Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Species Tab.
Species Tab.
Uploaded by
Kobee BacolodOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Species Tab.
Species Tab.
Uploaded by
Kobee BacolodCopyright:
Available Formats
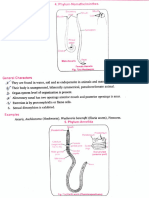
ANNELIDA
Genus Common Name Class Description Parts
Nereis Clamworm or Polychaeta Feeds on small animals o Acron - anterior and posterior
Sandworm Under rock crevices and inside prostomium and mouth
corals o Trunk - bears parapodia
Dorsoventrally flattened body o Pygidium - last segment bearing
80-120 segments anus
o Head
2 pairs of eyes
4 pairs of peristomial cirri
(tentacles)
Pharynx w/ pair of jaw
o Body
Parapodia with setae
(attachment to surfaces)
Notopodium - dorsal
Neuropodium -
ventral
Terminal segment w/ ventral
cirri
Sabella Fanworm or Polychaeta Tube dwelling o Head
Feather duster Sandy to muddy substratum of the Radioles (pinnate arm
worm seafloor processes)
Secretes non-calcareous tube W/ cilia directing food
particles down to the
radiole to mouth
Pheretima Earthworm Oligochaeta Burrow in moist soil o Clitellum - broader segment
Enrich the soil w/ their feces (sexual reproduction/storing
Dorsal side of body is more eggs)
pigmented o Chitinous Setae - ventro laterally
Prostomium - 1st segment
covers the ventral mouth
(pointed)
Peristomium - 2nd segment
Hirudo Leech Hirudinea o Dorso ventrally flat body
medicinalis o 2 suckers (anterior = mouth,
posterior = anus)
o Annuli
o Clitellum - segment 9-10
o Genital pore - found in 11th
segment
MOLLUSCA
Genus Common Name Subphylum Class Description Parts
Achatina Garden Snail Conchifera Gastropoda Shell (coiled)
o Whorl – one complete spiral turn
Body whorl – largest and
the last
Spire – whorls above it
o Mantle
o Mantle cavity
o Shell aperture
Head (only observed for live specimen)
o Mouth with radula (used for
piercing, scraping or drilling)
Muscular foot (only observed for live
specimen)
o Operculum – horny disc, found on
the postero-dorsal surface of the foot
Pila Kuhol Conchifera Gastropoda
Haliotis Abalone Conchifera Gastropoda
Turbo Turban Snails Conchifera Gastropoda
Lambis Conchs Conchifera Gastropoda
Cypraea Cowries Conchifera Gastropoda
Perna Mussels Conchifera Bivalvia Hinge ligament Umbo – the oldest and thickest part of the
Concentric lines – external shell
surface of the shell; Foot – small, brown, cylindrical, narrow
represent growth periods structure (observed in live specimen)
Byssal threads – cluster of dark brown,
threadlike structures that arise from the
heel of the foot (observed in live specimen)
Tridacna Giant Clams Conchifera Bivalvia
Spondylus Scallops Conchifera Bivalvia
Crassostrea Oysters Conchifera Bivalvia
Anondota Freshwater Clam Conchifera Bivalvia
Loligo Squid Conchifera Cephalopoda o Head
Arms
8 short
2 long tentacles
Mouth
Jaws
Radula
o Mantle – dorsally behind the head;
covers entire visceral mass
o Internal shell (gladius)/pen – found
behind the head
o Siphon – cylindrical funnel; part of the
modified foot
Sepia Cuttlefish Conchifera Cephalopoda
Octopus Octopus Conchifera Cephalopoda
Nautilus Nautaloid Conchifera Cephalopoda
Dentalium Elephant’s Tush Conchifera Scaphopoda o Shell – greenish
Shell Apical aperture – narrow end
(posterior)
Main aperture – anterior side of
the body
o Foot – found in the main aperture
Neopilina Conchifera Monoplacophor
a
Chiton Chitom Aculifera Polyplacophora Habitat: intertidal or subtidal o Plates – 8 articulating plates (dorsal
