Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pre ASTM D370 - 02e1
Pre ASTM D370 - 02e1
Uploaded by
RangaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre ASTM D370 - 02e1
Pre ASTM D370 - 02e1
Uploaded by
RangaCopyright:
Available Formats
American Association State
Designation: D 370 – 02e1 Highway Transportation Officials Standard
AASHTO No. T 83
Standard Practice for
Dehydration of Oil-Type Preservatives1
This standard is issued under the fixed designation D 370; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (e) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
e1 NOTE—Section 9, Precision and Bias, was removed editorially in May 2003.
1. Scope
1.1 This practice covers dehydrating oil-type preservatives.
When a quantitative determination of the amount of water is
desired, Test Method D 95 shall be used. Test Methods D 38
covers the sampling of wood preservatives prior to testing.
1.2 This standard does not purport to address all of the
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
priate safety and health practices and determine the applica-
bility of regulatory limitations prior to use.
2. Referenced Documents
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D 38 Test Methods for Sampling Wood Preservatives Prior
to Testing2
D 95 Test Method for Water in Petroleum Products and
Bituminous Materials by Distillation3
E 1 Specification for ASTM Thermometers4
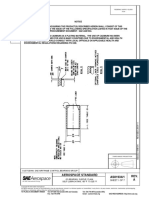
3. Summary of Test Method FIG. 1 Copper Still
3.1 Water is removed from the preservative solution by
distillation in a copper still.
5. Apparatus
4. Significance and Use 5.1 Still—A vertical, cylindrical copper still, with remov-
4.1 This is a practice for the preparation of oil-type preser- able flanged top and yoke, of the form and approximate
vatives to enable the results of distillation tests to be reported dimensions shown in Fig. 1.
more accurately on a dry basis. 5.2 Thermometer—An ASTM High Distillation Thermom-
eter, total immersion, graduated in either Celsius or Fahrenheit
1
degrees as specified, having a range from −2 to +400°C or 30
This practice is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee D07 on Wood and
is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee D07.06 on Treatments for Wood
to 760°F, and conforming to the requirements for Thermometer
Products. 8C or 8F as prescribed in Specification E 1.
Current edition approved Dec. 10, 2002. Published February 2003. Originally 5.3 Condenser—A copper trough condenser, with straight-
approved in 1933 as D 370 – 33 T. Last previous edition approved in 1995 as walled glass tube, having approximately the form and dimen-
D 370 – 84 (1995)e1.
This practice is substantially in agreement with the Standard Method for the sions shown in Fig. 2.
Determination of Water in Oil-Type Preservatives which is part of the American 5.4 Separatory Funnel, conforming to the requirements
Wood-Preservers’ Association Standard Methods for Analysis of Creosote and shown in Fig. 3. It shall have a total capacity of approximately
Oil-Type Preservatives (A1). Acknowledgement is made to the American Wood-
Preservers’ Association for its development of the subject matter covered in this
200 mL, with the lower 20 mL graduated accurately in 0.1 mL.
standard. The graduation marks shall be numbered for each millilitre. A
2
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 04.10. separatory funnel of the Squibb type, having a capacity of
3
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 05.01. approximately 100 mL, may be used.
4
Annual Book of ASTM Standards, Vol 14.03.
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959, United States.
