Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Introduction To Behavioral Finance
Introduction To Behavioral Finance
Uploaded by
Kimberly Serafica FeleoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- 6-7. Aligning Service Design and StandardsDocument23 pages6-7. Aligning Service Design and StandardsIrfan Ahmed Sakib100% (1)
- Methods of Comm Planning MiddletonDocument473 pagesMethods of Comm Planning MiddletonKoolet Gal100% (1)
- PRINTERS NotesDocument4 pagesPRINTERS NotesFridah Apondi83% (6)
- Annamalai UniversityDocument392 pagesAnnamalai UniversitySmiles PrintingNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Behavioral Finance On Stock Markets PDFDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Behavioral Finance On Stock Markets PDFprema100% (1)
- Behavioral Finance: by Sudeshna Dutta Assistant Professor BiitmDocument14 pagesBehavioral Finance: by Sudeshna Dutta Assistant Professor BiitmSudeshna RoyNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Dahiya FinalDocument46 pagesJyoti Dahiya FinalJyoti dahiyaNo ratings yet
- Pes Institute of Technology - Bangalore South Campus Dept. of MBADocument34 pagesPes Institute of Technology - Bangalore South Campus Dept. of MBADuma DumaiNo ratings yet
- Money Market FinalDocument6 pagesMoney Market FinalPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance Course OutlineDocument3 pagesBehavioral Finance Course OutlineprnishtalaNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument43 pagesCapital BudgetingKhan rufiNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control at Omaxe LimitedDocument81 pagesBudgetary Control at Omaxe Limitedanshul5410100% (1)
- Behavioral Finance: Mental Accounting Bias and Status Quo Bias & It's Impact On Investment Decision MakingDocument23 pagesBehavioral Finance: Mental Accounting Bias and Status Quo Bias & It's Impact On Investment Decision MakingSneha MallNo ratings yet
- Process of Merger and AcquisitionDocument5 pagesProcess of Merger and AcquisitionAnupam MishraNo ratings yet
- Ifim Unit 1 - NotesDocument17 pagesIfim Unit 1 - NotesJyot DhamiNo ratings yet
- BBA V Indian Financial Systems PDFDocument16 pagesBBA V Indian Financial Systems PDFAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument10 pagesDisaster ManagementAshima GoelNo ratings yet
- The Emotional and Social Intelligences of Effective Leadership Journal of Manageral PhycologyDocument17 pagesThe Emotional and Social Intelligences of Effective Leadership Journal of Manageral PhycologyRafael Rojas100% (1)
- SM-1 Presentation - Strategic LensesDocument11 pagesSM-1 Presentation - Strategic LensesShriyas BhartiaNo ratings yet
- Loan Syndication For Domestic Borrowings in Merchant BankingDocument24 pagesLoan Syndication For Domestic Borrowings in Merchant BankingKinjal ShahNo ratings yet
- FM Class Notes Day1Document5 pagesFM Class Notes Day1febycvNo ratings yet
- Mergers and AcquisitionDocument56 pagesMergers and AcquisitionRohit Singhal100% (1)
- The Impact of The Behavioral Factors On Investment Decision Making A Systemic Review On Financial Institutions PDFDocument15 pagesThe Impact of The Behavioral Factors On Investment Decision Making A Systemic Review On Financial Institutions PDFWiduri PutriNo ratings yet
- Types of NBFCDocument16 pagesTypes of NBFCathiraNo ratings yet
- Analysis Investment Decision Indiabulls PDFDocument72 pagesAnalysis Investment Decision Indiabulls PDFAkshata MasurkarNo ratings yet
- Yes Bank Corp Govn.Document24 pagesYes Bank Corp Govn.choco_pie_952No ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument56 pagesWorking Capital ManagementSahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Capital Market in IndiaDocument60 pagesCapital Market in IndiaR Rabi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Concept of Capital MarketDocument11 pagesMeaning and Concept of Capital Marketmanyasingh100% (1)
- Shraddha ProjectDocument70 pagesShraddha ProjectAkshay Harekar50% (2)
- Security Market Operations BookDocument282 pagesSecurity Market Operations BookAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System BBA Core Notes, EbookDocument261 pagesIndian Financial System BBA Core Notes, EbookNeel JoshiNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Financial SystemDocument12 pagesEvolution of Financial SystemGautam JayasuryaNo ratings yet
