Professional Documents
Culture Documents
4-4 Bioenergetics - Biology: 1.0 Figure 1 Shows A Plant Cell
4-4 Bioenergetics - Biology: 1.0 Figure 1 Shows A Plant Cell
Uploaded by
Meera ParaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
4-4 Bioenergetics - Biology: 1.0 Figure 1 Shows A Plant Cell
4-4 Bioenergetics - Biology: 1.0 Figure 1 Shows A Plant Cell
Uploaded by
Meera ParaCopyright:
Available Formats
4-4 Bioenergetics – Biology
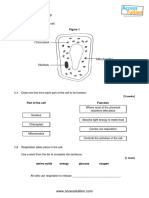
1.0 Figure 1 shows a plant cell.
Figure 1
1.1 Draw one line from each part of the cell to its function.
[3 marks]
Part of the cell Function
Where most of the chemical
reactions take place
Nucleus
Absorbs light energy to make food
Chloroplast
Carries out respiration
Mitochondria
Controls the activities of the cell
1.2 Respiration takes place in the cell.
Use a word from the list to complete the sentence.
[1 mark]
amino acids energy glucose oxygen
All cells use respiration to release _______________________________.
© Exampro 2017 Page 1
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
2.0 An athlete did a 6-month training programme.
Figure 2 shows the effect of the same amount of exercise on his heart rate before and
after the training programme.
Figure 2
2.1 What was the minimum heart rate of the athlete before the training programme?
[1 mark]
Minimum heart rate = ___________________________beats per minute
© Exampro 2017 Page 2
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
2.2 Give two differences between the heart rate of the athlete before and after the training
programme.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
2.3 Which two substances need to be supplied to the muscles in larger amounts during
exercise?
Draw a ring around two substances from the list.
[2 marks]
Carbon dioxide Glucose Lactic acid Oxygen Urea
2.4 Use Figure 2 to find the heart rate of the trained athlete 3 minutes after he stopped
exercising.
[1 mark]
Heart rate = _________________________ beats per minute
The stroke volume of the heart is the volume of blood pumped out of the left side of the
heart in one heart beat.
Figure 3 shows the relationship between the stroke volume and the heart rate before
and after the athlete did the training programme.
Figure 3
© Exampro 2017 Page 3
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
2.5 The cardiac output is calculated using the following equation:
cardiac output = heart rate × stroke volume
Calculate the cardiac output of the athlete after training, 8 minutes after the start of the
exercise. Use information from Figure 2 and Figure 3.
[2 marks]
Show clearly how you work out your answer.
Cardiac output = ___________________cm3 blood per minute
© Exampro 2017 Page 4
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
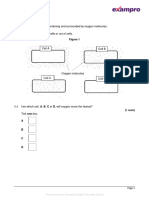
3.0 Figure 4 shows a single-celled alga which lives in fresh water.
Figure 4
3.1 Which part of the cell labelled above is made of cellulose?
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
3.2 Water enters and leaves the algal cell.
State the name of the process by which water moves into cells.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
3.3 Describe what happens to the algal cell as water moves into the cell.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
3.4 The flagellum helps the cell to move through water.
Scientists think that the flagellum and the light-sensitive spot work together to increase
photosynthesis.
Suggest how this might happen.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 5
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 6
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
4.0 This question is about photosynthesis.
4.1 Plants make glucose during photosynthesis.
Some of the glucose is changed into insoluble starch.
What happens to this starch?
Tick one box.
[1 mark]
The starch is converted into oxygen.
The starch is stored for use later.
The starch is used to make the leaf green.
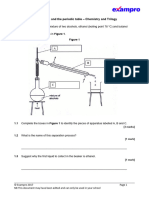
4.2 A student investigated the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis in
pondweed.
Figure 5 shows the way the experiment was set up.
Figure 5
The student needed to control some variables to make the investigation fair.
State two variables the student needed to control in this investigation.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 7
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
4.3 The bubbles of gas are only produced while photosynthesis is taking place.
What two measurements would the student make to calculate the rate of
photosynthesis?
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
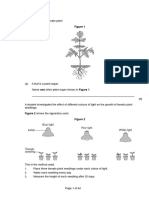
4.4 Figure 6 shows the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis in the
pondweed.
