Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Sources of Water Source Collection Advantages Disadvantages
Sources of Water Source Collection Advantages Disadvantages
Uploaded by
Jubillee MagsinoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Sources of Water Source Collection Advantages Disadvantages
Sources of Water Source Collection Advantages Disadvantages
Uploaded by
Jubillee MagsinoCopyright:
Available Formats
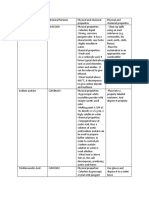
SOURCES OF WATER
For Domestic Use:
SOURCE COLLECTION ADVANTAGES DISADVANTAGES
- Roofs of buildings and
- Only collected
special water sheds
during wet season
- Stored in cisterns or
- Soft and pure - Storage becomes a
ponds
Rain Water - Suitable for the hot breeding place for
- Cistern water for
water supply system mosquitoes
drinking should be
- Possibility that it is
boiled, chlorinated, or
not clean
otherwise sterilized
- Contains large
- Easy to acquire
amounts of
- Large quantities
bacteria; organic
Natural - Used for irrigation,
- Obtained from ponds, and inorganic
Surface industrial purposes
lakes and rivers substances
Water and, when treated,
- Purification and
for community
treatment is
water supply
necessary
- Obtained underground
by means of - Abundant supply - May have organic
Ground mechanical and - Requires less matter and
Water manual equipment treatment because chemical elements
- Obtained from springs of natural filtering - Its hardness
and wells
WATER TREATMENT
PROBLEMS CAUSE EFFECTS CORRECTION
- Corrosion of non-
- Raising alkaline
Entrance of oxygen and ferrous pipes
Acidity content with a
carbon dioxide - Rusting and clogging
neutralizer
of steel pipes
- Clogging of pipes
Presence of magnesium - Boiling
Hardness - Impaired laundry
and calcium salts - Ion exchanger
and cooking
- Discoloration
Turbidity Silt or mud in surface - Filtration
- Bad taste
Presence of iron and - Discoloration of
Color - Oxidizing filter
manganese fixtures and laundry
Contamination by
Pollution organic matter or - Disease - Chlorination
sewage
OBJECTIONALBLE REASONS FOR TREATMENT
ELEMENT
Calcium, Magnesium Produces hardness OBJECTIONALBLE METHOD OF TREATMENT
Bad taste and odor ELEMENT
Highly corrosive to Carbon Dioxide Aeration
Sulfur
plumbing Hydrogen Sulfide
Stains clothing Suspended Coagulation and settling
Bad taste material process
Salt
Highly corrosive Chemicals
Stains clothing and Bacteria
Sand filtration
plumbing fixtures Calcium/ Addition of water softeners
Iron Interferes with water Magnesium
softeners Iron Iron filters
Iron bacteria clogs pipes Sulfur Chlorination
Unhealthy; may cause Pathogenic Disinfection
Pathogenic germs
poliomyelitis germs
Highly corrosive Marble
Acid Picks up lead Acid
Limestone filtration
Stains clothing
Algae Bad taste and color
PURIFICATION OF WATER
Two Types of Waste
Aeration 1. Solid Waste – discharged by water closet
- Sparing the water into the atmosphere 2. Liquid Waste – coming from various fixtures
through jets or passing it over rough
surfaces to remove unwanted chemicals Two Types of Drainage Piping
1. Soil Pipe – pipes that convey waste coming
Coagulation & Precipitation from water closet
- Addition of coagulants (ferrous sulfate, 2. Waste Pipe – pipe that conveys waste from
lime) to the water which cause the larger fixtures other than the water closet
suspended particles to form a gelatinous
mass which precipitates readily. Drainage Installation
- Sometimes referred to as DWV
Filtration o D – drainage of solid waste
- Water is passed through layers of sand and o W – waste coming from various
gravel in concrete basins to remove finer fixtures other than water closet
suspended particles o V – ventilation of the piping system
Sedimentation Definition of Terms
- Water is passed through basins so
sediments can settle through a period of Air Gap – unobstructed vertical distance through
time the free atmosphere between the lowest opening
from any pipe or faucet supplying water to a tank
Chlorination or other devices.
