Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
Uploaded by
Balpreet KaurCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Vertebrates Comparative Anatomy Function Evolution 7th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Vertebrates Comparative Anatomy Function Evolution 7th Edition PDFmary.ellis361100% (35)
- 2nd Term Biology Note For Ss2Document33 pages2nd Term Biology Note For Ss2Ukwuma Michael Chijioke100% (21)
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case StudyDocument38 pagesIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case Studygiadda100% (9)
- Human Support SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Support Systemkiongoc100% (1)
- Locomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLocomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemNathanael MfumbaikaNo ratings yet
- Support and Movement: Science Scrapbook Form 2 2010Document12 pagesSupport and Movement: Science Scrapbook Form 2 2010Cokelat DaimNo ratings yet
- Maktab Rendah Sains Mara Pengkalan Hulu, Perak.: Biology Notes (CHAPTER 2-4)Document38 pagesMaktab Rendah Sains Mara Pengkalan Hulu, Perak.: Biology Notes (CHAPTER 2-4)Nurul Aisyah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Biology ShazwaniDocument20 pagesEbook Biology ShazwaniNurul shazwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Faiz ApaiNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document15 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Gerard Selvaraj100% (23)
- The Skeletal System of The FrogDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal System of The FrogLuther Abaya MolinaNo ratings yet
- Tissue 2Document34 pagesTissue 2nneduchiemerieNo ratings yet
- Session 14 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSession 14 Skeletal SystemScience Of LifeNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human SkeletonDocument2 pages01 The Human SkeletonAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Skeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesSkeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacut amaliaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 Musculo SkeletalDocument9 pagesExercise 6 Musculo SkeletalJacob NoraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Biology Ss1Document33 pages2nd Term Biology Ss1dasiakennethNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- Movement 2024Document14 pagesMovement 2024HannahNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po CaDocument1 pageInvertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po CayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsilyNo ratings yet
- Bone and CartilageDocument61 pagesBone and CartilageMohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- $R4UVS5TDocument32 pages$R4UVS5Tnechtech6No ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Notes Chapter 2 Human SkeletalDocument22 pagesBiology Form 5 Notes Chapter 2 Human SkeletalzuraidaNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 3Document3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 3GHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System-ReviewerDocument12 pagesSkeletal System-ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- A1.0.8 The Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesA1.0.8 The Skeletal Systemfolinathan3No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Title 8 - SUPPORT SYSTEM AND LOCOMOTIONDocument10 pagesTopic 2 - Title 8 - SUPPORT SYSTEM AND LOCOMOTIONSN10621 Lim En YuNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementDocument22 pagesSupport and MovementAzrin MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Term 2 Week 6 - 2020Document10 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Term 2 Week 6 - 2020fmsr7wmtd5No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument23 pagesUntitled PresentationSamia MustafaNo ratings yet
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDocument8 pagesAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.No ratings yet
- Lab Rep 4 FinalDocument21 pagesLab Rep 4 FinalBella LopezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal SystemrosabelalebsNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System of VerteberatesDocument2 pagesSkeletal System of VerteberatesAfaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter III SkeletalDocument26 pagesChapter III SkeletalTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- CHNCGDocument7 pagesCHNCGDANIEL LANCE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Major Bones and Bone Groups: Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesMajor Bones and Bone Groups: Skeletal Systemtupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesSkeletal SystemRojan V Min KookNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4: Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesExercise 4: Skeletal SystemstevemacabsNo ratings yet
- Locomotion SystemDocument151 pagesLocomotion Systemaynurwepayewa40No ratings yet
- Tissue and Supporting SystemDocument15 pagesTissue and Supporting SystemjolaolumolusinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Systems SummaryDocument29 pagesVertebrate Systems SummaryHazel Grace Bellen100% (1)
