Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Case Study:: A) We Know That, Normal Distribution Is Distribution That Is Bell Shaped. It Is Symmetric
Case Study:: A) We Know That, Normal Distribution Is Distribution That Is Bell Shaped. It Is Symmetric
Uploaded by
Salar AhmadOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study:: A) We Know That, Normal Distribution Is Distribution That Is Bell Shaped. It Is Symmetric
Case Study:: A) We Know That, Normal Distribution Is Distribution That Is Bell Shaped. It Is Symmetric
Uploaded by
Salar AhmadCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Study:
Geoff Brown is the manager for a small telemarketing firm and is evaluating the sales rate of
experienced workers in order to set minimum standards for new hires. During the past few
weeks, he has recorded the number of successful calls per hour for the staff. These data appear
below along with some summary statistics he worked out with a statistical software package.
Geoff has been a student at the local community college and has heard of many different kinds of
probability distributions (binomial, normal, hyper geometric, Poisson, etc.). Could you give
Geoff some advice on which distribution to use to fit these data as well as possible and how to
decide when a probationary employee should be accepted as having reached full production
status? This is important because it means a pay raise for the employee, and there have been
some probationary employees in the past who have quit because of discouragement that they
would never meet the standard.
Successful sales calls per hour during the week of August 14:
4 2 3 1 4 5 5 2 3 2 2 4 5 2 5 3 3 0
1 3 2 8 4 5 2 2 4 1 5 5 4 5 1 2 4
Descriptive statistics:
N MEAN MEDIAN TRMEAN STDEV SEMEAN
35 3.229 3.000 3.194 1.682 0.284
MINNN MAX Q1 Q3
0.0 8.000 2.000 5.000
Which distribution do you think Geoff should use for his analysis? Support your
recommendations with your analysis. What standard should be used to determine if an employee
has reached “full production” status? Explain your recommendations.
Analysis:
a) We know that, Normal distribution is distribution that is bell shaped. It is symmetric
about mean.
Figure1. Normal vs Skewed Distribution
From figure we can see that:
Mean, median and mode are same normal distribution. As we can see from statistical data that
mean is approximately equal to median.
Mean ≈ Median
That is normal distribution can be used. Since the number of sales calls is a discrete number so
we cannot use normal distribution directly. Here binomial distribution can be used with normal
approximation.
Hence, normal distribution can be used.
b) Which standard should be used to determine if an employee has reached full production
status?
Manager of the firm is evaluating for sales.
Let x = Number of sales per hour.
If we consider poisson random variable (x) then multiply discrete random variable with count
data.
i.e. x is the number of observations in given time interval.
We can say that,
x ~ Poisson (λ)
where λ = Rate of observations and λ can be calculated from:
λ = x̄2 (sample mean)
So, if we set particular standard of number of calls/hour required to reach full production status
then comparing sample mean (x̄) of each employee to rate of observations (λ) we can decide
whether employee have reached the “full production” status.
You might also like
- Worksheet 4 - SolutionsDocument3 pagesWorksheet 4 - SolutionsKathy Thanh PKNo ratings yet
- BBBCDocument12 pagesBBBCDenise Wu0% (2)
- ωt + Φ) A = Amplitude Φ = Phase angle Ω = Frequency and t = Time periodDocument12 pagesωt + Φ) A = Amplitude Φ = Phase angle Ω = Frequency and t = Time periodSalar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 Test Bank - Version1Document31 pagesChapter 03 Test Bank - Version1lizarrdoNo ratings yet
