Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 1: Linear Relations Chapter Checklist: Success Criteria
Chapter 1: Linear Relations Chapter Checklist: Success Criteria
Uploaded by
A MOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 1: Linear Relations Chapter Checklist: Success Criteria
Chapter 1: Linear Relations Chapter Checklist: Success Criteria
Uploaded by
A MCopyright:
Available Formats
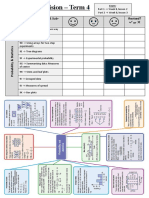
Chapter 1: Linear relations
Chapter checklist: Success criteria
Name ______________________
✔
1A 1. I can simplify expressions using the four operations , , , .
☐
e.g. Simplify 3 x 2 y 4 x y 2 xy 3x y .
2 2
1A 2. I can expand brackets using the distributive law.
☐
e.g. Expand and simplify 4 y ( 2 y 3) .
1A 3. I can factorise simple algebraic expressions with a common factor.
☐
e.g. Factorise 6 x 15 x .
2
1A 4. I can substitute numbers for pronumerals and evaluate.
☐
e.g. Given a 3 and b 4 , evaluate ab a .
2
1B 5. I can cancel common factors in algebraic fractions.
4x 2 ☐
e.g. Simplify 2 .
1B 6. I can multiply and divide algebraic fractions.
3x 9 2 x 6 ☐
e.g. Simplify 20 5 .
1C 7. I can add and subtract simple algebraic fractions using the lowest
common denominator.
4 5 ☐
e.g. Simplify x 6 .
1C 8. I can add and subtract algebraic fractions with binomial numerators or
denominators.
x3 x2 4 3 ☐
e.g. Simplify 3 7 and x 2 x 4 .
1D 9. I can solve linear equations with brackets and variables on both sides.
☐
e.g. Solve 4(3x 5) 7 x .
1D 10. I can solve linear equations involving algebraic fractions.
x 1 x 2 1 2x x 1 ☐
2
e.g. Solve 3 5 and 3 2 .
1E 11. I can interpret number lines to write inequalities.
e.g. Write as an inequality.
☐
12. I can represent a set of solutions on a number line. ☐
1E
© Cambridge University Press 2019
e.g. Graph the inequality x 3 on a number line.
1F 13. I can solve linear inequalities.
x ☐
4 8
e.g. Solve 3 .
1F 14. I can determine if a point is on a straight line.
☐
e.g. Decide if the point (3, 1) is on the line 3 x 2 y 7 .
1F 15. I can find the gradient and y-intercept from a straight line equation.
☐
e.g. State the gradient and y-intercept of 3 y 2 x 6 .
1F 16. I can use the gradient and y-intercept to sketch a graph.
☐
e.g. Find the gradient and y-intercept of y 2 x 7 and sketch its graph.
1F 17. I can find the x- and y-intercepts of a linear graph.
☐
e.g. Find the x- and y-intercepts and sketch the graph of 3 x y 9
1F 18. I can sketch a horizontal or vertical line.
☐
e.g. Sketch y 3 .
1F 19. I can sketch a line of the form y mx .
☐
e.g. Sketch y 2 x labelling the axis intercept and one other point.
1G 20. I can find the gradient of a line joining two points.
☐
e.g. Determine the gradient of the line joining the points ( 2, 4) and (3, 1) .
1G 21. I can find the equation of a line using a point and the y-intercept.
e.g. Find the equation of the straight
line shown.
1G 22. I can find the equation of a line given two points.
e.g. Find the equation of the straight line joining the points ( 2, 2) ☐
and
2, 3 .
1H 23. I can find the distance between two points.
e.g. Find the exact distance between the points
2, 4
and .
5, 2 ☐
1H 24. I can find the midpoint of a line segment joining two points.
e.g. Find the midpoint of the line segment joining ( 1, 5) and
5, 2 . ☐
1H 25. I can use a given distance to find coordinates.
e.g. Find the values of a if the distance between (3, a ) and
6, 10 is 34 . ☐
© Cambridge University Press 2019
1I 26. I can decide if lines are parallel, perpendicular or neither.
e.g. Decide if the graph of the lines y 2 x 5 and 2 y x 3 will be parallel, ☐
perpendicular or neither.
1I 27. I can find the equation of a parallel or perpendicular line.
e.g. Find the equation of the line that is parallel to y 3 x 4 and passes ☐
through
2, 4
.
1J 28. I can solve simultaneous equations using substitution.
e.g. Solve the pair of simultaneous equations x 2 y 4 and y x 3 using ☐
the method of substitution.
