Professional Documents
Culture Documents
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
Uploaded by
jockoCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Chapter 8 Blood Group Terminology and The Other Blood GroupsDocument62 pagesChapter 8 Blood Group Terminology and The Other Blood GroupsschemologyNo ratings yet
- IMH100 2nd Handout - Immunology Part II and ABO Blood GroupDocument4 pagesIMH100 2nd Handout - Immunology Part II and ABO Blood GroupnicholeNo ratings yet
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests For Covid-19Document4 pagesRapid Diagnostic Tests For Covid-19Febri RirinNo ratings yet
- Blood BankingDocument10 pagesBlood BankingSheen AmboyNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Test Covid - Texas ArticleDocument4 pagesPerbandingan Test Covid - Texas ArticlePutri SyawalNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedPrincess JanNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument4 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedJuan PeNo ratings yet
- COVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingDocument5 pagesCOVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingdaam naamNo ratings yet
- AntigenTestingFAQ EnglishDocument2 pagesAntigenTestingFAQ Englishcircuit circuitNo ratings yet
- BMJ m2284 FullDocument2 pagesBMJ m2284 FullSisca PrimaNo ratings yet
- Biozek Medical Reduced2Document21 pagesBiozek Medical Reduced2Adam LNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Document3 pagesCovid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Amy LawsonNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 TD Etudiant 3P UHSDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 TD Etudiant 3P UHSTIYOM SANo ratings yet
- Different Types of Coronavirus TestsDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Coronavirus TestsRosano Mario FloresNo ratings yet
- Covid19 TestingDocument3 pagesCovid19 TestingNational Content DeskNo ratings yet
- CMM COVID19 Antibody FAQsDocument1 pageCMM COVID19 Antibody FAQsdineshNo ratings yet
- Teste PCR Superbio2Document6 pagesTeste PCR Superbio2Guilherme MonteiroNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicDocument1 pageThe Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicChloe WrightNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument2 pagesFlowAlexander FrostNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Covid-19 TestsDocument3 pagesTwo Types of Covid-19 TestsFhea Fernandez CarinanNo ratings yet
- John HopkinsDocument38 pagesJohn HopkinskanchitsNo ratings yet
- The Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesDocument1 pageThe Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesqwNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Why Use Real Time RT-PCR?Document4 pagesWhy Use Real Time RT-PCR?Tanzila SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- تقرير ايوDocument9 pagesتقرير ايوAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Public Health Considerations: Serologic Testing For COVID-19 Version 1 - May 7, 2020Document6 pagesPublic Health Considerations: Serologic Testing For COVID-19 Version 1 - May 7, 2020Pablo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)Document2 pagesPost-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)Tati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- Self Care Guide Pantai 1Document33 pagesSelf Care Guide Pantai 1puterishaliza272No ratings yet
- Understanding Antigen Tests and Results ENG FinalDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Antigen Tests and Results ENG FinalAna CatarinaNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Antigen LectureDocument20 pagesCovid19 Antigen LectureUSI- CAMANO, JAY C.No ratings yet
- Clinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgADocument9 pagesClinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgAreginabrizolaraNo ratings yet
- The Journey of Antibody and Antigen Test During COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia, The Advantages & DisadvantagesDocument34 pagesThe Journey of Antibody and Antigen Test During COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia, The Advantages & DisadvantagesEldo TaufilaNo ratings yet
- BSI Resource COVID19 TestingDocument1 pageBSI Resource COVID19 TestingHelenaMarquezCruzadoNo ratings yet
