Professional Documents
Culture Documents
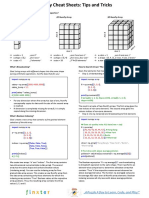
Python NumPy Cheat Sheet
Python NumPy Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Deepak as400Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Python NumPy Cheat Sheet
Python NumPy Cheat Sheet
Uploaded by
Deepak as400Copyright:
Available Formats
PYTHON FOR DATA •
Initial Placeholders Operations Array Mathematics
SCIENCE
np.zeros(3) - 1D array of length 3 all zeros Copying: Arithmetic Operations:
• np.copy(array) - Copies array to new memory array. • Addition: np.add(a,b)
• np.zeros((2,3)) - 2D array of all zeros • view(dtype) - Creates view of array elements with type • Subtraction: np.subtract(a,b)
CHEAT SHEET dtype
Sorting:
•
•
Multiplication: np.multiply(a,b)
Division: np.divide(a,b)
• array.sort() - Sorts array
•
Python NumPy
np.zeros((3,2,4)) - 3D array of all zeros • Exponentiation: np.exp(a)
• array.sort(axis=0) - Sorts specific axis of array
• Square Root: np.sqrt(b)
• array.reshape(2,3) - Reshapes array to 2 rows, 3 columns
without changing data. Comparison:
Adding: • Element-wise: a==b
• np.append(array,values) - Appends values to end of array • Array-wise: np.array_equal(a,b)
What is NumPy?
• np.insert(array,4,values) - Inserts values into array before
index 4
A library consisting of multidimensional array objects and a Functions
Removing:
collection of routines for processing those arrays.
• np.delete(array,2,axis=0) - Deletes row on index 2 of array • Array-wise Sum: a.sum()
• np.full((3,4),2) - 3x4 array with all values 2
• np.delete(array,3,axis=1) - Deletes column on index 3 of • Array-wise min value: a.min()
• np.random.rand(3,5) - 3x5 array of random floats array
Why NumPy? between 0-1 • Array row max value: a.max(axis=0)
Combining:
• np.ones((3,4)) - 3x4 array with all values 1 • Mean: a.mean()
• np.concatenate((array1,array2),axis=0) - Adds array2 as
Mathematical and logical operations on arrays can be • np.eye(4) - 4x4 array of 0 with 1 on diagonal • Median: a.median()
rows to the end of array1
performed. Also provides high performance. • np.concatenate((array1,array2),axis=1) - Adds array2 as
Saving and Loading columns to end of array1 • Learn from industry experts and be sought-after by
Splitting:
On disk: the industry!
Import Convention • np.split(array,3) - Splits array into 3 sub-arrays
• np.save("new_array",x) • Learn any technology, show exemplary skills and have
• np.load("new_array.npy") Indexing:
import numpy as np – Import numpy an unmatched career!
Text/CSV files: • a[0]=5 - Assigns array element on index 0 the value 5
• The most trending technology courses to help you
• np.loadtxt('New_file.txt') - From a text file • a[2,3]=1 - Assigns array element on index [2][3] the value 1
• np.genfromtxt('New_file.csv',delimiter=',') - From a CSV Subseting: fast-track your career!