- AP Calculus Ab BC Course at A GlanceDocument4 pagesAP Calculus Ab BC Course at A GlanceYanavNo ratings yet
- 1 StartDocument11 pages1 StartVikash KumarNo ratings yet
- How To Run Montecarlo Simulation in Ms ExcelDocument19 pagesHow To Run Montecarlo Simulation in Ms ExcelJibran SheikhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3-Numerical MeasuresDocument38 pagesChapter 3-Numerical MeasuresNadia TanzeemNo ratings yet
- Yash Singhal PGSF 2136 - SMBD Workshop ReportDocument16 pagesYash Singhal PGSF 2136 - SMBD Workshop ReportYash SinghalNo ratings yet
- Rec 12B - Confidence Intervals For MeansDocument3 pagesRec 12B - Confidence Intervals For MeansSkylar HsuNo ratings yet
- Think Pair Share Team G1 - 7Document8 pagesThink Pair Share Team G1 - 7Akash Kashyap100% (1)
- Assignment - 1 - El - Ajouz CorrectionDocument9 pagesAssignment - 1 - El - Ajouz CorrectionMaroNo ratings yet
- Ablan, Arjay I. Other Examples of Quantitative Models For Decision Making SimulationDocument13 pagesAblan, Arjay I. Other Examples of Quantitative Models For Decision Making SimulationVJ CarbonellNo ratings yet
- Central - Tendency Application in MarketingDocument20 pagesCentral - Tendency Application in MarketingNeha TajveNo ratings yet
- HW4 Fall1 2023 MSFDocument3 pagesHW4 Fall1 2023 MSFYutong ShaoNo ratings yet
- Assement FinancialDocument14 pagesAssement FinancialNerida TomeNo ratings yet
- Data Analysis Test - 19175 (Sanjana Srinath)Document10 pagesData Analysis Test - 19175 (Sanjana Srinath)Deekshith HegdeNo ratings yet
- Hints and Codes For The Final PaperDocument10 pagesHints and Codes For The Final Paperapi-348690980No ratings yet
- Mms Testing of HypothesisDocument69 pagesMms Testing of HypothesisKenneth MathewsNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Statistics PDFDocument51 pagesIntroduction To Statistics PDFEtoos EduNo ratings yet
- Lessons in Business Statistics Prepared by P.K. ViswanathanDocument27 pagesLessons in Business Statistics Prepared by P.K. ViswanathanLloyd LamingtonNo ratings yet
- CASE On A FMCG Firm-Solutions-30.10.17Document3 pagesCASE On A FMCG Firm-Solutions-30.10.17Kanav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Stat Ess Mod 3 Ses 1Document29 pagesStat Ess Mod 3 Ses 1Akila100% (1)
- IMT 24 Quantitative Techniques M1Document20 pagesIMT 24 Quantitative Techniques M1Divyangi WaliaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 9 Solutions S1 2015Document10 pagesTutorial 9 Solutions S1 2015cynthiaNo ratings yet
- Call Centre Forecasting - Explained - How To Predict Staff NeedsDocument32 pagesCall Centre Forecasting - Explained - How To Predict Staff NeedsJoão Carlos FernandesNo ratings yet
- Mba Semester 1 Mb0040 - Statistics For Management-4 Credits (Book ID: B1129) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Document10 pagesMba Semester 1 Mb0040 - Statistics For Management-4 Credits (Book ID: B1129) Assignment Set - 1 (60 Marks)Rajesh SinghNo ratings yet
- HBTopic 4Document10 pagesHBTopic 4david jenil nabuaNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument3 pagesResearch MethodologyphamuyenmaichiNo ratings yet
- Simple Linear RegressionDocument28 pagesSimple Linear Regressionlajwanti jethwaniNo ratings yet
- Assignment No. 02 Introduction To Educational Statistics (8614)Document19 pagesAssignment No. 02 Introduction To Educational Statistics (8614)somiNo ratings yet
- 6.1 Confidence Intervals For The Mean (Large Samples)Document30 pages6.1 Confidence Intervals For The Mean (Large Samples)Vinícius BastosNo ratings yet
- Mini-Project - Churn Analysis .Document15 pagesMini-Project - Churn Analysis .showm8272No ratings yet
- Mean Median Mode STD DevDocument4 pagesMean Median Mode STD Devkhan.pakiNo ratings yet
- CH04Document45 pagesCH04ISLAM KHALED ZSCNo ratings yet
