Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03
Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03
Uploaded by
Ranjan GandhiOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03
Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03
Uploaded by
Ranjan GandhiCopyright:
Available Formats
USN 1 S I 7EE03
Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru – 572 103
(An Autonomous Institution affiliated to VTU, Belagavi, Approved by AICTE, Programmes Accredited by NBA, New Delhi, An ISO9001:2008 Certified Institute)
Seventh Semester B.E. Electrical & Electronics Engg. Examinations Nov - Dec. 2016
Computer Techniques in Power Systems
Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 100
Note : 1. Question No. 1 is Compulsory
2. Answer any 4 full questions from question No. 2 to Question No. 6
1 a) Which of the bus is used to supply transmission losses in load flow solution? 1
b) Which are the unspecified quantities at a voltage controlled bus? 1
c) Write the formula to calculate Ybus using singular transformation. 1
d) State the transmission loss formula for a system of two units. 1
e) Write the expression to calculate penalty factor for ith plant. 1
f) Minimum fuel cost is obtained when the incremental fuel cost is multiplied by its _______ . 1
g) Which is the best method for accurate load flow calculation on large power systems? 1
h) In G-S method of power flow problem, the number of iterations may be reduced. If the
correction in voltage is multiplied by _______ . 1
i) In a power system network, the number of basic loops in equal to _______ . 1
j) What are the methods of formulating Ybus of a power system network? 1
k) Mathematical model of transient stability is _______ equations. 1
ℓ) In a power system network the number of basic cut-sets is equal to _______ . 1
m) Write the expression to calculate real power (P) and reactive power (Q) at any bus in N-R
method of conducting load flow analysis in polar form. 2
n) List any two properties of a tree, in a oriented connected graph. 2
o) Write the performance equations of an element in both impedance form and admittance form. 2
p) Without mutual coupling and ‘p’ is not the reference for addition of link, write the expression
for Zℓi and Zℓℓ. 2
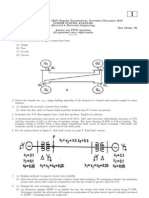
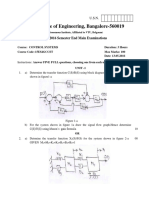
2 a) For the power system shown in Figure 2(a) draw the oriented graph and obtain the incidence
matrices  , A, B, B̂ , K choose bus ‘1’ as reference, take elements 4 and 5 as links.
Figure 2(a) 10
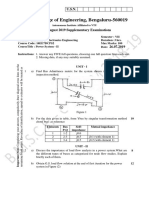
b) For the power system shown in Figure 2(b) with Bus 1 as reference and line data impedances in
PU as shown. Compute Zbus using building algorithm. Add the elements in sequence 1-2, 2-3
and 1-3.
Figure 2(b) 10
-1- Please Turn Over
-2- 7EE03
3 a) Explain what is meant by load flow analysis in a power system. Also state the classification
of buses with the quantities associated with each bus in a power system network. 6
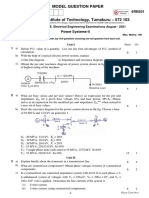
b) The Figure 3(b) shows a 3-bus power system using G-S method, determine the bus voltages
at the end of first iteration. The values shown are line impedances in P.U. Bus data are given
in table 3(b). Also calculate power delivered by slack bus.
generation Load
Bus Voltage Bus type
PG(p.u.) QG(p.u.) PD(p.u.) QD(p.u.)
1 - - - - 1.05 Slack Bus
2 3 - - - 1.0 PV Bus
3 - - 4 2 - PQ Bus
Table 3(b)
Figure 3(b) 14
4 a) Explain the algorithmic procedure for load flow analysis using Newton-Raphson’s method in
polar co-ordinators. 10
b) What are the assumptions made in fast decoupled load flow method? Explain algorithm
through a flowchart. 10
5 a) What is penalty factor? Derive an expression for optimal economic dispatch including
transmission losses. 10
b) What are ‘B’ coefficients? Derive an expression for the ‘B’ coefficients for 2 plants
supplying to multiple loads. Hence, arrive at an expression for the transmission line loss PL.
