Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Signs and Symptoms: o o o o
Signs and Symptoms: o o o o
Uploaded by
Mihnea Ganea0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
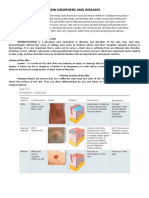
12 views1 pageAn ulcer is a sore on the skin or mucous membrane that results from a disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can penetrate through the epidermis and into the dermis or subcutaneous fat. They are commonly found on the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcers appear as open craters in the skin that may be red, swollen, tender, and oozing fluid. They can develop due to lack of mobility, pressure on tissues, or poor blood circulation and may become infected.
Original Description:
te ro g
Original Title
ulcero
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentAn ulcer is a sore on the skin or mucous membrane that results from a disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can penetrate through the epidermis and into the dermis or subcutaneous fat. They are commonly found on the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcers appear as open craters in the skin that may be red, swollen, tender, and oozing fluid. They can develop due to lack of mobility, pressure on tissues, or poor blood circulation and may become infected.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageSigns and Symptoms: o o o o
Signs and Symptoms: o o o o
Uploaded by
Mihnea GaneaAn ulcer is a sore on the skin or mucous membrane that results from a disintegration of tissue. Ulcers can penetrate through the epidermis and into the dermis or subcutaneous fat. They are commonly found on the lower extremities and in the gastrointestinal tract. Ulcers appear as open craters in the skin that may be red, swollen, tender, and oozing fluid. They can develop due to lack of mobility, pressure on tissues, or poor blood circulation and may become infected.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 1
n
ulcer is a sore on the skin or a mucous membrane, accompanied by the disintegration of
tissue. Ulcers can result in complete loss of the epidermis and often portions of the dermis and
even subcutaneous fat. Ulcers are most common on the skin of the lower extremities and in the
gastrointestinal tract. An ulcer that appears on the skin is often visible as an inflamed tissue with
an area of reddened skin. A skin ulcer is often visible in the event of exposure to heat or cold,
irritation, or a problem with blood circulation.
They can also be caused due to a lack of mobility, which causes prolonged pressure on the
tissues. This stress in the blood circulation is transformed to a skin ulcer, commonly known
as bedsores or decubitus ulcers.[1] Ulcers often become infected, and pus forms.
Contents
1Signs and symptoms
o 1.1Discharges
2Causes
3Diagnosis
o 3.1Grading
4Management
o 4.1Investigations
o 4.2Treatment
5See also
6References
7External links
Signs and symptoms[edit]
Skin ulcers appear as open craters, often round, with layers of skin that have eroded. The skin
around the ulcer may be red, swollen, and tender. Patients may feel pain on the skin around the
ulcer, and fluid may ooze from the ulcer. In some cases, ulcers can bleed and, rarely, patients
experience fever. Ulcers sometimes seem not to heal; healing, if it does occur, tends to be slow.
Ulcers that heal within 12 weeks are usually classified as acute, and longer-lasting ones
as chronic.
Ulcers develop in stages. In stage 1 the skin is red with soft underlying tissue. In the second
stage the redness of the skin becomes more pronounced, swelling appears, and there may be
some blisters and loss of outer skin layers. During the next stage, the skin may
become necrotic down through the deep layers of skin, and the fat beneath the skin may become
exposed and visible. In stage 4, deeper necrosis usually occurs, the fat underneath the skin is
completely exposed, and the muscle may also become exposed. In the last two stages the sore
may cause a deeper loss of fat and necrosis of the muscle; in severe cases it can extend down
to bone level, destruction of the bone may begin, and there may be sepsis of joints.