zones side)
o Mantle – where the plates are
embedded (not visible)
o Girdle – thickened marginal portion of
the mantle
o Foot – ventral side (only observable
for live specimen) ▪ Head – reduced
(only observable for live specimen)
Mouth
Radula
Girdle – mantle edge
Pallial groove – mantle cavity
Neomenia Aculifera Aplacophora
Chaetoderm Aculifera Aplacophora
a
ARTHROPODA
Genus Common Name Subphylum Class Parts
Trilobites Trilobita
Limulus Horseshoe crab Chelicerata Merostomata
Sea Spiders Chelicerata Pycnogonida Reduced bodies (abdomen has almost disappeared,
(Pycnogonids) legs are long and clawed)
Head – with long proboscis
o Mouth
o Simple eyes
Feed on soft-bodied invertebrates (i.e. cnidarians)
through sucking
Spiders Chelicerata Arachnida o Prosoma (anterior region of the body)
8 simple eyes (dorsal side)
o Opisthoma (posterior region of the body -
abdomen)
o Pedicel – connects the two (2) body regions
o Cephalothorax
Feeding appendages – first two pairs
Chelicerae – bears the fangs (first pair)
Pedipalps – 2nd pairs used in
manipulating the food
Walking legs
o Ventral portion of the abdomen
Spinnerets – three pairs; silk-producing glands
Scorpions Chelicerata Arachnida Prosoma
Mesosoma
Metasoma
o Telson - defense
Ticks Chelicerata Arachnida Similarities:
Have six legs during larval stage, eight legs = adult
Have one body mass
Capitulum – contains part for feeding
o Mouth – palps, chelicera, hypostome
Mites Chelicerata Arachnida Differences
Ticks = 1 mm long to 3mm (macroscopic); Mites = less
than a mm (microscopic)
Ticks = short hair with hypostome (anchorage) more
visible; Mites = long hairs; hypostome not visible
Ticks lives on their host (Cause lime disease); mites feed
on plants and animals (Scalise)
Penaeus Shrimp Crustacea Malacostraca Tagmata
o Cephalothorax – with 5 pairs of legs
Chelipeds – first pair of large pincers
o Abdomen
Swimmerets – swimming legs
Telson – terminal abdominal segment
Carapace
Rostrum
Eyes
Antennae
Antennules
Portunus Crab Crustacea Malacostraca Head
o Eyes
o Mouth
o Antennae
Carapace
Abdomen
o Determine the gender?
Male – triangular
Female – broad and round
Chelipeds or pincers
Legs
o Last pair has its terminal end modified into
paddle
Lobster Crustacea Malacostraca Cephalothorax
o Carapace
o Eyes
o Rostrum
o Antennae –
o Walking legs
Abdomen
o Six segments
o Telson – found at the tip (flat process) and
bears the anus
Daphnia Water fleas Crustacea Branchiopoda - Considered planktons
Artemia Fairy shrimp/Brine Crustacea Branchiopoda - Filter feeders
shrimp
Cypris Ostracods Crustacea Maxillopoda
Cyclops Copepods Crustacea Maxillopoda
Millipede Uniramia Diplopoda Somites with 2 pairs of legs
Head
Eyes
Antennae
Mandible
Maxillae
Scolopendra Centipede Uniramia Chilopoda - Inhabits moist places
o Head
Mouth
Mandibles (anterior to mouth)
First maxillae (lateral to mouth)
Second maxillae (posterior to the
mouth)
Trunk (divided into segments with paired
appendages)
Poison claws – first somite in the trunk
Telson – last segment that bears the anus
Pediculus Head Louse Uniramia Insecta Head
humanus o Pair of eyes
capitis o antennae
Thorax
o 3 pairs of legs
Abdomen
Ctenocephalide Cat Flea Uniramia Insecta Head
s felis o Eyes
o Antennae
o Bristles (comb)
Thorax
o Legs
Abdomen
Grasshopper Uniramia Insecta Head
o Eyes
2 large compound eyes
3 simple eyes or ocelli (2 are at the
based of the antennae and one in the groove
between them)
o Antennae
Thorax – bears the legs
o Prothorax