- Water is injected with hypo-chlorite or
chlorine gas to kill harmful bacteria Back flow – flow of water, or other liquid mixture
or substances into the distributing pipes of a
The Drainage System potable
supply of water form any source OTHER than its - Thickness is twice as that of the standard
intended source. cast iron pipe
- Superior for embedment in concrete
Plumbing Materials structure for having the same material
properties
1. Cast iron soil pipe
2. Acid resistant cast iron pipe Bituminous Fiber Sewer Pipe
3. Asbestos pipe - Cheapest of all types
4. Bituminous fiber sewer pipe - Light in weight, slightly flexible
5. Vitrified clay pipe - Can take slight soil movement without
6. Lead pipe danger
7. Galvanized steel pipe - May be softened/damaged
8. Galvanized wrought iron pipe
9. Brass pipe Vitrified Clay Pipe
10. Copper pipe - One of the oldest materials
11. Plastic or synthetic pipe - Highly resistant to most acids
12. Stainless steel pipe - Made in short lengths of 750mm
Cast iron pipe Lead Pipe
- Most popular and generally specified - One of the oldest plumbing materials used
material by the Egyptians, Greeks and Romans
- Used in buildings less than 25 storey high - Highly resistant to acid
- Commercial length: 600 cm - Suitable for underground installation
- Diameters: 50-150mm - Never used to convey water for human
- Two types of Cast Iron Pipe consumption because it is poisonous and
o SV type – used for building injurious to health
installations
o XV type – extra duty pipe used for Galvanized Wrought Iron Pipe
underground installations - Better in quality than the steel pipe for
- Four Varieties plumbing installation
o Standard pipe - More resistant to acid waste than steel pipe
o Single hub pipe
o Double hub pipe Brass Pipe
o Hubless pipe (bell-less pipe) - One of the most expensive types of pipe
- Made of an alloy or zinc and copper
Acid Resistant Cast iron pipe
- Made of an alloy, cast iron and silicon Copper Pipe
- Installed in chemical laboratories, - Durable and extremely corrosive resistant
industries, and other installations where material
acid wastes are discharged - Easy to install compared with types of pipe
- Brittles and cracks easily - Cost little more than the steel pipe but its
- Have to be supported at every 1.50m fittings cost lesser
interval - Three Types
o K type
Asbestos Pipe o Heaviest
- Made of asbestos fibers and Portland o Suitable for underground installation
cement
- L type
o Lighter than K
o Available in both flexible and rigid PARTS OF THE COLD WATER DISTRIBUTION
form SYSTEM (POTABLE AND TAP)
o Commonly used in residential water
supply line and for radiant heating Service Pipe
installations - Pipe from the street water main or other
- M type source to the building served
o Thinnest Water Meter
o Available only in rigid form - Device used to measure in liters or gallons
o Designed for small water supply the amount of water that passes through
lines and for radiant heating the water service
installations Horizontal Supply Main
- Principal water distribution pipe running
Plastic or Synthetic Pipes from the water meter
- New concept in the field of plumbing Riser
- Introduced in the Philippines at the early - Water supply extending vertically to one full
70’s story or more to convey water into fixture
- Types Fixture Branch
Rigid type (PIPES) - Water supply pipe between the fixture
o Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC) supply pipe and the water distributing pipe
o Chlorinated Polyvinyl Chloride Control & Valves
(CPVC) - Used for control, isolation and repair of the
o Unplasticized Polyvinyl Chloride water distribution system
(uPVC) Water main
o Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene - Water supply pipe for public community use