You might also like
- Astm D1384-05Document8 pagesAstm D1384-05Boris100% (1)
- D2709 Water&sediment PDFDocument3 pagesD2709 Water&sediment PDFAyman AyadiNo ratings yet
- Pre ASTM B117-19Document5 pagesPre ASTM B117-19Ranga100% (3)
- Setting Mikrotik LoadBalance 3 ISP No Lopping Ping Imut Full ScriptDocument2 pagesSetting Mikrotik LoadBalance 3 ISP No Lopping Ping Imut Full ScriptZhon Ocas100% (1)
- Total Immersion Corrosion Test For Aircraft Maintenance ChemicalsDocument4 pagesTotal Immersion Corrosion Test For Aircraft Maintenance ChemicalsJuanNo ratings yet
- D-6041 Fiber Glass Hand-Layup PipesDocument7 pagesD-6041 Fiber Glass Hand-Layup Pipesmanuel.ape6263No ratings yet
- Corrosion Test For Engine Coolants in GlasswareDocument7 pagesCorrosion Test For Engine Coolants in GlasswareAllan BarencoNo ratings yet
- Astm D972Document4 pagesAstm D972rhsousaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1264 - 03Document4 pagesAstm D 1264 - 03Jako Mishy0% (1)
- Pre ASTM D 1149-2018Document5 pagesPre ASTM D 1149-2018Ranga67% (3)
- CVL Consent PDFDocument5 pagesCVL Consent PDFGolam SarwarNo ratings yet
- D370 PDFDocument3 pagesD370 PDFROHITNo ratings yet
- Dehydration of Oil-Type Preservatives: Standard Practice ForDocument3 pagesDehydration of Oil-Type Preservatives: Standard Practice ForCasey RybackNo ratings yet
- D 370 - 84 R95 - Rdm3mc04nfi5nuuxDocument3 pagesD 370 - 84 R95 - Rdm3mc04nfi5nuuxAurelio Zambrano BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Distillation of Creosote and Creosote-Coal Tar Solutions: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesDistillation of Creosote and Creosote-Coal Tar Solutions: Standard Test Method ForCasey RybackNo ratings yet
- Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Steam Turbine Oil in The Presence of Water (Horizontal Disk Method)Document6 pagesRust-Preventing Characteristics of Steam Turbine Oil in The Presence of Water (Horizontal Disk Method)Sai HS BodduNo ratings yet
- Distillation of Cutback Asphaltic D402 08Document5 pagesDistillation of Cutback Asphaltic D402 08Pedro AlvelaisNo ratings yet
- 11 Sedimentos Por ExtracciónDocument5 pages11 Sedimentos Por ExtracciónDanixa Yuliana Muñoz BurbanoNo ratings yet
- Distillation of Cut-Back ASTM D402Document5 pagesDistillation of Cut-Back ASTM D402mohamedNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 2158 - 04 Standard Test Method For Residues by Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases.Document5 pagesASTM D 2158 - 04 Standard Test Method For Residues by Liquefied Petroleum (LP) Gases.Pham Lanphuong100% (2)
- Corrosiveness To Copper From Petroleum Products by Copper Strip TestDocument9 pagesCorrosiveness To Copper From Petroleum Products by Copper Strip TestFarid OrtizNo ratings yet
- Astm D402Document5 pagesAstm D402Mutyaba JohnsonNo ratings yet
- D402D402M-14 Standard Test Method For Distillation of Cutback Asphalt - AASHTO No. T78Document5 pagesD402D402M-14 Standard Test Method For Distillation of Cutback Asphalt - AASHTO No. T78Alabbas FadhelNo ratings yet
- D3603-07 - Standard Test Method For Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Steam Turbine Oil in The Presence of Water (Horizontal Disk Method)Document6 pagesD3603-07 - Standard Test Method For Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Steam Turbine Oil in The Presence of Water (Horizontal Disk Method)JoanneLimNo ratings yet
- Rust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oil in The Presence of WaterDocument9 pagesRust-Preventing Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oil in The Presence of WaterMuhannad NasifNo ratings yet
- Corrosion en Lamina de Cobre ASTM D130Document9 pagesCorrosion en Lamina de Cobre ASTM D130Coordinador LaboratorioNo ratings yet
- Astm d2235Document5 pagesAstm d2235Cristhian Andres100% (1)
- Saybolt Furol Viscosity of Bituminous Materials at High TemperaturesDocument3 pagesSaybolt Furol Viscosity of Bituminous Materials at High TemperaturesEdmundo Jaita CuellarNo ratings yet
- Astm D1384 04Document3 pagesAstm D1384 04fuenmayor.lilibethNo ratings yet