Chronic ulcers may be painful. Most patients complain of constant pain at night and during the
day. Chronic ulcer symptoms usually include incre
You might also like
- Becoming A Femme FataleDocument108 pagesBecoming A Femme Fataleкр100% (8)
- Description of Skin LesionsDocument30 pagesDescription of Skin LesionsHasrul MuslihNo ratings yet
- Assessment of Mental RetardationDocument56 pagesAssessment of Mental Retardationdrkadiyala2No ratings yet
- Skin Care PowerpointDocument52 pagesSkin Care Powerpointisapatrick812667% (3)
- Yoga For Skin Diseases Anna MayerDocument22 pagesYoga For Skin Diseases Anna Mayerjaideep negi100% (1)
- Skin LesionsDocument4 pagesSkin LesionsRose Marceline Patague TalubanNo ratings yet
- Ekakustha and CarmakushtaDocument32 pagesEkakustha and CarmakushtaVenkatesan VidhyaNo ratings yet
- 4 StagesDocument2 pages4 StagesCandice Maureen Riconalla-ChanNo ratings yet
- Module 3 HomeworkDocument6 pagesModule 3 HomeworkCj LinceNo ratings yet
- What Is A RashDocument8 pagesWhat Is A RashJudi Ann MagsacayNo ratings yet
- Q.1 Components of Skin: The Skin: Basic Structure and FunctionDocument7 pagesQ.1 Components of Skin: The Skin: Basic Structure and Functionnani100No ratings yet
- Ha HandoutsDocument13 pagesHa HandoutsNoymie BalopeñosNo ratings yet
- Integumentary DisorderDocument6 pagesIntegumentary Disorderhxqf25mbvvNo ratings yet
- Decubitus UlcerDocument1 pageDecubitus UlcerAkbarNo ratings yet
- Wound Care PresentationDocument4 pagesWound Care PresentationJJNo ratings yet
- The Wound CareDocument51 pagesThe Wound CareIosefina DudeanuNo ratings yet
- HeilDocument14 pagesHeilNoymie BalopeñosNo ratings yet
- ImpetigoDocument5 pagesImpetigoInges PSNo ratings yet
- 10.07.2022.kimmel N. Woundcare and UlcersDocument49 pages10.07.2022.kimmel N. Woundcare and UlcersJohn Jufel SimplicianoNo ratings yet
- Types of Primary Skin LesionsDocument5 pagesTypes of Primary Skin LesionsKat TaasinNo ratings yet
- final physical skin assessment - CopyDocument48 pagesfinal physical skin assessment - Copyhossam hablesNo ratings yet
- Primary Skin LesionDocument7 pagesPrimary Skin Lesion_carido_No ratings yet
- BED SORES - Stages of Pressure SoresDocument2 pagesBED SORES - Stages of Pressure SoresKaloy KamaoNo ratings yet
- Pressure UlcerDocument66 pagesPressure UlcerSwarnkar JayeshNo ratings yet
- Basic Skin Lesions: Presented By: Dr. Divyank A. Vankawala Jr. Resident, Dermatology Dept., NDMVPS VP Medical CollegeDocument46 pagesBasic Skin Lesions: Presented By: Dr. Divyank A. Vankawala Jr. Resident, Dermatology Dept., NDMVPS VP Medical CollegeniveditakartikNo ratings yet
- Sistem Integumentum 2Document19 pagesSistem Integumentum 2Andrianus SudarmonoNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis Eczema NotesDocument12 pagesAtopic Dermatitis Eczema Notes돼끼빈No ratings yet
- Skinlesionsteam 5Document33 pagesSkinlesionsteam 5Noemí TorresNo ratings yet
- Pressure Ulcers - Surgery I March 2019Document63 pagesPressure Ulcers - Surgery I March 2019daniyfondoNo ratings yet
- 2016 DermTerms & Dx-1Document53 pages2016 DermTerms & Dx-1vivekNo ratings yet
- Types of Primary Skin LesionsDocument4 pagesTypes of Primary Skin LesionsKat TaasinNo ratings yet
- LesionsDocument16 pagesLesionsKevin NelsonNo ratings yet
- PsoriasisDocument23 pagesPsoriasisvasavavipul38022No ratings yet
