Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Problem Set 1 (Review of Fundamental Soil Testing) : Answer Reference Solution File Here
Problem Set 1 (Review of Fundamental Soil Testing) : Answer Reference Solution File Here
Uploaded by
Jasper Kenneth PeraltaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Worksheet-Accuracy and Precision-FinalDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Accuracy and Precision-FinalSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Sem II Sesi20182019 (Answer Scheme)Document7 pagesTest 1 Sem II Sesi20182019 (Answer Scheme)Ashyra JamilNo ratings yet
- CivE381MidSample PDFDocument27 pagesCivE381MidSample PDFAbera Mamo100% (1)
- 2 Soil Classification - S21Document3 pages2 Soil Classification - S21hassanNo ratings yet
- Report Soil AssignmentDocument4 pagesReport Soil AssignmentWan FaizNo ratings yet
- Rumus Lab AdnanDocument33 pagesRumus Lab AdnanNaim DarmawanNo ratings yet
- CIV E 381 - Practice Exam 2Document15 pagesCIV E 381 - Practice Exam 2JohnNo ratings yet
- Soil Testing Lab: K.R. Soil Foundation & EngineersDocument2 pagesSoil Testing Lab: K.R. Soil Foundation & EngineersMd SohagNo ratings yet
- Ecg263 Mini Project Brendan Bungin Braoh 2021830544Document15 pagesEcg263 Mini Project Brendan Bungin Braoh 20218305442021830544No ratings yet
- 2305 - 15 - Hasil Trial Embankment FilterDocument12 pages2305 - 15 - Hasil Trial Embankment FilterAngghy NaghaNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 1 Albo GeorgeDocument3 pagesSeatwork 1 Albo GeorgeDaniel LambinoNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportACHIENG REBECCANo ratings yet
- Journal On Characteristics of Geotechnical Properties of SoilDocument10 pagesJournal On Characteristics of Geotechnical Properties of SoilAderemi AbidemiNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity TestDocument13 pagesSpecific Gravity Testsengthai100% (1)
- Report On Soil Moisture and CompactionDocument6 pagesReport On Soil Moisture and CompactionSzczepan KlimczakNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Lab Report 3 - Ecg263Document8 pagesGroup 1 - Lab Report 3 - Ecg263Muhammad Danial Ikmal Bin Mohamad ShukorNo ratings yet
- CHP TestsDocument3 pagesCHP TestshuneNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Chapter 1,2, Dan 3Document23 pagesSoil Mechanics Chapter 1,2, Dan 3Rakha Naufal DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Client Design and Build Contractor: Liquid Limit (Cone Penotrometer) and Plastic LimitDocument2 pagesClient Design and Build Contractor: Liquid Limit (Cone Penotrometer) and Plastic LimitMARTIN TIBANYENDERANo ratings yet
- Concrete TestDocument14 pagesConcrete TestPharès SOGNON-DESNo ratings yet
- Highway and Airports EngineeringDocument1 pageHighway and Airports EngineeringAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis DataDocument2 pagesSieve Analysis DataAT NM100% (2)
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document2 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Er VenkatNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 4 ReportDocument10 pagesLaboratory 4 ReportFahad KudaratNo ratings yet
- Effect of Boundary Conditions On The Hydraulic Behavior of Geotextile Filtration SystemDocument19 pagesEffect of Boundary Conditions On The Hydraulic Behavior of Geotextile Filtration Systemjavad khosraviNo ratings yet
- CE 200L Report 2 - SieveDocument8 pagesCE 200L Report 2 - SieveravenringsNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document2 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Rezkiya Laila BilkisNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering Btech Civil Enginneering Project Iii Group 4 Topic: To Redesign An Existing Assigned RoadDocument31 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering Btech Civil Enginneering Project Iii Group 4 Topic: To Redesign An Existing Assigned RoadSammy SafoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Particle Size Distribution (PSD) - Dry SievingDocument6 pagesLab Report - Particle Size Distribution (PSD) - Dry SievingSheikh BajunaidNo ratings yet
- Geo-Report NalbariDocument17 pagesGeo-Report NalbariShashankSinghNo ratings yet
