Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Accounting Concepts, Principles and Assumptions Fundamental Idea Other Notes
Accounting Concepts, Principles and Assumptions Fundamental Idea Other Notes
Uploaded by
Mysh PDOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Accounting Concepts, Principles and Assumptions Fundamental Idea Other Notes
Accounting Concepts, Principles and Assumptions Fundamental Idea Other Notes
Uploaded by
Mysh PDCopyright:
Available Formats
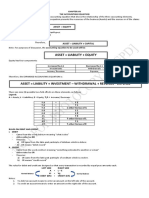
CHAPTER VI
ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS AND PRINCIPLES
ACCOUNTING CONCEPTS,
FUNDAMENTAL IDEA OTHER NOTES
PRINCIPLES and ASSUMPTIONS
Accrual Basis of Accounting “Revenue or income is recognized when -It results to a more accurate and more reliable
earned regardless of collection. Expenses are financial statements.
recognized when incurred regardless of -Cash basis accounting: income is recognized
payment.” when cash is received; expense is recognized
when cash is paid
Matching Principle There should be a simultaneous recognition -Closely related to accrual accounting
of income and the corresponding expenses -Revenues always come with expenses
that are directly or indirectly contributory to
the earnings of such income.
Going Concern Assumption “The business is a continuing concern or has -The operations of a business will not stop in
an indefinite existence.” the near future and it will not be forced to
liquidate its assets to off its liabilities
(Liquidating Concern)
Accounting Entity Assumption “The business is treated as a person separate -Personal transactions of an owner should not
and distinct from the owner or investor.” affect the financial statements of his business.
Time Period Assumption/ The indefinite life of a company can be -Normally, periods span for one year
Periodicity Assumption divided into periods of equal length for the -Calendar year: January 1 – December 31
preparation of financial reports. -Fiscal year: a period of 12 successive calendar
months ending with the last day of any month
other than December 31
Example: April 1 – March 31
Prudence/ Conservatism “In case of doubt, record any loss (expense)
and do not record any gain (income).”
Use of Judgment and Accounting estimates are approximations
Estimates made by accountants or the management in
the preparation of financial statements.
Substance over form Information presented in the financial
statements should truthfully and faithfully
represent the financial condition and financial
performance of the company.
ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
1. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
- Consists of accounting principles, standards, rules and guidelines that companies follow to achieve consistency and
comparability in their financial statements.
- Helps external users and the management
- Helps management in understanding trends persistent in the company. Management can compare past and current
performance to check the strong and weak points of company operations.
- Since the accountancy profession is continuously evolving, standards should adapt with such changes. Thus, GAAP is
being developed and improved continuously.
- It is created by individual in the accountancy profession and goes through a rigid process involving professional
judgment and research.
2. International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
- Pronouncements issued by the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) that intend to enhance the
comparability of the financial statements of all companies worldwide.
- Because of globalization, IFRS provided a way for users of accounting information to easily understand the results of
operations of companies all around the globe.
- Additional notes:
• International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC) – formerly performed the function of IASB
• International Accounting Standards (IAS) – pronouncements of IASC
• IASB adheres to IAS in addition to IFRS
3. Philippine Financial Reporting Standards (PFRS)
- Issued by Philippine Financial Reporting Standards Council (FRSC)
- It includes the following
a. PFRS which corresponds to the IFRS
b. Philippine Accounting Standards (PAS) which corresponds to IAS
c. Interpretations of accounting standards
- Issued by the Philippine Interpretations Committee (PIC) in accordance with the interpretations of the