- Behv FinanceDocument109 pagesBehv FinanceBhanupratapSinghRathoreNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour 2 PPT at Bec Doms 2009 Bagalkot MbaDocument12 pagesConsumer Behaviour 2 PPT at Bec Doms 2009 Bagalkot MbaBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)0% (1)
- The Effects of Deposits Mobilization On Financial Performance in Commercial Banks in Rwanda. A Case of Equity Bank Rwanda Limited PDFDocument28 pagesThe Effects of Deposits Mobilization On Financial Performance in Commercial Banks in Rwanda. A Case of Equity Bank Rwanda Limited PDFJohn FrancisNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project Report SbimfDocument41 pagesSummer Training Project Report SbimfPrateek PanchalNo ratings yet
- Project BodyDocument105 pagesProject BodyManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Mergers & AcquisitionsDocument123 pagesMergers & Acquisitionssmh9662No ratings yet
- Investment Analysis in BanksDocument63 pagesInvestment Analysis in Bankschandu_jjvrpNo ratings yet
- Akash 123Document44 pagesAkash 123praveshNo ratings yet
- Mergers and Acquisitions (Global Scenario) 10 Chapter 1Document25 pagesMergers and Acquisitions (Global Scenario) 10 Chapter 1bhagaban_fm8098No ratings yet
- Overview of Indian Financial Systems and MarketsDocument17 pagesOverview of Indian Financial Systems and MarketsPremendra SahuNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision MakingDocument24 pagesBehavioral Biases in Investment Decision MakingERika PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Debt Analysis and ManagementDocument47 pagesDebt Analysis and ManagementRahul AtodariaNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundDocument61 pagesMutual FundYogendra AmbadeNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure and Its Impact On ProfitabilityDocument26 pagesCapital Structure and Its Impact On ProfitabilityRajesh Mer100% (1)
- A Project On Capital Market: Submitted To: Punjab Technical University, JalandharDocument95 pagesA Project On Capital Market: Submitted To: Punjab Technical University, JalandharSourav ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 1 - Indian Companies Act, 1956Document4 pages1 - Indian Companies Act, 1956Sahil100% (1)
- ABHISHEK PROJECT UpdatedDocument64 pagesABHISHEK PROJECT UpdatedAbhishek khadeNo ratings yet
- Theory of Capital Structure (Assigement - 1) .Document7 pagesTheory of Capital Structure (Assigement - 1) .Ritesh Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Non-Banking Financial CompaniesDocument59 pagesNon-Banking Financial CompaniesFarhan JagirdarNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument14 pagesFinancial ServicesChaitanya NandaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Financial Performance On Stock PriceDocument14 pagesEffect of Financial Performance On Stock PriceMuhammad Yasir YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Modern BankingDocument15 pagesModern BankingRavi ChavdaNo ratings yet
- XXXXX MFDocument24 pagesXXXXX MFpratik0909No ratings yet
- Comparative Financial Strength of Sbi and Icici BankDocument64 pagesComparative Financial Strength of Sbi and Icici BankSupritee beheraNo ratings yet
- BFSM Unit IDocument30 pagesBFSM Unit IAbhinayaa SNo ratings yet
- Final Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHADocument67 pagesFinal Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHAYukta SalviNo ratings yet
- Behavioral FinanceDocument18 pagesBehavioral FinanceFebie Gayap FelixNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance Introduction ChapterDocument11 pagesBehavioral Finance Introduction Chapterkhush preetNo ratings yet
- Navigating Investor Behavior: Insights from Behavioral FinanceFrom EverandNavigating Investor Behavior: Insights from Behavioral FinanceNo ratings yet
- Summary of Michael M. Pompian's Behavioral Finance and Wealth ManagementFrom EverandSummary of Michael M. Pompian's Behavioral Finance and Wealth ManagementNo ratings yet
- ObliRaj SAP E REC 0801250580344Document4 pagesObliRaj SAP E REC 0801250580344Jashim MohammedNo ratings yet