- BJ Att ProctorDocument5 pagesBJ Att ProctorTaztika Audea PutriNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis DataDocument2 pagesSieve Analysis DataYsabelle TagarumaNo ratings yet
- Date: Location: Plastic Limit: ResultDocument3 pagesDate: Location: Plastic Limit: Resultalaa0jabbarNo ratings yet
- Soil Analysis Lab ReportDocument12 pagesSoil Analysis Lab ReportDanielle Del ConteNo ratings yet
- الشيت الثانىDocument1 pageالشيت الثانىAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyDocument3 pagesJomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyTinaNo ratings yet
- CV321 Lab 1Document10 pagesCV321 Lab 1dherdcarlNo ratings yet
- CE411 CE3105 Grp3 LR07Document18 pagesCE411 CE3105 Grp3 LR07KATE SARAH MARANANNo ratings yet
- Radhey Testing & Consultants Pvt. Ltd. Agra: Observation Cum Calculation SheetDocument1 pageRadhey Testing & Consultants Pvt. Ltd. Agra: Observation Cum Calculation SheetChandan MondalNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Thesis Presentation: Rajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument38 pagesWelcome To Our Thesis Presentation: Rajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyRajibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Lab # 5Document5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Lab # 5zainabNo ratings yet
- Grain Size AnalysisDocument13 pagesGrain Size AnalysisIna Therese Ardan100% (1)
- Report For Soil Sampling TestDocument92 pagesReport For Soil Sampling TestArham SheikhNo ratings yet
- Complex ENgineering Problem Letter of TransDocument13 pagesComplex ENgineering Problem Letter of TranshamzahayatNo ratings yet
- Amiel A. Cabatchete Bsce-4B Group No. 1 SEPTEMBER 19, 2017: Activity # 3Document10 pagesAmiel A. Cabatchete Bsce-4B Group No. 1 SEPTEMBER 19, 2017: Activity # 3EmanoAceNo ratings yet
- 05-Density ReverseDocument7 pages05-Density ReverseSAFE SERVICES LHRNo ratings yet
- Ministry of Public Works, Liberia: Flakiness Index - FiDocument2 pagesMinistry of Public Works, Liberia: Flakiness Index - FikwameNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document3 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Romel DecenillaNo ratings yet
- Normal Consistency For GgbsDocument12 pagesNormal Consistency For GgbssreehariNo ratings yet
- Particle Size Analysis of SoilDocument6 pagesParticle Size Analysis of SoilJunrey LumangyaoNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis TestDocument8 pagesSieve Analysis TestF1013 ShamimiNo ratings yet
- Aline Jacolo - Laboratory Exercise 4Document5 pagesAline Jacolo - Laboratory Exercise 4Aline JacoloNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document2 pagesExercise 2Ahmed NasserNo ratings yet
- Table 2.5 (Continued) : Hydrometer Hydrometer Reading ReadingDocument1 pageTable 2.5 (Continued) : Hydrometer Hydrometer Reading ReadingAlenNo ratings yet
- Omc & MDDDocument35 pagesOmc & MDDsuraj ChinttuNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and TestingDocument4 pagesConstruction Materials and TestingNicole May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 2024 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 2024 WorksheetShubham SarthakNo ratings yet
- Kyee Inn Mountain Soil)Document2 pagesKyee Inn Mountain Soil)rushmoore1111No ratings yet
- Soil Testing ReportDocument12 pagesSoil Testing ReportEinstein JeboneNo ratings yet
- Electron Scattering and Nuclear Structure PDFDocument44 pagesElectron Scattering and Nuclear Structure PDFFernanda RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Heat and Internal Energy: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument46 pagesHeat and Internal Energy: Multiple Choice QuestionsWaSx3lyNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Reality: Nilanjan Das Nilanjan - Das@ucl - Ac.ukDocument71 pagesKnowledge and Reality: Nilanjan Das Nilanjan - Das@ucl - Ac.ukZoé DOGBEAVOUNo ratings yet
- Are Ghosts RealDocument5 pagesAre Ghosts RealBogdan BerenghiaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Change: Differentiation: Essential UnderstandingsDocument24 pagesMeasuring Change: Differentiation: Essential UnderstandingsMath Student 1 -No ratings yet