International Financial Reporting Interpretations Committee (IFRIC) and the Standing Interpretation
Committee (SIC)
You might also like
- Summary: Financial Intelligence: Review and Analysis of Berman and Knight's BookFrom EverandSummary: Financial Intelligence: Review and Analysis of Berman and Knight's BookNo ratings yet
- PFN1223 - Set A - MSDocument8 pagesPFN1223 - Set A - MSalya farhanaNo ratings yet
- GAAP - AccountingDocument19 pagesGAAP - AccountingAndrew Brown100% (3)
- Strategic Planning - (Tutorial) VhunnnDocument24 pagesStrategic Planning - (Tutorial) VhunnnKatherine Castillerost0% (2)
- AccountingDocument11 pagesAccountingAryanna MapanaoNo ratings yet
- Welcome To The Journey of "Accounting For Managers" Thru' Mutual Interaction. - Prof. Puja KhannaDocument11 pagesWelcome To The Journey of "Accounting For Managers" Thru' Mutual Interaction. - Prof. Puja KhannaKopal ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- Presented By: M.Nauman SherDocument19 pagesPresented By: M.Nauman Shergaurav yadavNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument32 pagesAccounting Concepts and PrinciplesJill Alexandra Faye Ferrer100% (1)
- Topic OneDocument21 pagesTopic Onesammie celeNo ratings yet
- Wa0007.Document10 pagesWa0007.Shubra BiswasNo ratings yet
- 3.accounts Revision by Topper InstituteDocument24 pages3.accounts Revision by Topper InstituteDristi SaudNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assumptions and PrinciplesDocument2 pagesAccounting Assumptions and PrinciplesNoaj Palon100% (1)
- Topic: GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) : Presented By: M.Nauman SherDocument19 pagesTopic: GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles) : Presented By: M.Nauman SherShashank GuptaNo ratings yet
- Conceptual Framework For Financial Reporting 2Document6 pagesConceptual Framework For Financial Reporting 2Nikki RañolaNo ratings yet
- CPT Accounts ThoeryDocument6 pagesCPT Accounts ThoeryanandvkakuNo ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewerDocument4 pagesAccounting ReviewerKeon OrbisoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Financial AccountingDocument92 pages1 - Financial Accountingajbebera1999No ratings yet
- Simplified Notes Unit 1 and 2Document4 pagesSimplified Notes Unit 1 and 2John Paul Gaylan100% (1)
- Chapter 3A UnlockedDocument28 pagesChapter 3A UnlockedYashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Conceptual Framework of AccountingDocument21 pagesChapter 2 Conceptual Framework of AccountingBikas AdhikariNo ratings yet
- Accounts TheoryDocument73 pagesAccounts Theoryaneupane465No ratings yet
- Basic Concepts and ConventionsDocument5 pagesBasic Concepts and ConventionsAhmet BabayevNo ratings yet
- Financial, Cost and Management AccountingDocument82 pagesFinancial, Cost and Management Accountingmkpatidar100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument39 pagesChapter 6 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesCharlyn galahanNo ratings yet
- Valuation Concepts and MethodsDocument5 pagesValuation Concepts and MethodsYami HeatherNo ratings yet
- FABM 1 Lesson 6 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument3 pagesFABM 1 Lesson 6 Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesTiffany CenizaNo ratings yet
- Accounting Assumptions: Introduction To Basic AccountingDocument6 pagesAccounting Assumptions: Introduction To Basic AccountingJon Nell Laguador Bernardo100% (1)
- Accounting Concepts An PrinciplesDocument3 pagesAccounting Concepts An PrinciplesDanica QuinacmanNo ratings yet
- GAAPDocument14 pagesGAAPMr SuTtUNo ratings yet
- Fundamental of Financial AccountingDocument26 pagesFundamental of Financial AccountingShirish JhaNo ratings yet
- Accounting PrinciplesDocument4 pagesAccounting PrinciplesManjulaNo ratings yet
- Level Up - Conceptual Framework ReviewerDocument15 pagesLevel Up - Conceptual Framework Reviewerazithethird100% (1)
- Accounting Concepts and PrinciplesDocument9 pagesAccounting Concepts and PrinciplesJoana Marie BlancoNo ratings yet
- Acctg 2Document18 pagesAcctg 2Cindy GajelanNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument5 pagesAccountingCma Pushparaj KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Iam Notes - I - StudentsDocument16 pagesIam Notes - I - StudentsNic BrownNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of AccountingDocument18 pagesFundamentals of AccountingganeshvarmabattulaNo ratings yet