1K 29. I can solve simultaneous equations by adding or subtracting them.
e.g. Solve the simultaneous equations x 2 y 10 and x y 4 using ☐
elimination.
1K 30. I can use the elimination method to solve simultaneous equations.
e.g. Solve the pair of simultaneous equations 2 x 3 y 5 and 3x 4 y 18 ☐
using the elimination method.
1L 31. I can set up and solve simultaneous equations.
e.g. A teacher buys 5 of the same chocolate bars and 2 of the same
ice-creams for $18 while another teacher buys 4 of the same chocolate bar ☐
and 5 of the same ice-creams for $28 . Determine the individual costs of
these chocolate bars and ice-creams.
1M 32. I can sketch a half plane.
☐
e.g. Sketch the half plane y 2 x 5 .
1M 33. I can find the intersecting region.
e.g. Sketch both the inequalities 2 x y… 2 and 2 x 3 y 6 on ☐
the same set of axes, showing the point of intersection of the two
lines and the intersecting region.
© Cambridge University Press 2019
You might also like
- Triangle ProportionalityDocument52 pagesTriangle ProportionalityKesziah Jane CalambaNo ratings yet
- Term 2 Simple Familiar ChecklistDocument3 pagesTerm 2 Simple Familiar Checklistimar07059No ratings yet
- Math Grade9 Quarter3 Week4 Module4Document4 pagesMath Grade9 Quarter3 Week4 Module4ALLYSSA MAE PELONIANo ratings yet
- JC1 Math - H2 - 2019Document347 pagesJC1 Math - H2 - 2019GQGrace TohNo ratings yet
- A 1 - Syllabus 2020 - 2021Document3 pagesA 1 - Syllabus 2020 - 2021Burhan AzharNo ratings yet
- Hmath2 Test 1 - Right Triangle Trig and Square Roots Sample 1617 - KeyDocument3 pagesHmath2 Test 1 - Right Triangle Trig and Square Roots Sample 1617 - Keyapi-368121935No ratings yet
- TU3ed (E) s1 ch02Document6 pagesTU3ed (E) s1 ch02Jimmy Demetrius Rhys ForgerNo ratings yet
- End-of-Course Test: Solve. 1. 2. 3Document4 pagesEnd-of-Course Test: Solve. 1. 2. 3Tony LeeNo ratings yet
- Algebra Unidad 2Document84 pagesAlgebra Unidad 2Paula MorenoNo ratings yet
- DifferentiationDocument16 pagesDifferentiationapi-298592212No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Sample Papers 03 (2019-20)Document22 pagesCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Sample Papers 03 (2019-20)koteen547No ratings yet
- 2019 Asrjc Prelim p1 HuxyDocument7 pages2019 Asrjc Prelim p1 Huxysunguar.sanjayNo ratings yet
- Math8-Week6 (2ndquarter) HannahDocument3 pagesMath8-Week6 (2ndquarter) HannahHannah Jane ClerigoNo ratings yet
- 02 Basic AlgebraDocument20 pages02 Basic Algebramuhammad warisNo ratings yet
- FilipinoDocument9 pagesFilipinoCarylle BasarteNo ratings yet
- Math - Topic Knowledge RequirementDocument21 pagesMath - Topic Knowledge Requirementrandomsites7No ratings yet
- Precalculus - Worksheet: FX X X X FDocument3 pagesPrecalculus - Worksheet: FX X X X FteachopensourceNo ratings yet
- 5Document1 page5anis nabilah ismailNo ratings yet
- 7-5 Study Guide and Intervention: Parallel Lines and Proportional PartsDocument2 pages7-5 Study Guide and Intervention: Parallel Lines and Proportional Partsbd6cpynwmpNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - GENMATH 11Document14 pagesModule 3 - GENMATH 11Agustin L. IdausosNo ratings yet
- "Just The Maths" Unit Number 5.3 Geometry 3 (Straight Line Laws) by A.J.HobsonDocument8 pages"Just The Maths" Unit Number 5.3 Geometry 3 (Straight Line Laws) by A.J.HobsonTino KambaniNo ratings yet
- Chp6 Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Their ApplicationsDocument15 pagesChp6 Derivatives of Exponential and Logarithmic Functions and Their Applicationsihh cNo ratings yet
- Apollo Round 1 Solutions 2014Document2 pagesApollo Round 1 Solutions 2014scamper2015No ratings yet