Figure 6
Light intensity in arbitrary units
Name the factor that limits the rate of photosynthesis between the points labelled A
and B on the graph.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
4.5 Suggest which factor might be limiting the rate of photosynthesis between the points
labelled C and D on the graph.
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 8
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
5.0 Anaerobic respiration happens in muscle cells and yeast cells.
The equation describes anaerobic respiration in muscle cells
glucose lactic acid
5.1 How can you tell from the equation that this process is anaerobic?
[1 mark]
_____________________________________________________________________
5.2 Exercise cannot be sustained when anaerobic respiration takes place in muscle cells.
Explain why.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
5.3 Figure 7 shows an experiment to investigate anaerobic respiration in yeast cells.
Figure 7
What gas will bubble into Tube B?
[1 mark]
Draw a circle around one gas.
© Exampro 2017 Page 9
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Carbon dioxide Hydrogen Oxygen Nitrogen Water vapour
5.4 Describe how you could use tube B to measure the rate of the reaction in tube A.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
6.0 Green plants can make glucose.
6.1 Plants need energy to make glucose.
Describe how plants get this energy.
[2 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
6.2 Plants can use the glucose they have made to supply them with energy.
Describe four other ways in which plants use the glucose they have made.
[4 marks]
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
© Exampro 2017 Page 10
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
MARK SCHEME
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
1.1 Nucleus – Controls the activities… 1 mark for each correct line 3
Chloroplast – Absorbs light energy… mark each line from left hand box
Mitochondria – Carries out respiration two lines from left hand box cancels
mark for that box
1.2 energy 1
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
2.1 64 (beats per minute) 1
2.2 any two from: accept correct use of numbers 2
• lower resting pulse accept lower pulse rate
• lower rate during exercise if neither of the first two marking points
• recovers faster after exercise awarded, allow 1 mark for ‘lower rate’.
2.3 glucose 1
oxygen 1
2.4 68 1
2.5 (136 × 100.5) = 13,668 Allow 13000 to 13800. 2
if answer incorrect, allow one mark for
obvious attempt to read both graphs and
multiply
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
3.1 cell wall 1
3.2 osmosis allow diffusion 1
3.3 cell becomes turgid / swollen 1
3.4 any two from: 2
• light sensitive spot detects light
• tells flagellum to move towards light
• more light = more photosynthesis
© Exampro 2017 Page 11
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
4.1 the starch is stored for use later 1
4.2 any two from: ignore reference to time 2
• carbon dioxide (concentration)
• temperature allow 1 mark for light if colour is not
• light colour / wavelength already awarded.
• pH
• size of pondweed / plant
• same species / type of pondweed ignore volume of water unqualified
• volume of water in the tube
4.3 number / amount of bubbles or amount of ignore the bubbles unqualified 1
gas / oxygen
(relevant reference to) time / named time allow how long it bubbles for 1
interval do not allow time bubbles start / stop
ignore speed / rate of bubbling
ignore instruments
do not allow other factors e.g.
temperature
accept how many bubbles per minute for
2 marks
4.4 Light intensity 1
4.5 Temperature/carbon dioxide / CO2 Allow heat 1
allow CO2
do not allow CO2
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
5.1 no oxygen (is used) 1
5.2 muscles become fatigued / stop contracting 1
(because) not enough energy is transferred 1
5.3 carbon dioxide 1
5.4 count the bubbles or measure volume of 1
gas
in a given time 1
© Exampro 2017 Page 12
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
Qu No. Extra Information Marks
light is trapped / absorbed / used extra answers cancel mark 1
ignore solar / sunshine
6.1 by chlorophyll / chloroplasts if no other marks awarded, allow 1 mark 1
