Professional Documents
Culture Documents
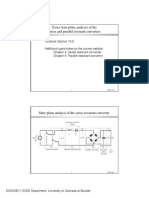
Time-Domain Analysis of Resonant and Soft-Switching Converters
Time-Domain Analysis of Resonant and Soft-Switching Converters
Uploaded by
djyOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Time-Domain Analysis of Resonant and Soft-Switching Converters
Time-Domain Analysis of Resonant and Soft-Switching Converters
Uploaded by
djyCopyright:
Available Formats
Time-Domain Analysis of
Resonant and Soft-Switching Converters
• So far:
• Steady-state and dynamic analyses based on sinusoidal approximation
• Advantages: it is possible to use frequency-domain techniques
• Shortcomings
• Approximate solutions even for traditional resonant converters
• Sinusoidal approximation does not apply in many important cases,
waveforms are not even close to sinusoidal
• Various resonant converter modes
• Various soft-switching converters
• Next: Time-Domain Analysis
• Introduction to state-plane approach
• Normalization, notation, and simple examples
• Averaging, charge and volt-second balance
• Exact solutions for series-resonant and parallel-resonant converters
• Various soft-switching converters
10 ECEN 5817
Introduction to state-plane analysis
L +
+ v t = 0, v(0) = Vo, i(0) = Io
V –
C _
I
In the next several lectures, this example (see HW1, problem 1), and several
other examples will be used to introduce state-plane analysis principles. These
lectures will be done by hand; there are no pre-prepared handout slides.
11 ECEN 5817
ECEN5817, ECEE Department, University of Colorado at Boulder
You might also like
- Fluent-Intro 18.0 Module07 Turbulence PDFDocument29 pagesFluent-Intro 18.0 Module07 Turbulence PDFAlex HolguinoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-Differential Approach To Flow AnalysisDocument36 pagesChapter 1-Differential Approach To Flow Analysisputerasyam39No ratings yet
- RLV's Re-Entry Trajectory Optimization Based On B-Spline TheoryDocument5 pagesRLV's Re-Entry Trajectory Optimization Based On B-Spline TheoryShubham KaduNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - CFD TheoryDocument27 pagesLecture 1 - CFD TheoryYogitha Sarah BabyNo ratings yet
- A Brief Review On The Convergence To Steady State Solutions of Euler Equations With High-Order WENO SchemesDocument25 pagesA Brief Review On The Convergence To Steady State Solutions of Euler Equations With High-Order WENO SchemesSunny KhadkaNo ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaNo ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaNo ratings yet
- Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument22 pagesComputational Fluid DynamicsSYED HASANNo ratings yet
- CFD Lecture 1Document61 pagesCFD Lecture 1Alaa AwedNo ratings yet
- Reservoir Modeling: SPE-CSPG Joint Luncheon Talk - February 9, 2016Document17 pagesReservoir Modeling: SPE-CSPG Joint Luncheon Talk - February 9, 2016BouregaNo ratings yet
- Lecture24 PDFDocument4 pagesLecture24 PDFalagarg137691No ratings yet
- CFD For Mixing: Daniel RibeiroDocument17 pagesCFD For Mixing: Daniel RibeiroLUIS ISAAC LEON PARONo ratings yet
- Chapter Ten Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument28 pagesChapter Ten Introduction To Computational Fluid DynamicsMisge ChekoleNo ratings yet
- Presentation Leandra CompressedDocument41 pagesPresentation Leandra CompressedLeandra AbreuNo ratings yet
- Resolvent-Based Modelling of Streaky Structures in Turbulent Pipe FlowDocument41 pagesResolvent-Based Modelling of Streaky Structures in Turbulent Pipe FlowLeandra AbreuNo ratings yet
- Transient and Steady-State Analysis of A SEPIC Converter by An Average State-Space ModellingDocument5 pagesTransient and Steady-State Analysis of A SEPIC Converter by An Average State-Space ModellingPablo PulacheNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 IntroductionDocument34 pagesUnit 1 Introductiongutha manikantaNo ratings yet
