Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsSTUDY OF SINGLE and Double Shear
STUDY OF SINGLE and Double Shear
Uploaded by
Suyog PatilSingle shear occurs when a load cuts a fastener into two pieces, while double shear cuts it into three. Shear strength is defined as the maximum load a fastener can support normal to its axis before fracturing. Shear stress within a structure can be calculated by modeling it as stringers carrying axial loads and webs carrying shear flows, with the highest stress occurring in the thinnest web under the greatest shear flow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- ES 205-Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Module 1: Introduction (Concept of Stress)Document39 pagesES 205-Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Module 1: Introduction (Concept of Stress)Steven Claude DigamonNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Test On MSDocument15 pagesDirect Shear Test On MSafzal tai100% (1)
- MD1 Topic 1 Simple StressesDocument11 pagesMD1 Topic 1 Simple StressesNowellNo ratings yet
- Module 1.0-SIMPLE STRESS - Axial-NormalDocument20 pagesModule 1.0-SIMPLE STRESS - Axial-NormalJoseph Berlin JuanzonNo ratings yet
- Introduction Stress and StrainDocument11 pagesIntroduction Stress and StrainHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Handout PrintDocument5 pagesHandout PrintBeverly Andres GalisteNo ratings yet
- Title of Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument1 pageTitle of Shear Force and Bending MomentMuhammad Yusoff ZakariaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Stress and Strain - The Efficient EngineerDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Stress and Strain - The Efficient Engineermysterioussecret771No ratings yet
- Mech 32B - Strength Of Materials: σ = Force / AreaDocument2 pagesMech 32B - Strength Of Materials: σ = Force / AreaJonathan PacaldoNo ratings yet
- ES311 Chapter 1Document20 pagesES311 Chapter 1Johannes Frucz RadaNo ratings yet
- Ce43-Strength of MaterialsDocument95 pagesCe43-Strength of MaterialsVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1Document23 pagesMekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1lia tyyanNo ratings yet
- Compendium of SomDocument13 pagesCompendium of SomVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Steel StrengthDocument8 pagesSteel StrengthVishalNo ratings yet
- RCH Som 01 IntroductionDocument51 pagesRCH Som 01 IntroductionSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Normal Stress, Bending Stress, & Shear StressDocument2 pagesNormal Stress, Bending Stress, & Shear Stressvprit100% (1)
- Som Study Notes 59Document29 pagesSom Study Notes 59Anubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- CEMDEF40 Module 2 - Simple StressesDocument27 pagesCEMDEF40 Module 2 - Simple StressesengrrrrNo ratings yet
- Torsional Analysis of Steel MembersDocument6 pagesTorsional Analysis of Steel MembersasdasNo ratings yet
- Material Is Called Stress.: Sample Questions For Material PropertiesDocument5 pagesMaterial Is Called Stress.: Sample Questions For Material PropertiesIbrahim HossainNo ratings yet
- Analysis of TrussDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Trussvj5agdalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strength of MaterialsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Strength of Materialsseylabuormah63No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Notes PDFDocument88 pagesStrength of Materials Notes PDFprernapatil1234No ratings yet
- Beton Prategang: Members Analysis Under ShearDocument45 pagesBeton Prategang: Members Analysis Under Shearzacoeb_a1669No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-II: Faisal AzizDocument9 pagesMechanics of Materials-II: Faisal AzizMuhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Member Takes.: Axial Loads: Here The Member Is Subjected To Loads That Act Parallel To The Axis and TendsDocument2 pagesMember Takes.: Axial Loads: Here The Member Is Subjected To Loads That Act Parallel To The Axis and TendsAnil kumar RNo ratings yet
- Concept of Stresses and StrainDocument30 pagesConcept of Stresses and StrainAshenafi Kena100% (1)
- Unit-1 Principal Stresses Theories of FailureDocument29 pagesUnit-1 Principal Stresses Theories of FailureNarender NarruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Stress & StrainDocument35 pagesChapter 1-Stress & StrainMUHAMMAD HAFIZ KAMAL MOHAMAD KAMALNo ratings yet
- The Normal StressDocument2 pagesThe Normal Stressdhananjaykpatel17No ratings yet
- CH 1Document38 pagesCH 1Ethio Dangote TubeNo ratings yet
- Strain MeasurementDocument66 pagesStrain MeasurementSatyanarayana VenkatNo ratings yet
- Pptby: ANURAG CHATURVEDI (1714101123) ASHISH KUMAR (1714101021) ASHISH MISHRA (1714101022) SUSHANT KUMAR (1714101109)Document10 pagesPptby: ANURAG CHATURVEDI (1714101123) ASHISH KUMAR (1714101021) ASHISH MISHRA (1714101022) SUSHANT KUMAR (1714101109)AnuragNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses: Force / AreaDocument1 pageSimple Stresses: Force / ArearaghumavathurNo ratings yet
