNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 6 - Independent Auditor's ReportDocument23 pagesTOPIC 6 - Independent Auditor's ReportLANGITBIRUNo ratings yet
- Trust Deed SampleDocument12 pagesTrust Deed SampleCA Sumanth AshokNo ratings yet
- Transfer of SharesDocument4 pagesTransfer of Shareskjvbhkxcj100% (1)
- Risk Management - Concepts and ApplicationsDocument20 pagesRisk Management - Concepts and ApplicationsStephen EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Stages in Implementing Export TransactionDocument19 pagesStages in Implementing Export TransactionGagan KauraNo ratings yet
- 4040 CD 89981928Document3 pages4040 CD 89981928Sachin N GudimaniNo ratings yet
- Finance Manager, FP&A ManagerDocument3 pagesFinance Manager, FP&A Managerapi-77611892No ratings yet
- QUIZ No. 1Document6 pagesQUIZ No. 1Kathleen FrondozoNo ratings yet
- Verification of Assets and LiabilitiesDocument51 pagesVerification of Assets and Liabilitiessherly joiceNo ratings yet
- ICA Ghana Course Content and RequirementDocument12 pagesICA Ghana Course Content and RequirementRosetta Renner0% (1)
- Accounting For Issunce of Shares Lecture 3Document49 pagesAccounting For Issunce of Shares Lecture 3Huneyn Ali QuadriNo ratings yet
- Huk 3Document2 pagesHuk 3Kharen Mae M. GulfoNo ratings yet
- Guidebook Productivity GainsharingDocument12 pagesGuidebook Productivity GainsharingSujatman SaputraNo ratings yet
- Corp GovernanceDocument37 pagesCorp GovernanceM Navneeth RoyNo ratings yet
- Preparatory Training Course BrochureDocument5 pagesPreparatory Training Course BrochuremuthakkerNo ratings yet
- CFO Chief Financial Officer in Chicago IL Resume Philip GrybasDocument3 pagesCFO Chief Financial Officer in Chicago IL Resume Philip GrybasPhilipGrybasNo ratings yet
- BFIA (Mortgage Finance Regulations)Document24 pagesBFIA (Mortgage Finance Regulations)KELVIN A JOHNNo ratings yet
- Contract Management PlanDocument19 pagesContract Management PlanErnest AlexNo ratings yet
- Thirteen: Reporting For Components Interim Reports Reporting For The SECDocument66 pagesThirteen: Reporting For Components Interim Reports Reporting For The SECFathinus SyafrizalNo ratings yet
- IC Internal Audit Checklist 8624Document3 pagesIC Internal Audit Checklist 8624Tarun KumarNo ratings yet