- SKINDocument12 pagesSKINJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Basic Skin LesionsDocument11 pagesBasic Skin LesionsNiko Daguno100% (1)
- Introduction To Dermatology: Lecture-1Document33 pagesIntroduction To Dermatology: Lecture-1Latika ChoudhuryNo ratings yet
- 1.introduction To DermatologyDocument57 pages1.introduction To DermatologyMutasım Battah100% (2)
- Pressure Ulcer StagesDocument3 pagesPressure Ulcer Stagesfreemind323No ratings yet
- Kulit-Perubahan Dasar Histologis PrintDocument38 pagesKulit-Perubahan Dasar Histologis PrintWirman RamadhanNo ratings yet
- Skin Manifestations of Common DiseasesDocument5 pagesSkin Manifestations of Common DiseasesAya AmerNo ratings yet
- Dermatology DDXDocument29 pagesDermatology DDXM.Dalani100% (2)
- Derma Slides 2017Document268 pagesDerma Slides 2017Nadia AlmahalawiNo ratings yet
- INTEGUMENTARY-FUNCTION-Acabo Ano BaliliDocument36 pagesINTEGUMENTARY-FUNCTION-Acabo Ano Balilicoosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- EfloresensiDocument3 pagesEfloresensiputriana safitriNo ratings yet
- Pressure SoresDocument20 pagesPressure SoresRupika Sodhi100% (1)
- OME OxforeDocument9 pagesOME OxforeFatima GamalNo ratings yet
- EfloresensiDocument40 pagesEfloresensimariamunsriNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Updated 2020Document57 pagesDermatology Updated 2020ElvisNo ratings yet
- What Is BedsoresDocument4 pagesWhat Is Bedsoresver_at_workNo ratings yet
- Dermatology Notes: Don't Forget The HistoryDocument21 pagesDermatology Notes: Don't Forget The HistorySlim SaaryNo ratings yet
- Fistuales, BedsoreDocument4 pagesFistuales, BedsoreSagar KhairwalNo ratings yet
- SKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES HandoutsDocument9 pagesSKIN DISORDERS AND DISEASES HandoutsMARIALUPE ESTOQUENo ratings yet
- Bed SoresDocument15 pagesBed Soresver_at_work100% (1)
- Chapter 54 IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesChapter 54 IntegumentaryRebeccaNo ratings yet
- Tissue Integrity Outline Spring 2023Document25 pagesTissue Integrity Outline Spring 2023morganstorey0No ratings yet
- WOUND CARE and BANDAGINGDocument9 pagesWOUND CARE and BANDAGINGJane BelvisNo ratings yet
- 008 Skin Hair NailsDocument35 pages008 Skin Hair NailsPauline An Toni CapurihanNo ratings yet
- Atopic Dermatitis: Unit 3: Diseases of The Integumentary & Musculoskeletal SystemsDocument21 pagesAtopic Dermatitis: Unit 3: Diseases of The Integumentary & Musculoskeletal Systemsunclet12No ratings yet
- General Surgery Copy 2Document37 pagesGeneral Surgery Copy 2sowmyaraja09No ratings yet
- Complete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisFrom EverandComplete Medical Guide for Disease Volume VII; Atopic DermatitisNo ratings yet
- Cellulitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsFrom EverandCellulitis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsNo ratings yet
- History of Chemotaxis ResearchDocument2 pagesHistory of Chemotaxis ResearchMihnea GaneaNo ratings yet
- Buna DimineataDocument1 pageBuna DimineataMihnea GaneaNo ratings yet
- O o o o o o : This Includes A List of Related Items That Share The Same Name (Or Similar Names)Document1 pageO o o o o o : This Includes A List of Related Items That Share The Same Name (Or Similar Names)Mihnea GaneaNo ratings yet
- Ganea Mihnea Tema Info Probleme Cu Solutie Eurisitca EtcDocument3 pagesGanea Mihnea Tema Info Probleme Cu Solutie Eurisitca EtcMihnea GaneaNo ratings yet