ND Array file
• a[2] - Returns the element of index 2 in array a. • Logical modules for both beginners and mid-level
• np.savetxt('New_file.txt',arr,delimiter=' ') - Writes to a
Space efficient multi-dimensional array, which provides • a[3,5] - Returns the 2D array element on index [3][5] learners
text file
vectorized arithmetic operations. • np.savetxt('New_file.csv',arr,delimiter=',') - Writes to a Slicing:
CSV file • a[0:4] - Returns the elements at indices 0,1,2,3
Properties:
• a[0:4,3] - Returns the elements on rows 0,1,2,3 at column 3
Creating Array • array.size - Returns number of elements in array
• a[:2] - Returns the elements at indices 0,1
• array.shape - Returns dimensions of array(rows,
• a=np.array([1,2,3]) columns) • a[:,1] - Returns the elements at index 1 on all rows
• b=np.array([(1,2,3,4),(7,8,9,10)],dtype=int) • array.dtype - Returns type of elements in array FURTHERMORE:
Python for Data Science Certification Training Course
You might also like
- 66 Job Interview Questions For Data ScientistsDocument10 pages66 Job Interview Questions For Data ScientistsRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- NumpyDocument40 pagesNumpyKhả UyênNo ratings yet
- Numpy 8Document46 pagesNumpy 8patilpatilNo ratings yet
- Aman Ai Primers NumpyDocument85 pagesAman Ai Primers NumpyS Mahapatra100% (1)
- Operator DescriptionDocument6 pagesOperator DescriptionSmart CrazyNo ratings yet
- Numerical Methods Using Python: (MCSC-202)Document34 pagesNumerical Methods Using Python: (MCSC-202)SANJEEV KUMAR KHATRINo ratings yet
- DataFrame StatisticsDocument41 pagesDataFrame Statisticsrohan jhaNo ratings yet
- Jyoti Shukla (SME)Document14 pagesJyoti Shukla (SME)dhirajkapilaNo ratings yet
- Numpy and Scipy: Numerical Computing in PythonDocument47 pagesNumpy and Scipy: Numerical Computing in PythonsivaNo ratings yet
- Working With Numpy: Chapter-01Document29 pagesWorking With Numpy: Chapter-01Kirti RoyNo ratings yet
- 9-10 August 21 - NumpyDocument47 pages9-10 August 21 - NumpyImtisal ChaudhryNo ratings yet
- NumPy Joining ArrayDocument1 pageNumPy Joining Arrayahmed salemNo ratings yet
- Numpy CheatsheetDocument1 pageNumpy CheatsheetChris SejNo ratings yet
- Numpy and Scipy: Numerical Computing in PythonDocument44 pagesNumpy and Scipy: Numerical Computing in PythonKa MoNo ratings yet
- Lec 4Document39 pagesLec 4Bint-E- Haw'waNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 Python NumpyDocument18 pagesUnit 4 Python NumpySagana C. CSENo ratings yet
- LT2 - 07 - Numpy Matplotlib PandasDocument101 pagesLT2 - 07 - Numpy Matplotlib PandasLe Thi Minh ThiNo ratings yet
- NumpyDocument64 pagesNumpyPRNo ratings yet
- CL2014 - MATLAB Programming - Lec03Document16 pagesCL2014 - MATLAB Programming - Lec03UmarNo ratings yet
- +100 Important Numpy OperationsDocument8 pages+100 Important Numpy Operationstikar69314No ratings yet
- Week 9Document27 pagesWeek 9Betül ÖztürkNo ratings yet
- NumpyDocument4 pagesNumpy46.SARANEDARAN S AI&DS studentNo ratings yet
- Linear Algebra: Assignment IDocument11 pagesLinear Algebra: Assignment ISamuel DharmaNo ratings yet
- Ai Workflow Data Preparation With Numpy: MR Hew Ka Kian Hew - Ka - Kian@Rp - Edu.SgDocument30 pagesAi Workflow Data Preparation With Numpy: MR Hew Ka Kian Hew - Ka - Kian@Rp - Edu.SgNg Kai TingNo ratings yet
- 10 NumpyDocument39 pages10 NumpyOguljan NuryyevaNo ratings yet
- HUAWEI - 04 Third-Party LibrariesDocument59 pagesHUAWEI - 04 Third-Party LibrariesPierpaolo VergatiNo ratings yet
- M2 - FDSDocument20 pagesM2 - FDS1NH20CS182 Rakshith M PNo ratings yet
- Numpy PythonDocument36 pagesNumpy PythonToni SanikNo ratings yet
- Working With NumpyDocument18 pagesWorking With NumpyJay PriyaNo ratings yet
- Acwinter Javascript Basic Advanced and MoreDocument5 pagesAcwinter Javascript Basic Advanced and MoreMuthurathinamNo ratings yet