- Opmanager Brochure 1 1Document4 pagesOpmanager Brochure 1 1a_yehia2005No ratings yet
- Z2pack Chapter-1Document30 pagesZ2pack Chapter-1Sayed Syful IslamNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions (Block 6) (Physics 0625)Document16 pagesPractice Questions (Block 6) (Physics 0625)NobodyNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis GuideDocument40 pagesVibration Analysis GuideSAGI RATHNA PRASAD me14d210No ratings yet
- Finite Volume Method Based Neutronic Solvers for Steady and Transient Analysis of Nuclear Reactors-吴宏春老师Document9 pagesFinite Volume Method Based Neutronic Solvers for Steady and Transient Analysis of Nuclear Reactors-吴宏春老师yaoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - MA3004 - Tutorial 5 (FEM) Solutions - AY2022-23Document15 pagesMicrosoft Word - MA3004 - Tutorial 5 (FEM) Solutions - AY2022-23Luna OpalNo ratings yet
- Math Gr. 1 ITC - Finals 2nd Trimester - EditedDocument5 pagesMath Gr. 1 ITC - Finals 2nd Trimester - EditedOmama HamedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8b Tangent Plane and Normal Vector To Level Surface Abd Lagrange MultiplierDocument22 pagesLesson 8b Tangent Plane and Normal Vector To Level Surface Abd Lagrange Multiplierangelo berinaNo ratings yet
- Physics S. L AroraDocument10 pagesPhysics S. L AroraAlu ChopaNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Modeling of The Fatigue Behavior of TPUDocument6 pagesCharacterization and Modeling of The Fatigue Behavior of TPUDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bayesian InferenceDocument22 pagesBayesian InferenceLavanya EaswarNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Questions and AnswersDocument34 pagesPhysical Education: Questions and AnswersQNo ratings yet
- The Message From Water: Hamada 3/3/2010Document2 pagesThe Message From Water: Hamada 3/3/2010Mohamed AbdrabouNo ratings yet
- Prokofyev - Public Education in The USSR - Novosti - 1969Document97 pagesProkofyev - Public Education in The USSR - Novosti - 1969Javier MazzoneNo ratings yet
- Lec12 2 韩卓烨Document3 pagesLec12 2 韩卓烨Wu PkNo ratings yet
- Tension Part-2 and CompressionDocument42 pagesTension Part-2 and Compressionsyed muneeb haiderNo ratings yet
- Tle Lesson 1Document23 pagesTle Lesson 1Ma Kristina Cassandra LunorNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 22 23 XI Phy Target 4 Level 1 Chapter 9Document40 pagesCLS ENG 22 23 XI Phy Target 4 Level 1 Chapter 9AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Temperature SensorsDocument10 pagesTemperature Sensorsdevashish.jo11No ratings yet
- BBA2003Document9 pagesBBA2003cubanosNo ratings yet
- Fluidic MEMS and Micro ChannelsDocument11 pagesFluidic MEMS and Micro ChannelsAnitha Kumari SivathanuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document2 pagesQuiz 1AHMED MSPNo ratings yet
- T H e Spectrum of Clipped Noise: J. H. Van Vlecr Middleton, FellowDocument18 pagesT H e Spectrum of Clipped Noise: J. H. Van Vlecr Middleton, FellowRaúl Díez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Flammability of Marine Surface Finishes: Standard Test Method ForDocument19 pagesFlammability of Marine Surface Finishes: Standard Test Method ForNada KhlifNo ratings yet
Problem Set 1 (Review of Fundamental Soil Testing) : Answer Reference Solution File Here
Problem Set 1 (Review of Fundamental Soil Testing) : Answer Reference Solution File Here
Uploaded by
Jasper Kenneth PeraltaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Problem Set 1 (Review of Fundamental Soil Testing) : Answer Reference Solution File Here
Problem Set 1 (Review of Fundamental Soil Testing) : Answer Reference Solution File Here
Uploaded by
Jasper Kenneth PeraltaCopyright:
Available Formats
Ateneo de Davao University
Graduate School of Engineering & Architecture
CE 707 - Advanced Geotechnical Engineering
Problem Set 1
(Review of Fundamental Soil Testing)
Question Answer Reference Solution
File
1 The results of a sieve analysis of a soil were as follows: Here
US Sieve Designation Mass retained (g) US Sieve Designation Mass retained (g)
¾” 0 #10 3.5
½” 1.7 #14 1.1
3/8” 2.3 #35 30.5
¼” 8.4 #45 45.3
#4 5.7 #80 25.4
#7 12.9 #200 7.4
The total mass of the soil sample was 147.2 grams.