- COVID Diagnostics GH 30april2020Document21 pagesCOVID Diagnostics GH 30april2020Buku DosaNo ratings yet
- Who RD Blueprint Diagnostics TPP Final v1 0 28 09 JC PPC Final CMP 2Document38 pagesWho RD Blueprint Diagnostics TPP Final v1 0 28 09 JC PPC Final CMP 2Đức HòaNo ratings yet
- FAQs Asymptomatic TestingDocument4 pagesFAQs Asymptomatic TestingAnonyNo ratings yet
- Lecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVDocument6 pagesLecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVreginaamondi133No ratings yet
- COV Test Blog - AB Edit - 12 FebDocument3 pagesCOV Test Blog - AB Edit - 12 FebmattramjiawanNo ratings yet
- ZOOL 143 Topic 7 Detection of HIV Infection 1Document10 pagesZOOL 143 Topic 7 Detection of HIV Infection 1nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- IGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishDocument1 pageIGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishAdhimasRadityaNo ratings yet
- SARS CoV 2 Testing TypesDocument4 pagesSARS CoV 2 Testing TypesFree PeepNo ratings yet
- Jama Hadaya 2020 PG 200021Document1 pageJama Hadaya 2020 PG 200021Tech MitNo ratings yet
- Covid-19: Testing TimesDocument2 pagesCovid-19: Testing TimeshgfksqdnhcuiNo ratings yet
- ArchitechDocument5 pagesArchitechERIE YUWITA SARINo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-28 at 11.26.36 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-12-28 at 11.26.36 AMradharani023No ratings yet
- Step 1.6 Role of DX 29jan2019Document5 pagesStep 1.6 Role of DX 29jan2019yuliaNo ratings yet
- Change in HIV Window Period A Clinical PerspectiveDocument46 pagesChange in HIV Window Period A Clinical PerspectiveSvarogNo ratings yet
- Caracterizacion NigeriaDocument9 pagesCaracterizacion NigeriaAndrea LunaNo ratings yet
- Sensing Self COVID-19 Rapid Test KitDocument1 pageSensing Self COVID-19 Rapid Test KittattvanishthaNo ratings yet
- Testing For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Document2 pagesTesting For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Types of COVID-19 Tests - COVID-19 - Minnesota Dept. of HealthDocument3 pagesTypes of COVID-19 Tests - COVID-19 - Minnesota Dept. of Healthgolden abidemNo ratings yet
- Serological Testing of HIVDocument4 pagesSerological Testing of HIVhamody662002No ratings yet
- COVID19Infographic8.5x11.FINAL 0 PDFDocument1 pageCOVID19Infographic8.5x11.FINAL 0 PDFKmo mastnNo ratings yet
- Lyme Disease Lab Testing ExplanationDocument2 pagesLyme Disease Lab Testing ExplanationAlina PirvNo ratings yet
- Influenza: What We Know: Mohammad Nuriman Bin Mohd Zainuddin (Aa0890) Lablink, KPJ Puteri Specialist HospitalDocument24 pagesInfluenza: What We Know: Mohammad Nuriman Bin Mohd Zainuddin (Aa0890) Lablink, KPJ Puteri Specialist Hospitaliman zainuddinNo ratings yet
- WHO Operational Handbook On TB Diagnosis - Tests For TB Infection - Module 3Document92 pagesWHO Operational Handbook On TB Diagnosis - Tests For TB Infection - Module 3SULISTYOWATI SULISTYOWATINo ratings yet
- Hiv in Pregnancy FinalDocument73 pagesHiv in Pregnancy Finalapi-3797079No ratings yet
- Rapid Antigen Tests For Voluntary Screen Testing: Key MessageDocument21 pagesRapid Antigen Tests For Voluntary Screen Testing: Key MessageToronto StarNo ratings yet
- (PPT) COVID-Ab 20200331 - FinalDocument27 pages(PPT) COVID-Ab 20200331 - FinalEko AdiwibowoNo ratings yet
- 23.04 Labs and Diagnostics K.voneijeDocument15 pages23.04 Labs and Diagnostics K.voneijeFira SukmagustinNo ratings yet
- Covid Update. Answers for curious minds: How's my health, doc?From EverandCovid Update. Answers for curious minds: How's my health, doc?No ratings yet
- HA-1 User Manual v1.2 USDocument32 pagesHA-1 User Manual v1.2 USjockoNo ratings yet
- Beyerdynamic T1 2ndDocument1 pageBeyerdynamic T1 2ndjockoNo ratings yet
- Audio Technica ATH-M50xDocument1 pageAudio Technica ATH-M50xjockoNo ratings yet
- 2016-8986 Final ORDocument31 pages2016-8986 Final ORjockoNo ratings yet
- Ni Farming GrowingDocument164 pagesNi Farming GrowingjockoNo ratings yet
- ISO 19011-2018 Rev.2Document56 pagesISO 19011-2018 Rev.2jockoNo ratings yet