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document14 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)NorhalizaIsmailNo ratings yet
- LOCOMOTIONDocument13 pagesLOCOMOTIONDerrick MNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy: Lesson 4: Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesBasic Human Anatomy: Lesson 4: Skeletal SystemIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument61 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliming8112No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver Talip100% (1)
- Grade 11 Biology Week 2 Lesson 1Document6 pagesGrade 11 Biology Week 2 Lesson 1NesiaNo ratings yet
- Science RemedialDocument3 pagesScience RemedialSalsa rsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Skeletal Systemjodi_clark_8100% (2)
- General AnatomyDocument17 pagesGeneral AnatomyAbubakar Umar GaladanchiNo ratings yet
- 38.1 Types of Skeletal SystemsDocument14 pages38.1 Types of Skeletal Systemsmoodapk34No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121No ratings yet
- Body MovementsDocument54 pagesBody MovementsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System of FishesDocument18 pagesSkeletal System of FishesYousaf AnwarNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionFrom EverandBones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionNo ratings yet
- 1184bns 1Document14 pages1184bns 1Daniela GanchasNo ratings yet
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 pagesGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNo ratings yet
- Prokariotik Dan Eukariotik 2Document22 pagesProkariotik Dan Eukariotik 2hanumNo ratings yet
- Print SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHDocument21 pagesPrint SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHSagita Wulan SariNo ratings yet
- Semen Analysis: Syed Mahsan HussainDocument1 pageSemen Analysis: Syed Mahsan Hussainmedicine ki dunia OfficialNo ratings yet
- 2007 National Hippology ContestkeyExam2Document7 pages2007 National Hippology ContestkeyExam2Clara SelleNo ratings yet
- 171-199 Embryologic and Anatomic Basis of Duodenal Surgery PDFDocument29 pages171-199 Embryologic and Anatomic Basis of Duodenal Surgery PDFРоман МошнягаNo ratings yet
- Development of The Inner Ear - M. Kelley, Et Al., (Springer, 2005) WWDocument250 pagesDevelopment of The Inner Ear - M. Kelley, Et Al., (Springer, 2005) WWNudiya Dina Ramadhani100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Biology NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 1 - Biology Noteshuman tie lineNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument93 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- ICCR Ovary 2nd Edn v1 BookmarkDocument40 pagesICCR Ovary 2nd Edn v1 BookmarkildoctorNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesDocument10 pagesStudy Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen BalanceDocument16 pagesNitrogen BalanceAli MajidNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument24 pagesTyphoid FeverHazielle BondocNo ratings yet
- Puc Biology Practical Examination Question PaperDocument4 pagesPuc Biology Practical Examination Question PaperosmanNo ratings yet
- GoitreDocument2 pagesGoitresuggaplumNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection Lab Report GuideDocument6 pagesHeart Dissection Lab Report GuideNicolas GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Etiological Potential of Immature Platelet Fraction in Children With ThrombocytopeniaDocument29 pagesEtiological Potential of Immature Platelet Fraction in Children With Thrombocytopeniajhanavi rajeshNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASDocument10 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASFherry Mae UsmanNo ratings yet
- Extra Embryonic Membrane of Eutherian MammalsDocument8 pagesExtra Embryonic Membrane of Eutherian MammalsFurrydian KhairunissaNo ratings yet
- 8- General embryolog د.خالد ميلاد (@USEM - BOT)Document28 pages8- General embryolog د.خالد ميلاد (@USEM - BOT)Ayoub ZaatoutNo ratings yet
- Is BB Final Coaching NotesDocument8 pagesIs BB Final Coaching NotesLeomill MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 2 AnswersdanielNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument70 pagesLymphatic SystemMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Retdem ScriptDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Retdem ScriptAllyssaNo ratings yet
- The Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypesDocument12 pagesThe Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypestigriochelitoNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The Liver Nursing Care Management Symptoms NCLEXDocument10 pagesCirrhosis of The Liver Nursing Care Management Symptoms NCLEXParallelNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles.: Group 1Document87 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles.: Group 1CONNIE MEDINANo ratings yet
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
Uploaded by
Balpreet KaurOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
2.1 Support and Locomotion in Humans and Animals
Uploaded by
Balpreet KaurCopyright:
Available Formats
2.
1 SUPPORT AND LOCOMOTION IN HUMANS AND ANIMALS
2.1.1 Introduction
1. Locomotion = The ability of an organism to move in a particular direction in its
environment.