- 3 - Algebra I business mathsDocument44 pages3 - Algebra I business mathsAthiNo ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Ma. Rica Mae Rosete100% (1)
- Lecture Note Chapter 1 Part 1Document25 pagesLecture Note Chapter 1 Part 1nurul izwaniNo ratings yet
- Bridging Program AlgebraDocument56 pagesBridging Program AlgebraPrincess Jerlyn M. TagudNo ratings yet
- Solution Practice 22-24Document3 pagesSolution Practice 22-24Syed Abdul Mussaver ShahNo ratings yet
- Geometry Skill BuildersDocument74 pagesGeometry Skill BuildersthouartuNo ratings yet
- Grade 9 Algebra: X 3x 4xy 2 (X 3)Document20 pagesGrade 9 Algebra: X 3x 4xy 2 (X 3)Sheryl BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Advanced Calculus: Topics in Vector CalculusDocument36 pagesAdvanced Calculus: Topics in Vector CalculusnanauswatunNo ratings yet
- 6.5 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesDocument20 pages6.5 Parallel and Perpendicular LinesAlvie Mae MagparocNo ratings yet
- 2nd Quarter ExamDocument3 pages2nd Quarter ExamSarah SaraelNo ratings yet
- Four I HandoutDocument50 pagesFour I HandoutRonald PerezNo ratings yet
- Tmcsoln 3 NDocument2 pagesTmcsoln 3 Ncodewizard.19No ratings yet
- Maths Assignment XiiDocument2 pagesMaths Assignment Xiiparasharhimanshu5201No ratings yet
- Basic Algebra FinalDocument20 pagesBasic Algebra FinalAjay VermaNo ratings yet
- (Edu - Joshuatly.com) Terengganu STPM Trial 2010 Maths T (W Ans) (FABA1910)Document28 pages(Edu - Joshuatly.com) Terengganu STPM Trial 2010 Maths T (W Ans) (FABA1910)Sarah LeeNo ratings yet
- Chap15 - 240-253Document14 pagesChap15 - 240-253jfarrell_ie5767No ratings yet
- Math Challenge Reviewer Grade 8 PDFDocument2 pagesMath Challenge Reviewer Grade 8 PDFCharlie MilayaNo ratings yet
- CH 11 Three Dimensional GeometryDocument20 pagesCH 11 Three Dimensional GeometrysudersanaviswanathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 ExercisesDocument21 pagesChapter 3 ExercisesFrederick BuizaNo ratings yet
- ?year 9 Revision - Term 4Document7 pages?year 9 Revision - Term 4Hannah LeeNo ratings yet
- Midterm 1 Review-3Document3 pagesMidterm 1 Review-3enricoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3: Joint Variation Content Standard: Xy 17 P 5 QDocument6 pagesLesson 3: Joint Variation Content Standard: Xy 17 P 5 QCindy BononoNo ratings yet
- Math in The Modern WorldDocument7 pagesMath in The Modern WorldJam KaiiNo ratings yet
- Topic 1.1 Linear EquationsDocument24 pagesTopic 1.1 Linear EquationsnshoulyNo ratings yet
- Writing and Graphing Linear Equations 1Document62 pagesWriting and Graphing Linear Equations 1Sabreena RataniNo ratings yet
- C 1 - N Name - I D Date - BlockDocument3 pagesC 1 - N Name - I D Date - BlockMufaro ChimutumbiraNo ratings yet
- 10 Algebra PDFDocument10 pages10 Algebra PDFmaryNo ratings yet
- Grade 9Document6 pagesGrade 9Karen GardoseNo ratings yet
- A Level Mathematics - Practice Paper - 20 - Algebra and FunctionsDocument10 pagesA Level Mathematics - Practice Paper - 20 - Algebra and FunctionsSemaNo ratings yet
- Math 2Document8 pagesMath 2gambitpunisherNo ratings yet
- Amusing and Challenging Math ProblemsDocument4 pagesAmusing and Challenging Math ProblemsmichaelfindlayNo ratings yet
- Partial Derivatives: y X Z ZDocument10 pagesPartial Derivatives: y X Z ZAbdul Sami RajputNo ratings yet
- Number and AlgebraDocument36 pagesNumber and Algebra019914No ratings yet
- Introduction To Algebraic Expressions: ConstantDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Algebraic Expressions: ConstantdfhfNo ratings yet
- IGCSE AlgebraDocument24 pagesIGCSE Algebrademiyang030No ratings yet
- Multilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryFrom EverandMultilinear Functions Of Direction And Their Uses In Differential GeometryNo ratings yet