- Jriver Dlna Configuration Mac / PC: 1. Launch Jriver Media Center and Navigate From The Top Menu To "Tools - Options"Document5 pagesJriver Dlna Configuration Mac / PC: 1. Launch Jriver Media Center and Navigate From The Top Menu To "Tools - Options"jockoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topic in Blood BankingDocument6 pagesThesis Topic in Blood Bankingashleygomezalbuquerque100% (2)
- Hemolytic Diseases of The Fetus and NewbornDocument30 pagesHemolytic Diseases of The Fetus and Newbornkristine_camerinoNo ratings yet
- Crossmatch Transfusion Ratio As Indicators Blood Service QualityDocument6 pagesCrossmatch Transfusion Ratio As Indicators Blood Service QualityAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guide To Blood TransfusionDocument181 pagesClinical Guide To Blood TransfusionMohamed Elmasry100% (3)
- ABO Incompatibility Disease of The NewbornDocument10 pagesABO Incompatibility Disease of The NewbornupuanNo ratings yet
- Pubmed Telemedici SetDocument5,537 pagesPubmed Telemedici SetValencia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Blood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsDocument32 pagesBlood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohammed H Saiemaldahr Blood Bank Med Tech Dep @kaauDocument20 pagesDr. Mohammed H Saiemaldahr Blood Bank Med Tech Dep @kaauKristiann lourine ProvidoNo ratings yet
- Isoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityDocument2 pagesIsoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityAriaNo ratings yet
- ASO Latex Package InsertDocument2 pagesASO Latex Package Insertita91itaNo ratings yet
- The Serological Investigation of Red Cell Incompatible Transfusion ReactionsDocument5 pagesThe Serological Investigation of Red Cell Incompatible Transfusion ReactionsKAILA SOPHIA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Clariza ACEBES - Narrative Report 4th RotationDocument6 pagesClariza ACEBES - Narrative Report 4th RotationJung Soo MiNo ratings yet
- Forensic BiologyDocument5 pagesForensic BiologyNurul HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Bursal Health Monitoring With Elanco Htsi: RatriastutiDocument15 pagesBursal Health Monitoring With Elanco Htsi: RatriastutiYoga RivaldiNo ratings yet
- Blood ReservationDocument1 pageBlood Reservationfritzie dara f adjilaniNo ratings yet
- Labs and DrugsDocument10 pagesLabs and DrugsSteven ConejosNo ratings yet
- Antihuman Globulin Testing - BOOKDocument12 pagesAntihuman Globulin Testing - BOOKANNE CZARINA RAMIELLE DE VILLANo ratings yet
- Pi Is 1440244020305284Document6 pagesPi Is 1440244020305284NisaNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of NewbornDocument41 pagesHemolytic Disease of NewbornRaja100% (3)
- Blood Componant Therapy (Autosaved)Document47 pagesBlood Componant Therapy (Autosaved)drkapiltNo ratings yet
- Blood TranfusionDocument18 pagesBlood TranfusionVishnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Guideline (MSF) 2019Document169 pagesBlood Transfusion Guideline (MSF) 2019hiba.khellow100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion PocedureDocument9 pagesBlood Transfusion PocedureRaman Samrao100% (1)
- ABO DiscrepanciesDocument40 pagesABO DiscrepanciesAlondra Sagario100% (1)
- BB Lab 4 RH Phenotype Spring 2012Document12 pagesBB Lab 4 RH Phenotype Spring 2012Dane EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Time in Time Out: Temperature Monitoring Log Sheet For The Month of February 2019Document6 pagesTime in Time Out: Temperature Monitoring Log Sheet For The Month of February 2019Waqas VickyNo ratings yet
- BloodtransfusieDocument79 pagesBloodtransfusieGod RaNo ratings yet
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
Uploaded by
jockoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
Uploaded by
jockoCopyright:
Available Formats
COVID-19 Testing: PCR, Antigen, and Antibody Tests Explained
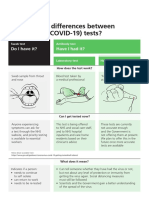
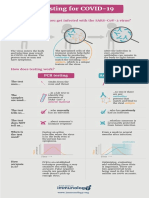
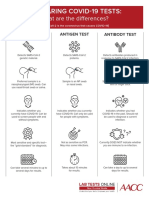
There are three types of tests available for COVID-19: polymerase chain reaction (PCR), antigen, and antibody
(serology) testing. PCR and antigen tests detect whether a person is currently infected, and serology detects whether a
person had an infection in the past. This document is designed to explain the differences between PCR, antigen, and
serology testing, and when one test might be used over another.