Gate Valve
(ABS)
- Valve in which the flow of water is cut off by
o Polypropylene (PP)
means of a circular disc fitted against
o Styrene Rubber Plastic (SR)
machine smoothed faces, at right angles to
Flexible type (TUBING)
the direction of the flow
o The Polyethylene (PE) – coil form;
Check Valve
30m long
- Valve that automatically closes to prevent
o The Polybutylene (PB) – coil form;
the flow of liquid or gas in a reverse
30m -150m long
direction
Globe Valve
Considerations in choosing materials:
- Valve in which the flow of water is cut off by
1. Quality and durability
means of a disk that fits against the valve
2. Resistance to external and internal contact
seal (tortuous passage)
with foreign matters
Building Supply Pipe
3. Resistance to acid waste and other chemical
- Pipe carrying potable water from the water
elements that will pass into it
meter or other source of water supply to a
4. Cost of materials and labor
building or other point of use or distribution
on the lot
COLD WATER DISTRIBUTION SYSTEM
- Water service connection
Water Supply System
Fixture Supply
- Consists of water service pipe, water supply
- Water supply pipe connecting the fixture
line, water distributing pipe and necessary
and fixture branch
branch pipes, fittings and all appurtenances
Direct / Upfeed system
required for the supply of potable water
- Water is provided by the city water
companies using normal pressure from
public water main
You might also like
- Elements, Compounds Mixtures Worksheet 3ADocument8 pagesElements, Compounds Mixtures Worksheet 3AMinorNo ratings yet
- CII Water Technology PPT Rreview 0Document21 pagesCII Water Technology PPT Rreview 0AmodNo ratings yet
- Lec3 - Basic ConceptsDocument4 pagesLec3 - Basic ConceptsRafia AsifNo ratings yet
- Lime For Water PurificationDocument8 pagesLime For Water PurificationXiaomiNo ratings yet
- Plumbing and Sanitary Systems Module 2 Topic 2 LectureDocument39 pagesPlumbing and Sanitary Systems Module 2 Topic 2 Lecturechristian001 LatagNo ratings yet
- Group 2 - Properties of WaterDocument25 pagesGroup 2 - Properties of WaterKade julian RentaNo ratings yet
- Hardness: Intro To 11.15 and 11.15Document2 pagesHardness: Intro To 11.15 and 11.15mortezasabetiNo ratings yet
- Brochure Fujifilm Ion Exchange MembranesDocument6 pagesBrochure Fujifilm Ion Exchange MembranesDiegoNo ratings yet
- Water Chemistry Part 1Document25 pagesWater Chemistry Part 1KUMAR SHANTANUNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Water QualityDocument11 pagesChapter 4 Water Qualityleahsmith1821No ratings yet
- Plumbing File No.2PDFDocument42 pagesPlumbing File No.2PDFMarvel GomezNo ratings yet
- Treatment of Water AND Its Methods: Mr. Rishabh Sood, Graphic Era University DehradunDocument26 pagesTreatment of Water AND Its Methods: Mr. Rishabh Sood, Graphic Era University DehradunRishabh SoodNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 - Water Distribution SystemDocument54 pagesLesson 1 - Water Distribution SystemNicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- ENVE 303 Unit Operations and Processes of Water TreatmentDocument21 pagesENVE 303 Unit Operations and Processes of Water TreatmentAslı GözpınarNo ratings yet
- Iron & Manganese Removal: Advanced Water Treatment SolutionsDocument2 pagesIron & Manganese Removal: Advanced Water Treatment SolutionssalcedopozasNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument68 pagesWater TreatmentHimanshu spoliaNo ratings yet
- Plumbing ReviewerDocument21 pagesPlumbing ReviewerPat BelardoNo ratings yet
- Module 7-Ut2Document2 pagesModule 7-Ut2dxjmotorcyclepartsaccessoriesNo ratings yet
- Grundfosliterature 3153478 PDFDocument5 pagesGrundfosliterature 3153478 PDFRobin GomezNo ratings yet