(a) Plot the grain-size distribution curve.
(b) Determine the percentage of Gravel, Sand, and Fine Materials based on (b.1) AASHTO and (b.2) USCS
standards.
(c) Determine the effective grain size, uniformity coefficient, coefficient of gradation, and sorting coefficient.
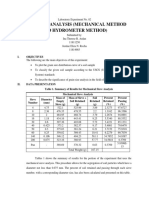
2 Following are the results of hydrometer analysis from a dry 50-gram clay sample. Here
Time (min) Hydrometer reading, Time (min) Hydrometer Check the
R reading, R hydrometer
0.25 51 30 42 analysis
0.50 48 60 40 bookmark
1 47 120 38
2 46 240 34
4 45 480 32
8 44 1440 29
15 43 2880 27
Assuming that Gs = 2.75, and the corrections pertaining to the test are all equal to zero, (a) determine the % of silt
and clay. (b) Plot the particle size distribution curve. ATSM 152H hydrometer was used during the test.
3 The following results were obtained from a liquid limit test on a clay using the Casagrande cup device. Here
Mass of Container Mass of Container and Wet Mass of Container
Test No. Blow Count
(grams) Soil (grams) and dry soil (grams)
1 45.3 57.1 54.4 28
2 43.0 59.8 56.0 31
3 45.2 61.7 57.9 22
4 45.6 58.4 55.3 18
Determine the following: (a) liquid limit, (b) average flow index (c) liquidity index , and (d) consistency index if the
natural water content is 38% and the plastic limit is 23%.
4 Following are the results of a liquid limit test using a fall cone. (a) Estimate the liquid limit. Here
Cone penetration, d (mm) Moisture content (%)
15 29.5
26 35.5
34 38.5
43 41.5
(b) If we assume that only one liquid limit test is conducted using the fall cone for the soil reported such that w =
29.5% at depth of penetration of 15 mm. Search for literatures that will estimate the liquid limit using this one trial
only. Cite the study accordingly.
5 The following results were recorded in a shrinkage limit test using mercury. Here
Mass of container 17.0 grams
Mass of wet soil and container 72.3 grams
Mass of dish 132.40 grams
Ateneo de Davao University
Graduate School of Engineering & Architecture
CE 707 - Advanced Geotechnical Engineering
Problem Set 1
(Review of Fundamental Soil Testing)
Mass of dish and displaced mercury 486.1 grams
Mass of dry soil and container 58.2 grams
Volume of wet soil 32.4 cm3
Determine the shrinkage limit.
6 Classify the following soil using the US Department of Agriculture textural classification chart. Here
Soil % Sand % Silt % Clay
A 20 20 60
B 55 55 40
C 45 35 20
D 50 15 35
E 70 15 15
-
7 Following are the results of the soil testing from five soil samples. Classify the soil using the AASHTO classification Buhati!
system and give the group indexes.
Soil % Passing in % Passing in % Passing in Liquid Limit Plastic
Sieve No. 10 Sieve No. 40 Sieve No. 200 Limit
A 100 92 80 56 23
B 85 55 45 28 20
C 48 28 6 - NP
D 90 76 34 37 25
E 92 74 32 44 35
-
8 Classify the following soils using the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS). Give the group symbols and group Buhati!
names.
Soil % Passing in % Passing in Liquid Limit Plastic Additional Data
Sieve No. 4 Sieve No. 200 Limit
A 99 76 60 32
B 60 40 26 4
C 92 48 30 8
D 100 45 36 22
E 94 3 - NP Cu = 4.5, Cc = 1.2
-
9 A standard proctor test was carried in the laboratory for a fine-grained soil having a natural water content of 6%. The Here
following data were recorded.