o Mesothorax – has a pair of wing (forewing –
leathery)
o Metathorax – has a pair of wing (hindwing –
membranous)
Abdomen – consists of 11 somites
o Spiracle – paired openings lateral to the
abdomen
o Female
Abdomen has a pair of stout, pointed
structure (ovipositor)
o Male
Abdomen has rounded end
o Cercus – small projection on each side behind
the 10th segment
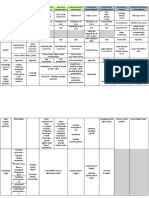
Echinodermata
Genus Common Name Subphylum Class
Linckia Sea Star Asterozoa Asteroidea Arms or rays
Madreporite
Anus
Nonmovable spines (aboral surface)
Pedicellariae
Mouth
Ambulacral groove with tube feet or podia (not
seen in dried specimen)
Archaster Asterozoa Asteroidea
Protoreaster Asterozoa Asteroidea
Culcita Cushion Star Asterozoa Asteroidea
Ophiocoma Brittle Star Asterozoa Ophiuroidea Arms
Central disc - flat with round, pentagonal or
star-shaped appearance
Aboral surface – maybe smooth or have tiny
spines, calcareous plates or shields
Oral surface
o Five triangular-shaped jaws – mouth
o Bursal slits
o Tube feet (podia) or tentacles – small
and devoid of suckers
Ophioplucos Asterozoa Ophiuroidea
Ophioderma Asterozoa Ophiuroidea
Gorgonocephalu Basket Star Asterozoa Ophiuroidea
s
Diadema Sea Urchin Echinozoa Echinodea Mouth with peristomial membrane
Anus (may not be seen in dried specimen)
Madreporite (may not be seen in dried
specimen)
Individual plates
o Perforated plates (ambulacra)
o Nonperforated plates (interambulacral)
Tube feet
Tubercles
Pedicellariae
Laganum Sea Biscuit Echinozoa Echinodea Oral surface
Aboral side
o Mouth
o Petaloids – ambulacral areas arranges
like the petals of a flower
o Podial gills – function for respiration
Ambulacral areas – contains holes for the tube
feet
Echinocardium Heart Urchin Echinozoa Echinodea
Arachnoides True Sand Dollar Echinozoa Echinodea
Holothuria Sea Cucumber Echinozoa Holothuroidea Mouth
Tentacles
Anus = apex of the aboral end
Madreporite – internal
Leptosynapta Echinozoa Holothuroidea
Synapta Echinozoa Holothuroidea
Thyone Echinozoa Holothuroidea
Cucumaria Echinozoa Holothuroidea
Antedon Feather Star Crinozoa Crinoidea Presence of stem or stalk
Attached to a substratum
Parts to label:
o Arms with pinnules
o Calyx (theca)
o Oral surface – only observed among live
specimen
Mouth
Ambulacral areas (5)
Ambulacral grooves and
pinnules
Podia or tube feet (without
sucker)
o Aboral side
Cirri
You might also like
- Oosterbroek 2006 European Families of DipteraDocument209 pagesOosterbroek 2006 European Families of DipteraSimona Lungu50% (4)
- LBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity20 Solidum TanDocument13 pagesLBOBI12 XB1 Group7 Lab-Activity20 Solidum TanFernando Martin BarbaNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom enDocument16 pagesAnimal Kingdom enandrea.tomeo.salvatierraNo ratings yet
- Scan 08 Sep 2020Document3 pagesScan 08 Sep 2020Zenia XoNo ratings yet
- Animalia File 2023-1Document12 pagesAnimalia File 2023-1Syed Zee Waqar GillaniNo ratings yet
- Lec 03Document5 pagesLec 03LAIHAG, CHARINA AIRA L.No ratings yet
- Crustacea (Rakovi) : Insecta MyriapodaDocument37 pagesCrustacea (Rakovi) : Insecta MyriapodadjokalotricNo ratings yet
- Basics of Biology: Professor Vishal Trivedi Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, IIT Guwahati, Assam, IndiaDocument32 pagesBasics of Biology: Professor Vishal Trivedi Department of Biosciences and Bioengineering, IIT Guwahati, Assam, IndiaAKKARSHANA P BIOTECH-2018 BATCHNo ratings yet
