Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Solar System
Solar System
Uploaded by
Maria MercedesCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Illusrative ProblemsDocument8 pagesIllusrative ProblemsMechanical ZombieNo ratings yet
- Glass Ceramics: Satyendra Prasad Gond, 214CR2117Document1 pageGlass Ceramics: Satyendra Prasad Gond, 214CR2117Baijayanti DasNo ratings yet
- Motion in One DimentionDocument4 pagesMotion in One DimentionYashNo ratings yet
- Bef 23903 - Chapter 3 - DC Bridge - Wheatstone BridgeDocument19 pagesBef 23903 - Chapter 3 - DC Bridge - Wheatstone BridgeMuhammad Izz IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- Sensor and Transducer PDFDocument52 pagesSensor and Transducer PDFRAJAN KUMAR SINHA100% (2)
- PAS Genap Daring V MathsDocument3 pagesPAS Genap Daring V MathsAngel & Bryan SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- 109 TOP Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument11 pages109 TOP Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsShashank Kothiyal50% (6)
- Base Design - SecondaryDocument20 pagesBase Design - SecondaryFarah Diba Pos-PosNo ratings yet
- Numatics FRL Flexiblok Catalog PDFDocument33 pagesNumatics FRL Flexiblok Catalog PDFAlexander Bayona ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Tension Members - Part 1Document10 pagesLecture 2 - Tension Members - Part 1Dad MeNo ratings yet
- Grade9 Math Intervention-Plan 2022-2023Document2 pagesGrade9 Math Intervention-Plan 2022-2023Erwin Joaquin Cabigao50% (2)
- Vertrel XF Technical InformationDocument4 pagesVertrel XF Technical InformationklopezibarguenNo ratings yet
- Back Calculated P-Y Relation of Liquefied Soils From Large Shaking Table TestsDocument7 pagesBack Calculated P-Y Relation of Liquefied Soils From Large Shaking Table TestsEmreNo ratings yet
- Wire and Cable Management: Product OverviewDocument18 pagesWire and Cable Management: Product OverviewOjog Ciprian Alin100% (1)
- 7.2 - The T-Junction Power Divider: Reading AssignmentDocument16 pages7.2 - The T-Junction Power Divider: Reading AssignmentRodrigo Ruiz CaveroNo ratings yet
- Viscosity - WikipediaDocument35 pagesViscosity - WikipediaHamza MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Question Paper 45Document1 pageApplied Physics Question Paper 45RA.......VANo ratings yet
- Bray, Travasarou - 2007 - Simplified Procedure For Estimating EQ Slope DisplacementsDocument12 pagesBray, Travasarou - 2007 - Simplified Procedure For Estimating EQ Slope DisplacementsAbdel KhediriNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: IsotopesDocument3 pagesStudent Exploration: Isotopestmorales1726No ratings yet
- APFC Relay Catalogue - 12 StepDocument5 pagesAPFC Relay Catalogue - 12 SteparunNo ratings yet
- Zimsec Nov 2003 Paper 1 and 2-1Document9 pagesZimsec Nov 2003 Paper 1 and 2-1Emily Ncube0% (1)
- TechRef Series CapacitanceDocument14 pagesTechRef Series CapacitanceromulanecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Molecules of Life Subtopic: 1.1 Water Learning OutcomeDocument20 pagesChapter 1: Molecules of Life Subtopic: 1.1 Water Learning Outcomemuhamad aqilhamdiNo ratings yet
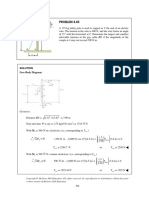
- PROBLEM 4.45: SolutionDocument3 pagesPROBLEM 4.45: SolutionA CNo ratings yet
- схема и сервис мануал на английском LG CF-20F39 шасси MC-994ADocument17 pagesсхема и сервис мануал на английском LG CF-20F39 шасси MC-994AАндрій БілявськийNo ratings yet
- Test # 3 Redox RreactionsDocument2 pagesTest # 3 Redox RreactionsAzain CardenasNo ratings yet
- 5.03 Optical ActivityDocument4 pages5.03 Optical ActivityKartik RanaNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes Extra PracticeDocument2 pagesEnthalpy Changes Extra Practiceapi-210028385No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Statics 31Document27 pagesChapter 1 Statics 31ameena ameeraliNo ratings yet
- National Public School WhitefieldDocument2 pagesNational Public School WhitefieldSameera KurhekarNo ratings yet
Solar System
Solar System
Uploaded by
Maria MercedesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Solar System
Solar System
Uploaded by
Maria MercedesCopyright:
Available Formats
The solar system is made up of the Sun and the objects that orbit around it.
These include EIGHT planets, and their satellites
(moons).
