Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Lrcture Introduction
Lrcture Introduction
Uploaded by
basharfarhan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pagePower electronics uses solid state devices to control electrical power by supplying optimized voltages, currents, and frequencies for different loads. Power semiconductor devices include uncontrolled devices like diodes and controlled devices like thyristors, GTOs, BJTs, MOSFETs, and IGBTs. Power electronics has applications in power supplies, air conditioning, elevators, electric drives, lighting control, HVDC systems, FACT systems, solar power, microgrids, and wind generation. Power electronics converters can be divided into AC-DC rectifiers, DC-DC choppers, AC-AC cycloconverters, and DC-AC inverters.
Original Description:
Original Title
lrcture introduction
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentPower electronics uses solid state devices to control electrical power by supplying optimized voltages, currents, and frequencies for different loads. Power semiconductor devices include uncontrolled devices like diodes and controlled devices like thyristors, GTOs, BJTs, MOSFETs, and IGBTs. Power electronics has applications in power supplies, air conditioning, elevators, electric drives, lighting control, HVDC systems, FACT systems, solar power, microgrids, and wind generation. Power electronics converters can be divided into AC-DC rectifiers, DC-DC choppers, AC-AC cycloconverters, and DC-AC inverters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views1 pageLrcture Introduction
Lrcture Introduction
Uploaded by
basharfarhanPower electronics uses solid state devices to control electrical power by supplying optimized voltages, currents, and frequencies for different loads. Power semiconductor devices include uncontrolled devices like diodes and controlled devices like thyristors, GTOs, BJTs, MOSFETs, and IGBTs. Power electronics has applications in power supplies, air conditioning, elevators, electric drives, lighting control, HVDC systems, FACT systems, solar power, microgrids, and wind generation. Power electronics converters can be divided into AC-DC rectifiers, DC-DC choppers, AC-AC cycloconverters, and DC-AC inverters.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
Introduction Author Dr.
Ali Hussein Numan
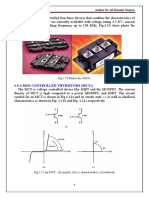
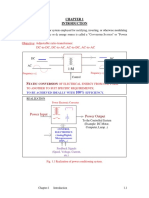
1-1 Power Electronic: Solid state electronic used to control the flow of electrical
power by supplying voltages, currents, and frequencies in a form that is optimally
suited for user load. Fig.1-1 shows a simple power electronic system.
1-2 Power semiconductor devices: An Electronic switches (power processor)
controlled by control signals that is generated by controller (integrated circuits and/
or digital signal processor).These power semiconductor devices can be broadly
classified into three groups according to their degree of controllability:
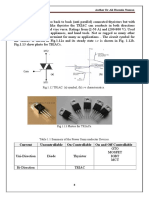
1. Uncontrolled turn on and off (Power Diode).
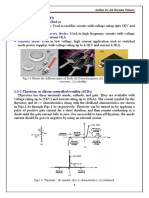
2. Controlled turn on uncontrolled turn off (Thyristors).
3. Controlled turn on and off (GTO, BJT, MOSFET, IGBT).
1-3 POWER ELECTRONICS APPLICATIONS:
Power electronics has a wide range of applications including:-
1. Power supplies (TV, Radio, Receiver, PC and its Peripherals, UPS, mobile phone
battery charger).
2. Air Conditioning and Refrigeration.
3. Elevators.
4. Electric drives.
5. Light control (dimmer).
6. High Voltage Direct Current (HVDC) systems.
7. Flexible AC Transmission (FACT) system.
8. Solar power.
9. Micro grid.
10. Wind generation.
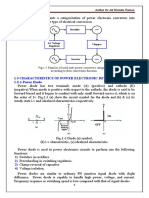
1-4 CLASSIFICATION OF POWER ELECTRONIC CONVERTERS
Power electronics converters can be divided into the following categories:
1. AC-DC converter (rectifier): Convert input AC voltage into a DC output voltage.
2. DC-DC converter (DC Chopper): Convert fixed input DC voltage into variable
DC output voltage or vice versa.
3. AC-AC converter (AC voltage regulator also called cycloconverter): Convert
fixed input AC voltage and frequency into variable AC output voltage and variable
(lower) frequency.