- D 1881Document4 pagesD 1881seterisparigusNo ratings yet
- Total Immersion Corrosion Test For Aircraft Maintenance ChemicalsDocument4 pagesTotal Immersion Corrosion Test For Aircraft Maintenance ChemicalsJuanNo ratings yet
- D 402 - 97 Rdqwmi05nwDocument5 pagesD 402 - 97 Rdqwmi05nwel kevinsio el kevinsoNo ratings yet
- Astm D36Document4 pagesAstm D36Esteban FinoNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extractables in Petroleum Waxes: Standard Test Method ForDocument7 pagesSolvent Extractables in Petroleum Waxes: Standard Test Method ForPaulo SantosNo ratings yet
- ASTM D-130 Detection of Copper Corrosion From Petroleum Products by The Copper Strip Tarnish TestDocument7 pagesASTM D-130 Detection of Copper Corrosion From Petroleum Products by The Copper Strip Tarnish TestGabriela EhlertNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 6470-99 Salt in Crude Oils (Potentiometric Method) 1 PDFDocument6 pagesASTM D 6470-99 Salt in Crude Oils (Potentiometric Method) 1 PDFsofiane ouchaouaNo ratings yet
- Saybolt Furol Viscosity of Bituminous Materials at High TemperaturesDocument3 pagesSaybolt Furol Viscosity of Bituminous Materials at High TemperaturesJGD123No ratings yet
- D 130 - 04 RDEZMA - CorrosivenessDocument9 pagesD 130 - 04 RDEZMA - CorrosivenessMd Abid AfridiNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 36-95-Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus) E (Document4 pagesASTM D 36-95-Softening Point of Bitumen (Ring-and-Ball Apparatus) E (anjanaNo ratings yet
- D 740 - 94 R01 - Rdc0maDocument2 pagesD 740 - 94 R01 - Rdc0maMarcel NascimentoNo ratings yet
- E-CTFE-Fluoroplastic Molding, Extrusion, and Coating MaterialsDocument5 pagesE-CTFE-Fluoroplastic Molding, Extrusion, and Coating MaterialsEver Antonio MorenoNo ratings yet
- Astm d4007Document11 pagesAstm d4007Juan David Velez EsquivelNo ratings yet
- Astm D 1881 - 97 PDFDocument4 pagesAstm D 1881 - 97 PDFJulian Felipe Noguera CruzNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils: Standard Test Method ForDocument11 pagesOxidation Characteristics of Inhibited Mineral Oils: Standard Test Method ForROHITNo ratings yet
- ASTM D3241 02ae1Document13 pagesASTM D3241 02ae1Antony Bruno GenewinNo ratings yet
- Solvent Extractables in Petroleum Waxes: Standard Test Method ForDocument7 pagesSolvent Extractables in Petroleum Waxes: Standard Test Method ForAbdallah ElkasbyNo ratings yet
- F 482 - 84 R99 Rjq4mi1sruqDocument7 pagesF 482 - 84 R99 Rjq4mi1sruqJuanNo ratings yet
- Astmd4607 94R06Document5 pagesAstmd4607 94R06dffbbaNo ratings yet
- D 740 - 94 R97 - Rdc0mc05nfi5nwDocument2 pagesD 740 - 94 R97 - Rdc0mc05nfi5nwMarcel NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Copper Strip Corrosion by Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesCopper Strip Corrosion by Industrial Aromatic Hydrocarbons: Standard Test Method ForMarcel NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Salt in Crude Oils (Potentiometric Method) : Standard Test Method ForDocument6 pagesSalt in Crude Oils (Potentiometric Method) : Standard Test Method ForLuis Ernesto Marin JaimesNo ratings yet
- ASTM D 130-10 - Corrosiveness To Copper From Petroleum Products by Copper Strip TestDocument9 pagesASTM D 130-10 - Corrosiveness To Copper From Petroleum Products by Copper Strip TestAnak Ayam100% (1)
- Modified ETFE Fluoropolymer Molding and Extrusion Materials: Standard Specification ForDocument5 pagesModified ETFE Fluoropolymer Molding and Extrusion Materials: Standard Specification ForDeepak AryaNo ratings yet
- Astm D 5853-06Document7 pagesAstm D 5853-06ТNo ratings yet
- Solvent Cement For Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe and FittingsDocument5 pagesSolvent Cement For Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene (ABS) Plastic Pipe and FittingsAndres Camilo BenitezNo ratings yet
- D 4607 - 94 R99 - RDQ2MDC - 1 PDFDocument5 pagesD 4607 - 94 R99 - RDQ2MDC - 1 PDFWynona BasilioNo ratings yet
- ASTM E100-15aDocument11 pagesASTM E100-15aPippozzo Pipini50% (4)