1. Support and humans and animals is provided by a framework called a skeleton.
1. There are 3 types of skeleton:
(a) Hydrostatic skeleton
- The support is derived from the body fluid contained within the body
cavity
- The fluid maintains the body shape and provide support for internal
organs
- Examples: earthworms, leeches and caterpillars
(b) Exoskeleton
- Found in the bodies of arthropods, the shell of molluscs and the
bony plates of tortoise.
- The exoskeleton supports important body organs, protects the
internal structure from damage and allows the animals to move
from place to place.
- Examples: insects, crabs, snails
(c) Endoskeleton
- Found in the bodies of all vertebrates
- The endoskeleton consists of hard skeleton of bones found inside
the body.
- The endoskeleton supports the body and also protects the organs
- Examples: human, fish, amphibians and birds
1. The functions of skeleton:
(a) Protection
- The skeleton protects the organs
- Example: The skull protects the brain, the vertebral column protects
the spinal cord and the rib cage protects the heart and lungs
(b) Support
- The skeleton acts as a framework to support soft body parts, to
maintain the upright position and to keep the body stable.
(c) Movement
- Bones interact with the skeletal muscle to enable the movement of
the body.
(d) Blood cell formation
- Most of the blood cells are formed in the bone marrow of the long
bones
(e) Mineral storage
- Bones act as a reservoir for calcium and phosphorus.
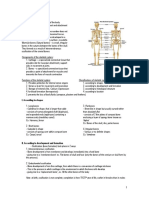
2.1.2 The human skeletal system
1. The skeletal system can be divided into the axial skeleton and the appendicular
skeleton.
1. The axial skeleton:
- Made up of the bones that form the vertical axis of the body.
- It supports and protects the organs of head, neck and trunk.
- Includes: the skull, vertebral column and rib cage
1. The appendicular skeleton:
- Made up of the bones that are attached to the axial skeleton
- Includes: bones of the limbs (forelimb and hindlimb), the pectoral
girdle and the pelvic girdl
You might also like
- Ebook PDF Vertebrates Comparative Anatomy Function Evolution 7th Edition PDFDocument41 pagesEbook PDF Vertebrates Comparative Anatomy Function Evolution 7th Edition PDFmary.ellis361100% (35)
- 2nd Term Biology Note For Ss2Document33 pages2nd Term Biology Note For Ss2Ukwuma Michael Chijioke100% (21)
- Idiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case StudyDocument38 pagesIdiopathic Thrombocytopenic Purpura Case Studygiadda100% (9)
- Human Support SystemDocument9 pagesHuman Support Systemkiongoc100% (1)
- Locomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesLocomotiom & The Human Skeletal SystemNathanael MfumbaikaNo ratings yet
- Support and Movement: Science Scrapbook Form 2 2010Document12 pagesSupport and Movement: Science Scrapbook Form 2 2010Cokelat DaimNo ratings yet
- Maktab Rendah Sains Mara Pengkalan Hulu, Perak.: Biology Notes (CHAPTER 2-4)Document38 pagesMaktab Rendah Sains Mara Pengkalan Hulu, Perak.: Biology Notes (CHAPTER 2-4)Nurul Aisyah ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Ebook Biology ShazwaniDocument20 pagesEbook Biology ShazwaniNurul shazwaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document35 pagesChapter 2Faiz ApaiNo ratings yet
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document15 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Gerard Selvaraj100% (23)
- The Skeletal System of The FrogDocument3 pagesThe Skeletal System of The FrogLuther Abaya MolinaNo ratings yet
- Tissue 2Document34 pagesTissue 2nneduchiemerieNo ratings yet
- Session 14 Skeletal SystemDocument17 pagesSession 14 Skeletal SystemScience Of LifeNo ratings yet
- 01 The Human SkeletonDocument2 pages01 The Human SkeletonAnnabelle Poniente HertezNo ratings yet
- Skeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument11 pagesSkeleton: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediacut amaliaNo ratings yet
- Exercise 6 Musculo SkeletalDocument9 pagesExercise 6 Musculo SkeletalJacob NoraNo ratings yet