for photosynthesis / equation for
photosynthesis
(to make) starch (for storage) ignore for growth (unqualified) 1
ignore respiration
(to make) fat / oil (for storage) 1
(to make) amino acids / proteins / enzymes allow for active transport 1
6.2
allow any other correct, named organic
substances (eg DNA / ATP / chlorophyll /
hormone)
(to make) cellulose / cell walls if no named examples, allow ‘to make 1
named cell structures’ for max. 1 mark
© Exampro 2017 Page 13
NB This document may have been edited and can only be used in your school
You might also like
- Exercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance Eleventh Edition Scott K Powers Full ChapterDocument68 pagesExercise Physiology Theory and Application To Fitness and Performance Eleventh Edition Scott K Powers Full Chapterhoward.mcguirl51483% (6)
- Lehninger Test Bank 13Document14 pagesLehninger Test Bank 13Hina Batool100% (2)
- Gr.11 SBA Practical Task 2 AUG 2023Document7 pagesGr.11 SBA Practical Task 2 AUG 2023Cebiswa MambaNo ratings yet
- Practice Paper 1 Biology: WWW - Oxfordsecodary.co - UkDocument11 pagesPractice Paper 1 Biology: WWW - Oxfordsecodary.co - UkOHNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocument15 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableRenee DisaNo ratings yet
- Science KS3 Sample TestDocument4 pagesScience KS3 Sample TestIslam Osman100% (1)
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B3.2 TransportDocument22 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B3.2 TransportMeera Para100% (1)
- Bioenergetics Lesson 1Document37 pagesBioenergetics Lesson 1SalMaNaNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Fundamentals and Practice, Vol 1, Seventh EditionDocument16 pagesLife Sciences Fundamentals and Practice, Vol 1, Seventh EditionRebati Raman Panda0% (1)
- B4 BioenergeticsDocument10 pagesB4 Bioenergeticsisaaceden24No ratings yet
- 4-4 Bioenergetics - Trilogy: 1.0 Figure 1 Shows A Plant CellDocument10 pages4-4 Bioenergetics - Trilogy: 1.0 Figure 1 Shows A Plant Cellmgybh8vm6nNo ratings yet
- Biology Trilogy BioenergeticsDocument10 pagesBiology Trilogy Bioenergeticsakio haruNo ratings yet
- Biology_Trilogy_OrganisationDocument11 pagesBiology_Trilogy_Organisationsritan.parupudiNo ratings yet
- Biology Trilogy Cell BiologyDocument11 pagesBiology Trilogy Cell BiologyShalini MishraNo ratings yet
- Cover Booklet KS4 Biology 1Document38 pagesCover Booklet KS4 Biology 1Peter HoskinsNo ratings yet
- Animal CellDocument9 pagesAnimal Cellblooa049.302No ratings yet
- B1 Cell BiologyDocument11 pagesB1 Cell Biologyisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics Questions GcseDocument50 pagesBioenergetics Questions GcseDharm GajjarNo ratings yet
- B2 OrganisationDocument9 pagesB2 Organisationisaaceden24No ratings yet
- Physics Trilogy Atomic StructureDocument10 pagesPhysics Trilogy Atomic Structuremanjula.shiwanthiNo ratings yet
- Biology Term2 Assessment Y10Document10 pagesBiology Term2 Assessment Y109hgdpyk96jNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Enzymes QuestionsDocument2 pagesAn Introduction To Enzymes QuestionsA.R.No ratings yet
- 3 X Biology Paper 2 On 3 Nov 2020Document12 pages3 X Biology Paper 2 On 3 Nov 2020HajiBabaNo ratings yet
- 5-8 Chemical Analysis - Trilogy: 1.0 This Question Is About Pure Substances and MixturesDocument11 pages5-8 Chemical Analysis - Trilogy: 1.0 This Question Is About Pure Substances and MixturesKhadijahNo ratings yet
- Unit Test Nervous System 14.1Document4 pagesUnit Test Nervous System 14.1ArnelNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableDocument17 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Atomic Structure Periodic TableVictor WuNo ratings yet
- Exams 2022 Paper 3 SCDXPKDocument39 pagesExams 2022 Paper 3 SCDXPKQueen Bee (Tt)No ratings yet
- S8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestDocument2 pagesS8 - End-of-Unit 1 TestaloonaothmanNo ratings yet
- Biology Higher ExtendedDocument47 pagesBiology Higher ExtendedAbhinNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Respiration QPDocument26 pages4.2 Respiration QPliufanjing07No ratings yet
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesЕгор БиндерNo ratings yet