- DEWESoft Training DocumentDocument67 pagesDEWESoft Training DocumentMustafa YildizNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and CreepDocument14 pagesStrength of Materials and Creepfabyan mayharNo ratings yet
- CE2252 Strength of Materials Lecture NotesDocument88 pagesCE2252 Strength of Materials Lecture NotesKA VENo ratings yet
- File 1567673653Document107 pagesFile 1567673653angeloNo ratings yet
- Simple - Stress-Strain and TrussDocument131 pagesSimple - Stress-Strain and Trussdarshan100% (3)
- An Analysis of Shear Stress in Beams of Various Cross SectionsDocument10 pagesAn Analysis of Shear Stress in Beams of Various Cross SectionsGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Design Against Static LoadDocument23 pagesDesign Against Static LoadDiVik BhargAvaNo ratings yet
- ES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesDocument15 pagesES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesErikNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument50 pagesLectureIsmailNo ratings yet
- Torsion - of - Sections Warping PasDocument3 pagesTorsion - of - Sections Warping PasPrantik Adhar Samanta100% (1)
- Stiffness Elastic Stress Axis Strain Hooke's Law Solid Mechanics Stress-Strain Curve Tangent ModulusDocument2 pagesStiffness Elastic Stress Axis Strain Hooke's Law Solid Mechanics Stress-Strain Curve Tangent ModulusJai SinghNo ratings yet
- Tension. The Forces On The Rope Are The Wight of The Load Acting Downwards andDocument3 pagesTension. The Forces On The Rope Are The Wight of The Load Acting Downwards andAnonymous TX2OckgiZNo ratings yet
- Dersnot 5517 1697194133Document30 pagesDersnot 5517 1697194133Soner InanNo ratings yet
- TAM251 Chapter1 Stress Prelecture JohnsonDocument18 pagesTAM251 Chapter1 Stress Prelecture JohnsonRian Marc AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Ae2302 NolDocument42 pagesAe2302 NolShwetha BhatNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Part 1 2Document12 pagesCH1 - Part 1 2مهدي ماجد حميدNo ratings yet
- CH 0 Introduction - Stress AnalsisDocument6 pagesCH 0 Introduction - Stress AnalsisadelashrafengNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsZoe FallurinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Unit 2 - StressDocument6 pagesStrength of Material Unit 2 - StressJulius EtukeNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain and TorsionDocument65 pagesStress Strain and Torsionharrahedaine.tabotaboNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingFrom EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet
STUDY OF SINGLE and Double Shear
STUDY OF SINGLE and Double Shear
Uploaded by
Suyog Patil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesSingle shear occurs when a load cuts a fastener into two pieces, while double shear cuts it into three. Shear strength is defined as the maximum load a fastener can support normal to its axis before fracturing. Shear stress within a structure can be calculated by modeling it as stringers carrying axial loads and webs carrying shear flows, with the highest stress occurring in the thinnest web under the greatest shear flow.
Original Description:
Original Title
STUDY OF SINGLE and double shear
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentSingle shear occurs when a load cuts a fastener into two pieces, while double shear cuts it into three. Shear strength is defined as the maximum load a fastener can support normal to its axis before fracturing. Shear stress within a structure can be calculated by modeling it as stringers carrying axial loads and webs carrying shear flows, with the highest stress occurring in the thinnest web under the greatest shear flow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesSTUDY OF SINGLE and Double Shear
STUDY OF SINGLE and Double Shear
Uploaded by
Suyog PatilSingle shear occurs when a load cuts a fastener into two pieces, while double shear cuts it into three. Shear strength is defined as the maximum load a fastener can support normal to its axis before fracturing. Shear stress within a structure can be calculated by modeling it as stringers carrying axial loads and webs carrying shear flows, with the highest stress occurring in the thinnest web under the greatest shear flow.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
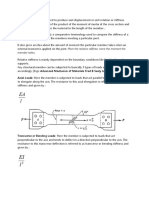
STUDY OF SINGLE&DOUBLE SHEAR FORCES
Single Shear Diagram
Double Shear Diagram
Shear Strength is defined as the maximum load typically applied normal to a fastener's axis that
can be supported prior to fracture. Single shear is load applied in one plane that would result in
the fastener being cut into two pieces, while double shear would result in three fastener pieces.