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
Why is the PCR tests look for pieces of Antigen tests look for pieces of Serology looks for antibodies 1
test used? SARS-CoV-2, the virus that proteins that make up the SARS- against SARS-CoV-2 in the blood
causes COVID-19, in the nose, CoV-2 virus to determine if the to determine if there was a past
throat, or other areas in the person has an active infection. infection.
respiratory tract to determine if
the person has an active
infection.
How is the In most cases, a nasal or throat In most cases, a nasal or throat In most cases, a blood sample is
test swab is taken by a healthcare swab is taken by a healthcare taken and sent to a lab for
performed? provider and tested. Sometimes provider and tested. Sometimes testing.
the test can be run while you the test can be run while you
wait, and sometimes the swab wait, and sometimes the swab
needs to be sent to a lab for needs to be sent to a lab for
testing. testing.
What does a A positive PCR test means that A positive antigen test means A positive antibody test means
positive test the person being tested has an that the person being tested has that the person being tested was
result active COVID-19 infection. an active COVID-19 infection. infected with COVID-19 in the
mean? past and that their immune
system developed antibodies to
try to fight it off.
1
Antibodies are formed by the body to fight off infections. Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is the first antibody that is formed against a germ, so
it appears on tests first, usually within 1-2 weeks. The body then forms immunoglobulin G (IgG), which appears on tests about 2 weeks
after the illness starts. IgM usually disappears from the blood within a few months, but IgG can last for years. Some antibody tests test for
IgM and IgG, and some only test for IgG.
Version 2.1 – Released 8/31/2020 Page 1 of 5
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
What does a A negative PCR test means that A negative antigen test means A negative antibody test means
negative person was probably not infected that SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins that the person may not have
test result at the time their sample was were not detected. However, a had COVID-19 in the past.
mean? collected. However, it doesn’t negative test does not rule out However, they could still have a
mean they won’t get sick – it COVID-19. If there is still current infection, and the
only means that they didn’t have concern that a person has antibody test was collected too
COVID-19 at the time of testing. COVID-19 after a negative soon to give a positive result.
antigen test, then that person
should be tested again with a
PCR test.
When is it • It can be used to determine • It can be used to quickly • It can identify people who had
helpful? who has an active infection. determine who has an active an infection in the past, even
• It can help identify people infection. if they had no symptoms of
who are contagious to others. • It can help identify people the illness.
who are contagious to • In some cases, it could help
others. determine when COVID-19
• It is a less expensive test illness occurred, since we
than PCR. know that IgM is formed
before IgG and that IgM goes
away before IgG.
• It can help determine who
qualifies to donate
convalescent plasma (a blood
product that contains
antibodies against COVID-19
and can be used as a COVID-
19 treatment).
• If lots of people take the test
in a community, it can help
public health leaders and
researchers know what
Version 2.1 – Released 8/31/2020 Page 2 of 5
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
percentage of the population
has already had COVID-19.
When is it • It does not help determine • It does not accurately rule out • It may be negative if it is
not as who had an infection in the those who are not infected. used too close to the
helpful? past. • Antigen tests are less beginning of an infection,
• It also does not help sensitive than PCR tests, which is why it should not be
determine if a person who meaning there may be false used to detect active COVID-
was exposed to COVID-19 will negative results. 19 infection.
develop active infection • Negative tests should be • In areas where there have
during the two weeks after treated as presumptive. If a not been many cases of
exposure. healthcare provider is COVID-19, many of the
In some people, the virus can concerned that the person positive test results will
only be found by PCR for a has COVID-19, even after a actually be false positives
few days at the beginning of negative antigen test, then (see Positive Predictive
the infection, so the test the test result should be Value2). Some antibody tests
might not find the virus if the confirmed with PCR testing. have low sensitivity 3 and
swab is taken more than a specificity 4 and thus may not
few days after the illness produce reliable results.
