Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Standard Ratings of Breakers Are: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 6A, 10A, 13A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A, 100A and Even Much More Ka
Standard Ratings of Breakers Are: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 6A, 10A, 13A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A, 100A and Even Much More Ka
Uploaded by
Mahabub Alam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesCircuit breaker is a device that interrupts fault current or short circuit current under abnormal conditions. Standard ratings range from 1A to 100A or more kA. It has a moving contact and fixed contact that are touching during normal operation. When a fault occurs, the trip coil is energized and the moving contact is pulled away, opening the breaker and interrupting the current. Production of an arc during opening delays the current interruption process and generates heat that can damage the system.
Original Description:
what is circuit breaker. circuit breaker explanation.
Original Title
CIRCUIT BREAKER
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCircuit breaker is a device that interrupts fault current or short circuit current under abnormal conditions. Standard ratings range from 1A to 100A or more kA. It has a moving contact and fixed contact that are touching during normal operation. When a fault occurs, the trip coil is energized and the moving contact is pulled away, opening the breaker and interrupting the current. Production of an arc during opening delays the current interruption process and generates heat that can damage the system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
9 views2 pagesStandard Ratings of Breakers Are: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 6A, 10A, 13A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A, 100A and Even Much More Ka
Standard Ratings of Breakers Are: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 6A, 10A, 13A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A, 50A, 63A, 100A and Even Much More Ka
Uploaded by
Mahabub AlamCircuit breaker is a device that interrupts fault current or short circuit current under abnormal conditions. Standard ratings range from 1A to 100A or more kA. It has a moving contact and fixed contact that are touching during normal operation. When a fault occurs, the trip coil is energized and the moving contact is pulled away, opening the breaker and interrupting the current. Production of an arc during opening delays the current interruption process and generates heat that can damage the system.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
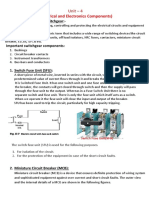
CIRCUIT BREAKER
Circuit Breaker Circuit breaker is a device that interrupts fault current or short circuit
current under abnormal condition
Standard ratings of breakers are: 1A, 2A, 3A, 4A, 6A, 10A, 13A, 16A, 20A, 25A, 32A, 40A,
50A, 63A, 100A and even much more kA.
S full form – Uninterrupted Power Supply.
SP full form – Single Pole.
DP full form – Double Pole.
TP full form – Triple Pole.
MCB full form – Miniature Circuit Breaker. MCCB
full form – Moulded Case Circuit Breaker.
RCCB full form – Residual Current Circuit Breaker.
RCBO full form – Residual Current Circuit Breaker with Overload
Protection.
ELCB full form – Earth Leakage Circuit Breaker.
OCB full form – Oil Circuit Breaker.
VCB full form – Vacuum Circuit Breaker.
ACB full form – Air Circuit Breaker
Operating Principle It has a moving contact and a fixed contact. Both
the contacts are touching each other during normal condition i.e.
when the breaker is closed. During closing of the breaker the moving
contact is held under by the pressure of a spring. Normally, it can be
closed or opened manually by a person or an operator for switching
and maintenance purpose. But when fault occurs and heavy short
circuit current flows through the breaker. The trip coil of the breaker
gets energized and moving contacts are pulled apart by some
mechanism resulting in opening of the breaker. Arc is formed when
the contacts separates. Until the discharge of arc ceases current
continues to flow. Production of arc delays the current interruption
process thereby generating enormous amount of heat which may
damage the system or the breaker itself.