Diameter of mold = 101.40 mm
Height of mold = 116.70 mm
Mass of mold = 4196.50 grams
Specific Gravity of Solids = 2.69
Unit Weight
Water Content Determination
Determination
Mass of wet Mass of can Mass of can
Mass of can
soil and mold and wet soil and dry soil
(grams)
(grams) (grams) (grams)
6257 105.05 103.10 42.10
6356 100.69 97.9 40.90
6400 114.71 110.7 42.70
6421 134.26 128.5 42.50
6400 109.34 104.8 41.80
(a) Determine the two laboratory compaction parameters.
(b) Draw the Zero Air Voids (ZAV) line. Also draw the air voids line corresponding to the saturation at the maximum
dry density.
10 A modified Proctor compaction test was carried out in a clayey sand in a cylindrical mold that has a volume of 944 Here
cm3. The specific gravity of the soil grains is 2.68. The moisture content and the mass of the six compacted
specimens are given below.
Moisture 5.0 7.0 9.5 11.8 14.1 17.0
content
(%)
Ateneo de Davao University
Graduate School of Engineering & Architecture
CE 707 - Advanced Geotechnical Engineering
Problem Set 1
(Review of Fundamental Soil Testing)
Mass of 1776 1890 2006 2024 2005 1977
moist
specimen
in the
mold (g)
a. Using the compaction test data, determine the optimum moisture content and the maximum dry unit weight.
b. Plot the zero-air void (ZAV) curve and check whether it intersects the compaction curve.
c. Plot the void ratio and the degree of saturation against the moisture content.
d. What are the void ratio and degree of saturation at the optimum moisture content?
11 A sand cone test was conducted for quality control during the compaction of sandy clay. The data are as follows: Here
Sand Calibration
Mass of Proctor mold 4178 grams
Mass of Proctor mold and sand 5609 grams
Volume of mold 0.00095 m3
Cone Calibration
Mass of sand cone apparatus and jar filled with sand 5466 grams
Mass of sand cone apparatus with remaining sand in jar 3755 grams
Field Test Results
Mass of sand cone apparatus and jar filled with sand 7387 grams
Mass of excavated soil 2206 grams
Mass of sand cone apparatus with remaining sand in jar 3919 grams
Water content of excavated soil 9.2%
-
12 The results of a constant-head permeability test for a fine sand sample having a diameter of 150 mm and a length of Here
300 mm are as follows:
Constant head difference = 500 mm
Time of collection of water = 5 minutes
Volume of water collected = 350 cm3
Temperature of water = 240C
Determine the hydraulic conductivity for the soil at 200C.
13 For a falling-head permeability test, the following values are given: Here
Length of specimen = 200 mm
Area of soil specimen = 1000 mm2
Area of standpipe = 40 mm2
At time t = 0, the head difference was 500 mm
At time t = 180 sec, the head difference was 300 mm
Compute the hydraulic conductivity of the soil in cm/sec.
14 The hydraulic conductivity of sandy soil may be estimated according to the Carrier equation (Carrier, 2003). The
equation is:
⎡ 100% ⎤ 1 𝑒
𝑘 = 1.99 × 10 ⎢ ⎥
⎢∑ 𝑓 ⎥ 𝑆𝐹 1+𝑒
⎣ 𝐷 . ×𝐷 .
⎦
where
𝑆𝐹 = shape factor
𝑓 = fraction of particles between two sieve sizes, in % (Note: subscript 𝑙 denotes larger sieve, subscript 𝑠
denotes smaller sieve)
𝐷( ) = [𝐷 ] . × [𝐷 ] .
= all units are in centimeters
Estimate the hydraulic conductivity of the coarse-grained soil in Problem 1 at a void ratio of 0.77 and shape factor of
7.