- Animal Kingdom Mind MapDocument4 pagesAnimal Kingdom Mind MapVedanti Naik100% (4)
- Trematode - Lecture Notes - 2018Document10 pagesTrematode - Lecture Notes - 2018Ochieng Emmanuel JosephNo ratings yet
- Maribeth ALE ReviewDocument69 pagesMaribeth ALE ReviewJayson BasiagNo ratings yet
- Families AnimaliaDocument1 pageFamilies Animaliaimranminhas2006No ratings yet
- Bat AnatomyDocument10 pagesBat AnatomyAlejo RuilovaNo ratings yet
- PoriferaDocument4 pagesPoriferachildicuNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To EntomologyDocument38 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To EntomologySitti Aminah SalamNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Bio460 Experiment 2Document19 pagesLab Report Bio460 Experiment 2syahira izwaniNo ratings yet
- Dioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaDocument4 pagesDioecious Sexual Commensal Free-Living Locomotion: ParapodiaRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Frog DissectionDocument30 pagesFrog DissectionAubrey Sophia Magdasoc MisolaniaNo ratings yet
- 34 Lecture Presentation 0Document73 pages34 Lecture Presentation 0Sam AbasNo ratings yet
- Maturation Manual Litopenaeus Vannamei (Aug2017)Document28 pagesMaturation Manual Litopenaeus Vannamei (Aug2017)phymell vera100% (1)
- 4 Field Guide To SA Offshore Marine Invertebrates - Phylum AnnelidaDocument12 pages4 Field Guide To SA Offshore Marine Invertebrates - Phylum AnnelidaLuthfia PramikaNo ratings yet
- Natural Heritage Cours 2024-02-20 BONESDocument13 pagesNatural Heritage Cours 2024-02-20 BONESYasmin Nabila SarapiNo ratings yet
- Nema TableDocument3 pagesNema Tableanon_574497805No ratings yet
- EarthwormDocument24 pagesEarthworm10306anshkumarNo ratings yet
- Kebo 104Document7 pagesKebo 104ABDUL HADINo ratings yet
- CestodesDocument6 pagesCestodesKathryn JeuelNo ratings yet
- Biology Final ReviewDocument8 pagesBiology Final Reviewminhui0307No ratings yet
- Batrachocephalus Bagre Osteogeneiosus Osteogeneiosus: Order Siluriformes AriidaeDocument21 pagesBatrachocephalus Bagre Osteogeneiosus Osteogeneiosus: Order Siluriformes AriidaeYusrina AfrohNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary of Invertebrates PDFDocument2 pagesVocabulary of Invertebrates PDFnatalescorNo ratings yet
- Agnatha Gnathostomata: - Jawless Vertebrates - Jawed VertebratesDocument2 pagesAgnatha Gnathostomata: - Jawless Vertebrates - Jawed VertebratesCharles Jeff DoriaNo ratings yet
- Plant ClassificationDocument3 pagesPlant ClassificationAshutosh MishraNo ratings yet
- Z3 Chordata PDFDocument7 pagesZ3 Chordata PDFPat Peralta DaizNo ratings yet
- Deiuliis2019 VERTEBRADOS LA PERCA 4Document10 pagesDeiuliis2019 VERTEBRADOS LA PERCA 4Fernando Melo GarciaNo ratings yet
- Lab 1Document17 pagesLab 1NoyaNo ratings yet
- 8 Pharynx Larynx and Nasal CavityDocument13 pages8 Pharynx Larynx and Nasal CavityAmbg GhalyNo ratings yet
- Zoo111 Activity8 SanicoDocument2 pagesZoo111 Activity8 SanicoKai Gabrielle SanicoNo ratings yet
- 11.6.domain Eukarya (Kingdom Animalia 4)Document32 pages11.6.domain Eukarya (Kingdom Animalia 4)ollie tikaNo ratings yet
- BIOL1263 11 Vertebrate Chordates 2020 PDFDocument17 pagesBIOL1263 11 Vertebrate Chordates 2020 PDFJordan LewisNo ratings yet
- Phylum PlatyhelminthesDocument4 pagesPhylum PlatyhelminthesRenz GarciaNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Document1 pageAdobe Scan 07-Mar-2023Vriddhi AhujaNo ratings yet