- D6079-02. Test Method For Evaluating Lubricity of Diesel Fluids by The High Frequency Reciprocating RigDocument4 pagesD6079-02. Test Method For Evaluating Lubricity of Diesel Fluids by The High Frequency Reciprocating RigNavneet YadavNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Stability of Distillate Fuel Oil (Accelerated Method)Document6 pagesOxidation Stability of Distillate Fuel Oil (Accelerated Method)Dennise ChicaizaNo ratings yet
- Oxidation Stability of Lubricants by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT) Catalyst BDocument9 pagesOxidation Stability of Lubricants by Thin-Film Oxygen Uptake (TFOUT) Catalyst BMohanadNo ratings yet
- Saybolt Furol Viscosity of Bituminous Materials at High TemperaturesDocument3 pagesSaybolt Furol Viscosity of Bituminous Materials at High TemperaturesAhmad Zubair RasulyNo ratings yet
- Water Separability of Petroleum Oils and Synthetic Fluids: Standard Test Method ForDocument4 pagesWater Separability of Petroleum Oils and Synthetic Fluids: Standard Test Method ForMuhammad FidzrusNo ratings yet
- Phosphorus in Gasoline: Standard Test Method ForDocument5 pagesPhosphorus in Gasoline: Standard Test Method ForAbdallah ElkasbyNo ratings yet
- Comments On The "Draft Scenario" Document: Page 5 What Will Be Disseminated and To Whom?Document3 pagesComments On The "Draft Scenario" Document: Page 5 What Will Be Disseminated and To Whom?RangaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Standard AS81934/1 Rev. A: Custodian: Sae Airframe Control Bearings GroupDocument3 pagesAerospace Standard AS81934/1 Rev. A: Custodian: Sae Airframe Control Bearings GroupRangaNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Accreditation United Kingdom Accreditation ServiceDocument4 pagesSchedule of Accreditation United Kingdom Accreditation ServiceRangaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Standard AS81934/2 Rev. A: Custodian: Sae Airframe Control Bearings GroupDocument3 pagesAerospace Standard AS81934/2 Rev. A: Custodian: Sae Airframe Control Bearings GroupRanga100% (1)
- ID83. Amfori - Position Paper - ECHA Database - Final - AmforiDocument3 pagesID83. Amfori - Position Paper - ECHA Database - Final - AmforiRangaNo ratings yet
- ANSI/ASME NQA-1c-1988 AddendaDocument34 pagesANSI/ASME NQA-1c-1988 AddendaRangaNo ratings yet
- Landing Gear Weekly Change Reports Dated 02-21-2021 NSRDocument1,492 pagesLanding Gear Weekly Change Reports Dated 02-21-2021 NSRRangaNo ratings yet
- HT Steel-Operator SKILLSDocument12 pagesHT Steel-Operator SKILLSRangaNo ratings yet
- Hightempaerospace Private Limited: Job Qualification / Requirement MatrixDocument1 pageHightempaerospace Private Limited: Job Qualification / Requirement MatrixRangaNo ratings yet
- METHODOLOGY FOR Vendor Rating SystemDocument5 pagesMETHODOLOGY FOR Vendor Rating SystemRangaNo ratings yet
- BS 817M40 Equivalents 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43Document2 pagesBS 817M40 Equivalents 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43RangaNo ratings yet
- 5.2.7 Aqueous Wash Reference PFMEA - v2Document7 pages5.2.7 Aqueous Wash Reference PFMEA - v2RangaNo ratings yet
- PD 6103 HTBoK 002OW 3 Pyrometry Process Owner Level BoK 08feb16 Name ChangeDocument18 pagesPD 6103 HTBoK 002OW 3 Pyrometry Process Owner Level BoK 08feb16 Name ChangeRangaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Information Report: Fire Test Equipment For Flexible Hose and Tube AssembliesDocument5 pagesAerospace Information Report: Fire Test Equipment For Flexible Hose and Tube AssembliesRangaNo ratings yet
- Pre ASTM D2137-11 (2018)Document3 pagesPre ASTM D2137-11 (2018)RangaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Standard: Fire Testing of Flexible Hose, Tube Assemblies, Coils, Fittings, and Similar System ComponentsDocument3 pagesAerospace Standard: Fire Testing of Flexible Hose, Tube Assemblies, Coils, Fittings, and Similar System ComponentsRangaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Standard: Hose Assembly, Polytetrafluoroethylene, Metallic Reinforced, 3000 Psi, 400 °F, Heavyweight, HydraulicDocument5 pagesAerospace Standard: Hose Assembly, Polytetrafluoroethylene, Metallic Reinforced, 3000 Psi, 400 °F, Heavyweight, HydraulicRangaNo ratings yet