You might also like
- Worksheet-Accuracy and Precision-FinalDocument4 pagesWorksheet-Accuracy and Precision-FinalSabeeh Ul HassanNo ratings yet
- Test 1 Sem II Sesi20182019 (Answer Scheme)Document7 pagesTest 1 Sem II Sesi20182019 (Answer Scheme)Ashyra JamilNo ratings yet
- CivE381MidSample PDFDocument27 pagesCivE381MidSample PDFAbera Mamo100% (1)
- 2 Soil Classification - S21Document3 pages2 Soil Classification - S21hassanNo ratings yet
- Report Soil AssignmentDocument4 pagesReport Soil AssignmentWan FaizNo ratings yet
- Rumus Lab AdnanDocument33 pagesRumus Lab AdnanNaim DarmawanNo ratings yet
- CIV E 381 - Practice Exam 2Document15 pagesCIV E 381 - Practice Exam 2JohnNo ratings yet
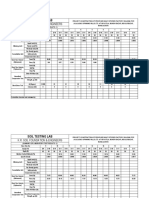
- Soil Testing Lab: K.R. Soil Foundation & EngineersDocument2 pagesSoil Testing Lab: K.R. Soil Foundation & EngineersMd SohagNo ratings yet
- Ecg263 Mini Project Brendan Bungin Braoh 2021830544Document15 pagesEcg263 Mini Project Brendan Bungin Braoh 20218305442021830544No ratings yet
- 2305 - 15 - Hasil Trial Embankment FilterDocument12 pages2305 - 15 - Hasil Trial Embankment FilterAngghy NaghaNo ratings yet
- Seatwork 1 Albo GeorgeDocument3 pagesSeatwork 1 Albo GeorgeDaniel LambinoNo ratings yet
- Lab ReportDocument12 pagesLab ReportACHIENG REBECCANo ratings yet
- Journal On Characteristics of Geotechnical Properties of SoilDocument10 pagesJournal On Characteristics of Geotechnical Properties of SoilAderemi AbidemiNo ratings yet
- Specific Gravity TestDocument13 pagesSpecific Gravity Testsengthai100% (1)
- Report On Soil Moisture and CompactionDocument6 pagesReport On Soil Moisture and CompactionSzczepan KlimczakNo ratings yet
- Group 1 - Lab Report 3 - Ecg263Document8 pagesGroup 1 - Lab Report 3 - Ecg263Muhammad Danial Ikmal Bin Mohamad ShukorNo ratings yet
- CHP TestsDocument3 pagesCHP TestshuneNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Chapter 1,2, Dan 3Document23 pagesSoil Mechanics Chapter 1,2, Dan 3Rakha Naufal DarmawanNo ratings yet
- Client Design and Build Contractor: Liquid Limit (Cone Penotrometer) and Plastic LimitDocument2 pagesClient Design and Build Contractor: Liquid Limit (Cone Penotrometer) and Plastic LimitMARTIN TIBANYENDERANo ratings yet
- Concrete TestDocument14 pagesConcrete TestPharès SOGNON-DESNo ratings yet
- Highway and Airports EngineeringDocument1 pageHighway and Airports EngineeringAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis DataDocument2 pagesSieve Analysis DataAT NM100% (2)
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document2 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Er VenkatNo ratings yet
- Laboratory 4 ReportDocument10 pagesLaboratory 4 ReportFahad KudaratNo ratings yet
- Effect of Boundary Conditions On The Hydraulic Behavior of Geotextile Filtration SystemDocument19 pagesEffect of Boundary Conditions On The Hydraulic Behavior of Geotextile Filtration Systemjavad khosraviNo ratings yet
- CE 200L Report 2 - SieveDocument8 pagesCE 200L Report 2 - SieveravenringsNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document2 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Rezkiya Laila BilkisNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering Btech Civil Enginneering Project Iii Group 4 Topic: To Redesign An Existing Assigned RoadDocument31 pagesFaculty of Engineering Department of Civil Engineering Btech Civil Enginneering Project Iii Group 4 Topic: To Redesign An Existing Assigned RoadSammy SafoNo ratings yet
- Lab Report - Particle Size Distribution (PSD) - Dry SievingDocument6 pagesLab Report - Particle Size Distribution (PSD) - Dry SievingSheikh BajunaidNo ratings yet