- (Hicman) Onychophora y TardigradaDocument4 pages(Hicman) Onychophora y TardigradaEmmanuel OrtizNo ratings yet
- Key - Classification of Vertebrates Table WorksheetDocument2 pagesKey - Classification of Vertebrates Table Worksheetramsha.sadaf2007No ratings yet
- Key - Classification of Vertebrates Table WorksheetDocument2 pagesKey - Classification of Vertebrates Table Worksheetramsha.sadaf2007No ratings yet
- Animal KingdomDocument13 pagesAnimal KingdomAngel MaryNo ratings yet
- Structures and Functions of Vertebrates (The Frog) : A. Anatomical RegionsDocument3 pagesStructures and Functions of Vertebrates (The Frog) : A. Anatomical RegionsJanee JaneNo ratings yet
- Kebo 104Document8 pagesKebo 104ABDUL HADINo ratings yet
- AgnathaDocument14 pagesAgnathaPuran BistaNo ratings yet
- NG 1998Document11 pagesNG 1998jovano15No ratings yet
- Buku Ident KepitingDocument111 pagesBuku Ident KepitingihsanNo ratings yet
- Cockroach - Endgame Handwritten and SupernotesDocument27 pagesCockroach - Endgame Handwritten and Supernotesmansilamba1006No ratings yet
- Filum ChordataDocument46 pagesFilum Chordatayohanna theresiaNo ratings yet
- Frog External AnatomyDocument8 pagesFrog External AnatomyQwerty UiopNo ratings yet
- SCAPULA /shoulder Blade/: Biceps Brachii MuscleDocument5 pagesSCAPULA /shoulder Blade/: Biceps Brachii MuscleFor AstroNo ratings yet
- ZLY111 Class Arthropoda 2017 Lecture NoteDocument7 pagesZLY111 Class Arthropoda 2017 Lecture Notevavafo7699No ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 02-Sep-2021Document16 pagesAdobe Scan 02-Sep-2021akijain20095No ratings yet
- Bio1AL Diveristy MammalsDocument26 pagesBio1AL Diveristy MammalsThet PhyoeNo ratings yet
- Amphibia and ReptiliaDocument18 pagesAmphibia and ReptiliaVet StudentNo ratings yet
- Lung Flukes: - Antemelania DactylusDocument4 pagesLung Flukes: - Antemelania DactylusDAN JR. M. BAUSANo ratings yet
- ZOOLOGY FINALS - AmphibiansDocument3 pagesZOOLOGY FINALS - AmphibiansanonymousNo ratings yet
- Gradual Resumption of In-Person Classes: Guidelines As of October 15, 2021Document8 pagesGradual Resumption of In-Person Classes: Guidelines As of October 15, 2021Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Types of Yolk: Structure Specific Origin Fate in Adult Body System FunctionDocument2 pagesTypes of Yolk: Structure Specific Origin Fate in Adult Body System FunctionKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- 8 Terminologies 2020-1220Document2 pages8 Terminologies 2020-1220Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Notes CompanaDocument10 pagesNotes CompanaKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Unicellular Mostly Flagellated/ciliated Hetero/AutotrophsDocument9 pagesUnicellular Mostly Flagellated/ciliated Hetero/AutotrophsKobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Fruit Name Fruit Type Diagnostic Characteristics (Based On The Provided Dichotomous Key)Document1 pageFruit Name Fruit Type Diagnostic Characteristics (Based On The Provided Dichotomous Key)Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- Saccoglossus Kowalevskyi (Dolichoglossus)Document4 pagesSaccoglossus Kowalevskyi (Dolichoglossus)Kobee BacolodNo ratings yet
- EchinodermsDocument7 pagesEchinodermsChristian Arm100% (1)
- Biodiversity Part 2/2Document25 pagesBiodiversity Part 2/2Kim Say Chun / Sc.KIMNo ratings yet
- CrinoidDocument12 pagesCrinoidCarlos de la Calleja100% (1)