- Java CheatsheetDocument17 pagesJava CheatsheetPrecious AjiboyeNo ratings yet
- CheatSheet Python 7 - NumPy 1Document1 pageCheatSheet Python 7 - NumPy 1MashineGunNo ratings yet
- " A Puzzle A Day To Learn, Code, and Play " Visit: Name Description ExampleDocument1 page" A Puzzle A Day To Learn, Code, and Play " Visit: Name Description ExampleSATYAJEET SARFARE (Alumni)No ratings yet
- PythonCheatSheet Zaka AcademyDocument1 pagePythonCheatSheet Zaka Academyoutsiderlb.businessNo ratings yet
- NumpyDocument8 pagesNumpyNada ElokabyNo ratings yet
- EI4005W2Document12 pagesEI4005W2PyiAungNo ratings yet
- NumpyDocument44 pagesNumpySaif JuttNo ratings yet
- Data Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesData Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat Sheetpao paoNo ratings yet
- Data Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesData Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetbreathtakingbehaviorNo ratings yet
- Data Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesData Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetfrsalazarNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument4 pagesProjectsatyam upadhayayNo ratings yet
- Numpy ArrayDocument2 pagesNumpy Arrayshabberali993No ratings yet
- Introduction To NUMPY Lecture NoteDocument12 pagesIntroduction To NUMPY Lecture NoteAzri HamimNo ratings yet
- 11 Numpy Cheat SheetDocument1 page11 Numpy Cheat SheetToldo94No ratings yet
- Week2-1 NumpyDocument43 pagesWeek2-1 NumpyJiaqi MEINo ratings yet
- 22mbada303 Module 4Document32 pages22mbada303 Module 4Kiran VinnuNo ratings yet
- Python Numpy (1) : Intro To Multi-Dimensional Array & Numerical Linear AlgebraDocument27 pagesPython Numpy (1) : Intro To Multi-Dimensional Array & Numerical Linear AlgebraBania Julio Fonseca100% (1)
- Numpy Basics Cheatsheet 1.0Document1 pageNumpy Basics Cheatsheet 1.0Akshay Yawale100% (1)
- 7 Days Analytics Course 3feiz7 5Document8 pages7 Days Analytics Course 3feiz7 5anupamakarupiahNo ratings yet
- Javascript: Basic, Advanced, & More Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument5 pagesJavascript: Basic, Advanced, & More Cheat Sheet: by ViaOusmane DiamariNo ratings yet
- Matlab StudentDocument19 pagesMatlab Studentkiran100% (2)
- Name: Areeb Akhtar Roll No: 2k18 Ele 059 Section: P2Document17 pagesName: Areeb Akhtar Roll No: 2k18 Ele 059 Section: P2Areeb AkhtarNo ratings yet
- R Programming Cheat Sheet: by ViaDocument2 pagesR Programming Cheat Sheet: by ViaKimondo KingNo ratings yet
- Mastering NumPy - Part 2 (Array Manipulation)Document12 pagesMastering NumPy - Part 2 (Array Manipulation)adrian IosifNo ratings yet
- Solucion-Parcial-.. - Jupyter NotebookDocument11 pagesSolucion-Parcial-.. - Jupyter NotebookDaniel Alberto Peña DiazNo ratings yet
- IT ELEC1 Midterm Discussion 3Document59 pagesIT ELEC1 Midterm Discussion 3Crash OverrideNo ratings yet
- Matlab Lecture 3Document15 pagesMatlab Lecture 3waqasNo ratings yet
- CSE110 - Array SlideDocument34 pagesCSE110 - Array SlideRatul HasanNo ratings yet
- Data Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetDocument2 pagesData Transformation With Data - Table: Cheat SheetKGAOGELO MolokoNo ratings yet
- Dsa F22 04 01Document35 pagesDsa F22 04 01Radish KumarNo ratings yet
- Setll, Setgt, ChainDocument4 pagesSetll, Setgt, ChainDeepak as400No ratings yet
- C# ConstructorsDocument7 pagesC# ConstructorsDeepak as400No ratings yet
- Mass Housing CERTDocument12 pagesMass Housing CERTDeepak as400No ratings yet
- CIS Updated VersionDocument2 pagesCIS Updated VersionDeepak as400No ratings yet
- Region Id Inst # Loan # Selection TypeDocument9 pagesRegion Id Inst # Loan # Selection TypeDeepak as400No ratings yet
- Selene CERT Test Data LatestDocument1 pageSelene CERT Test Data LatestDeepak as400No ratings yet