- Geo-Report NalbariDocument17 pagesGeo-Report NalbariShashankSinghNo ratings yet
- BJ Att ProctorDocument5 pagesBJ Att ProctorTaztika Audea PutriNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis DataDocument2 pagesSieve Analysis DataYsabelle TagarumaNo ratings yet
- Date: Location: Plastic Limit: ResultDocument3 pagesDate: Location: Plastic Limit: Resultalaa0jabbarNo ratings yet
- Soil Analysis Lab ReportDocument12 pagesSoil Analysis Lab ReportDanielle Del ConteNo ratings yet
- الشيت الثانىDocument1 pageالشيت الثانىAhmed KhaledNo ratings yet
- Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyDocument3 pagesJomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and TechnologyTinaNo ratings yet
- CV321 Lab 1Document10 pagesCV321 Lab 1dherdcarlNo ratings yet
- CE411 CE3105 Grp3 LR07Document18 pagesCE411 CE3105 Grp3 LR07KATE SARAH MARANANNo ratings yet
- Radhey Testing & Consultants Pvt. Ltd. Agra: Observation Cum Calculation SheetDocument1 pageRadhey Testing & Consultants Pvt. Ltd. Agra: Observation Cum Calculation SheetChandan MondalNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Our Thesis Presentation: Rajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyDocument38 pagesWelcome To Our Thesis Presentation: Rajshahi University of Engineering & TechnologyRajibul HasanNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering Lab # 5Document5 pagesGeotechnical Engineering Lab # 5zainabNo ratings yet
- Grain Size AnalysisDocument13 pagesGrain Size AnalysisIna Therese Ardan100% (1)
- Report For Soil Sampling TestDocument92 pagesReport For Soil Sampling TestArham SheikhNo ratings yet
- Complex ENgineering Problem Letter of TransDocument13 pagesComplex ENgineering Problem Letter of TranshamzahayatNo ratings yet
- Amiel A. Cabatchete Bsce-4B Group No. 1 SEPTEMBER 19, 2017: Activity # 3Document10 pagesAmiel A. Cabatchete Bsce-4B Group No. 1 SEPTEMBER 19, 2017: Activity # 3EmanoAceNo ratings yet
- 05-Density ReverseDocument7 pages05-Density ReverseSAFE SERVICES LHRNo ratings yet
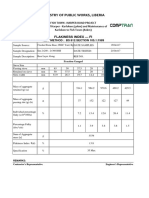
- Ministry of Public Works, Liberia: Flakiness Index - FiDocument2 pagesMinistry of Public Works, Liberia: Flakiness Index - FikwameNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Document3 pagesSieve Analysis Data Sheet: ASTM D422-63 (2007)Romel DecenillaNo ratings yet
- Normal Consistency For GgbsDocument12 pagesNormal Consistency For GgbssreehariNo ratings yet
- Particle Size Analysis of SoilDocument6 pagesParticle Size Analysis of SoilJunrey LumangyaoNo ratings yet
- Sieve Analysis TestDocument8 pagesSieve Analysis TestF1013 ShamimiNo ratings yet
- Aline Jacolo - Laboratory Exercise 4Document5 pagesAline Jacolo - Laboratory Exercise 4Aline JacoloNo ratings yet
- Exercise 2Document2 pagesExercise 2Ahmed NasserNo ratings yet
- Table 2.5 (Continued) : Hydrometer Hydrometer Reading ReadingDocument1 pageTable 2.5 (Continued) : Hydrometer Hydrometer Reading ReadingAlenNo ratings yet
- Omc & MDDDocument35 pagesOmc & MDDsuraj ChinttuNo ratings yet
- Construction Materials and TestingDocument4 pagesConstruction Materials and TestingNicole May Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 2024 WorksheetDocument4 pagesAssignment 5 2024 WorksheetShubham SarthakNo ratings yet
- Kyee Inn Mountain Soil)Document2 pagesKyee Inn Mountain Soil)rushmoore1111No ratings yet
- Soil Testing ReportDocument12 pagesSoil Testing ReportEinstein JeboneNo ratings yet
- Electron Scattering and Nuclear Structure PDFDocument44 pagesElectron Scattering and Nuclear Structure PDFFernanda RibeiroNo ratings yet