- 2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Practical Booklet-Ch1-6Document32 pages2324 Level M (Gr11 UAE - GULF) Biology Practical Booklet-Ch1-6Van halenNo ratings yet
- S9 Mid-Point Test U1and4Document4 pagesS9 Mid-Point Test U1and4Moganoni MogaNo ratings yet
- Proteins and EnzymesDocument94 pagesProteins and Enzymesdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- 3 - Particle - ModelDocument13 pages3 - Particle - ModelHaleemahNo ratings yet
- B Test 4Document2 pagesB Test 4LAKIESHANo ratings yet
- Populations in Ecosystems Summer Holiday Homework QsDocument11 pagesPopulations in Ecosystems Summer Holiday Homework QsSohail AliNo ratings yet
- Ques Blue3 KMKTDocument17 pagesQues Blue3 KMKTfatihah abdullahNo ratings yet
- F4 Midterm Exam 2019 (Ans)Document13 pagesF4 Midterm Exam 2019 (Ans)Hua Xin LeeNo ratings yet
- Modul Sains Tahun 4 PKP (DLP)Document15 pagesModul Sains Tahun 4 PKP (DLP)why da100% (1)
- Soalan Set 2Document6 pagesSoalan Set 2Zazol Al-KiraniNo ratings yet
- B5 - Homeostasis-And-ResponseDocument11 pagesB5 - Homeostasis-And-Responseisaaceden24No ratings yet
- 3 X Biology Paper 2 On 3 Nov 2020 Full and FinalDocument11 pages3 X Biology Paper 2 On 3 Nov 2020 Full and FinalHajiBabaNo ratings yet
- c6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change HTDocument73 pagesc6 The Rate and Extent of Chemical Change HTewfjehwjfNo ratings yet
- Midterm Paper 22008Document10 pagesMidterm Paper 22008husnaihsanNo ratings yet
- Guided Notes-Teacher LectureDocument8 pagesGuided Notes-Teacher Lectureapi-417232384No ratings yet
- Bio Unit 4Document38 pagesBio Unit 4Mei NgNo ratings yet
- Oxo AQA16 ORCBH Xs01 XxaannDocument11 pagesOxo AQA16 ORCBH Xs01 XxaannOHNo ratings yet
- What's More: Activity 1.1 Understanding The LeafDocument8 pagesWhat's More: Activity 1.1 Understanding The LeafRosana AquinoNo ratings yet
- B 4 Revision PackDocument64 pagesB 4 Revision PackKrish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Set 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9Document20 pagesSet 2 Bioenergetics Grades 7 9tnishtalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 2B Guided Notes 2022Document6 pagesUnit 2B Guided Notes 2022Victoria WarrenNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Separate and Trilogy Rate and Extent Chemical Change-2Document13 pagesChemistry Separate and Trilogy Rate and Extent Chemical Change-2wolfergemerioNo ratings yet
- Respiration QuestionsDocument12 pagesRespiration Questionsoghieghie jattoNo ratings yet
- A01 Short Answer QuestionsDocument21 pagesA01 Short Answer Questionsmsuria06No ratings yet
- Plant Hormones QPDocument11 pagesPlant Hormones QPlizablatchfordNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument25 pagesEarth and Life ScienceJonathan MercadoNo ratings yet
- GCSE B H Paper 1 RespirationDocument25 pagesGCSE B H Paper 1 RespirationKayNo ratings yet
- Cambridge S8 CH3 - 9 TESTDocument15 pagesCambridge S8 CH3 - 9 TESTsohambhole2011100% (2)
- PhotosynthesisDocument103 pagesPhotosynthesisdfq67gtkqsNo ratings yet
- Stage 8 Practice ScienceDocument4 pagesStage 8 Practice ScienceSannati Deshpande100% (1)
- Kidney Dissection Lab ReportDocument2 pagesKidney Dissection Lab ReportPatricia CroweNo ratings yet
- Practice Test: Obtained MarksDocument2 pagesPractice Test: Obtained MarksAhmed HamimNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Ellam Unnale - Infaa AlociousDocument357 pagesEllam Unnale - Infaa AlociousMeera Para100% (1)
- Inheritance Variation and Evolution - Mendel I ANS.137947888Document1 pageInheritance Variation and Evolution - Mendel I ANS.137947888Meera ParaNo ratings yet