- (Topic 1) Accounting and Its EnvironmentDocument3 pages(Topic 1) Accounting and Its EnvironmentLovely JaneNo ratings yet
- Cfas Prelims Notes by FygDocument15 pagesCfas Prelims Notes by FygFrey Angeleigh GalvezoNo ratings yet
- BAM 1 - Fundamentals of AccountingDocument33 pagesBAM 1 - Fundamentals of AccountingimheziiyyNo ratings yet
- Inbound 3522308407029868205Document18 pagesInbound 3522308407029868205KupalNo ratings yet
- FA Unit 1 - PPTDocument24 pagesFA Unit 1 - PPTDibyadish DasNo ratings yet
- Accounting For Managers - 1 PDFDocument53 pagesAccounting For Managers - 1 PDFBUSHRA FATIMA ANo ratings yet
- Wa0053.Document4 pagesWa0053.shll1771llhs9No ratings yet
- Accounting ReviewerDocument9 pagesAccounting ReviewerLearni SarabiaNo ratings yet
- Study Notes: Business Finance & Accounting Accounting Concepts and ConventionsDocument10 pagesStudy Notes: Business Finance & Accounting Accounting Concepts and ConventionsNeed IsolationNo ratings yet
- Accounting Concepts and ConventionsDocument29 pagesAccounting Concepts and ConventionsSaad SulemanNo ratings yet
- Basics of Accounting - I: Financial Accounting / Isu Manufacturing Prithwiraj Sen SarmaDocument40 pagesBasics of Accounting - I: Financial Accounting / Isu Manufacturing Prithwiraj Sen Sarmakadir2613No ratings yet
- Meaning of AccountingDocument50 pagesMeaning of AccountingAyushi KhareNo ratings yet
- Elements of Financial StatementDocument33 pagesElements of Financial StatementKertik Singh100% (1)
- Muh213U-Accounting I: Chapter 1: Accounting and Business EnvironmentDocument21 pagesMuh213U-Accounting I: Chapter 1: Accounting and Business EnvironmentÖmer Faruk AYDINNo ratings yet
- Presentation of FS & Its' AuditingDocument27 pagesPresentation of FS & Its' AuditingTeamAudit Runner GroupNo ratings yet
- CA. Praveen Tawania The Only Book That Balance Your Books: Group-IDocument2 pagesCA. Praveen Tawania The Only Book That Balance Your Books: Group-IABHISHEKNo ratings yet
- AccountingDocument4 pagesAccountingYana Xelca Mari NegadoNo ratings yet
- Generally Accepted Accounting PrinciplesDocument29 pagesGenerally Accepted Accounting Principlesarpit vora100% (3)
- Accounting ConceptsDocument4 pagesAccounting ConceptsYessameen Franco R. CastilloNo ratings yet
- FMA NotesDocument19 pagesFMA NotesLAXIANo ratings yet
- 1 - Understanding AccountingDocument12 pages1 - Understanding AccountingNicole DuranteNo ratings yet
- 12 Basic Accounting PrinciplesDocument5 pages12 Basic Accounting PrinciplesUmer BhuttaNo ratings yet
- FA-Accounting Principles PresentationDocument42 pagesFA-Accounting Principles PresentationAbhishek SinghNo ratings yet
- "The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"From Everand"The Language of Business: How Accounting Tells Your Story" "A Comprehensive Guide to Understanding, Interpreting, and Leveraging Financial Statements for Personal and Professional Success"No ratings yet
- Applied Economics ActivityDocument6 pagesApplied Economics ActivityMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Chapter Vii PDFDocument1 pageChapter Vii PDFMysh PDNo ratings yet
- ACCOUNTING - Five Major AccountsDocument1 pageACCOUNTING - Five Major AccountsMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Petition For Declaratory ReliefDocument16 pagesPetition For Declaratory ReliefMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Diamond Drilling Corp Vs Crescent Mining and Dev't CorpDocument8 pagesDiamond Drilling Corp Vs Crescent Mining and Dev't CorpMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Distillers of The Far East, Inc. v. Rogel N. ZaragozaDocument3 pagesConsolidated Distillers of The Far East, Inc. v. Rogel N. ZaragozaMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Hayden Kho Sr. Vs Dolores Nagbanua, Et. Al. G.R. No. 237246. July 29, 2019Document10 pagesHayden Kho Sr. Vs Dolores Nagbanua, Et. Al. G.R. No. 237246. July 29, 2019Mysh PDNo ratings yet
- Turks Shawarma Vs Pajaron: Dutch Movers, Inc. V. LequinDocument7 pagesTurks Shawarma Vs Pajaron: Dutch Movers, Inc. V. LequinMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Case Digest Labor DisputeDocument5 pagesCase Digest Labor DisputeMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Case DigestDocument6 pagesCase DigestMysh PDNo ratings yet