- Plumbing PPT 2021 File 3Document63 pagesPlumbing PPT 2021 File 3Marvel GomezNo ratings yet
- Mod 1 - 18BT751 - BTSE - Mod 1 - Add Notes - Pptx. 16860413393636Document11 pagesMod 1 - 18BT751 - BTSE - Mod 1 - Add Notes - Pptx. 16860413393636Bhuvan s GaneshkarNo ratings yet
- Coagulation and FlocculationDocument5 pagesCoagulation and FlocculationJay GaleNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument6 pagesReportjazNo ratings yet
- Ion Exchange Resin Data SheetDocument17 pagesIon Exchange Resin Data Sheetiwan prasetyoNo ratings yet
- 6D. Pharmaceutical WatersDocument4 pages6D. Pharmaceutical WatersKim Xiarisse BalugayNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument3 pagesDocumentKyllene Leonor BigsotNo ratings yet
- Eh Water enDocument8 pagesEh Water enmrashid286No ratings yet
- Description of Water Analysis ParametersDocument4 pagesDescription of Water Analysis ParametersMaria Teresa Asmat BautistaNo ratings yet
- Vatren Jurin Micronutrient Uptake and Sources 2015Document26 pagesVatren Jurin Micronutrient Uptake and Sources 2015dya97No ratings yet
- Amine Data SheetDocument1 pageAmine Data SheetMohammad Al-TamimiNo ratings yet
- Water TreatmentDocument153 pagesWater Treatmentsada sivaNo ratings yet
- Tratamiento de Agua Potable Suavizacion Del Agua Intercambio Ionico InglesDocument4 pagesTratamiento de Agua Potable Suavizacion Del Agua Intercambio Ionico Ingleshenry molinaNo ratings yet
- Welcome: Water Chemistry and Operation of DM PlantDocument126 pagesWelcome: Water Chemistry and Operation of DM PlantahmadrNo ratings yet
- Fertilizer Ind 2Document16 pagesFertilizer Ind 2Shraddha MalveNo ratings yet
- Pond Type and DescriptionDocument2 pagesPond Type and DescriptionAbd Manaf Abu BakarNo ratings yet
- Agricultural and Biological Engineering: Water SofteningDocument4 pagesAgricultural and Biological Engineering: Water SofteningMohamad RidzwanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 - Shear Force at A Section of A Determinate BeamDocument53 pagesChapter 6 - Shear Force at A Section of A Determinate Beammoneesha sriNo ratings yet
- WEEK7 AUDIO 2020 - sscc4233 WTPDocument63 pagesWEEK7 AUDIO 2020 - sscc4233 WTPchennivoon00No ratings yet
- 1 - Water and The Human NeedsDocument25 pages1 - Water and The Human NeedsE&N CommissionNo ratings yet
- The Leachate Treatment by Using NaturalDocument4 pagesThe Leachate Treatment by Using NaturalA Nicole Rodríguez OportoNo ratings yet
- Madhu PaperDocument16 pagesMadhu PaperJaisy PatelNo ratings yet
- Inorgchem Lec Prelim Reviewer 2Document5 pagesInorgchem Lec Prelim Reviewer 2Raven Janica DeangNo ratings yet
- Treatment RO Treatment: DeionizationDocument7 pagesTreatment RO Treatment: DeionizationZAHID HUSSAINNo ratings yet
- A Boiler Water ChemistryDocument14 pagesA Boiler Water ChemistryMuhammad MusharrafNo ratings yet
- Wae Oarp WebDocument8 pagesWae Oarp WebRoberto Leon MendezNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Water Quality and TreatmentDocument56 pagesLecture 6 - Water Quality and Treatmentjustdopa14No ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureeksonwilliamsdavina79No ratings yet
- Removal of Lead From Waste Water Using Chemically Modified Jackfruit LeavesDocument1 pageRemoval of Lead From Waste Water Using Chemically Modified Jackfruit LeavesSachintha ManojNo ratings yet
- Raw Water TreatmentDocument85 pagesRaw Water TreatmentHeru PramudyaNo ratings yet
- Cew 555 - Topic 3: Water Supply Infrastructure (Preliminary Treatment)Document3 pagesCew 555 - Topic 3: Water Supply Infrastructure (Preliminary Treatment)Nadhirah LnfNo ratings yet
- 8-Media CatalogDocument6 pages8-Media CatalogWilson JustinoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Water TreatmentDocument177 pagesIndustrial Water TreatmentMostafa Sharaf100% (1)