4. DC-AC converter (Inverter): Convert input DC voltage into a variable AC
output voltage
2
You might also like
- 1 Electrical Systems Module 2Document101 pages1 Electrical Systems Module 2Pinky NE OrtegaNo ratings yet
- EE Curs ScurtDocument325 pagesEE Curs ScurtAnca IonitzaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics (Benny Yeung)Document9 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics (Benny Yeung)Souvik GanguliNo ratings yet
- University of Anbar College of EngineeringDocument24 pagesUniversity of Anbar College of EngineeringMustafa AlhumayreNo ratings yet
- Power Electronic Module - Chapter 1Document27 pagesPower Electronic Module - Chapter 1jayxcell100% (1)
- Chapter 1-Introduction To Power SuppliesDocument7 pagesChapter 1-Introduction To Power SuppliesBricksoe NgwenyaNo ratings yet
- Review of Power Electronics - Chapter-1Document3 pagesReview of Power Electronics - Chapter-1NagababuMutyalaNo ratings yet
- Nergy Conversions: University of TechnologyDocument9 pagesNergy Conversions: University of TechnologyFadhil A. HasanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lesson OneDocument40 pagesPower Electronics Lesson Onedalisoullemu02No ratings yet
- Chapter1 PDFDocument18 pagesChapter1 PDFANKIT KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1. INTRODUCTION: 1.1. Definition of Electronic PowerDocument5 pagesChapter 1. INTRODUCTION: 1.1. Definition of Electronic PowerGeofanggaNo ratings yet
- Module 1-18EE53-NotesDocument20 pagesModule 1-18EE53-NotesAshwiniNo ratings yet
- Chapter-1: 1.1 Concept of Power ElectronicsDocument35 pagesChapter-1: 1.1 Concept of Power ElectronicsHãrshã SmîlęýNo ratings yet
- EE331 ChapterI PartIDocument4 pagesEE331 ChapterI PartIMohamed Ouail CHARAOUINo ratings yet
- Over and Under Voltage Protection RelayDocument44 pagesOver and Under Voltage Protection RelaySeven Hills100% (3)
- Module 1 Notes 2Document36 pagesModule 1 Notes 2canusha820No ratings yet
- Security Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1Document30 pagesSecurity Alarm For Doors, Almirah, Cupboards Using Opam Design in Protieus 4 1DebashishParida100% (1)
- Power 1Document6 pagesPower 1john enockNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Power ElectronicsRajaiah JagariNo ratings yet
- Powerelectronics BookDocument6 pagesPowerelectronics BookSANDRA B SREEKUMARNo ratings yet
- Powerelectronics BookDocument6 pagesPowerelectronics BookHari vNo ratings yet
- Part I:Power Electronics: Chapter OneDocument37 pagesPart I:Power Electronics: Chapter Onefor lifeNo ratings yet
- 426 18ec36 PEEI Module1 NewDocument15 pages426 18ec36 PEEI Module1 NewShruthi ShilluNo ratings yet
- Pe Whole PDFDocument165 pagesPe Whole PDFHarshithaPuretiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power ElectronicsDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronicsviciousmoron3No ratings yet
- vedic1[2]Document10 pagesvedic1[2]sivatejaghostNo ratings yet
- An On Line UPS System With Power FactorDocument9 pagesAn On Line UPS System With Power FactormaasifmustafaNo ratings yet
- 1-Introduction To Power Electronics-WEEK 1Document8 pages1-Introduction To Power Electronics-WEEK 1WAHYUDINNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1aaDocument164 pagesUNIT 1aaDr.K.Krishna VeniNo ratings yet
- Elias, Habtamu and HunegnawDocument28 pagesElias, Habtamu and HunegnaweliasNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Power Electronics, History & Applications (1), Semiconductor Devices EtcDocument73 pagesIntroduction To Power Electronics, History & Applications (1), Semiconductor Devices Etckomal phulpotoNo ratings yet
- Introduction Author DR - Ali Hussein NumanDocument95 pagesIntroduction Author DR - Ali Hussein NumanYarr DuNo ratings yet
- Lec 1 Module 1,2Document69 pagesLec 1 Module 1,2Sanjoy PathakNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrical SystemsDocument102 pages1 Electrical SystemsJeff CallantaNo ratings yet
- 1 Electrical SystemsDocument102 pages1 Electrical SystemsCollenne Kaye-Lie Garcia Uy100% (1)
- Design of Regulated Power SupplyDocument18 pagesDesign of Regulated Power SupplyDanish KhanNo ratings yet
- Jbilou 2015Document6 pagesJbilou 2015rahim oneNo ratings yet
- 1.2 Applications of Power ElectronicsDocument7 pages1.2 Applications of Power ElectronicsSwamy100% (1)
- PowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Document15 pagesPowerElec-Course Outline Intro Assign1Ndunya WestleyNo ratings yet
- 30 WattDocument81 pages30 WattMadham KondaiahNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument21 pagesPower SupplyAkashi SeijuroNo ratings yet
- TWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersDocument17 pagesTWO Power Conversion Systems 2.1 Power Electronic ConvertersAlhussain EmbarkNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)Document61 pagesPower Electronics PPT 1st Module (Autosaved)chetan100% (1)
- 20EE530 - Chapter1Document45 pages20EE530 - Chapter1Vivek.RNo ratings yet
- Kabeya Muya Power Electronic DSDocument4 pagesKabeya Muya Power Electronic DSMoïse KabeyaNo ratings yet
- AN-556 Introduction To Power Supplies: Application ReportDocument11 pagesAN-556 Introduction To Power Supplies: Application ReportDhanyasriNo ratings yet
- PE Lecture 1Document32 pagesPE Lecture 1ahmed el-sayedNo ratings yet
- RX TX and Power SupplyDocument10 pagesRX TX and Power SupplyPrashant LochamNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageChapter 1: Fundamentals of Power Electronicsbasharfarhan0% (1)
- Chapter - I 1.1 GeneralDocument67 pagesChapter - I 1.1 GeneralJilly ArasuNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument57 pagesPower ElectronicsSumit SahuNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument9 pagesPower SupplyMuhammed HuzaifaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of SubstationDocument53 pagesIntroduction of SubstationDiaa MostafaNo ratings yet
- Iare Pe Lecture NotesDocument177 pagesIare Pe Lecture NotesShewan DebretsionNo ratings yet
- Ece Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionDocument77 pagesEce Vii Power Electronics (06ec73) SolutionVijay SaiNo ratings yet
- Power SupplyDocument91 pagesPower SupplyshreekadapaNo ratings yet
- Power Supply FundamentalsDocument4 pagesPower Supply FundamentalsgarimapandeyokiciciNo ratings yet
- Power ElectronicsDocument3 pagesPower ElectronicspanjiNo ratings yet
- EE4532 Part A Lecture - pdf0Document83 pagesEE4532 Part A Lecture - pdf0Denise Isebella LeeNo ratings yet
- QSC1Document1 pageQSC1basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- E23TDocument1 pageE23TbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Q12WDocument1 pageQ12WbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- A4Document1 pageA4basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Power ElectronicsDocument1 pageChapter 1: Fundamentals of Power Electronicsbasharfarhan0% (1)
- A3Document1 pageA3basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- 3Document1 page3basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- A1Document1 pageA1basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Part I:Power Electronics: Chapter OneDocument1 pagePart I:Power Electronics: Chapter OnebasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- 2Document1 page2basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Author DR - Ali Hussein NumanDocument1 pageIntroduction Author DR - Ali Hussein NumanbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Book Fundamentals of Electric Machinery by Chapman 4ed 1Document1 pageBook Fundamentals of Electric Machinery by Chapman 4ed 1basharfarhan33% (3)
- Book Fundamentals of Electric Machinery by Chapman 4ed 1Document1 pageBook Fundamentals of Electric Machinery by Chapman 4ed 1basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Lecture Introduction8Document1 pageLecture Introduction8basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- 1-5 Characteristics of Power Electronic Devices 1-5-1 Power DiodeDocument1 page1-5 Characteristics of Power Electronic Devices 1-5-1 Power DiodebasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- 1-5-3 Gate Turn Off Thyristor (GTO)Document1 page1-5-3 Gate Turn Off Thyristor (GTO)basharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Introduction Author DR - Ali Hussein NumanDocument1 pageIntroduction Author DR - Ali Hussein NumanbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- General Purpose Diodes Fast and Ultra Fast Recovery Diodes Schottky DiodeDocument1 pageGeneral Purpose Diodes Fast and Ultra Fast Recovery Diodes Schottky DiodebasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- 1 - 3 - 3 Energy Management SystemsDocument3 pages1 - 3 - 3 Energy Management SystemsbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Hybrid Renewable Energy SystemDocument5 pagesModeling of Hybrid Renewable Energy SystembasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Access Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsDocument8 pagesAccess Full Complete Solution Manual Here: Chapter 1 SolutionsbasharfarhanNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Hybrid Renewable Energy SystemDocument5 pagesModeling of Hybrid Renewable Energy SystembasharfarhanNo ratings yet























![vedic1[2]](https://imgv2-2-f.scribdassets.com/img/document/747670266/149x198/49ffe9e63b/1720034355?v=1)