- Region Id Inst # Loan # ML-CLS-CD Ml-Ln-Type Ml-Sub-Type Inv-CodeDocument8 pagesRegion Id Inst # Loan # ML-CLS-CD Ml-Ln-Type Ml-Sub-Type Inv-CodeDeepak as400No ratings yet
- TravellersDocument1 pageTravellersDeepak as400No ratings yet
- Brms BrochureDocument4 pagesBrms BrochureDeepak as400No ratings yet
- Short Version Bio Based Building Blocks and Polymers 2018 2023Document16 pagesShort Version Bio Based Building Blocks and Polymers 2018 2023phaniraj_c100% (1)
- Corpo 106 01Document49 pagesCorpo 106 01Richie SalubreNo ratings yet
- Shipham Special Alloy ValvesDocument62 pagesShipham Special Alloy ValvesYogi173No ratings yet
- XrayDocument9 pagesXraySohail AhmedNo ratings yet
- ESOMAR Codes Guidelines InterviewingChildren 1Document9 pagesESOMAR Codes Guidelines InterviewingChildren 1Dilaksha PereraNo ratings yet
- Insights Bullish Near Term OutlookDocument62 pagesInsights Bullish Near Term OutlookHandy HarisNo ratings yet
- Souce Najib LeadershipDocument12 pagesSouce Najib LeadershipSharanya Ramasamy100% (1)
- Biobase GoupDocument11 pagesBiobase Goupfrancheska bacaNo ratings yet
- Operating System (5th Semester) : Prepared by Sanjit Kumar Barik (Asst Prof, Cse) Module-IiiDocument41 pagesOperating System (5th Semester) : Prepared by Sanjit Kumar Barik (Asst Prof, Cse) Module-IiiJeevanantham KannanNo ratings yet
- 5 Basement Cu Belt Zambia PDFDocument51 pages5 Basement Cu Belt Zambia PDFAlberto Lobo-Guerrero SanzNo ratings yet
- Definition and Objective of AuditDocument7 pagesDefinition and Objective of AuditZednem JhenggNo ratings yet
- CDUXLSIMDocument336 pagesCDUXLSIMlocoboeingNo ratings yet
- Etabloc Syt Operating InstructionsDocument50 pagesEtabloc Syt Operating InstructionsFayeez MukadamNo ratings yet
- NJM072B/082B/072/082: Dual J-Fet Input Operational AmplifierDocument5 pagesNJM072B/082B/072/082: Dual J-Fet Input Operational Amplifieryuni supriatinNo ratings yet
- Group 8 Design Main Report + Appendix (1) 1 400Document400 pagesGroup 8 Design Main Report + Appendix (1) 1 400Manishaa Varatha RajuNo ratings yet
- Corona Rakshak Policy - Oriental Insurance Policy Schedule UIN: OICHLIP21064V012021Document4 pagesCorona Rakshak Policy - Oriental Insurance Policy Schedule UIN: OICHLIP21064V012021raghuNo ratings yet
- David M. Kroenke's: Database ProcessingDocument25 pagesDavid M. Kroenke's: Database ProcessingasalajalagiNo ratings yet
- FEA - Calculation of The Hydroforming Process With LS-DYNADocument8 pagesFEA - Calculation of The Hydroforming Process With LS-DYNAadrianNo ratings yet
- International StandardDocument24 pagesInternational Standardalvaro cardenas100% (1)
- A Framework For Improving Advertising Creative Using Digital MeasurementDocument15 pagesA Framework For Improving Advertising Creative Using Digital MeasurementMs Mariia MykhailenkoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2-Groundwater MovementDocument2 pagesAssignment 2-Groundwater MovementPhước LêNo ratings yet
- Upshur County ReportDocument16 pagesUpshur County ReportAnna SaundersNo ratings yet
- Installation Guide Andalay Solar ModulesDocument60 pagesInstallation Guide Andalay Solar ModulesdarkleonzNo ratings yet
- Temidayo Cybercrime ReportDocument13 pagesTemidayo Cybercrime ReportMAYOWA ADEBAYONo ratings yet
- Amendment of Information, Formal Vs SubstantialDocument2 pagesAmendment of Information, Formal Vs SubstantialNikkoCataquiz100% (3)
- Customer Satisfaction Employee InvolvementDocument35 pagesCustomer Satisfaction Employee InvolvementSARA JANE CAMBRONERONo ratings yet
- Pilz PNOZ Sigma PDFDocument16 pagesPilz PNOZ Sigma PDFCristopher Entena100% (1)
- Example of Research Paper About Science and TechnologyDocument6 pagesExample of Research Paper About Science and Technologygz8aqe8wNo ratings yet
- Parallelizing Partial Digest Problem On Multicore System PDFDocument10 pagesParallelizing Partial Digest Problem On Multicore System PDFnazibNo ratings yet