- Pre ASTM D573-04 (2019)Document3 pagesPre ASTM D573-04 (2019)RangaNo ratings yet
- Development of Titanium Alloy Hemispherical Forging For Pressure Vessel of Launch VehicleDocument5 pagesDevelopment of Titanium Alloy Hemispherical Forging For Pressure Vessel of Launch VehicleRangaNo ratings yet
- Aerospace Standard: Hose Assemblies, Metal, Medium Pressure, High TemperatureDocument3 pagesAerospace Standard: Hose Assemblies, Metal, Medium Pressure, High TemperatureRangaNo ratings yet
- Pre ASTM E18-20Document5 pagesPre ASTM E18-20Ranga100% (1)
- Is 1586Document22 pagesIs 1586RangaNo ratings yet
- Additive Manufacturing of Optically Transparent Glass PDFDocument14 pagesAdditive Manufacturing of Optically Transparent Glass PDFRangaNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication NetworksDocument4 pagesOptical Communication Networksarivurp100% (1)
- 4thh Quarter Pre TestDocument1 page4thh Quarter Pre TestAlona Camino100% (2)
- Sap fb08 Amp f80 Tutorial Document ReversalDocument16 pagesSap fb08 Amp f80 Tutorial Document Reversalsaeedawais47No ratings yet
- Bryce Boerste - Personal College Essay - Draft 2Document3 pagesBryce Boerste - Personal College Essay - Draft 2api-492128881No ratings yet
- HUC Program Grading SchemeDocument1 pageHUC Program Grading SchemeThanis RaoNo ratings yet
- Designing English Learning Materials For Tourism Police OfficerDocument3 pagesDesigning English Learning Materials For Tourism Police OfficerArga AnggaraNo ratings yet
- Crating Web Forms Applications: by Ms. Madhura KutreDocument47 pagesCrating Web Forms Applications: by Ms. Madhura KutreAjit PatilNo ratings yet
- Jacques Berlinerblau's CVDocument17 pagesJacques Berlinerblau's CVjdb75100% (1)
- Yudkin Music in Medieval EuropeDocument316 pagesYudkin Music in Medieval EuropeAndrew Franklin O'ConnorNo ratings yet
- Note On Marsh Crocodile, Presentation On Marsh Crocodile or Marsh Crocodile LifeDocument18 pagesNote On Marsh Crocodile, Presentation On Marsh Crocodile or Marsh Crocodile LifeKirfan 123No ratings yet
- Fermi LevelDocument13 pagesFermi LevelArchit P. MeshramNo ratings yet
- IMAP TRANSTEC Complete Drive ShaftsDocument16 pagesIMAP TRANSTEC Complete Drive Shaftslv621048No ratings yet
- Shravni Ragoor ResDocument1 pageShravni Ragoor Resapi-705833851No ratings yet
- TR - Dressmaking NC IIDocument60 pagesTR - Dressmaking NC IIMR. CHRISTIAN DACORONNo ratings yet
- M65845AFP: Digital Echo With Microphone Mixing CircuitDocument14 pagesM65845AFP: Digital Echo With Microphone Mixing CircuitahmedNo ratings yet
- Indian Heart JournalDocument18 pagesIndian Heart JournalSanaSofiyahNo ratings yet
- EDN 2104-4 MidtermsDocument40 pagesEDN 2104-4 MidtermsJuls LolNo ratings yet
- Leadership by Dr. Arpita KaulDocument65 pagesLeadership by Dr. Arpita KaulArpita KaulNo ratings yet
- MSDSDocument6 pagesMSDSMuhammad Iqbal NiyaziNo ratings yet
- Sika Colorflo Yellow: Safety Data SheetDocument7 pagesSika Colorflo Yellow: Safety Data SheetKartika Setia RiniNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion StoryboardsDocument7 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion StoryboardsJudy AndalNo ratings yet
- Rise and Decline of Charismatic Leadership - HouseDocument75 pagesRise and Decline of Charismatic Leadership - Housemsaqibraza93No ratings yet
- Organizational ReadinessDocument12 pagesOrganizational Readinessovidiu buneaNo ratings yet
- Breast CA SeminarDocument60 pagesBreast CA SeminarAliyi MuktarNo ratings yet
- Prezentare AGS en +romDocument34 pagesPrezentare AGS en +romGina Daniela BorcanNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Example On Steam Pipe InsulationDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Example On Steam Pipe InsulationRamses Uriel Torres CanoNo ratings yet
- Lab Sheet HighwayDocument36 pagesLab Sheet Highwaynaryna adrynNo ratings yet
- Module Qtr4 Lesson3Document6 pagesModule Qtr4 Lesson3Yusef John NebridaNo ratings yet