starts. • Some antibody tests may
• In some people, the virus can cross-react with other
be found by PCR in the nose coronaviruses that are not
2
Positive predictive value is a measure of how likely it is that a positive test is a true positive rather than a false positive. This is
dependent on how many people in the population being tested have had the disease. When there are very few people in the population
that have had the disease, then there is a higher chance that a positive test is a false positive. When there are many people in a population
that have had the disease, then there is a higher chance that a positive test is a true positive.
3
Sensitivity is sometimes called the “true positive rate.” It measures how frequently the test is positive when the person being tested
actually has the disease. For example, when a test has 80% sensitivity, the test detects 80% of patients with the disease (true positives).
However, 20% of patients with the disease are not detected (false negatives) by the test.
4
Specificity is sometimes called the “true negative rate.” It measures how frequently the test is negative when the person being tested
doesn’t have the disease. For example, when a test has 80% specificity, the test correctly reports 80% of patients without the disease as
test negative (true negatives). However, 20% of patients without the disease are incorrectly identified as testing positive (false positives)
by the test.
Version 2.1 – Released 8/31/2020 Page 3 of 5
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
and throat for several weeks, SARS-CoV2, the virus that
even longer than the time causes COVID-19, leading to
that they are actually false test results.
contagious to other people. • We do not know yet if having
• This test requires certain antibodies to the virus that
kinds of swabs that may be in causes COVID-19 can protect
short supply. someone from getting
infected again or, if they do,
how long this protection
might last. Until scientists get
more information about
whether antibodies protect
against reinfection with this
virus, everyone should
continue to take steps to
protect themselves and
others, including staying at
least 6 feet away from other
people outside of their home
(social distancing), even if
they have had a positive
antibody test.
What public • If positive, the health • If positive, the health • If positive, the health
health department will conduct a department will interview the department will interview the
activities case investigation. Contact antigen-positive person about antibody-positive person
will be tracing will be performed to symptoms and if they were about symptoms and if they
conducted? 5 identify individuals who might around someone who had were around someone who
have been exposed to the COVID-19. Contact tracing had COVID-19. If the person
PCR-positive person when will be performed. had symptoms or was around
5
Case investigations and contact tracing are conducted in accordance with local jurisdictional capacity. Public health departments may
prioritize PCR positive cases in the event of capacity limitations.
Version 2.1 – Released 8/31/2020 Page 4 of 5
Topic PCR Test Antigen Test Antibody (Serology) Test
they could have spread • If negative, no public health someone with COVID-19, the
COVID-19. activities will be performed. health department may
• If negative, no public health recommend they get a PCR
activities will be performed. test. No contact tracing will
be performed.
• If negative, no public health
activities will be performed.