- 2nd Term Biology Ss1Document33 pages2nd Term Biology Ss1dasiakennethNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- I. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Document6 pagesI. What Are The Different Components of The Skeletal System?Aria IsipNo ratings yet
- Movement 2024Document14 pagesMovement 2024HannahNo ratings yet
- Invertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po CaDocument1 pageInvertebrate - : Caco Caf So Ca Po CayashsodhaniNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument59 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsilyNo ratings yet
- Bone and CartilageDocument61 pagesBone and CartilageMohamed AtefNo ratings yet
- $R4UVS5TDocument32 pages$R4UVS5Tnechtech6No ratings yet
- Biology Form 5 Notes Chapter 2 Human SkeletalDocument22 pagesBiology Form 5 Notes Chapter 2 Human SkeletalzuraidaNo ratings yet
- Material Downloaded From - 1 / 3Document3 pagesMaterial Downloaded From - 1 / 3GHAPRC RUDRAPURNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System-ReviewerDocument12 pagesSkeletal System-ReviewerRenjyl Gay DeguinionNo ratings yet
- A1.0.8 The Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesA1.0.8 The Skeletal Systemfolinathan3No ratings yet
- Topic 2 - Title 8 - SUPPORT SYSTEM AND LOCOMOTIONDocument10 pagesTopic 2 - Title 8 - SUPPORT SYSTEM AND LOCOMOTIONSN10621 Lim En YuNo ratings yet
- Support and MovementDocument22 pagesSupport and MovementAzrin MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Grade 10 Term 2 Week 6 - 2020Document10 pagesLife Sciences Grade 10 Term 2 Week 6 - 2020fmsr7wmtd5No ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument23 pagesUntitled PresentationSamia MustafaNo ratings yet
- Act08 The Skeletal System DiscussionDocument8 pagesAct08 The Skeletal System DiscussionSofia A.No ratings yet
- Lab Rep 4 FinalDocument21 pagesLab Rep 4 FinalBella LopezNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument23 pagesSkeletal SystemrosabelalebsNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System of VerteberatesDocument2 pagesSkeletal System of VerteberatesAfaqNo ratings yet
- Chapter III SkeletalDocument26 pagesChapter III SkeletalTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- CHNCGDocument7 pagesCHNCGDANIEL LANCE NEVADONo ratings yet
- Major Bones and Bone Groups: Skeletal SystemDocument4 pagesMajor Bones and Bone Groups: Skeletal Systemtupe salcedoNo ratings yet
- Skeletal SystemDocument12 pagesSkeletal SystemRojan V Min KookNo ratings yet
- Exercise 4: Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesExercise 4: Skeletal SystemstevemacabsNo ratings yet
- Locomotion SystemDocument151 pagesLocomotion Systemaynurwepayewa40No ratings yet
- Tissue and Supporting SystemDocument15 pagesTissue and Supporting SystemjolaolumolusinNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Human Skeletal System:: Components of Human SkeletonElyka Alivan Valdez PolonioNo ratings yet
- Vertebrate Systems SummaryDocument29 pagesVertebrate Systems SummaryHazel Grace Bellen100% (1)
- Form 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)Document14 pagesForm 5 Biology (Chapter 2: Locomotion & Support)NorhalizaIsmailNo ratings yet
- LOCOMOTIONDocument13 pagesLOCOMOTIONDerrick MNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver TalipNo ratings yet
- Basic Human Anatomy: Lesson 4: Skeletal SystemDocument24 pagesBasic Human Anatomy: Lesson 4: Skeletal SystemIshita SinghNo ratings yet
- 2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & AnimalsDocument61 pages2.1 (A) - Support & Locomotion in Humans & Animalsliming8112No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsDocument157 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Farm AnimalsOliver Talip100% (1)
- Grade 11 Biology Week 2 Lesson 1Document6 pagesGrade 11 Biology Week 2 Lesson 1NesiaNo ratings yet
- Science RemedialDocument3 pagesScience RemedialSalsa rsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Skeletal SystemDocument3 pagesAssignment 1 Skeletal Systemjodi_clark_8100% (2)
- General AnatomyDocument17 pagesGeneral AnatomyAbubakar Umar GaladanchiNo ratings yet
