Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory System
Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory System
Uploaded by
inno so qt0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology - Respiratory System
Anatomy and Physiology - Respiratory System
Uploaded by
inno so qtCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
Anatomy and Physiology
Lungs
FUNCTIONS OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The functions of the respiratory system are:
Oxygen supplier The job of the respiratory system is to keep the body
constantly supplied with oxygen.
Elimination Elimination of carbon dioxide.
Gas exchange The respiratory system organs oversee the gas exchanges
that occur between the blood and the external environment.
Passageway Passageways that allow air to reach the lungs.
Humidifier Purify, humidify, and warm incoming air.
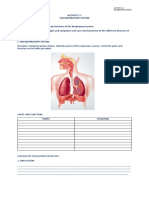
ANATOMY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea,
bronchi, and their smaller branches, and the lungs, which contain the alveoli.
Nose – Air enters nostrils, is filtered by hairs, warmed, moistened, and sampled for
odors as it flows through a maze of nasal passages.
Pharynx (Throat) – Intersection where pathway for air and food cross. Most of the time,
the pathway for air is open, except when we swallow.
Larynx (Voice Box) – Reinforced with cartilage. Contains vocal cords, which allow us
to make sounds by voluntarily tensing muscles.
High pitched sounds: Vocal cords are tense, vibrate fast.
Low pitched sounds: Vocal cords are relaxed, vibrate slowly.
More prominent in males (Adam’s apple).
Trachea (Windpipe) – Rings of cartilage maintain shape of trachea, to prevent it from
closing. Forks into two bronchi.
Bronchi (Sing. Bronchus) – Each bronchus leads into a lung and branches into
smaller and smaller bronchioles, resembling an inverted tree.
Bronchioles – Fine tubes that allow passage of air. Epithelium of bronchioles is
covered with cilia and mucus to trap and remove dust and other particles.
Alveoli – air sacs at the end of bronchioles where gas exchange takes place.
PHYSIOLOGY OF THE RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
The major function of the respiratory system is to supply the body with oxygen and to
dispose of carbon dioxide. To do this, at least four distinct events, collectively called
respiration, must occur.
Respiration
Pulmonary ventilation Air must move into and out of the lungs so that gasses in the
air sacs are continuously refreshed, and this process is commonly called breathing.
External respiration Gas exchange between the pulmonary blood and alveoli must
take place.
Respiratory gas transport Oxygen and carbon dioxide must be transported to and
from the lungs and tissue cells of the body via the bloodstream.
Internal respiration At systemic capillaries, gas exchanges must be made between
the blood and tissue cells.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Test Bank For Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation, 4th Edition, Chang, ISBN-10: 1111539588, ISBN-13: 9781111539580Document36 pagesTest Bank For Clinical Application of Mechanical Ventilation, 4th Edition, Chang, ISBN-10: 1111539588, ISBN-13: 9781111539580moviequilter3ouid100% (21)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Nursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan Impaired Gas ExchangeKarylle PetilNo ratings yet
- Readings in Philippine History: Mr. Isaac NavarroDocument25 pagesReadings in Philippine History: Mr. Isaac Navarroinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Mga Gunita NG Himagsikan Ni Emilio AguinaldoDocument8 pagesMga Gunita NG Himagsikan Ni Emilio Aguinaldoinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Using NANDA, NIC, and NOC: A Client Having SurgeryDocument2 pagesUsing NANDA, NIC, and NOC: A Client Having Surgeryinno so qtNo ratings yet
- PSL301 Midterm 2 ReviewDocument24 pagesPSL301 Midterm 2 Reviewtapi0ca100% (1)
- NCM 118 Lesson 2 CcuDocument44 pagesNCM 118 Lesson 2 Ccuinno so qtNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 Lesson 2 Theories of LeadershipDocument23 pagesNCM 119 Lesson 2 Theories of Leadershipinno so qtNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 Juris - Nursing EthicsDocument57 pagesNCM 119 Juris - Nursing Ethicsinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Surgical Ward PPTDocument29 pagesSurgical Ward PPTinno so qt100% (4)
- Nursing Juris Lesson 1: The Code of Ethics For Filipino NursesDocument20 pagesNursing Juris Lesson 1: The Code of Ethics For Filipino Nursesinno so qtNo ratings yet
- NCM 119 Lesson 3 Patient Care Delivery SystemDocument66 pagesNCM 119 Lesson 3 Patient Care Delivery Systeminno so qtNo ratings yet
- Et TubeDocument31 pagesEt Tubeinno so qtNo ratings yet
- White and Green Elegant Corporate Fashion Brand Guidelines PresentationDocument1 pageWhite and Green Elegant Corporate Fashion Brand Guidelines Presentationinno so qtNo ratings yet
- The Phuilippine Health Statistics Definition of TermsDocument8 pagesThe Phuilippine Health Statistics Definition of Termsinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment Form: Monitor Action RequiredDocument1 pageComprehensive Geriatric Assessment Form: Monitor Action Requiredinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Cough or Difficult Breathing: Distance Learning CourseDocument39 pagesCough or Difficult Breathing: Distance Learning Courseinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Module 2 RPHDocument3 pagesModule 2 RPHinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Political Caricature of The American Era 1900Document7 pagesPolitical Caricature of The American Era 1900inno so qtNo ratings yet