- VoyagerMulti 5.6.1.26 - Release BulletinDocument16 pagesVoyagerMulti 5.6.1.26 - Release Bulletincristhian alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Monday OBD Symposium PresentationsDocument10 pagesMonday OBD Symposium PresentationsChaos XiaNo ratings yet
- Business Forecasting Using RDocument32 pagesBusiness Forecasting Using RshanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Environmental Pollution ObjectivesDocument10 pagesUnit - 3 Environmental Pollution ObjectivesKavitha SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Role of Students Disaster ManagementDocument4 pagesRole of Students Disaster ManagementDILIP VIJAY RAM.A100% (2)
- 3-Cyrus Mistry Vs Ratan Tata, A Valuable Lesson For B-School StudentsDocument3 pages3-Cyrus Mistry Vs Ratan Tata, A Valuable Lesson For B-School StudentsMadhura DamleNo ratings yet
- Newmed Bagian 3 Abdul BarDocument10 pagesNewmed Bagian 3 Abdul BarRafa Abar OfficialNo ratings yet
- Suppression of Drill-String Stick-Slip VibrationDocument5 pagesSuppression of Drill-String Stick-Slip VibrationYan Nazareth SimõesNo ratings yet
- DR Vijay Pahwa VS Samir Mukhopadhyay Deputy Commissioner 129CTR64Document2 pagesDR Vijay Pahwa VS Samir Mukhopadhyay Deputy Commissioner 129CTR64Mukesh RathodNo ratings yet
- Solution To CW Game Theory Part 3Document2 pagesSolution To CW Game Theory Part 3Francine Kye DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes Far210Document23 pagesChapter 1 Notes Far210Muzzammil Azfar Merzuki100% (1)
- Level3 ChargingDocument19 pagesLevel3 Chargingtarx441No ratings yet
- Abbreviations and AcronymsDocument5 pagesAbbreviations and AcronymsTania GalitchiNo ratings yet
- Sample Cover Letter For Banking InternshipDocument6 pagesSample Cover Letter For Banking InternshipYip Tuck WaiNo ratings yet
- Ab Und AufzugDocument5 pagesAb Und AufzugelvagojpNo ratings yet
- Are Nsukka People Northern IgbosDocument11 pagesAre Nsukka People Northern IgbosKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Calgarth Investments, Ltd. v. Bank Saderat Iran, and Bank Saderat Iran, New York Agency, 108 F.3d 329, 2d Cir. (1997)Document2 pagesCalgarth Investments, Ltd. v. Bank Saderat Iran, and Bank Saderat Iran, New York Agency, 108 F.3d 329, 2d Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- English Formative Test - 11 Form - Block 3Document4 pagesEnglish Formative Test - 11 Form - Block 3FragyNo ratings yet
- P12 HilgendorfDocument9 pagesP12 HilgendorfrutwickNo ratings yet
- Log 115404299 06.01.2024Document4 pagesLog 115404299 06.01.2024massayyrasbussinesmanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative-Methods-for-Business - Summer 2020Document6 pagesQuantitative-Methods-for-Business - Summer 2020Nlh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 6 Statistical Process ControlDocument47 pages6 Statistical Process ControlLaxerNo ratings yet
- Day 2 FW Training DeckDocument234 pagesDay 2 FW Training DeckMac GinolosNo ratings yet
- Road Safety: Mass Media CampaignsDocument88 pagesRoad Safety: Mass Media CampaignsMohammed MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- Xm8inside PDFDocument1 pageXm8inside PDFMark YatesNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation and Ranking The Branches of Bank Using FAHP and TOPSISDocument19 pagesPerformance Evaluation and Ranking The Branches of Bank Using FAHP and TOPSISZach LeulNo ratings yet
Introduction To Behavioral Finance
Introduction To Behavioral Finance
Uploaded by
Kimberly Serafica FeleoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction To Behavioral Finance
Introduction To Behavioral Finance
Uploaded by
Kimberly Serafica FeleoCopyright:
Available Formats
INTRODUCTION TO BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
DENIA H . MARADDAG INSTRUCTOR
BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
• Behavioral finance is an area of study focused on how psychological influences can affect
market outcomes.
• Behavioral finance can be analyzed to understand different outcomes across a variety of
sectors and industries.
• One of the key aspects of behavioral finance studies is the influence of psychological biases.