- G.R. No. 229920 July 04, 2018Document2 pagesG.R. No. 229920 July 04, 2018Mysh PDNo ratings yet
- Serious Misconduct, Willful Disobedience of An Employer's Lawful Order, or FraudDocument3 pagesSerious Misconduct, Willful Disobedience of An Employer's Lawful Order, or FraudMysh PDNo ratings yet
- GR No. 211273 18 April 2018Document3 pagesGR No. 211273 18 April 2018Mysh PDNo ratings yet
- LW Case Summary AsylumDocument3 pagesLW Case Summary AsylumMysh PDNo ratings yet
- E. Last Clear ChanceDocument34 pagesE. Last Clear ChanceMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Cases 50-57Document34 pagesCases 50-57Mysh PDNo ratings yet
- Canon 3-6 Full CasesDocument45 pagesCanon 3-6 Full CasesMysh PDNo ratings yet
- NEGLIGENCECAUSATIONDocument57 pagesNEGLIGENCECAUSATIONMysh PDNo ratings yet
- 5change of Working Hours-Post Emp BanDocument24 pages5change of Working Hours-Post Emp BanMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Active Learning StrategiesDocument2 pagesActive Learning StrategiesMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Local Government Notes PDFDocument115 pagesLocal Government Notes PDFMysh PD100% (1)
- 4grants of Bonus and AllowancesDocument29 pages4grants of Bonus and AllowancesMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Fabm 1 Q3 Performance Task: OutputDocument2 pagesFabm 1 Q3 Performance Task: OutputMysh PDNo ratings yet
- Project SCMDocument12 pagesProject SCMtusharNo ratings yet
- Assignment - CargillsDocument7 pagesAssignment - CargillsPradeep AthurugirigeNo ratings yet
- Scope of Managerial AccountingDocument2 pagesScope of Managerial AccountingAlexNo ratings yet
- Managerial EconomicsDocument55 pagesManagerial EconomicsCristiSantínNo ratings yet
- Accounting AssmntDocument11 pagesAccounting AssmntasadNo ratings yet
- Financial Accounting AssignmentDocument2 pagesFinancial Accounting AssignmentHu. A. Hussein'sNo ratings yet
- Financial Statement AnalysisDocument11 pagesFinancial Statement AnalysisramyamohandossNo ratings yet
- Adjusting Entries Part 1Document3 pagesAdjusting Entries Part 1Jacob BabaranNo ratings yet
- Final Report Renault KWIDDocument6 pagesFinal Report Renault KWIDrajesh100% (1)
- International Franchise NetworkDocument12 pagesInternational Franchise NetworkAmarjeet LeishangthemNo ratings yet
- Audcis Quiz 1Document4 pagesAudcis Quiz 1alexissosing.cpaNo ratings yet
- OfBusiness - DeckDocument9 pagesOfBusiness - DeckRobertNo ratings yet
- 4R6 S4CLD2202 BPD en deDocument22 pages4R6 S4CLD2202 BPD en deAndewNo ratings yet
- The Amazon FBA Business Model ExplainedDocument9 pagesThe Amazon FBA Business Model ExplainedShaheryar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Management and Cost Accounting 44Document4 pagesManagement and Cost Accounting 44Themba Patrick MolefeNo ratings yet
- Kristopher Charlz Rodriguez - ResumeDocument2 pagesKristopher Charlz Rodriguez - Resumeapi-341071945No ratings yet
- Applied Economics - Lesson 2Document48 pagesApplied Economics - Lesson 2Ma Nicole Ann ManteleNo ratings yet
- Working Capital and Fund Flow Statement of Modest Infrastucture LTDDocument27 pagesWorking Capital and Fund Flow Statement of Modest Infrastucture LTDMegha HumbalNo ratings yet
- Productos Ramo Sas (Colombia) : Emis 12Th Floor 30 Crown Place London, EC2A 4EB, United KingdomDocument4 pagesProductos Ramo Sas (Colombia) : Emis 12Th Floor 30 Crown Place London, EC2A 4EB, United KingdomAndres RamirezNo ratings yet
- Chap 028Document33 pagesChap 028Danny FarmerNo ratings yet
- Abdhini Biswas Product CannibalisationDocument45 pagesAbdhini Biswas Product Cannibalisationabdhini biswasNo ratings yet
- Sasktel Case StudyDocument8 pagesSasktel Case StudyPerryRimanda100% (1)
- MS08 - Activity-Based Costing (Abc) - Total Quality Management (TQM)Document5 pagesMS08 - Activity-Based Costing (Abc) - Total Quality Management (TQM)Elsie GenovaNo ratings yet
- GodaddyDocument4 pagesGodaddyMarcosLbivNo ratings yet
- Chapter 23 28Document104 pagesChapter 23 28Xander Clock50% (2)
- Project Report ON: Masters of Business Administration (2016-2018)Document82 pagesProject Report ON: Masters of Business Administration (2016-2018)pradhan poovaiah100% (1)
- Azad-Sir - ParvezDocument31 pagesAzad-Sir - Parvez0084 Arshadul HossainNo ratings yet
- OMG Rich Media - Case StudiesDocument11 pagesOMG Rich Media - Case Studiesvarun.ramakrishnaNo ratings yet