- Plants and Their Interaction To Environmental Pollution: Damage Detection, Adaptation, Tolerance, Physiological and Molecular Responses - Ebook PDFDocument41 pagesPlants and Their Interaction To Environmental Pollution: Damage Detection, Adaptation, Tolerance, Physiological and Molecular Responses - Ebook PDFjudy.hamamoto874100% (20)
- Lesson 11. Phylum Echinodermata PDFDocument37 pagesLesson 11. Phylum Echinodermata PDFJonard PedrosaNo ratings yet
- An Anthology of Aquatic Life - Dorling KindersleyDocument226 pagesAn Anthology of Aquatic Life - Dorling KindersleyAchmad TitoNo ratings yet
- Echinoderm at ADocument9 pagesEchinoderm at ARiyah Zuhriyah TokappaNo ratings yet
- CRINOIDEADocument12 pagesCRINOIDEAAlfina Wulandari100% (2)
- Deuterostomia Wanninger2015Document220 pagesDeuterostomia Wanninger2015Isabella Maria Trujillo Pulgar100% (1)
- Invertebrate Palaeontology and EvolutionDocument9 pagesInvertebrate Palaeontology and EvolutionManav RanaNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 14: Geologic TimelineDocument10 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 14: Geologic TimelineCocomelon WILDRIFTNo ratings yet
- PDF Writing A Research Paper in Political Science 4Th Edition Lisa A Baglione Ebook Full ChapterDocument53 pagesPDF Writing A Research Paper in Political Science 4Th Edition Lisa A Baglione Ebook Full Chapterroxanne.lacour632100% (1)
- Weird Deep Sea CreaturesDocument88 pagesWeird Deep Sea Creaturesbernard_boulanger_1No ratings yet
- 2015 Marine Biodiversity CelebesDocument26 pages2015 Marine Biodiversity CelebesAurelia Izzatul AzkaNo ratings yet
- Echinoderms LectureDocument6 pagesEchinoderms LectureMarjorie Rose TeodosioNo ratings yet
- Webster y Jell 1999Document172 pagesWebster y Jell 1999Yazawa Nico ChanNo ratings yet
- Echinoids & CrinoidsDocument14 pagesEchinoids & CrinoidsPriyanka GuptaNo ratings yet
- Understanding Business Ethics 3Rd Edition Stanwick Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument36 pagesUnderstanding Business Ethics 3Rd Edition Stanwick Test Bank Full Chapter PDFcraig.frazier964100% (11)
- PDF A Game Design Vocabulary Exploring The Foundational Principles Behind Good Game Design 1st Edition Anthropy All ChapterDocument24 pagesPDF A Game Design Vocabulary Exploring The Foundational Principles Behind Good Game Design 1st Edition Anthropy All Chapterbadylparmo7100% (4)
- Webster Et Al 2003Document36 pagesWebster Et Al 2003Yazawa Nico ChanNo ratings yet
- Zoomorphology: Morphology and Function of The Tube Feet of (Echinodermata: Crinoidea)Document13 pagesZoomorphology: Morphology and Function of The Tube Feet of (Echinodermata: Crinoidea)Indra SatriaNo ratings yet
- GEO 405: Life Through Time (Spring 2021) : Lab 7: Survey of InvertebratesDocument28 pagesGEO 405: Life Through Time (Spring 2021) : Lab 7: Survey of InvertebratesRisa CrossNo ratings yet
- S-236546 CompletoDocument361 pagesS-236546 CompletoGustavo MathiasNo ratings yet
- Echinoderm Larvae PDFDocument15 pagesEchinoderm Larvae PDFMadhav GoelNo ratings yet
- Module 14Document27 pagesModule 14Najmah Sirad AmpaNo ratings yet
- GEOL 126 Lab 3Document10 pagesGEOL 126 Lab 3Amanda AngelesNo ratings yet
- Filum EchinodermataDocument15 pagesFilum EchinodermataForman SihombingNo ratings yet
- Identificar Fosiles Por Su FormaDocument10 pagesIdentificar Fosiles Por Su FormaManuel ElescanoNo ratings yet
- Echinodermata Notes - 2023Document2 pagesEchinodermata Notes - 2023BHEKUMUSA MASEKONo ratings yet
- Phylum EchinodermataDocument23 pagesPhylum EchinodermataIsaacNo ratings yet