State the assumptions made. 10
6 a) Explain Runga-Kutta method used in solution of swing equation for transient stability
analysis. 10
b) With the help of a flow chart, explain modified Euler’s method used for transient stability
studies in power system. 10
________
You might also like
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- EE75 August 2014Document2 pagesEE75 August 2014MSGNo ratings yet
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Model Question Paper-I With Effect From 2018-19: Seventh Semester B.E. (CBCS) ExaminationDocument5 pagesModel Question Paper-I With Effect From 2018-19: Seventh Semester B.E. (CBCS) ExaminationVinod KohliNo ratings yet
- Subject: Power System Analysis - 2 Subject Code: 15EE71 Model Question Paper MarksDocument2 pagesSubject: Power System Analysis - 2 Subject Code: 15EE71 Model Question Paper MarksVinod KohliNo ratings yet
- PSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemesterDocument4 pagesPSG College of Technology, Coimbatore - 641 004 Semester Examinations, SemestermahesNo ratings yet
- 07a70202 PowersystemanalysisDocument12 pages07a70202 PowersystemanalysisSamiullah MohammedNo ratings yet
- JNTUA - B Tech - 2018 - 3 2 - Dec - R15 - EEE - 15A02603 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISDocument2 pagesJNTUA - B Tech - 2018 - 3 2 - Dec - R15 - EEE - 15A02603 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISVinay ChinthaNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityHImanshu JoshiNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityTNo ratings yet
- R7410203-Power System AnalysisDocument4 pagesR7410203-Power System AnalysissivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesDepartment of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringAlesso RossiNo ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Document3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Electrical and Electronics Engineering)Anonymous MYbA037ikNo ratings yet
- NR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsDocument6 pagesNR - 410203 - Computer Methods in Power SystemsSrinivasa Rao GNo ratings yet
- ICPS Gtu PaperDocument7 pagesICPS Gtu PaperHrushikesh DalichaNo ratings yet
- EEP3623 Sem I 20202021 Test 2Document6 pagesEEP3623 Sem I 20202021 Test 2taufiqishak09No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.co - In: Power System AnalysisDocument2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.co - In: Power System AnalysisHyma GelliNo ratings yet
- Dayananda Sagar College of EngineeringDocument3 pagesDayananda Sagar College of EngineeringPower System Analysis-1No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument3 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: Electrical and Electronics EngineeringSrîkår SríNo ratings yet
- Psa Unitwise Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesPsa Unitwise Important QuestionsyvkrishnareddyNo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: July / August 2017 Supplementary Semester ExaminationsDocument3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: July / August 2017 Supplementary Semester Examinationskoushik bhatNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem PapersDocument12 pages6th Sem Papers21BEE044 MANOJ KHEMANINo ratings yet
- Inter Connected Power System - CombinedDocument11 pagesInter Connected Power System - CombinedPalak AriwalaNo ratings yet
- Seventh Sem 2015 BDocument3 pagesSeventh Sem 2015 BMonisha S.No ratings yet
- L-4rr-2/EEE 28/3/2022: DateDocument39 pagesL-4rr-2/EEE 28/3/2022: DateSanjid ElahiNo ratings yet
- EENG 457 Experiment 5Document7 pagesEENG 457 Experiment 5Alexander VoltaNo ratings yet
- Eds R07 2011Document5 pagesEds R07 2011kumarreddy247No ratings yet
- 9A02602 Power System AnalysisDocument4 pages9A02602 Power System Analysissivabharathamurthy100% (1)
- JNTUH 3-2 R16 QP Power Systems Analysis May - 2019Document3 pagesJNTUH 3-2 R16 QP Power Systems Analysis May - 2019Kiran KunchamNo ratings yet
- 2019 SupDocument4 pages2019 SupGovind KiranNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityHImanshu JoshiNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation and ControlDocument7 pagesPower System Operation and Controlrv_andeNo ratings yet