- Inheritance Variation and Evolution - Fossilisation ANS.137947888Document2 pagesInheritance Variation and Evolution - Fossilisation ANS.137947888Meera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B3.3 HomeostasisDocument26 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B3.3 HomeostasisMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceDocument35 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B2.5 InheritanceMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B2.2 PhotosynthesisDocument27 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B2.2 PhotosynthesisMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 2 CoordinationDocument26 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 2 CoordinationMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B2.3 EnzymesDocument33 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B2.3 EnzymesMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 4 AdaptationDocument27 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 4 AdaptationMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 6 VariationDocument26 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 6 VariationMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Exampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 1 Keeping HealthyDocument26 pagesExampro GCSE Biology: B1 Chapter 1 Keeping HealthyMeera ParaNo ratings yet
- Nutrition: Study Guide For Module No. 3Document7 pagesNutrition: Study Guide For Module No. 3MC BlancoNo ratings yet
- Lee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeDocument25 pagesLee, Thonylet E. Mabinta, Dianne Melad, Maria FeShivaveerakumar S. Chandrikimath100% (1)
- BioenergeticsDocument37 pagesBioenergeticsTristan NatsirtNo ratings yet
- 9 Introduction To Metabolism and Bioenergetics Reading ModuleDocument17 pages9 Introduction To Metabolism and Bioenergetics Reading ModuleSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Creative Writing 12Document12 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan in Creative Writing 12ASELA PE?FIELNo ratings yet
- BioenergeticsDocument2 pagesBioenergeticsafzal0026No ratings yet
- Life Sciences Fundamentals and Practice, Vol 1, Seventh EditionDocument16 pagesLife Sciences Fundamentals and Practice, Vol 1, Seventh EditionShalini SinhaNo ratings yet
- Ix-Biology - Target Paper 2024 - Homelander GroupDocument3 pagesIx-Biology - Target Paper 2024 - Homelander GroupTaroobaNo ratings yet
- Holdings in The Crop Science LibraryDocument27 pagesHoldings in The Crop Science LibraryAnotidaishe NyakudyaNo ratings yet
- FrequenciesDocument35 pagesFrequenciesAbhi M.V.No ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Muscle MetabolismDocument56 pagesBioenergetics and Muscle MetabolismJustin DoepkerNo ratings yet
- Outlining A Text-STUDENTDocument6 pagesOutlining A Text-STUDENTJulieSanchezErsandoNo ratings yet
- 3 BiochemistryDocument19 pages3 BiochemistryAbout PondicherryNo ratings yet
- Anexo 1. Botham, K Mayes, P. (2022) - Chapter 11 - Bioenergetics - The Role of ATP. McGraw Hill.Document9 pagesAnexo 1. Botham, K Mayes, P. (2022) - Chapter 11 - Bioenergetics - The Role of ATP. McGraw Hill.Liliana LNo ratings yet
- Topic: Bioenergetics: Living OrganismsDocument9 pagesTopic: Bioenergetics: Living OrganismsNaiomiNo ratings yet
- Biology 10th Edition Solomon Solutions ManualDocument5 pagesBiology 10th Edition Solomon Solutions Manualspawnerminutiaxae7n100% (41)
- Full Chapter Present Knowledge in Nutrition Volume 1 Basic Nutrition and Metabolism 11Th Edition Bernadette P Marriott PDFDocument45 pagesFull Chapter Present Knowledge in Nutrition Volume 1 Basic Nutrition and Metabolism 11Th Edition Bernadette P Marriott PDFryan.king862100% (8)
- The Energetics of Genome ComplexitDocument7 pagesThe Energetics of Genome Complexitnome sobrenomeNo ratings yet
- Biology IX-X Syllabus 2022Document57 pagesBiology IX-X Syllabus 2022Samar IqbalNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics, Photosynthesis and Energy Flow HandoutDocument2 pagesBioenergetics, Photosynthesis and Energy Flow Handout1DerfulHarrehNo ratings yet
- Bioenergetics and Regulation of Metabolism FlashcardsDocument48 pagesBioenergetics and Regulation of Metabolism FlashcardsLejNo ratings yet
- Anaerobic Energy MetabolismDocument1 pageAnaerobic Energy MetabolismSoham DibyachintanNo ratings yet
- Biochem Chapter Bioenergetics MCQDocument14 pagesBiochem Chapter Bioenergetics MCQGeorges Bi100% (1)
- Cellular EnergeticDocument37 pagesCellular EnergeticmiomodgNo ratings yet
- Chapter 13 Bioenergetics and Biochemical Reaction Types CHEM 641 Prof.Document9 pagesChapter 13 Bioenergetics and Biochemical Reaction Types CHEM 641 Prof.nahnah1No ratings yet
- Chapter 14Document12 pagesChapter 14Marie St. LouisNo ratings yet