Version 2.1 – Released 8/31/2020 Page 5 of 5
You might also like
- Chapter 8 Blood Group Terminology and The Other Blood GroupsDocument62 pagesChapter 8 Blood Group Terminology and The Other Blood GroupsschemologyNo ratings yet
- IMH100 2nd Handout - Immunology Part II and ABO Blood GroupDocument4 pagesIMH100 2nd Handout - Immunology Part II and ABO Blood GroupnicholeNo ratings yet
- Rapid Diagnostic Tests For Covid-19Document4 pagesRapid Diagnostic Tests For Covid-19Febri RirinNo ratings yet
- Blood BankingDocument10 pagesBlood BankingSheen AmboyNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Test Covid - Texas ArticleDocument4 pagesPerbandingan Test Covid - Texas ArticlePutri SyawalNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument5 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: Molecular, Antigen, and Antibody Tests ExplainedPrincess JanNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedDocument4 pagesCOVID-19 Testing: PCR and Antibody Tests ExplainedJuan PeNo ratings yet
- COVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingDocument5 pagesCOVID19 PCRvsSerologyTestingdaam naamNo ratings yet
- AntigenTestingFAQ EnglishDocument2 pagesAntigenTestingFAQ Englishcircuit circuitNo ratings yet
- BMJ m2284 FullDocument2 pagesBMJ m2284 FullSisca PrimaNo ratings yet
- Biozek Medical Reduced2Document21 pagesBiozek Medical Reduced2Adam LNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Document3 pagesCovid19 Testing 5 18 Final 508Amy LawsonNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 TD Etudiant 3P UHSDocument10 pagesCOVID-19 TD Etudiant 3P UHSTIYOM SANo ratings yet
- Different Types of Coronavirus TestsDocument1 pageDifferent Types of Coronavirus TestsRosano Mario FloresNo ratings yet
- Covid19 TestingDocument3 pagesCovid19 TestingNational Content DeskNo ratings yet
- CMM COVID19 Antibody FAQsDocument1 pageCMM COVID19 Antibody FAQsdineshNo ratings yet
- Teste PCR Superbio2Document6 pagesTeste PCR Superbio2Guilherme MonteiroNo ratings yet
- The Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicDocument1 pageThe Differences Between Coronavirus COVID-19 Tests InfographicChloe WrightNo ratings yet
- FlowDocument2 pagesFlowAlexander FrostNo ratings yet
- Two Types of Covid-19 TestsDocument3 pagesTwo Types of Covid-19 TestsFhea Fernandez CarinanNo ratings yet
- John HopkinsDocument38 pagesJohn HopkinskanchitsNo ratings yet
- The Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesDocument1 pageThe Facts About COVID-19 Tests: The Two Test TypesqwNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Sars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningDocument13 pagesSars Covid-19 Antibody ScreeningSadia AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Why Use Real Time RT-PCR?Document4 pagesWhy Use Real Time RT-PCR?Tanzila SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- تقرير ايوDocument9 pagesتقرير ايوAhmed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Public Health Considerations: Serologic Testing For COVID-19 Version 1 - May 7, 2020Document6 pagesPublic Health Considerations: Serologic Testing For COVID-19 Version 1 - May 7, 2020Pablo AvilaNo ratings yet
- Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)Document2 pagesPost-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)Tati MaryatiNo ratings yet
- Self Care Guide Pantai 1Document33 pagesSelf Care Guide Pantai 1puterishaliza272No ratings yet
- Understanding Antigen Tests and Results ENG FinalDocument4 pagesUnderstanding Antigen Tests and Results ENG FinalAna CatarinaNo ratings yet
- Covid19 Antigen LectureDocument20 pagesCovid19 Antigen LectureUSI- CAMANO, JAY C.No ratings yet
- Clinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgADocument9 pagesClinical Applications of Detecting IgG, IgM or IgAreginabrizolaraNo ratings yet