• Daniel Kahnneman and Amos Tversky – considered as the Fathers of Behavioral Finance
“ Behavioral Finance is afield of finance that proposes psychology-based theories to
explain stock market anomalies such as severe rises or falls in stock price. Within behavioural
finance, it is assumed the information structure and the characteristics of market participants
systematically influence individual’s investment decisions as well as market outcomes”
WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
• Behavioral Finance seeks to account for this behaviour, and covers the rationality or otherwise
of people making financial investment decisions. Understanding Behavioural Finance helps us to
avoid emotion-driven speculation leading to losses, and thus devise an appropriate wealth
management strategy.
NATURE OF BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
• Behavioral Finance is just not a part of finance. It is something which is much broader and
wider and includes the insights from behavioural economics, psychology and microeconomic
theory. The main theme of the traditional finance is to avoid all the possible effects of
individual’s personality and mindset.
• Behavioral Finance studies the psychology of financial decisionmaking.
• It makes the understanding of investment decision.
• It is the study of investor’s psychology.
BRANCHES OF BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
• MICRO BEHAVIORAL FINANCE:
- This deals with the behaviour of individual investors. In this, the irrational investors are
compared to rational investors (also known as homo economics or rational economic man)
• MACRO BEHAVIORAL FINANCE:
- This deals with the drawbacks of efficient market hypothesis. EMH is one of the
models in conventional finance that helps us understand the trend of financial markets.
SCOPE OF BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
• To understand the Reasons of Market Anomalies: (like creation of bubbles, the effect of any
event, calendar effect, etc.)
• To identify Investor’s Personalities: Various new financial instruments can be developed to
huge unwanted biases created in financial markets
. • Helps to identify the risks and their hedging strategies.
• Provides an explanation to various corporate activities: Effect of good or bad news, stock split,
dividend decision. Etc.
• To enhance the skill set of investment advisors: Done by better understanding of investor’s
goal, maintaining a systematic approach to advise.
OBJECTIVES OF BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
• To review the debatable issues in Standard Finance.
• To protect the interest of stakeholders in volatile investment scenario.
• To examine the relationship between theories of Standard Finance and Behavioral Finance.
• To analyse the influence of biases on the investment process because of different personalities
in the financial markets.
• To examine the various social responsibilities of the subject.
• To discuss emerging issues in the financial world.
• To discuss the development of new financial instruments to hedge the conventional instruments
against various market anomalies.
• To get the feel of trend of changed events over years, across various economies.
• To examine the contagion effect of various events.
• An effort towards more elaborated identification of investor’s personalities.
• More elaborated discussion on optimum Asset Allocation according to behavioural aspects as
well as aspects like age, gender, income,etc.,of the investors.
STANDARD (TRADITIONAL) FINANCE
• Standard Finance is the body of knowledge built on the pillars of the arbitrage principles of
Miller and Modigliani, the portfolio principles of Markowitz, capital asset prising model
(CAPM) of William Sharpe, Linter and Black, and option pricing medel of Black and Scholes,
and Merton.
ASSUMPTIONS OF BEHAVIOURAL FINANCE
• LOSS AVERSION : The characteristics of seeking to limit the size of the potential loss rather
than seeking to minimise the variability of the potential returns.
• BOUNDED RATIONALITY: The manner in which human being behave, limits their
rationality.
• DENIAL OF RISK: They may know statistical odds but refuse to believe these odds.
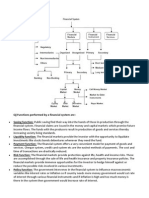
Behavioural Finance is integration of various fields as explained in this figure:
SOCIOLOGY: is the systematic study of human
social behaviour and groups, and influence of
social relationship on attitude and behaviour.
BAHAVIORAL
FINANCE
PSYCHOLOGY: is the scientific study of FINANCE; is the discipline concerned with
behaviour and mental processes, which is determining value and making decisions.
affected by human’s physical, mental, The finance function allocates capital,
and external including the acquisition and allocation.