- Design Modeling and Control of A Wall CL PDFDocument6 pagesDesign Modeling and Control of A Wall CL PDFRam KumarNo ratings yet
- PreviewpdfDocument45 pagesPreviewpdfOtto DexterNo ratings yet
- Pair of Linear EquationDocument10 pagesPair of Linear EquationSakshamNo ratings yet
- Test Report: Dilip Buildcon LimitedDocument5 pagesTest Report: Dilip Buildcon LimitedRitesh TiwariNo ratings yet
- Ground Characterization and Structural Analyses For Tunnel DesignDocument473 pagesGround Characterization and Structural Analyses For Tunnel Designsvs dmrNo ratings yet
- New MCQ EMD An DME 2020 F1 - FinalDocument4 pagesNew MCQ EMD An DME 2020 F1 - FinalSandipkumar Vhanakade100% (1)
- ECON1003 Tut10 2023s2Document44 pagesECON1003 Tut10 2023s2guohaolan0804No ratings yet
- Motion in One Dimension: Science 9 Quarter 4 Module 1 Week 1Document4 pagesMotion in One Dimension: Science 9 Quarter 4 Module 1 Week 1KkkkkNo ratings yet
- SPLM 1Document7 pagesSPLM 1John Charlie CadanoNo ratings yet
- 1138 FullDocument7 pages1138 Full6dttfhjzbfNo ratings yet
- Learning Activity Sheets: ScienceDocument7 pagesLearning Activity Sheets: ScienceBen Josiah BayotNo ratings yet
- Momentum Transfer Syllabus2022Document6 pagesMomentum Transfer Syllabus2022Shit AssNo ratings yet
- Type N Vs Type K ThermocoupleDocument2 pagesType N Vs Type K ThermocouplebasdownloadNo ratings yet
- Solubility Lab ReportDocument3 pagesSolubility Lab ReportJampathippong SorraveeNo ratings yet
- TD InPro8000 Series TurbiditySensor en 52800246 May15Document8 pagesTD InPro8000 Series TurbiditySensor en 52800246 May15Guy MesikaNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Acoustics in Hearing Speech and Language Sciences An Introduction LLV 0132897083Document6 pagesSolution Manual For Acoustics in Hearing Speech and Language Sciences An Introduction LLV 0132897083Scarlett Bryant100% (37)
- Moving Bed ProcessorsDocument11 pagesMoving Bed ProcessorsWaqar AhmedNo ratings yet
- HW3 2023Document3 pagesHW3 2023BlooD LOVERNo ratings yet
- A Method of Solving Certain Nonlinear DiophantineDocument3 pagesA Method of Solving Certain Nonlinear DiophantineArsh TewariNo ratings yet
- N.004 - ASTM B557 - Standard Methods of Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum - and Magnesium - Alloy ProductsDocument20 pagesN.004 - ASTM B557 - Standard Methods of Tension Testing Wrought and Cast Aluminum - and Magnesium - Alloy ProductsAdriene SantosNo ratings yet
- VCF Aviation GasolineDocument5 pagesVCF Aviation GasolineEdgar GuardiaNo ratings yet
- 1st Year Chemistry Chapter No. 5-6 - SQs - NOTESPKDocument14 pages1st Year Chemistry Chapter No. 5-6 - SQs - NOTESPKZeeshan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Design of Abutment Excel SheetDocument14 pagesDesign of Abutment Excel SheetAmit Kumar PaulNo ratings yet
- Resistance Investigation Lab ReportDocument7 pagesResistance Investigation Lab Report9름100% (1)
- Mathematics Grade 11 Elite Volume 1 - Student Book 2021-2022 (C)Document284 pagesMathematics Grade 11 Elite Volume 1 - Student Book 2021-2022 (C)enekoxmaNo ratings yet
- 3-Dimensioning Tolerancing FitsDocument36 pages3-Dimensioning Tolerancing FitsthelearningaceNo ratings yet
- Lessonsections-24 2Document11 pagesLessonsections-24 2Ghazi DallyNo ratings yet
- GLASS Jiang-Zhang2015 - Article - TheFormationOfGlassAQuantitatiDocument48 pagesGLASS Jiang-Zhang2015 - Article - TheFormationOfGlassAQuantitatiRenato EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- 2021 GDT CatalogDocument23 pages2021 GDT CatalogAdrian MartínezNo ratings yet
- TOEFL Insight 1 - StructureDocument7 pagesTOEFL Insight 1 - StructureRimaNo ratings yet