- Rediet Effect of Marketing Strategy Practice On Organizational PerformanceDocument12 pagesRediet Effect of Marketing Strategy Practice On Organizational PerformanceEndalk AragawNo ratings yet
- BSDM Hypothesis Testing PresentationDocument11 pagesBSDM Hypothesis Testing PresentationPreethiNo ratings yet
- A Comprehensive Statistics Cheat Sheet For Data Science 1685659812Document39 pagesA Comprehensive Statistics Cheat Sheet For Data Science 1685659812Prakhar ThamkeNo ratings yet
- Homework 5 - Logistic Regression in RDocument3 pagesHomework 5 - Logistic Regression in RJohn SmithNo ratings yet
- Qnt561 r7 Descriptive Statistics and Interpretation Example Week4Document8 pagesQnt561 r7 Descriptive Statistics and Interpretation Example Week4janette0216No ratings yet
- 1aabstat Discussion Module 5 and 6Document2 pages1aabstat Discussion Module 5 and 6Clare Matugas VallespinNo ratings yet
- Illustration 1: Break-Even AnalysisDocument3 pagesIllustration 1: Break-Even AnalysisAsif Rajian Khan AponNo ratings yet
- Employee Turnover PredictionDocument16 pagesEmployee Turnover Predictionbhanu prakash100% (1)
- Example - 1 For UA - Practice by AHRIDocument10 pagesExample - 1 For UA - Practice by AHRInadia jalilNo ratings yet
- Business Economics AssignmentDocument9 pagesBusiness Economics AssignmentShoebNo ratings yet
- InferentialStats SPSSDocument14 pagesInferentialStats SPSSMd Didarul AlamNo ratings yet
- AE11 Man Econ Module 3-4Document51 pagesAE11 Man Econ Module 3-4Jynilou PinoteNo ratings yet
- PS 3 Bus 310 ResubmitDocument7 pagesPS 3 Bus 310 ResubmitAshley PlemmonsNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Population Parameters: 1) Estimating The Population MeanDocument19 pagesEstimation of Population Parameters: 1) Estimating The Population MeanLaxmish PrakashNo ratings yet
- AP Statistics: Module 6 Free Response and Essay TipsDocument7 pagesAP Statistics: Module 6 Free Response and Essay TipsSiena HurwitzNo ratings yet
- Get Fully Solved Assignment. PLZ Drop A Mail With Your Sub CodeDocument206 pagesGet Fully Solved Assignment. PLZ Drop A Mail With Your Sub CodeProjectHelpForuNo ratings yet
- Break Even AnalysisalanDocument15 pagesBreak Even AnalysisalanFelipe Irazábal0% (1)
- Chapter-04: Measures of Central TendencyDocument71 pagesChapter-04: Measures of Central TendencySamir SiddiqueNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis Research PaperDocument6 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis Research Paperfysygx5k100% (1)
- AI & ML NotesDocument22 pagesAI & ML Noteskarthik singaraoNo ratings yet
- Break Even Analysis ThesisDocument7 pagesBreak Even Analysis Thesisangeljordancincinnati100% (2)
- Interval EstimationDocument33 pagesInterval EstimationArvind ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- Data Science Interview Questions - Statistics: Mohit Kumar Dec 12, 2018 11 Min ReadDocument14 pagesData Science Interview Questions - Statistics: Mohit Kumar Dec 12, 2018 11 Min ReadHaythem Mzoughi100% (1)
- Statistical Inference NewDocument25 pagesStatistical Inference NewAbhinav SinghNo ratings yet
- Binary Logistic Regression Using Stata 17 Drop-Down MenusDocument53 pagesBinary Logistic Regression Using Stata 17 Drop-Down Menuszuberi12345No ratings yet
- Transcription+-+4 3 3Document10 pagesTranscription+-+4 3 3Vibhav NavandarNo ratings yet
- A Short Guide to Marketing Model Alignment & Design: Advanced Topics in Goal Alignment - Model FormulationFrom EverandA Short Guide to Marketing Model Alignment & Design: Advanced Topics in Goal Alignment - Model FormulationNo ratings yet
- Anodic Aluminium Oxide Catalytic Membranes For Asymmetric EpoxidationDocument4 pagesAnodic Aluminium Oxide Catalytic Membranes For Asymmetric EpoxidationSalar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Lab Report Template - 15FMCE211Document17 pagesLab Report Template - 15FMCE211Salar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Case Stude 2Document1 pageCase Stude 2Salar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Prof. J. Sedaitis Quantitative Paper Rubric SBS 2000: Table 1: Descriptive StatisticsDocument4 pagesProf. J. Sedaitis Quantitative Paper Rubric SBS 2000: Table 1: Descriptive StatisticsSalar AhmadNo ratings yet