- Assisted History Matching and Optimization: Remus HaneaDocument51 pagesAssisted History Matching and Optimization: Remus HaneashowravNo ratings yet
- Fluent Intro 16 0 L07 TurbulenceDocument50 pagesFluent Intro 16 0 L07 TurbulencelighthilljNo ratings yet
- Tr-Cse-04-006Document15 pagesTr-Cse-04-006Sebastian ReyesNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2Document17 pagesLecture 2Atikom SombatmaiNo ratings yet
- Fluent-Intro 16.0 L07 TurbulenceDocument50 pagesFluent-Intro 16.0 L07 Turbulenceghoshna jyotiNo ratings yet
- Lecture-1 CFDDocument34 pagesLecture-1 CFDAjayNo ratings yet
- 2020-04-28 - QX Simulator - EQC - w2Document38 pages2020-04-28 - QX Simulator - EQC - w2Aritra SarkarNo ratings yet
- WAsP Limitations and CFD PresentationDocument37 pagesWAsP Limitations and CFD PresentationHéctor LodosoNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design A Series-Parallel Resonant Converter: Ashoka K. S - BhatDocument11 pagesAnalysis and Design A Series-Parallel Resonant Converter: Ashoka K. S - BhatChAmirShokatGujjarNo ratings yet
- Finite Element AnalysisDocument25 pagesFinite Element Analysistagore 87No ratings yet
- Robot Model Auto2013 PDFDocument6 pagesRobot Model Auto2013 PDFShadNo ratings yet
- Module 08: TurbulenceDocument27 pagesModule 08: TurbulenceReytingNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3Document19 pagesLecture 3Ramakant GarhewalNo ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument3 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaNo ratings yet
- Class 4.1Document17 pagesClass 4.1Daystar YtNo ratings yet
- Chapter11 (W) HorizontalWellTestAnalysis (D.tiab)Document140 pagesChapter11 (W) HorizontalWellTestAnalysis (D.tiab)aoua1999No ratings yet
- 7.0 Optimization of Batch ProcessesDocument18 pages7.0 Optimization of Batch ProcessesHubert BoulicNo ratings yet
- Differential Analysis of Fluid FlowDocument48 pagesDifferential Analysis of Fluid FlowsineNo ratings yet
- S1 Fluid-Mechanics pp.421-423Document3 pagesS1 Fluid-Mechanics pp.421-42372245304No ratings yet
- Notes-Ch 10. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis PDFDocument39 pagesNotes-Ch 10. Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis PDFnanekNo ratings yet
- J Ces 2005 11 032Document9 pagesJ Ces 2005 11 032BheemannaChandurNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NewDocument28 pagesChapter 1 NewGemechu B. JiruNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NewDocument28 pagesChapter 1 NewBeki TadNo ratings yet
- Introduction To CFDDocument16 pagesIntroduction To CFDu2000988No ratings yet
- Nonlinear and Time Varying ElementDocument7 pagesNonlinear and Time Varying ElementKiran VedanteNo ratings yet
- Pushover by MPDocument103 pagesPushover by MPdebsstrNo ratings yet
- An Adaptive Turbulence Model For Swirling FlowDocument5 pagesAn Adaptive Turbulence Model For Swirling FlowFolpoNo ratings yet
- Workshop 4 - Part 2 - Advanced Time Series Econometrics With EViewsDocument99 pagesWorkshop 4 - Part 2 - Advanced Time Series Econometrics With EViewsLyana Zainol100% (2)
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument5 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaNo ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument4 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaNo ratings yet
- Investigation of The Performance of Journal Bearing: Using Theoretical and Experimental MethodDocument23 pagesInvestigation of The Performance of Journal Bearing: Using Theoretical and Experimental MethodBaraa ShaheenNo ratings yet
- CFD Lecture 0Document27 pagesCFD Lecture 0Don Poul JoseNo ratings yet
- Numerical Computation of Diffuse View Factor Between Planar SurfacDocument14 pagesNumerical Computation of Diffuse View Factor Between Planar SurfacSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Transport Phenomena I: Department of Chemical Engineering Cairo UniversityDocument27 pagesTransport Phenomena I: Department of Chemical Engineering Cairo UniversityMZ0% (1)