- Heat and Internal Energy: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument46 pagesHeat and Internal Energy: Multiple Choice QuestionsWaSx3lyNo ratings yet
- Knowledge and Reality: Nilanjan Das Nilanjan - Das@ucl - Ac.ukDocument71 pagesKnowledge and Reality: Nilanjan Das Nilanjan - Das@ucl - Ac.ukZoé DOGBEAVOUNo ratings yet
- Are Ghosts RealDocument5 pagesAre Ghosts RealBogdan BerenghiaNo ratings yet
- Measuring Change: Differentiation: Essential UnderstandingsDocument24 pagesMeasuring Change: Differentiation: Essential UnderstandingsMath Student 1 -No ratings yet
- Opmanager Brochure 1 1Document4 pagesOpmanager Brochure 1 1a_yehia2005No ratings yet
- Z2pack Chapter-1Document30 pagesZ2pack Chapter-1Sayed Syful IslamNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions (Block 6) (Physics 0625)Document16 pagesPractice Questions (Block 6) (Physics 0625)NobodyNo ratings yet
- Vibration Analysis GuideDocument40 pagesVibration Analysis GuideSAGI RATHNA PRASAD me14d210No ratings yet
- Finite Volume Method Based Neutronic Solvers for Steady and Transient Analysis of Nuclear Reactors-吴宏春老师Document9 pagesFinite Volume Method Based Neutronic Solvers for Steady and Transient Analysis of Nuclear Reactors-吴宏春老师yaoNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Word - MA3004 - Tutorial 5 (FEM) Solutions - AY2022-23Document15 pagesMicrosoft Word - MA3004 - Tutorial 5 (FEM) Solutions - AY2022-23Luna OpalNo ratings yet
- Math Gr. 1 ITC - Finals 2nd Trimester - EditedDocument5 pagesMath Gr. 1 ITC - Finals 2nd Trimester - EditedOmama HamedNo ratings yet
- Lesson 8b Tangent Plane and Normal Vector To Level Surface Abd Lagrange MultiplierDocument22 pagesLesson 8b Tangent Plane and Normal Vector To Level Surface Abd Lagrange Multiplierangelo berinaNo ratings yet
- Physics S. L AroraDocument10 pagesPhysics S. L AroraAlu ChopaNo ratings yet
- Characterization and Modeling of The Fatigue Behavior of TPUDocument6 pagesCharacterization and Modeling of The Fatigue Behavior of TPUDeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- Bayesian InferenceDocument22 pagesBayesian InferenceLavanya EaswarNo ratings yet
- Physical Education: Questions and AnswersDocument34 pagesPhysical Education: Questions and AnswersQNo ratings yet
- The Message From Water: Hamada 3/3/2010Document2 pagesThe Message From Water: Hamada 3/3/2010Mohamed AbdrabouNo ratings yet
- Prokofyev - Public Education in The USSR - Novosti - 1969Document97 pagesProkofyev - Public Education in The USSR - Novosti - 1969Javier MazzoneNo ratings yet
- Lec12 2 韩卓烨Document3 pagesLec12 2 韩卓烨Wu PkNo ratings yet
- Tension Part-2 and CompressionDocument42 pagesTension Part-2 and Compressionsyed muneeb haiderNo ratings yet
- Tle Lesson 1Document23 pagesTle Lesson 1Ma Kristina Cassandra LunorNo ratings yet
- CLS ENG 22 23 XI Phy Target 4 Level 1 Chapter 9Document40 pagesCLS ENG 22 23 XI Phy Target 4 Level 1 Chapter 9AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Temperature SensorsDocument10 pagesTemperature Sensorsdevashish.jo11No ratings yet
- BBA2003Document9 pagesBBA2003cubanosNo ratings yet
- Fluidic MEMS and Micro ChannelsDocument11 pagesFluidic MEMS and Micro ChannelsAnitha Kumari SivathanuNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1Document2 pagesQuiz 1AHMED MSPNo ratings yet
- T H e Spectrum of Clipped Noise: J. H. Van Vlecr Middleton, FellowDocument18 pagesT H e Spectrum of Clipped Noise: J. H. Van Vlecr Middleton, FellowRaúl Díez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- Flammability of Marine Surface Finishes: Standard Test Method ForDocument19 pagesFlammability of Marine Surface Finishes: Standard Test Method ForNada KhlifNo ratings yet