You might also like
- Switching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookFrom EverandSwitching Power Supply Design: A Concise Practical HandbookNo ratings yet
- Elcb, RCCB, ElboDocument5 pagesElcb, RCCB, ElboNisitha Tharushan DarmarathnaNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCBDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCBSebastianCicognaNo ratings yet
- Electrical NotesDocument11 pagesElectrical NotesEr Prince KhalidNo ratings yet
- MCB, MCCB, Elcb, and RCCBDocument8 pagesMCB, MCCB, Elcb, and RCCBMD SHAMSE ALAMNo ratings yet
- MCB - MCCB - ELCB - RCCB - Electrical Notes & ArticlesDocument11 pagesMCB - MCCB - ELCB - RCCB - Electrical Notes & ArticlesLalantha KodikaraNo ratings yet
- Ravivarma A/L Ramanathan 18746 PCSDocument21 pagesRavivarma A/L Ramanathan 18746 PCSGreenhearthazel Varma PdgNo ratings yet
- Residual Current Circuit Breaker RCCBDocument3 pagesResidual Current Circuit Breaker RCCBKurreemunNo ratings yet
- Switches and BreakersDocument32 pagesSwitches and BreakersJely Taburnal BermundoNo ratings yet
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, RCCB, ELCBDocument3 pagesDifference Between MCB, MCCB, RCCB, ELCBJaved HasanNo ratings yet
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)Document4 pagesMCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)Chandrakumar TNo ratings yet
- MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) : CharacteristicsDocument8 pagesMCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker) : CharacteristicsWael AlmassriNo ratings yet
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCBDocument6 pagesDifference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCBNirmalKumarSelvarajNo ratings yet
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPDocument6 pagesDifference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPAbhishek RoyNo ratings yet
- MCB MCCB Elcb RCCBDocument4 pagesMCB MCCB Elcb RCCBSubramaniam NPNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCBDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCBYousif_AbdalhalimNo ratings yet
- Difference BN MCB, MCCB, Elcb, RCCB, Acb & VCBDocument5 pagesDifference BN MCB, MCCB, Elcb, RCCB, Acb & VCBsrinivasaphanikiranNo ratings yet
- LT CBDocument4 pagesLT CBANOOP KRISHNANNo ratings yet
- Angga Giovanny Taqy (2270021003) RCCB Ashuman Protection From ElectricityDocument11 pagesAngga Giovanny Taqy (2270021003) RCCB Ashuman Protection From ElectricityAngga TaqyNo ratings yet
- RCCBDocument16 pagesRCCBHarnoor Singh AhluwaliaNo ratings yet
- Wiring of MCB, Elcb, RCCB, MCCB MANUALDocument7 pagesWiring of MCB, Elcb, RCCB, MCCB MANUALSreenidhi Srungaram100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPDocument47 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPXuxu TooNo ratings yet
- 18BCM0078 Degapudi Prabhaditya EeeDocument10 pages18BCM0078 Degapudi Prabhaditya Eeedegapudi prabhadityaNo ratings yet
- MCB, MCCB, ElcbDocument3 pagesMCB, MCCB, ElcbMonirul Islam0% (1)
- MCB, MCCB, Elcb, RCCBDocument4 pagesMCB, MCCB, Elcb, RCCBJeya KannanNo ratings yet
- SGP 5Document7 pagesSGP 5Soumajit PoddarNo ratings yet
- MCBDocument6 pagesMCBjaveeed0401No ratings yet
- HV Circuit Breaker BasicsDocument3 pagesHV Circuit Breaker Basicsabdul basitNo ratings yet
- Basic WorkshopDocument9 pagesBasic Workshopawady862No ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCB PDFDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCB PDFMrinal Kanti RoyNo ratings yet
- Miniature Circuit Breakers Voltage: Function: Purpose: How It WorksDocument2 pagesMiniature Circuit Breakers Voltage: Function: Purpose: How It WorksVenkata Suresh Mandava100% (1)
- Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Types of Circuit Breakers, Their Features and FunctionsDocument32 pagesLow-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Types of Circuit Breakers, Their Features and FunctionsArjun DasNo ratings yet
- MCB, MCCB, Elcb, RCCBDocument5 pagesMCB, MCCB, Elcb, RCCBRohit Bhogle100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPcurazaq100% (1)