- HVDC QB R13Document10 pagesHVDC QB R13Thavva GaneshNo ratings yet
- MODULE 10 HECRAS Unsteady Flow Introduction 2016Document50 pagesMODULE 10 HECRAS Unsteady Flow Introduction 2016sugendengalNo ratings yet
- ME451 L15 Timeresp2nd 240116 183552Document6 pagesME451 L15 Timeresp2nd 240116 183552epe3630No ratings yet
- ME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapDocument6 pagesME451: Control Systems Course RoadmapVu NghiaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 NewDocument29 pagesChapter 1 NewMikias YimerNo ratings yet
- Tangential and Normal ComponentsDocument15 pagesTangential and Normal ComponentsOmar DoskyNo ratings yet
- Handout Che f244 Sem II, 2016-17Document3 pagesHandout Che f244 Sem II, 2016-17KAUSTUBHNo ratings yet
- Irjet V4i5102 PDFDocument6 pagesIrjet V4i5102 PDFAnonymous plQ7aHUNo ratings yet
- Level Set Method: Advancing Computer Vision, Exploring the Level Set MethodFrom EverandLevel Set Method: Advancing Computer Vision, Exploring the Level Set MethodNo ratings yet
- Capacitor PhasorDocument1 pageCapacitor PhasordjyNo ratings yet
- Magnetics Core Dimensional Effects - Flux Propagation in Ferrites (Marcin Kacki, SMA Magnetics)Document37 pagesMagnetics Core Dimensional Effects - Flux Propagation in Ferrites (Marcin Kacki, SMA Magnetics)djyNo ratings yet
- Snubber Circuit in The Flyback Converter: Transformer Model I L C R + DDocument1 pageSnubber Circuit in The Flyback Converter: Transformer Model I L C R + DdjyNo ratings yet
- Equivalent Circuit of A Capacitor Using The Phasor Transform ApproachDocument1 pageEquivalent Circuit of A Capacitor Using The Phasor Transform ApproachdjyNo ratings yet
- Signature Signature Redacted : Enabling HF Power Conversion: Components and A Wide Voltage Range ConverterDocument162 pagesSignature Signature Redacted : Enabling HF Power Conversion: Components and A Wide Voltage Range ConverterdjyNo ratings yet
- Lumped Model To Explain and Approximate Dimensional Effects in Ferrite Cores (Charles Sullivan, Dartmouth)Document25 pagesLumped Model To Explain and Approximate Dimensional Effects in Ferrite Cores (Charles Sullivan, Dartmouth)djyNo ratings yet
- Sinusoidal Approximations: HapterDocument27 pagesSinusoidal Approximations: HapterdjyNo ratings yet
- Signature Redacted: Enabling Miniaturized Grid-Interface Power ConversionDocument281 pagesSignature Redacted: Enabling Miniaturized Grid-Interface Power ConversiondjyNo ratings yet
- High Frequency Effects in The Core (Gerald Hurley National University of Ireland, Galway)Document44 pagesHigh Frequency Effects in The Core (Gerald Hurley National University of Ireland, Galway)djyNo ratings yet
- L35 ECEN5817 Out1Document15 pagesL35 ECEN5817 Out1djyNo ratings yet
- Exact State-Plane Analyses of The Series and Parallel Resonant ConvertersDocument10 pagesExact State-Plane Analyses of The Series and Parallel Resonant ConvertersdjyNo ratings yet
- L8 ECEN5817 Out1Document12 pagesL8 ECEN5817 Out1djyNo ratings yet
- L33 ECEN5817 Out1Document14 pagesL33 ECEN5817 Out1djyNo ratings yet
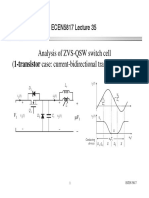
- Analysis of ZVS-QSW Switch Cell (1 T Bidi I L I Did) (1-Transistor Case: Current-Bidirectional Transistor + Diode)Document15 pagesAnalysis of ZVS-QSW Switch Cell (1 T Bidi I L I Did) (1-Transistor Case: Current-Bidirectional Transistor + Diode)djyNo ratings yet
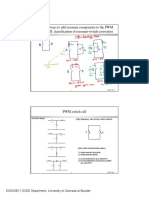
- Possible Ways To Add Resonant Components To The PWM Switch Cell: Classification of Resonant-Switch ConvertersDocument11 pagesPossible Ways To Add Resonant Components To The PWM Switch Cell: Classification of Resonant-Switch ConvertersdjyNo ratings yet
- Possible Ways To Add Resonant Components To The PWM Switch Cell: Classification of Resonant-Switch ConvertersDocument11 pagesPossible Ways To Add Resonant Components To The PWM Switch Cell: Classification of Resonant-Switch ConvertersdjyNo ratings yet