A shear stress, often denoted by τ (tau), is the component of stress coplanar with a material cross
section. Shear stress arises from the vector component parallel to the cross section of the
material. Normal stress, on the other hand, arises from the force vector
component perpendicular to the material cross section on which it acts.
Shear stresses within a semi-monologue structure may be calculated by idealizing the cross-
section of the structure into a set of stringers (carrying only axial loads) and webs (carrying
only shear flows). Dividing the shear flow by the thickness of a given portion of the semi-
monologue structure yields the shear stress. Thus, the maximum shear stress will occur either in
the web of maximum shear flow or minimum thickness.
Single shear is load applied in one plane that would result the fastener being cut into two pieces,
while double three pieces strength defined as maximum typically normal to a fastener`s axis can
be supported prior fracture.
The formula to calculate average shear stress is force per unit area:
MADE BY: Suyog Bansode (36), Sachin Dahihande (34) GUIDED BY: S.D Bhople
You might also like
- ES 205-Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Module 1: Introduction (Concept of Stress)Document39 pagesES 205-Mechanics of Deformable Bodies: Module 1: Introduction (Concept of Stress)Steven Claude DigamonNo ratings yet
- Direct Shear Test On MSDocument15 pagesDirect Shear Test On MSafzal tai100% (1)
- MD1 Topic 1 Simple StressesDocument11 pagesMD1 Topic 1 Simple StressesNowellNo ratings yet
- Module 1.0-SIMPLE STRESS - Axial-NormalDocument20 pagesModule 1.0-SIMPLE STRESS - Axial-NormalJoseph Berlin JuanzonNo ratings yet
- Introduction Stress and StrainDocument11 pagesIntroduction Stress and StrainHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Handout PrintDocument5 pagesHandout PrintBeverly Andres GalisteNo ratings yet
- Title of Shear Force and Bending MomentDocument1 pageTitle of Shear Force and Bending MomentMuhammad Yusoff ZakariaNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Stress and Strain - The Efficient EngineerDocument10 pagesAn Introduction To Stress and Strain - The Efficient Engineermysterioussecret771No ratings yet
- Mech 32B - Strength Of Materials: σ = Force / AreaDocument2 pagesMech 32B - Strength Of Materials: σ = Force / AreaJonathan PacaldoNo ratings yet
- ES311 Chapter 1Document20 pagesES311 Chapter 1Johannes Frucz RadaNo ratings yet
- Ce43-Strength of MaterialsDocument95 pagesCe43-Strength of MaterialsVel MuruganNo ratings yet
- Mekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1Document23 pagesMekanika Kekuatan Material - Kul 1lia tyyanNo ratings yet
- Compendium of SomDocument13 pagesCompendium of SomVivek BajpaiNo ratings yet
- Steel StrengthDocument8 pagesSteel StrengthVishalNo ratings yet
- RCH Som 01 IntroductionDocument51 pagesRCH Som 01 IntroductionSatish DhanyamrajuNo ratings yet
- Normal Stress, Bending Stress, & Shear StressDocument2 pagesNormal Stress, Bending Stress, & Shear Stressvprit100% (1)
- Som Study Notes 59Document29 pagesSom Study Notes 59Anubhav KumarNo ratings yet
- CEMDEF40 Module 2 - Simple StressesDocument27 pagesCEMDEF40 Module 2 - Simple StressesengrrrrNo ratings yet
- Torsional Analysis of Steel MembersDocument6 pagesTorsional Analysis of Steel MembersasdasNo ratings yet
- Material Is Called Stress.: Sample Questions For Material PropertiesDocument5 pagesMaterial Is Called Stress.: Sample Questions For Material PropertiesIbrahim HossainNo ratings yet
- Analysis of TrussDocument2 pagesAnalysis of Trussvj5agdalesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Strength of MaterialsDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Strength of Materialsseylabuormah63No ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Notes PDFDocument88 pagesStrength of Materials Notes PDFprernapatil1234No ratings yet
- Beton Prategang: Members Analysis Under ShearDocument45 pagesBeton Prategang: Members Analysis Under Shearzacoeb_a1669No ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials-II: Faisal AzizDocument9 pagesMechanics of Materials-II: Faisal AzizMuhammad AbubakarNo ratings yet