- MCB/MCCB/ Elcb /rcbo/ RCCBDocument4 pagesMCB/MCCB/ Elcb /rcbo/ RCCBraveendra_yandaNo ratings yet
- Angga Giovanny Taqy (2270021003) RCCB Ashuman Protection From Electricity3Document12 pagesAngga Giovanny Taqy (2270021003) RCCB Ashuman Protection From Electricity3Angga TaqyNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCBDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCBVENKATESAN RNo ratings yet
- Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, RCCB and Its CharacteristicsDocument6 pagesDifference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, RCCB and Its CharacteristicsKen ScalesNo ratings yet
- Group 4: Electrical Installation Group AssignmentDocument12 pagesGroup 4: Electrical Installation Group AssignmentLaras Dwi SenliNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCBDocument5 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCBana1901No ratings yet
- RCCB & ElcbDocument5 pagesRCCB & ElcbRakesh Joshi100% (1)
- What Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCBDocument6 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB MCCB ELCB and RCCBjena_anshumanNo ratings yet
- Fuse/Mcb/Mccb/Rsd/Rccb: MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)Document12 pagesFuse/Mcb/Mccb/Rsd/Rccb: MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)Prashant ShahNo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Unit 4Document13 pagesBEE Assignment Unit 4Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- CIRCUIT BREAKERS For NptiDocument56 pagesCIRCUIT BREAKERS For NptiJayPrakash YadavNo ratings yet
- Low-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Types of Circuit Breakers, Their Features and FunctionsDocument32 pagesLow-Voltage Circuit Breakers: Types of Circuit Breakers, Their Features and FunctionsMohammad FaisalNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCBDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCBJeya KannanNo ratings yet
- MCB and ElcbDocument8 pagesMCB and ElcbRayanNo ratings yet
- MCB MCCB RCCBDocument0 pagesMCB MCCB RCCBtceterexNo ratings yet
- RCCB OperationDocument6 pagesRCCB OperationNavneet SinghNo ratings yet
- Class - IX Section-A To E Subject-Work Experience Topic-Electrical Circuit Breaker & ELCBDocument4 pagesClass - IX Section-A To E Subject-Work Experience Topic-Electrical Circuit Breaker & ELCBBirlal SinghNo ratings yet
- Difference Between ELCB and RCCBDocument4 pagesDifference Between ELCB and RCCBMuhammad Yasir JavedNo ratings yet
- Capsule NotesDocument26 pagesCapsule NoteselecenggNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB: MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)Document4 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB: MCB (Miniature Circuit Breaker)racNo ratings yet
- What Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPDocument7 pagesWhat Is The Difference Between MCB, MCCB, ELCB, and RCCB - EEPlam266No ratings yet
- Familiarization With Different Types of Circuit BreakerDocument3 pagesFamiliarization With Different Types of Circuit BreakerSajjadul IslamNo ratings yet
- 6.3 - MCB & MCCBDocument25 pages6.3 - MCB & MCCBAnonymous qJXSQDSoE100% (2)
- Circuit BreakerDocument14 pagesCircuit BreakerAviral OjhaNo ratings yet
- 1 Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) (ELCB)Document6 pages1 Residual Current Circuit Breaker (RCCB) (ELCB)Anirudh VN100% (1)
- GSM Based Fire Alert & Gas Leakage Detector System: Israth Jahan Romana Abdullah Al-MamunDocument49 pagesGSM Based Fire Alert & Gas Leakage Detector System: Israth Jahan Romana Abdullah Al-MamunMahabub AlamNo ratings yet
- LPG Gas Leakage Monitoring and Alert System Using Arduino: Ayesha Siddika, Imam HossainDocument4 pagesLPG Gas Leakage Monitoring and Alert System Using Arduino: Ayesha Siddika, Imam HossainMahabub AlamNo ratings yet
- How To Use Arduino GSM Shield SIM900: InstructablesDocument9 pagesHow To Use Arduino GSM Shield SIM900: InstructablesMahabub AlamNo ratings yet
- Arduino Based Fire Detection and Alarm System Using Smoke SensorDocument6 pagesArduino Based Fire Detection and Alarm System Using Smoke SensorMahabub AlamNo ratings yet