- 26 - Treatment of Surface and Ground Water For Drinking Water Generation - CompressedDocument28 pages26 - Treatment of Surface and Ground Water For Drinking Water Generation - CompressedDurgesh Kumar NatNo ratings yet
- TreatmentMitigation PDFDocument38 pagesTreatmentMitigation PDFFraztya HebbyNo ratings yet
- Name: Date: Score 1. Answer The Questions. (4 Ptos)Document4 pagesName: Date: Score 1. Answer The Questions. (4 Ptos)Constante ParedesNo ratings yet
- Research 2 Mind Map Draft Q1Document1 pageResearch 2 Mind Map Draft Q1Danielle CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Properties of WaterDocument16 pagesLesson 2 Properties of WaterJunnaz BalacuitNo ratings yet
- 13 Water Treatment Training Pretreatment FiltrationDocument32 pages13 Water Treatment Training Pretreatment Filtrationsantoshkumar gurmeNo ratings yet
- Water Tratment Training For Engineer by Eng A.hussienDocument35 pagesWater Tratment Training For Engineer by Eng A.hussienMohamed MoüsaNo ratings yet
- Ts Tds + TSS: BOD DO V VDocument3 pagesTs Tds + TSS: BOD DO V VJohn Andrew GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12Document22 pagesChapter 12Jubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 Relative Equilibrium On FluidsDocument42 pagesChapter 10 Relative Equilibrium On FluidsJubillee Magsino0% (1)
- MODULE 2-EXPERIMENT NO. 5-Grain Size Analysis of A Soil Using Iimprovised SievesDocument5 pagesMODULE 2-EXPERIMENT NO. 5-Grain Size Analysis of A Soil Using Iimprovised SievesJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Construction Manpower - SafetyDocument42 pagesLesson 7 - Construction Manpower - SafetyJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 10 - Construction - FieldworkDocument66 pagesLesson 10 - Construction - FieldworkJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 11-Construction - DisputesDocument47 pagesLesson 11-Construction - DisputesJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 - Construction Methods & OperationDocument72 pagesLecture 5 - Construction Methods & OperationJubillee Magsino100% (2)
- Cost Benefit Analysis For Signal Free Traffic at Intersection: A Case StudyDocument6 pagesCost Benefit Analysis For Signal Free Traffic at Intersection: A Case StudyJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8 - Computer Application in Construction ManagementDocument43 pagesLecture 8 - Computer Application in Construction ManagementJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 2 Reynolds Number: January 26, 2022Document8 pagesExperiment No. 2 Reynolds Number: January 26, 2022Jubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- The Requirements Needed in Material and DesignDocument26 pagesThe Requirements Needed in Material and DesignJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6 - Construction Equipment, Maintenance and OperationDocument43 pagesLesson 6 - Construction Equipment, Maintenance and OperationJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 9-Construction ReportsDocument34 pagesLesson 9-Construction ReportsJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- 8A PERT and CPMDocument38 pages8A PERT and CPMJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 - Construction Manpower - SafetyDocument42 pagesLesson 7 - Construction Manpower - SafetyJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- STS Group 2 Advocacy-1Document13 pagesSTS Group 2 Advocacy-1Jubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- Senior High School Basic Education Department: Transfer GoalDocument3 pagesSenior High School Basic Education Department: Transfer GoalJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- RAP TeamDocument1 pageRAP TeamJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- AlbayDocument6 pagesAlbayJubillee Magsino100% (1)
- Rectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFDocument28 pagesRectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- PROSTAT Lecture9 HandoutsDocument6 pagesPROSTAT Lecture9 HandoutsJubillee MagsinoNo ratings yet
- 03AB - A Review On Hydrotropy A Novel Concept For Solubility EnhancementDocument8 pages03AB - A Review On Hydrotropy A Novel Concept For Solubility EnhancementSiti NurohmahhNo ratings yet
- Coal Mill SafetyDocument17 pagesCoal Mill SafetyPaulo VidasNo ratings yet
- Shafer Paint SpecificationsDocument2 pagesShafer Paint SpecificationsRafael Jose Tasco ZabaletaNo ratings yet
- Pine Tar C260 Â - TDS (04-12)Document1 pagePine Tar C260 Â - TDS (04-12)Abhinav BansalNo ratings yet
- Shades by Kolours: Week #: Period CoveredDocument5 pagesShades by Kolours: Week #: Period CoveredChristian TerribleNo ratings yet
- Rexroth Lubrication GuideDocument28 pagesRexroth Lubrication Guidefurkan100% (1)
- SECTION 03310-1 Portland Cement Rev 1Document10 pagesSECTION 03310-1 Portland Cement Rev 1Abdalrahman AntariNo ratings yet
- Penukar Ion 07Document34 pagesPenukar Ion 07Dila AdilaNo ratings yet
- EP0412516A1Document10 pagesEP0412516A1Safiullah KhanNo ratings yet
- Sterilization - Validation, Qualification Requirements: Mrs Robyn IsaacsonDocument49 pagesSterilization - Validation, Qualification Requirements: Mrs Robyn IsaacsonboddarambabuNo ratings yet
- Fire Resistance of AluminiumDocument10 pagesFire Resistance of Aluminiummister_no34No ratings yet
- BelgJBotJansenetal1998 PDFDocument10 pagesBelgJBotJansenetal1998 PDFalexNo ratings yet
- Simple Silicate Anion Sio (A) Pyrisilicate or Disilicate Anion Si O (B)Document8 pagesSimple Silicate Anion Sio (A) Pyrisilicate or Disilicate Anion Si O (B)Puneet KaurNo ratings yet
- Atomic BasicsDocument4 pagesAtomic BasicsDaniela JibeteanNo ratings yet
- JB P DPP16 17 WaDocument10 pagesJB P DPP16 17 WaJyöt SîlvērNo ratings yet
- Final: Laboratory Experiment No. 5Document5 pagesFinal: Laboratory Experiment No. 5Dej IdleNo ratings yet
- The White Horse Pharmaceuticals LimitedDocument5 pagesThe White Horse Pharmaceuticals LimitedSalahUddinNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conversion of Biomass and Waste, The StatusDocument25 pagesThermal Conversion of Biomass and Waste, The StatusCamilo Augusto Ramírez L.100% (1)
- PHB-7-1998 The Everyday Pocket Handbook For Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) PDFDocument33 pagesPHB-7-1998 The Everyday Pocket Handbook For Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) PDFTee Klong RungNo ratings yet
- Colligative Properties of SolutionDocument8 pagesColligative Properties of SolutionJerome FernandezNo ratings yet
- Guide To AS/NZS 2312.1:2014Document10 pagesGuide To AS/NZS 2312.1:2014mp87_ingNo ratings yet
- Loxanol PL 5060Document2 pagesLoxanol PL 5060JohnNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet Brazetec H 280 Paste: StandardDocument1 pageTechnical Data Sheet Brazetec H 280 Paste: StandardNavin ChandarNo ratings yet
- Aluminium - The Metal of ChoiceDocument5 pagesAluminium - The Metal of ChoiceCristianBanciuNo ratings yet
- Acids and Bases Part IDocument23 pagesAcids and Bases Part IAngelo Bon BalmesNo ratings yet
- Refinaacion Thyssenkrupp PDFDocument6 pagesRefinaacion Thyssenkrupp PDFjimmy1894No ratings yet
- TDS - Plastistrength 770 - ArkemaDocument2 pagesTDS - Plastistrength 770 - ArkemaOscar Jimenez GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Atoms and The Periodic TableDocument17 pagesChapter 4: Atoms and The Periodic Tabletronton mogokNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Internasional Fisika DasarDocument8 pagesJurnal Internasional Fisika DasarTiya TululiNo ratings yet