CHARACTERISTICS OF BEHAVIOURAL FINANCE
1. Heuristics
2. Framing
3. Emotions
4. Market Impact
APPLICATIONS OF BEHAVIORAL FINANCE
1. Investors
2. Corporations
3. Markets
4. Regulators
5. Educations
You might also like
- 6-7. Aligning Service Design and StandardsDocument23 pages6-7. Aligning Service Design and StandardsIrfan Ahmed Sakib100% (1)
- Methods of Comm Planning MiddletonDocument473 pagesMethods of Comm Planning MiddletonKoolet Gal100% (1)
- PRINTERS NotesDocument4 pagesPRINTERS NotesFridah Apondi83% (6)
- Annamalai UniversityDocument392 pagesAnnamalai UniversitySmiles PrintingNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Behavioral Finance On Stock Markets PDFDocument11 pagesThe Impact of Behavioral Finance On Stock Markets PDFprema100% (1)
- Behavioral Finance: by Sudeshna Dutta Assistant Professor BiitmDocument14 pagesBehavioral Finance: by Sudeshna Dutta Assistant Professor BiitmSudeshna RoyNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Dahiya FinalDocument46 pagesJyoti Dahiya FinalJyoti dahiyaNo ratings yet
- Pes Institute of Technology - Bangalore South Campus Dept. of MBADocument34 pagesPes Institute of Technology - Bangalore South Campus Dept. of MBADuma DumaiNo ratings yet
- Money Market FinalDocument6 pagesMoney Market FinalPriyanka SharmaNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance Course OutlineDocument3 pagesBehavioral Finance Course OutlineprnishtalaNo ratings yet
- Capital BudgetingDocument43 pagesCapital BudgetingKhan rufiNo ratings yet
- Budgetary Control at Omaxe LimitedDocument81 pagesBudgetary Control at Omaxe Limitedanshul5410100% (1)
- Behavioral Finance: Mental Accounting Bias and Status Quo Bias & It's Impact On Investment Decision MakingDocument23 pagesBehavioral Finance: Mental Accounting Bias and Status Quo Bias & It's Impact On Investment Decision MakingSneha MallNo ratings yet
- Process of Merger and AcquisitionDocument5 pagesProcess of Merger and AcquisitionAnupam MishraNo ratings yet
- Ifim Unit 1 - NotesDocument17 pagesIfim Unit 1 - NotesJyot DhamiNo ratings yet
- BBA V Indian Financial Systems PDFDocument16 pagesBBA V Indian Financial Systems PDFAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Disaster ManagementDocument10 pagesDisaster ManagementAshima GoelNo ratings yet
- The Emotional and Social Intelligences of Effective Leadership Journal of Manageral PhycologyDocument17 pagesThe Emotional and Social Intelligences of Effective Leadership Journal of Manageral PhycologyRafael Rojas100% (1)
- SM-1 Presentation - Strategic LensesDocument11 pagesSM-1 Presentation - Strategic LensesShriyas BhartiaNo ratings yet
- Loan Syndication For Domestic Borrowings in Merchant BankingDocument24 pagesLoan Syndication For Domestic Borrowings in Merchant BankingKinjal ShahNo ratings yet
- FM Class Notes Day1Document5 pagesFM Class Notes Day1febycvNo ratings yet
- Mergers and AcquisitionDocument56 pagesMergers and AcquisitionRohit Singhal100% (1)
- The Impact of The Behavioral Factors On Investment Decision Making A Systemic Review On Financial Institutions PDFDocument15 pagesThe Impact of The Behavioral Factors On Investment Decision Making A Systemic Review On Financial Institutions PDFWiduri PutriNo ratings yet
- Types of NBFCDocument16 pagesTypes of NBFCathiraNo ratings yet
- Analysis Investment Decision Indiabulls PDFDocument72 pagesAnalysis Investment Decision Indiabulls PDFAkshata MasurkarNo ratings yet
- Yes Bank Corp Govn.Document24 pagesYes Bank Corp Govn.choco_pie_952No ratings yet
- Working Capital ManagementDocument56 pagesWorking Capital ManagementSahil KhanNo ratings yet
- Capital Market in IndiaDocument60 pagesCapital Market in IndiaR Rabi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Concept of Capital MarketDocument11 pagesMeaning and Concept of Capital Marketmanyasingh100% (1)