- 38.1 Types of Skeletal SystemsDocument14 pages38.1 Types of Skeletal Systemsmoodapk34No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/RationaleDocument16 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Unit III: Objectives/Rationaleyachiru121No ratings yet
- Body MovementsDocument54 pagesBody MovementsTapas BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- Skeletal System of FishesDocument18 pagesSkeletal System of FishesYousaf AnwarNo ratings yet
- Bones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionFrom EverandBones in The Human Body: 2nd Grade Science Workbook | Children's Anatomy Books EditionNo ratings yet
- 1184bns 1Document14 pages1184bns 1Daniela GanchasNo ratings yet
- Group 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Document24 pagesGroup 10: Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)Tara DolotaNo ratings yet
- Prokariotik Dan Eukariotik 2Document22 pagesProkariotik Dan Eukariotik 2hanumNo ratings yet
- Print SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHDocument21 pagesPrint SGD Ein Fix Gastritis BHSagita Wulan SariNo ratings yet
- Semen Analysis: Syed Mahsan HussainDocument1 pageSemen Analysis: Syed Mahsan Hussainmedicine ki dunia OfficialNo ratings yet
- 2007 National Hippology ContestkeyExam2Document7 pages2007 National Hippology ContestkeyExam2Clara SelleNo ratings yet
- 171-199 Embryologic and Anatomic Basis of Duodenal Surgery PDFDocument29 pages171-199 Embryologic and Anatomic Basis of Duodenal Surgery PDFРоман МошнягаNo ratings yet
- Development of The Inner Ear - M. Kelley, Et Al., (Springer, 2005) WWDocument250 pagesDevelopment of The Inner Ear - M. Kelley, Et Al., (Springer, 2005) WWNudiya Dina Ramadhani100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Biology NotesDocument22 pagesUnit 1 - Biology Noteshuman tie lineNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument93 pagesCardiovascular System Anatomy and PhysiologyJonald Pulgo IcoyNo ratings yet
- ICCR Ovary 2nd Edn v1 BookmarkDocument40 pagesICCR Ovary 2nd Edn v1 BookmarkildoctorNo ratings yet
- Study Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesDocument10 pagesStudy Guide 1 Assessment of Digestive and Gastrointestinal Function and Treatment ModalitiesKc Cabanilla LizardoNo ratings yet
- Nitrogen BalanceDocument16 pagesNitrogen BalanceAli MajidNo ratings yet
- Typhoid FeverDocument24 pagesTyphoid FeverHazielle BondocNo ratings yet
- Puc Biology Practical Examination Question PaperDocument4 pagesPuc Biology Practical Examination Question PaperosmanNo ratings yet
- GoitreDocument2 pagesGoitresuggaplumNo ratings yet
- Heart Dissection Lab Report GuideDocument6 pagesHeart Dissection Lab Report GuideNicolas GuevaraNo ratings yet
- Etiological Potential of Immature Platelet Fraction in Children With ThrombocytopeniaDocument29 pagesEtiological Potential of Immature Platelet Fraction in Children With Thrombocytopeniajhanavi rajeshNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASDocument10 pagesANAPHY Lec Session #4 - SASFherry Mae UsmanNo ratings yet
- Extra Embryonic Membrane of Eutherian MammalsDocument8 pagesExtra Embryonic Membrane of Eutherian MammalsFurrydian KhairunissaNo ratings yet
- 8- General embryolog د.خالد ميلاد (@USEM - BOT)Document28 pages8- General embryolog د.خالد ميلاد (@USEM - BOT)Ayoub ZaatoutNo ratings yet
- Is BB Final Coaching NotesDocument8 pagesIs BB Final Coaching NotesLeomill MendiolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 AnswersDocument3 pagesChapter 2 AnswersdanielNo ratings yet
- Lymphatic SystemDocument70 pagesLymphatic SystemMarin Jr., Reynaldo J.No ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal Retdem ScriptDocument1 pageMusculoskeletal Retdem ScriptAllyssaNo ratings yet
- The Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypesDocument12 pagesThe Behavioral Table of Elements: Cell Key Index Gesture TypestigriochelitoNo ratings yet
- Cirrhosis of The Liver Nursing Care Management Symptoms NCLEXDocument10 pagesCirrhosis of The Liver Nursing Care Management Symptoms NCLEXParallelNo ratings yet
- The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles.: Group 1Document87 pagesThe Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning Principles.: Group 1CONNIE MEDINANo ratings yet