- 15FMCE214 - Assignment 1Document7 pages15FMCE214 - Assignment 1Salar AhmadNo ratings yet
- Inequalities MuirheadDocument4 pagesInequalities MuirheadAyush AryanNo ratings yet
- Lesson Operations Management and Operations Function: ObjectivesDocument8 pagesLesson Operations Management and Operations Function: ObjectivesHayna Marie AguilarNo ratings yet
- HW01 Solutions PDFDocument5 pagesHW01 Solutions PDFDevanshu DerashriNo ratings yet
- On The Use of Jacobians in Thermodynamics: Benjamin CarrollDocument4 pagesOn The Use of Jacobians in Thermodynamics: Benjamin CarrollDew DropsNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument13 pagesResearch Articledheybigrover4680No ratings yet
- Classification and Regression Trees (CART - I) : Dr. A. RameshDocument34 pagesClassification and Regression Trees (CART - I) : Dr. A. RameshVaibhav GuptaNo ratings yet
- Quiz#2 Review - Promgt3Document144 pagesQuiz#2 Review - Promgt3Razel Justine MendezNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Methods Unit - IDocument2 pagesMathematical Methods Unit - IMr. CuriousNo ratings yet
- 501 OptimizationtechniquesDocument26 pages501 OptimizationtechniquesRajendra ThakareNo ratings yet
- Differential Calculus: Engr. Denver MagtibayDocument74 pagesDifferential Calculus: Engr. Denver MagtibayViene BagsitNo ratings yet
- B41-R4 Mathmatics and StaticsDocument12 pagesB41-R4 Mathmatics and StaticsAYUSH PRADHANNo ratings yet
- A Study of Juvenile in Conflict With Law and Rehabilitation - An AbstractDocument6 pagesA Study of Juvenile in Conflict With Law and Rehabilitation - An AbstractJuvill CariñoNo ratings yet
- The Laplace Transform FileDocument42 pagesThe Laplace Transform FilegainchoudharyNo ratings yet
- Mixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) - MATLAB IntlinprogDocument15 pagesMixed-Integer Linear Programming (MILP) - MATLAB IntlinprogDick Arnie BadangNo ratings yet
- Denis Abao TanDocument18 pagesDenis Abao TanriskiNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document47 pagesCH 7probability2No ratings yet
- MCQ in Calculus Part 2 ECE Board Exam PDFDocument11 pagesMCQ in Calculus Part 2 ECE Board Exam PDFxXx uuNo ratings yet
- FINAL Procedings - OP Jindal UnivDocument116 pagesFINAL Procedings - OP Jindal Univrajib royNo ratings yet
- QualitativeDocument2 pagesQualitativeWendy Marquez TababaNo ratings yet
- 7.4 Assignment: Stakeholder Engagement 1Document5 pages7.4 Assignment: Stakeholder Engagement 1PaulNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 (Measures of Central Tendency pt.1) Business StatisticsDocument25 pagesChapter 3 (Measures of Central Tendency pt.1) Business StatisticsRishika ParmarNo ratings yet
- CS 210a Assignment 1 (Concept) SolutionsDocument3 pagesCS 210a Assignment 1 (Concept) Solutionsenayat atalNo ratings yet
- 4.119 MSC Chem Analytical Sem IIIand IVDocument25 pages4.119 MSC Chem Analytical Sem IIIand IVpratikNo ratings yet
- Reliability Engineering and System Safety: Min OuyangDocument18 pagesReliability Engineering and System Safety: Min OuyangBianca Anisa MaemunahNo ratings yet
- Course OutlineDocument11 pagesCourse OutlineCard CardNo ratings yet
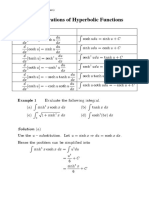
- Integrations of Hyperbolic Functions: TheoremDocument18 pagesIntegrations of Hyperbolic Functions: TheoremcikguhafidzuddinNo ratings yet
- 10 - Thermodynamics of The Solubility of Borax 2009Document5 pages10 - Thermodynamics of The Solubility of Borax 2009Bagus OktiNo ratings yet
- SP Day3 Q4Document15 pagesSP Day3 Q4Elvie A. LlamasNo ratings yet