- Gomputer Techniques Power System Analysis: I A. B,:4,11rDocument3 pagesGomputer Techniques Power System Analysis: I A. B,:4,11rAbhishek ChandelNo ratings yet
- Power System Analysis MCQ 8 PDFDocument13 pagesPower System Analysis MCQ 8 PDFBALAKRISHNAN75% (8)
- 2017 - EE5102 - Distribution SystemsDocument6 pages2017 - EE5102 - Distribution SystemsChathura SenanayakeNo ratings yet
- Power System Operation and Control 6th Sem EEE ELECTRICAL M508Document2 pagesPower System Operation and Control 6th Sem EEE ELECTRICAL M508santoshsahoo2507No ratings yet
- Methods For Load Flow Analysis of Weakly Meshed Distribution SystemDocument4 pagesMethods For Load Flow Analysis of Weakly Meshed Distribution SystemragvshahNo ratings yet
- NR-320203 - Modeling of Power System ComponentsDocument9 pagesNR-320203 - Modeling of Power System ComponentsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Model Question Paper: USN 1 S I 6REE01Document3 pagesModel Question Paper: USN 1 S I 6REE01MSGNo ratings yet
- PS7101 AdvancedPowerSystemAnalysisDocument20 pagesPS7101 AdvancedPowerSystemAnalysismadhes14No ratings yet
- Please Check Whether You Have Got The Right Question Paper.Document1 pagePlease Check Whether You Have Got The Right Question Paper.Gnanaseharan ArunachalamNo ratings yet
- 3 Ee - B000311 (024) - 02.12.2020 - Elect. Circuit - 59 - Tushar VermaDocument4 pages3 Ee - B000311 (024) - 02.12.2020 - Elect. Circuit - 59 - Tushar VermaSandeep BhuaryaNo ratings yet
- Linear Approximation Power FlowDocument3 pagesLinear Approximation Power FlowORK BUNSOKRAKMUNYNo ratings yet
- Be Winter 2020Document2 pagesBe Winter 2020Rushikesh PandyaNo ratings yet
- Question Paper - CAPS S-18 PAPERDocument4 pagesQuestion Paper - CAPS S-18 PAPERPrasanna P TitarmareNo ratings yet
- R7410210-Electrical Distribution SystemsDocument4 pagesR7410210-Electrical Distribution SystemssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- IEEE Conf Feb2018Document5 pagesIEEE Conf Feb2018Abhishek GuptaNo ratings yet
- 1 MarksDocument1 page1 MarksIjal JaminNo ratings yet
- Power System AnalysisDocument5 pagesPower System AnalysisVidyavihar ReddyNo ratings yet
- Amcat Computer Science Questions-Part-1Document4 pagesAmcat Computer Science Questions-Part-1SuryaNo ratings yet
- JNTUA - B Tech - 2018 - 3 2 - May - R15 - EEE - 15A02603 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISDocument2 pagesJNTUA - B Tech - 2018 - 3 2 - May - R15 - EEE - 15A02603 POWER SYSTEM ANALYSISVinay ChinthaNo ratings yet
- Group-A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Document3 pagesGroup-A (Multiple Choice Type Questions)Anikendu MaitraNo ratings yet
- Control Systems 6Document8 pagesControl Systems 6paramkusamNo ratings yet
- CEP PSA and D Spring 2024Document3 pagesCEP PSA and D Spring 2024bajwaumair320No ratings yet
- DDDC87ECAA084E5DA4D2D77F7DC80391Document5 pagesDDDC87ECAA084E5DA4D2D77F7DC80391Sameer NandagaveNo ratings yet
- BMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: May 2016 Semester End Main ExaminationsDocument3 pagesBMS College of Engineering, Bangalore-560019: May 2016 Semester End Main Examinationskoushik bhatNo ratings yet
- Aishwirya College of Engineering and Technology: E-MailDocument3 pagesAishwirya College of Engineering and Technology: E-MailSujesh ChittarikkalNo ratings yet
- LCS (4th) May2018Document2 pagesLCS (4th) May2018VêRmã SàábNo ratings yet
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Section 5 Power Flow PDFDocument128 pagesSection 5 Power Flow PDFRanjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Siddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Document2 pagesSiddaganga Institute of Technology, Tumakuru - 572 103: Usn 1 S I 7EE03Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Environment PDFDocument21 pagesEnvironment PDFRanjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- List and Explain Various Characteristics of Waste Water 2Document7 pagesList and Explain Various Characteristics of Waste Water 2Ranjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- PDF Environmental Pollution Control by Cs Rao PDFDocument371 pagesPDF Environmental Pollution Control by Cs Rao PDFRanjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Power Systems by Bakshi PDFDocument486 pagesPower Systems by Bakshi PDFRanjan Gandhi100% (1)