- Shraddha ProjectDocument70 pagesShraddha ProjectAkshay Harekar50% (2)
- Security Market Operations BookDocument282 pagesSecurity Market Operations BookAbhishek AnandNo ratings yet
- Indian Financial System BBA Core Notes, EbookDocument261 pagesIndian Financial System BBA Core Notes, EbookNeel JoshiNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Financial SystemDocument12 pagesEvolution of Financial SystemGautam JayasuryaNo ratings yet
- Behv FinanceDocument109 pagesBehv FinanceBhanupratapSinghRathoreNo ratings yet
- Consumer Behaviour 2 PPT at Bec Doms 2009 Bagalkot MbaDocument12 pagesConsumer Behaviour 2 PPT at Bec Doms 2009 Bagalkot MbaBabasab Patil (Karrisatte)0% (1)
- The Effects of Deposits Mobilization On Financial Performance in Commercial Banks in Rwanda. A Case of Equity Bank Rwanda Limited PDFDocument28 pagesThe Effects of Deposits Mobilization On Financial Performance in Commercial Banks in Rwanda. A Case of Equity Bank Rwanda Limited PDFJohn FrancisNo ratings yet
- Summer Training Project Report SbimfDocument41 pagesSummer Training Project Report SbimfPrateek PanchalNo ratings yet
- Project BodyDocument105 pagesProject BodyManjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Mergers & AcquisitionsDocument123 pagesMergers & Acquisitionssmh9662No ratings yet
- Investment Analysis in BanksDocument63 pagesInvestment Analysis in Bankschandu_jjvrpNo ratings yet
- Akash 123Document44 pagesAkash 123praveshNo ratings yet
- Mergers and Acquisitions (Global Scenario) 10 Chapter 1Document25 pagesMergers and Acquisitions (Global Scenario) 10 Chapter 1bhagaban_fm8098No ratings yet
- Overview of Indian Financial Systems and MarketsDocument17 pagesOverview of Indian Financial Systems and MarketsPremendra SahuNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Biases in Investment Decision MakingDocument24 pagesBehavioral Biases in Investment Decision MakingERika PratiwiNo ratings yet
- Debt Analysis and ManagementDocument47 pagesDebt Analysis and ManagementRahul AtodariaNo ratings yet
- Mutual FundDocument61 pagesMutual FundYogendra AmbadeNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure and Its Impact On ProfitabilityDocument26 pagesCapital Structure and Its Impact On ProfitabilityRajesh Mer100% (1)
- A Project On Capital Market: Submitted To: Punjab Technical University, JalandharDocument95 pagesA Project On Capital Market: Submitted To: Punjab Technical University, JalandharSourav ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- 1 - Indian Companies Act, 1956Document4 pages1 - Indian Companies Act, 1956Sahil100% (1)
- ABHISHEK PROJECT UpdatedDocument64 pagesABHISHEK PROJECT UpdatedAbhishek khadeNo ratings yet
- Theory of Capital Structure (Assigement - 1) .Document7 pagesTheory of Capital Structure (Assigement - 1) .Ritesh Singh RathoreNo ratings yet
- Non-Banking Financial CompaniesDocument59 pagesNon-Banking Financial CompaniesFarhan JagirdarNo ratings yet
- Financial ServicesDocument14 pagesFinancial ServicesChaitanya NandaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Financial Performance On Stock PriceDocument14 pagesEffect of Financial Performance On Stock PriceMuhammad Yasir YaqoobNo ratings yet
- Modern BankingDocument15 pagesModern BankingRavi ChavdaNo ratings yet
- XXXXX MFDocument24 pagesXXXXX MFpratik0909No ratings yet
- Comparative Financial Strength of Sbi and Icici BankDocument64 pagesComparative Financial Strength of Sbi and Icici BankSupritee beheraNo ratings yet
- BFSM Unit IDocument30 pagesBFSM Unit IAbhinayaa SNo ratings yet
- Final Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHADocument67 pagesFinal Blackbook by Sanju PDF VARSHAYukta SalviNo ratings yet
- Behavioral FinanceDocument18 pagesBehavioral FinanceFebie Gayap FelixNo ratings yet