- Member Takes.: Axial Loads: Here The Member Is Subjected To Loads That Act Parallel To The Axis and TendsDocument2 pagesMember Takes.: Axial Loads: Here The Member Is Subjected To Loads That Act Parallel To The Axis and TendsAnil kumar RNo ratings yet
- Concept of Stresses and StrainDocument30 pagesConcept of Stresses and StrainAshenafi Kena100% (1)
- Unit-1 Principal Stresses Theories of FailureDocument29 pagesUnit-1 Principal Stresses Theories of FailureNarender NarruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Stress & StrainDocument35 pagesChapter 1-Stress & StrainMUHAMMAD HAFIZ KAMAL MOHAMAD KAMALNo ratings yet
- The Normal StressDocument2 pagesThe Normal Stressdhananjaykpatel17No ratings yet
- CH 1Document38 pagesCH 1Ethio Dangote TubeNo ratings yet
- Strain MeasurementDocument66 pagesStrain MeasurementSatyanarayana VenkatNo ratings yet
- Pptby: ANURAG CHATURVEDI (1714101123) ASHISH KUMAR (1714101021) ASHISH MISHRA (1714101022) SUSHANT KUMAR (1714101109)Document10 pagesPptby: ANURAG CHATURVEDI (1714101123) ASHISH KUMAR (1714101021) ASHISH MISHRA (1714101022) SUSHANT KUMAR (1714101109)AnuragNo ratings yet
- Simple Stresses: Force / AreaDocument1 pageSimple Stresses: Force / ArearaghumavathurNo ratings yet
- DEWESoft Training DocumentDocument67 pagesDEWESoft Training DocumentMustafa YildizNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials and CreepDocument14 pagesStrength of Materials and Creepfabyan mayharNo ratings yet
- CE2252 Strength of Materials Lecture NotesDocument88 pagesCE2252 Strength of Materials Lecture NotesKA VENo ratings yet
- File 1567673653Document107 pagesFile 1567673653angeloNo ratings yet
- Simple - Stress-Strain and TrussDocument131 pagesSimple - Stress-Strain and Trussdarshan100% (3)
- An Analysis of Shear Stress in Beams of Various Cross SectionsDocument10 pagesAn Analysis of Shear Stress in Beams of Various Cross SectionsGaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Design Against Static LoadDocument23 pagesDesign Against Static LoadDiVik BhargAvaNo ratings yet
- ES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesDocument15 pagesES 1022y Engineering Statics Structural Analysis - TrussesErikNo ratings yet
- LectureDocument50 pagesLectureIsmailNo ratings yet
- Torsion - of - Sections Warping PasDocument3 pagesTorsion - of - Sections Warping PasPrantik Adhar Samanta100% (1)
- Stiffness Elastic Stress Axis Strain Hooke's Law Solid Mechanics Stress-Strain Curve Tangent ModulusDocument2 pagesStiffness Elastic Stress Axis Strain Hooke's Law Solid Mechanics Stress-Strain Curve Tangent ModulusJai SinghNo ratings yet
- Tension. The Forces On The Rope Are The Wight of The Load Acting Downwards andDocument3 pagesTension. The Forces On The Rope Are The Wight of The Load Acting Downwards andAnonymous TX2OckgiZNo ratings yet
- Dersnot 5517 1697194133Document30 pagesDersnot 5517 1697194133Soner InanNo ratings yet
- TAM251 Chapter1 Stress Prelecture JohnsonDocument18 pagesTAM251 Chapter1 Stress Prelecture JohnsonRian Marc AbellanaNo ratings yet
- Ae2302 NolDocument42 pagesAe2302 NolShwetha BhatNo ratings yet
- CH1 - Part 1 2Document12 pagesCH1 - Part 1 2مهدي ماجد حميدNo ratings yet
- CH 0 Introduction - Stress AnalsisDocument6 pagesCH 0 Introduction - Stress AnalsisadelashrafengNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials, Also Called Mechanics of Materials, Deals With The Behavior of Solid ObjectsZoe FallurinNo ratings yet
- Strength of Material Unit 2 - StressDocument6 pagesStrength of Material Unit 2 - StressJulius EtukeNo ratings yet
- Stress Strain and TorsionDocument65 pagesStress Strain and Torsionharrahedaine.tabotaboNo ratings yet
- The Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingFrom EverandThe Mechanical Properties of Wood: Including a Discussion of the Factors Affecting the Mechanical Properties, and Methods of Timber TestingNo ratings yet
- Theory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsFrom EverandTheory of Elastisity, Stability and Dynamics of Structures Common ProblemsNo ratings yet