- EnvironmentDocument21 pagesEnvironmentRanjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Decoding Strategies For CTC Acoustic ModelsDocument5 pagesComparison of Decoding Strategies For CTC Acoustic ModelsRanjan GandhiNo ratings yet
- Mattoslg Gendream ArticleDocument7 pagesMattoslg Gendream ArticleBhakti Screamyz Mechanic MidnhightracingspeedNo ratings yet
- Using Lagrangian Relaxation in Optimisation of Unit Commitment and PlanningDocument12 pagesUsing Lagrangian Relaxation in Optimisation of Unit Commitment and PlanningsireeNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing SlidesDocument184 pagesDigital Signal Processing SlidesChinmay Anand100% (1)
- MATH WorksheetsDocument10 pagesMATH WorksheetsVannce KhempNo ratings yet
- Homothetic FunctionsDocument2 pagesHomothetic FunctionsAli LatifNo ratings yet
- DDD NDD DND DDN DNN NDN NND NNN S N Denotes "Non-Defective" andDocument3 pagesDDD NDD DND DDN DNN NDN NND NNN S N Denotes "Non-Defective" andLabonnoAkterLabonnoNo ratings yet
- f5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Document6 pagesf5 Add Maths Annual Scheme (2008)Abdul ManafNo ratings yet
- Random Variables + Distribution Models + Linear RegressionDocument8 pagesRandom Variables + Distribution Models + Linear RegressionBasoko_LeaksNo ratings yet
- Statics of Rigid Bodies:: Resultant of Concurrent Force SystemDocument9 pagesStatics of Rigid Bodies:: Resultant of Concurrent Force SystemLance CastilloNo ratings yet
- Normal Sections On The EllipsoidDocument8 pagesNormal Sections On The EllipsoidKismet100% (3)
- Math Prize For Girls (2009-2012)Document13 pagesMath Prize For Girls (2009-2012)AceeNo ratings yet
- L23-25 Moment of InertiaDocument47 pagesL23-25 Moment of InertiaChrisNo ratings yet
- Edma360 Assessment 3-4 4 1Document17 pagesEdma360 Assessment 3-4 4 1api-265542260No ratings yet
- UPSC Civil Services Main 1984 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder LalDocument6 pagesUPSC Civil Services Main 1984 - Mathematics Calculus: Sunder Lalsayhigaurav07No ratings yet
- System of Linear Equations MatlabDocument3 pagesSystem of Linear Equations MatlabJohn RoaNo ratings yet
- Networked Control SystemsDocument2 pagesNetworked Control SystemsWalid AlFuhaidNo ratings yet
- HTML Symbols PDFDocument3 pagesHTML Symbols PDFSaisri KNo ratings yet
- Mathematical Habits of MindDocument16 pagesMathematical Habits of MindFajar MartaNo ratings yet
- Gen MathDocument313 pagesGen MathEdgar GuillermoNo ratings yet
- PRC - Math EmaticsDocument17 pagesPRC - Math EmaticsMommyPokaNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Approaches - SVMDocument34 pagesMachine Learning Approaches - SVMKarem SaadNo ratings yet
- O'level MATHEMATICS TRIGONOMETRY REVISIONDocument9 pagesO'level MATHEMATICS TRIGONOMETRY REVISIONelishabagalwNo ratings yet
- Physics-Informed Deep Neural Operator NetworksDocument34 pagesPhysics-Informed Deep Neural Operator Networksdata scienceNo ratings yet
- EECI Session 2Document23 pagesEECI Session 2Riccardo Tc BertolloNo ratings yet
- Integration (Ans)Document9 pagesIntegration (Ans)Naim RahmanNo ratings yet
- Phys 481 Homework 1 SolutionsDocument6 pagesPhys 481 Homework 1 SolutionsJeffSchuelerNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: CS6659/Artificial Intelligence L. No Topics To Be Covered Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesLesson Plan: CS6659/Artificial Intelligence L. No Topics To Be Covered Learning ObjectivesVasu DevanNo ratings yet
- Excel Formulas and Functions Cheat SheetDocument116 pagesExcel Formulas and Functions Cheat Sheetsiddu karriNo ratings yet
- Sahoo88Document28 pagesSahoo88vishwanathNo ratings yet
- ICE EM Mathematics Year 7 Third Edition Complete TextbookDocument633 pagesICE EM Mathematics Year 7 Third Edition Complete Textbooksidashok.work100% (1)