- Behavioral Finance Introduction ChapterDocument11 pagesBehavioral Finance Introduction Chapterkhush preetNo ratings yet
- Navigating Investor Behavior: Insights from Behavioral FinanceFrom EverandNavigating Investor Behavior: Insights from Behavioral FinanceNo ratings yet
- Summary of Michael M. Pompian's Behavioral Finance and Wealth ManagementFrom EverandSummary of Michael M. Pompian's Behavioral Finance and Wealth ManagementNo ratings yet
- ObliRaj SAP E REC 0801250580344Document4 pagesObliRaj SAP E REC 0801250580344Jashim MohammedNo ratings yet
- VoyagerMulti 5.6.1.26 - Release BulletinDocument16 pagesVoyagerMulti 5.6.1.26 - Release Bulletincristhian alfonsoNo ratings yet
- Monday OBD Symposium PresentationsDocument10 pagesMonday OBD Symposium PresentationsChaos XiaNo ratings yet
- Business Forecasting Using RDocument32 pagesBusiness Forecasting Using RshanNo ratings yet
- Unit - 3 Environmental Pollution ObjectivesDocument10 pagesUnit - 3 Environmental Pollution ObjectivesKavitha SubramaniamNo ratings yet
- Role of Students Disaster ManagementDocument4 pagesRole of Students Disaster ManagementDILIP VIJAY RAM.A100% (2)
- 3-Cyrus Mistry Vs Ratan Tata, A Valuable Lesson For B-School StudentsDocument3 pages3-Cyrus Mistry Vs Ratan Tata, A Valuable Lesson For B-School StudentsMadhura DamleNo ratings yet
- Newmed Bagian 3 Abdul BarDocument10 pagesNewmed Bagian 3 Abdul BarRafa Abar OfficialNo ratings yet
- Suppression of Drill-String Stick-Slip VibrationDocument5 pagesSuppression of Drill-String Stick-Slip VibrationYan Nazareth SimõesNo ratings yet
- DR Vijay Pahwa VS Samir Mukhopadhyay Deputy Commissioner 129CTR64Document2 pagesDR Vijay Pahwa VS Samir Mukhopadhyay Deputy Commissioner 129CTR64Mukesh RathodNo ratings yet
- Solution To CW Game Theory Part 3Document2 pagesSolution To CW Game Theory Part 3Francine Kye DelaCruzNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Notes Far210Document23 pagesChapter 1 Notes Far210Muzzammil Azfar Merzuki100% (1)
- Level3 ChargingDocument19 pagesLevel3 Chargingtarx441No ratings yet
- Abbreviations and AcronymsDocument5 pagesAbbreviations and AcronymsTania GalitchiNo ratings yet
- Sample Cover Letter For Banking InternshipDocument6 pagesSample Cover Letter For Banking InternshipYip Tuck WaiNo ratings yet
- Ab Und AufzugDocument5 pagesAb Und AufzugelvagojpNo ratings yet
- Are Nsukka People Northern IgbosDocument11 pagesAre Nsukka People Northern IgbosKolade YousuffNo ratings yet
- Calgarth Investments, Ltd. v. Bank Saderat Iran, and Bank Saderat Iran, New York Agency, 108 F.3d 329, 2d Cir. (1997)Document2 pagesCalgarth Investments, Ltd. v. Bank Saderat Iran, and Bank Saderat Iran, New York Agency, 108 F.3d 329, 2d Cir. (1997)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- English Formative Test - 11 Form - Block 3Document4 pagesEnglish Formative Test - 11 Form - Block 3FragyNo ratings yet
- P12 HilgendorfDocument9 pagesP12 HilgendorfrutwickNo ratings yet
- Log 115404299 06.01.2024Document4 pagesLog 115404299 06.01.2024massayyrasbussinesmanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative-Methods-for-Business - Summer 2020Document6 pagesQuantitative-Methods-for-Business - Summer 2020Nlh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- 6 Statistical Process ControlDocument47 pages6 Statistical Process ControlLaxerNo ratings yet
- Day 2 FW Training DeckDocument234 pagesDay 2 FW Training DeckMac GinolosNo ratings yet
- Road Safety: Mass Media CampaignsDocument88 pagesRoad Safety: Mass Media CampaignsMohammed MuzakkirNo ratings yet
- Xm8inside PDFDocument1 pageXm8inside PDFMark YatesNo ratings yet
- Performance Evaluation and Ranking The Branches of Bank Using FAHP and TOPSISDocument19 pagesPerformance Evaluation and Ranking The Branches of Bank Using FAHP and TOPSISZach LeulNo ratings yet