- The Journey of Antibody and Antigen Test During COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia, The Advantages & DisadvantagesDocument34 pagesThe Journey of Antibody and Antigen Test During COVID-19 Pandemic in Indonesia, The Advantages & DisadvantagesEldo TaufilaNo ratings yet
- BSI Resource COVID19 TestingDocument1 pageBSI Resource COVID19 TestingHelenaMarquezCruzadoNo ratings yet
- COVID Diagnostics GH 30april2020Document21 pagesCOVID Diagnostics GH 30april2020Buku DosaNo ratings yet
- Who RD Blueprint Diagnostics TPP Final v1 0 28 09 JC PPC Final CMP 2Document38 pagesWho RD Blueprint Diagnostics TPP Final v1 0 28 09 JC PPC Final CMP 2Đức HòaNo ratings yet
- FAQs Asymptomatic TestingDocument4 pagesFAQs Asymptomatic TestingAnonyNo ratings yet
- Lecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVDocument6 pagesLecture VI DIAGNOSIS AND TREATMENT OF HIVreginaamondi133No ratings yet
- COV Test Blog - AB Edit - 12 FebDocument3 pagesCOV Test Blog - AB Edit - 12 FebmattramjiawanNo ratings yet
- ZOOL 143 Topic 7 Detection of HIV Infection 1Document10 pagesZOOL 143 Topic 7 Detection of HIV Infection 1nattydreadfathelahNo ratings yet
- IGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishDocument1 pageIGRA-TB MN LAC EnglishAdhimasRadityaNo ratings yet
- SARS CoV 2 Testing TypesDocument4 pagesSARS CoV 2 Testing TypesFree PeepNo ratings yet
- Jama Hadaya 2020 PG 200021Document1 pageJama Hadaya 2020 PG 200021Tech MitNo ratings yet
- Covid-19: Testing TimesDocument2 pagesCovid-19: Testing TimeshgfksqdnhcuiNo ratings yet
- ArchitechDocument5 pagesArchitechERIE YUWITA SARINo ratings yet
- Screenshot 2023-12-28 at 11.26.36 AMDocument1 pageScreenshot 2023-12-28 at 11.26.36 AMradharani023No ratings yet
- Step 1.6 Role of DX 29jan2019Document5 pagesStep 1.6 Role of DX 29jan2019yuliaNo ratings yet
- Change in HIV Window Period A Clinical PerspectiveDocument46 pagesChange in HIV Window Period A Clinical PerspectiveSvarogNo ratings yet
- Caracterizacion NigeriaDocument9 pagesCaracterizacion NigeriaAndrea LunaNo ratings yet
- Sensing Self COVID-19 Rapid Test KitDocument1 pageSensing Self COVID-19 Rapid Test KittattvanishthaNo ratings yet
- Testing For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Document2 pagesTesting For Tuberculosis (TB) : Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)Descargar scribdNo ratings yet
- Types of COVID-19 Tests - COVID-19 - Minnesota Dept. of HealthDocument3 pagesTypes of COVID-19 Tests - COVID-19 - Minnesota Dept. of Healthgolden abidemNo ratings yet
- Serological Testing of HIVDocument4 pagesSerological Testing of HIVhamody662002No ratings yet
- COVID19Infographic8.5x11.FINAL 0 PDFDocument1 pageCOVID19Infographic8.5x11.FINAL 0 PDFKmo mastnNo ratings yet
- Lyme Disease Lab Testing ExplanationDocument2 pagesLyme Disease Lab Testing ExplanationAlina PirvNo ratings yet
- Influenza: What We Know: Mohammad Nuriman Bin Mohd Zainuddin (Aa0890) Lablink, KPJ Puteri Specialist HospitalDocument24 pagesInfluenza: What We Know: Mohammad Nuriman Bin Mohd Zainuddin (Aa0890) Lablink, KPJ Puteri Specialist Hospitaliman zainuddinNo ratings yet
- WHO Operational Handbook On TB Diagnosis - Tests For TB Infection - Module 3Document92 pagesWHO Operational Handbook On TB Diagnosis - Tests For TB Infection - Module 3SULISTYOWATI SULISTYOWATINo ratings yet
- Hiv in Pregnancy FinalDocument73 pagesHiv in Pregnancy Finalapi-3797079No ratings yet
- Rapid Antigen Tests For Voluntary Screen Testing: Key MessageDocument21 pagesRapid Antigen Tests For Voluntary Screen Testing: Key MessageToronto StarNo ratings yet
- (PPT) COVID-Ab 20200331 - FinalDocument27 pages(PPT) COVID-Ab 20200331 - FinalEko AdiwibowoNo ratings yet
- 23.04 Labs and Diagnostics K.voneijeDocument15 pages23.04 Labs and Diagnostics K.voneijeFira SukmagustinNo ratings yet
- Covid Update. Answers for curious minds: How's my health, doc?From EverandCovid Update. Answers for curious minds: How's my health, doc?No ratings yet