- Meaning and Service Value of Medical CareDocument15 pagesMeaning and Service Value of Medical Careinno so qt100% (2)
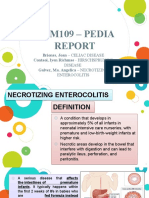
- Ncm109 - Pedia: Briones, Joan - CELIAC DISEASE Contaoi, Iyen Richmae - HIRSCHSPRUNG'S Galvez, Ma. Angelica - NECROTIZINGDocument22 pagesNcm109 - Pedia: Briones, Joan - CELIAC DISEASE Contaoi, Iyen Richmae - HIRSCHSPRUNG'S Galvez, Ma. Angelica - NECROTIZINGinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care of Child With LIFE THREATENING CONDITIONSDocument70 pagesNursing Care of Child With LIFE THREATENING CONDITIONSinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Malnutrition and Anemia: Integrated Management of Childhood IllnessDocument28 pagesMalnutrition and Anemia: Integrated Management of Childhood Illnessinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument121 pagesRespiratory Distress Syndromeinno so qtNo ratings yet
- NSTP Bill of RightsDocument14 pagesNSTP Bill of Rightsinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Article Iii Bill of RightsDocument31 pagesArticle Iii Bill of Rightsinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Care of The Client With Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome During Postpartum PeriodDocument22 pagesCare of The Client With Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome During Postpartum Periodinno so qtNo ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: 9ba 9BbDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: 9ba 9BbOneth RajapakseNo ratings yet
- Activity-1 1Document2 pagesActivity-1 1chary villanuevaNo ratings yet
- Minimum VentilationDocument4 pagesMinimum VentilationNathan Smith100% (1)
- X - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 MarksDocument11 pagesX - Biology - Chapter 6 - Life Processes: 2 Marksvalliammai thiagarajanNo ratings yet
- Cough: by Dr. Meghana Patil (Intern Batch 2016)Document24 pagesCough: by Dr. Meghana Patil (Intern Batch 2016)Meghana PatilNo ratings yet
- AutoflowDocument12 pagesAutoflowDaniela Merino FuentealbaNo ratings yet
- G 9 1ST QUARTER PRETEST POST TEST and WORKSHEETS 2Document5 pagesG 9 1ST QUARTER PRETEST POST TEST and WORKSHEETS 2Dominic M. LubitaniaNo ratings yet
- Panduan Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran PDP KSSR Semakan 2017 Sains Tahun 4 Versi Bahasa Inggeris-CompressedDocument112 pagesPanduan Pengajaran Dan Pembelajaran PDP KSSR Semakan 2017 Sains Tahun 4 Versi Bahasa Inggeris-CompressedNur Adila Binti AzmanNo ratings yet
- L3 NotesDocument5 pagesL3 Notes17 ERMINO, Nicole AngelaNo ratings yet
- Preface: TN Skills Manual July 2003Document141 pagesPreface: TN Skills Manual July 2003Sarah Lynn McAnly Wade100% (1)
- Ambu® Auragain™: Product Information Single Use Laryngeal Mask - SterileDocument11 pagesAmbu® Auragain™: Product Information Single Use Laryngeal Mask - SterileAnish H DaveNo ratings yet
- Group 1: Medico Legal Aspect of DeathDocument19 pagesGroup 1: Medico Legal Aspect of DeathTIPAY, EMELIE L.100% (1)
- Unit 3 Plan - Grade 11 Biology - Transportation and Respiration - Michelle Romanuk - 7786294Document9 pagesUnit 3 Plan - Grade 11 Biology - Transportation and Respiration - Michelle Romanuk - 7786294api-536171687No ratings yet
- Names: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentDocument70 pagesNames: MANIRAHO Cyprien Reg. Numbers: 020/04/GN/933 Individual AssignimentCyprien Silencer ManirahoNo ratings yet
- Agricultural Science For Secondary School Book 3 PDFDocument224 pagesAgricultural Science For Secondary School Book 3 PDFCesarAnte75% (12)
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument16 pagesAnaphy ReviewerPauleen FejeNo ratings yet
- Bio Abhyasa Deepika PDFDocument93 pagesBio Abhyasa Deepika PDFArogya Raju Pudhota75% (20)
- Fireworks 1Document29 pagesFireworks 1Deepak ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Airway ManagementDocument38 pagesAirway ManagementyafetNo ratings yet
- Essentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition Hillegass Test BankDocument14 pagesEssentials of Cardiopulmonary Physical Therapy 4th Edition Hillegass Test Banksiennaclimatal1bk6t6100% (27)
- 1cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical TherapyDocument347 pages1cardiovascular and Pulmonary Physical TherapyLiviu CuvoiNo ratings yet
- Presentation Outline Nursing Pulmonary Tuberculosis Revised 1Document10 pagesPresentation Outline Nursing Pulmonary Tuberculosis Revised 1Alfaera Rahma FarestyNo ratings yet
- 2 Upper Airway Disorders PDFDocument33 pages2 Upper Airway Disorders PDFMonica BorjaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory DisordersDocument48 pagesRespiratory DisordersJean Cabigao100% (1)
- 4 RespirationDocument6 pages4 Respirationनिरज न्यौपानेNo ratings yet
- Science Time!: With Ma'am Melanie!Document19 pagesScience Time!: With Ma'am Melanie!Melanie CoronaNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing - LectureDocument77 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing - LecturePink Majaila GludoNo ratings yet