- Metropolitan Health Care System.Document5 pagesMetropolitan Health Care System.Diane ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Novarc Veterinary BrochureDocument12 pagesNovarc Veterinary BrochureAryan JainNo ratings yet
- Panel 3 Presentation JuliaheissDocument18 pagesPanel 3 Presentation JuliaheissJenny AbdullahNo ratings yet
- CAHOCON 23 - SponsorshipBrochure PDFDocument11 pagesCAHOCON 23 - SponsorshipBrochure PDFsubhraj7027No ratings yet
- Tugas Sistem Informasi KesehatanDocument37 pagesTugas Sistem Informasi Kesehatandewi shintaNo ratings yet
- Hope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessDocument11 pagesHope - 1 Grade 11: Exercise For FitnessVernalyn TamayoNo ratings yet
- Netram EMR: Create PDF in Your Applications With The PdfcrowdDocument5 pagesNetram EMR: Create PDF in Your Applications With The PdfcrowdELI Health EMRNo ratings yet
- MS Ii MT2Document11 pagesMS Ii MT2Rika MaeNo ratings yet
- Kangaroo Mother CareDocument24 pagesKangaroo Mother CareAjeesh100% (1)
- Management Micronutrients in Exchange ListDocument13 pagesManagement Micronutrients in Exchange Listgeovannii CarreraNo ratings yet
- Dapagliflozin LinagliptinDocument13 pagesDapagliflozin Linagliptinkristie.kankenNo ratings yet
- Biology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionDocument5 pagesBiology Form 4 Chapter 6 NutritionzaedmohdNo ratings yet
- GRP 4 Lydia HallDocument19 pagesGRP 4 Lydia HallMeiji YanNo ratings yet
- Ancylostoma-Duodenale NematodesDocument16 pagesAncylostoma-Duodenale NematodesRoy Mujeres CabueñasNo ratings yet
- Thesis of Agha Khan UniversityDocument40 pagesThesis of Agha Khan UniversityAHSAN ANSARINo ratings yet
- Key Areas OF Responsibility: Core Competencies and IndicatorsDocument12 pagesKey Areas OF Responsibility: Core Competencies and Indicatorschristine_bayonaNo ratings yet
- Dialog Bhs InggrisDocument6 pagesDialog Bhs InggrisDheya AprianiNo ratings yet
- ABC V ST George's Healthcare NHS TrustDocument16 pagesABC V ST George's Healthcare NHS Trustzac mankirNo ratings yet
- 8a Food and Nutrition Scheme of Learning PDFDocument4 pages8a Food and Nutrition Scheme of Learning PDFFarhatNo ratings yet
- 2023 Template - Undergraduate Thesis ManuscriptDocument153 pages2023 Template - Undergraduate Thesis Manuscriptel janeNo ratings yet
- Carskadon Edt321 Resume2Document1 pageCarskadon Edt321 Resume2api-346526760No ratings yet
- The Molecular Basis of Human CancerDocument868 pagesThe Molecular Basis of Human Cancerfamp_carrijo100% (8)
- Ams t17 Rev0 Ucua ReportDocument2 pagesAms t17 Rev0 Ucua ReportJeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Lactose Intolerance and HomeopathyDocument3 pagesLactose Intolerance and Homeopathyavinash.gourNo ratings yet
- Between Japan & Germany Related To Dentistry 1Document9 pagesBetween Japan & Germany Related To Dentistry 1Dr Riktesh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Zaka Ur Rehman Muhammad Zaka Ur Rehman: Career SummaryDocument4 pagesMuhammad Zaka Ur Rehman Muhammad Zaka Ur Rehman: Career SummaryZaka RehmanNo ratings yet
- HypokalemiaDocument40 pagesHypokalemiaNadila Putri100% (1)
- High Functioning CPR Bringing Science To The Pit Crew FINAL 3-1-13Document68 pagesHigh Functioning CPR Bringing Science To The Pit Crew FINAL 3-1-13Willie KitsNo ratings yet