- HA-1 User Manual v1.2 USDocument32 pagesHA-1 User Manual v1.2 USjockoNo ratings yet
- Beyerdynamic T1 2ndDocument1 pageBeyerdynamic T1 2ndjockoNo ratings yet
- Audio Technica ATH-M50xDocument1 pageAudio Technica ATH-M50xjockoNo ratings yet
- 2016-8986 Final ORDocument31 pages2016-8986 Final ORjockoNo ratings yet
- Ni Farming GrowingDocument164 pagesNi Farming GrowingjockoNo ratings yet
- ISO 19011-2018 Rev.2Document56 pagesISO 19011-2018 Rev.2jockoNo ratings yet
- Jriver Dlna Configuration Mac / PC: 1. Launch Jriver Media Center and Navigate From The Top Menu To "Tools - Options"Document5 pagesJriver Dlna Configuration Mac / PC: 1. Launch Jriver Media Center and Navigate From The Top Menu To "Tools - Options"jockoNo ratings yet
- Thesis Topic in Blood BankingDocument6 pagesThesis Topic in Blood Bankingashleygomezalbuquerque100% (2)
- Hemolytic Diseases of The Fetus and NewbornDocument30 pagesHemolytic Diseases of The Fetus and Newbornkristine_camerinoNo ratings yet
- Crossmatch Transfusion Ratio As Indicators Blood Service QualityDocument6 pagesCrossmatch Transfusion Ratio As Indicators Blood Service QualityAnonymous izrFWiQNo ratings yet
- Clinical Guide To Blood TransfusionDocument181 pagesClinical Guide To Blood TransfusionMohamed Elmasry100% (3)
- ABO Incompatibility Disease of The NewbornDocument10 pagesABO Incompatibility Disease of The NewbornupuanNo ratings yet
- Pubmed Telemedici SetDocument5,537 pagesPubmed Telemedici SetValencia NatashaNo ratings yet
- Blood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsDocument32 pagesBlood Products. Preparation of Blood ComponentsSanthiya MadhavanNo ratings yet
- Dr. Mohammed H Saiemaldahr Blood Bank Med Tech Dep @kaauDocument20 pagesDr. Mohammed H Saiemaldahr Blood Bank Med Tech Dep @kaauKristiann lourine ProvidoNo ratings yet
- Isoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityDocument2 pagesIsoimmunization and Anemia RH IncompatibilityAriaNo ratings yet
- ASO Latex Package InsertDocument2 pagesASO Latex Package Insertita91itaNo ratings yet
- The Serological Investigation of Red Cell Incompatible Transfusion ReactionsDocument5 pagesThe Serological Investigation of Red Cell Incompatible Transfusion ReactionsKAILA SOPHIA CRUZNo ratings yet
- Clariza ACEBES - Narrative Report 4th RotationDocument6 pagesClariza ACEBES - Narrative Report 4th RotationJung Soo MiNo ratings yet
- Forensic BiologyDocument5 pagesForensic BiologyNurul HaziqahNo ratings yet
- Bursal Health Monitoring With Elanco Htsi: RatriastutiDocument15 pagesBursal Health Monitoring With Elanco Htsi: RatriastutiYoga RivaldiNo ratings yet
- Blood ReservationDocument1 pageBlood Reservationfritzie dara f adjilaniNo ratings yet
- Labs and DrugsDocument10 pagesLabs and DrugsSteven ConejosNo ratings yet
- Antihuman Globulin Testing - BOOKDocument12 pagesAntihuman Globulin Testing - BOOKANNE CZARINA RAMIELLE DE VILLANo ratings yet
- Pi Is 1440244020305284Document6 pagesPi Is 1440244020305284NisaNo ratings yet
- Hemolytic Disease of NewbornDocument41 pagesHemolytic Disease of NewbornRaja100% (3)
- Blood Componant Therapy (Autosaved)Document47 pagesBlood Componant Therapy (Autosaved)drkapiltNo ratings yet
- Blood TranfusionDocument18 pagesBlood TranfusionVishnu PriyaNo ratings yet
- Blood Transfusion Guideline (MSF) 2019Document169 pagesBlood Transfusion Guideline (MSF) 2019hiba.khellow100% (1)
- Blood Transfusion PocedureDocument9 pagesBlood Transfusion PocedureRaman Samrao100% (1)
- ABO DiscrepanciesDocument40 pagesABO DiscrepanciesAlondra Sagario100% (1)
- BB Lab 4 RH Phenotype Spring 2012Document12 pagesBB Lab 4 RH Phenotype Spring 2012Dane EdwardsNo ratings yet
- Time in Time Out: Temperature Monitoring Log Sheet For The Month of February 2019Document6 pagesTime in Time Out: Temperature Monitoring Log Sheet For The Month of February 2019Waqas VickyNo ratings yet
- BloodtransfusieDocument79 pagesBloodtransfusieGod RaNo ratings yet