The centre of our solar system is the sun, which is a star. It is a gigantic ball of hot gas which gives off heat and light energy. Full
moon is a lunar phase that occurs when the Moon is on the opposite side of the Earth from the Sun. More precisely, a full moon
occurs when the geocentric apparent (ecliptic) longitudes of the Sun and Moon differ by 180 degrees; the Moon is then
in opposition with the Sun.[1] As seen from Earth, the hemisphere of the Moon that is facing the earth (the near side) is almost
fully illuminated by the Sun and appears round. Only during a full moon is the opposite hemisphere of the Moon, which is not
visible from Earth (the far side), completely unilluminated. The time interval between similar lunar phases—the synodic month—
is on average about 29.53 days. Therefore, in those lunar calendars in which each month begins on the new moon, the full moon
falls on either the 14th or 15th of the lunar month. Because lunar months have a whole number of days, lunar months may be
either 29 or 30 days long.
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite[nb 4][6] and the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System. It is the largest natural satellite in
the Solar System relative to the size of its planet, a quarter the diameter of Earth and 1/81 its mass. The Moon is the second
densest satellite after Io. It is in synchronous rotation with Earth, always showing the same face; the near side is marked with
dark volcanic maria among the bright ancient crustal highlands and prominent impact craters. It is the brightest object in the sky
after theSun, although its surface is actually very dark, with a similar reflectance to coal. Its prominence in the sky and its regular
cycle ofphases have since ancient times made the Moon an important cultural influence on language,
the calendar, art and mythology. The Moon's gravitational influence produces the ocean tides and the minute lengthening of the
day. The Moon's current orbital distance, about thirty times the diameter of the Earth, causes it to appear almost the same size in
the sky as the Sun, allowing it to cover the Sun nearly precisely in total solar eclipses.
Winter is the coldest season of the year in temperate climate, between autumn and spring. At the winter solstice, the days are
shortest and the nights are longest, with days lengthening as the season progresses after the solstice.
Earth (1 AU from the Sun) is the largest and densest of the inner planets, the only one known to have current geological activity,
and is the only place in the universe where life is known to exist.[37] Its liquid hydrosphere is unique among the terrestrial planets,
and it is also the only planet where plate tectonics has been observed. Earth's atmosphere is radically different from those of the
other planets, having been altered by the presence of life to contain 21% free oxygen.[38] It has one natural satellite, the Moon,
the only large satellite of a terrestrial planet in the Solar System.
A planet (from Greek πλανήτης αστήρ "wandering star") is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive
enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring
region of planetesimals.[a][1][2]
Objects in space are in constant motion, but some follow specific patterns called orbits. Our understanding of the orbits of
planetary bodies is contingent on scientific principles laid out by British mathematician and physicist Sir Isaac Newton, German
mathematician and astronomer Johannes Kepler and German-born physicist Albert Einstein.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Illusrative ProblemsDocument8 pagesIllusrative ProblemsMechanical ZombieNo ratings yet
- Glass Ceramics: Satyendra Prasad Gond, 214CR2117Document1 pageGlass Ceramics: Satyendra Prasad Gond, 214CR2117Baijayanti DasNo ratings yet
- Motion in One DimentionDocument4 pagesMotion in One DimentionYashNo ratings yet
- Bef 23903 - Chapter 3 - DC Bridge - Wheatstone BridgeDocument19 pagesBef 23903 - Chapter 3 - DC Bridge - Wheatstone BridgeMuhammad Izz IzzuddinNo ratings yet
- Sensor and Transducer PDFDocument52 pagesSensor and Transducer PDFRAJAN KUMAR SINHA100% (2)
- PAS Genap Daring V MathsDocument3 pagesPAS Genap Daring V MathsAngel & Bryan SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- 109 TOP Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsDocument11 pages109 TOP Measurement and Instrumentation - Electrical Engineering Multiple Choice Questions and Answers - MCQs Preparation For Engineering Competitive ExamsShashank Kothiyal50% (6)
- Base Design - SecondaryDocument20 pagesBase Design - SecondaryFarah Diba Pos-PosNo ratings yet
- Numatics FRL Flexiblok Catalog PDFDocument33 pagesNumatics FRL Flexiblok Catalog PDFAlexander Bayona ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 - Tension Members - Part 1Document10 pagesLecture 2 - Tension Members - Part 1Dad MeNo ratings yet
- Grade9 Math Intervention-Plan 2022-2023Document2 pagesGrade9 Math Intervention-Plan 2022-2023Erwin Joaquin Cabigao50% (2)
- Vertrel XF Technical InformationDocument4 pagesVertrel XF Technical InformationklopezibarguenNo ratings yet
- Back Calculated P-Y Relation of Liquefied Soils From Large Shaking Table TestsDocument7 pagesBack Calculated P-Y Relation of Liquefied Soils From Large Shaking Table TestsEmreNo ratings yet
- Wire and Cable Management: Product OverviewDocument18 pagesWire and Cable Management: Product OverviewOjog Ciprian Alin100% (1)
- 7.2 - The T-Junction Power Divider: Reading AssignmentDocument16 pages7.2 - The T-Junction Power Divider: Reading AssignmentRodrigo Ruiz CaveroNo ratings yet
- Viscosity - WikipediaDocument35 pagesViscosity - WikipediaHamza MurtazaNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Question Paper 45Document1 pageApplied Physics Question Paper 45RA.......VANo ratings yet
- Bray, Travasarou - 2007 - Simplified Procedure For Estimating EQ Slope DisplacementsDocument12 pagesBray, Travasarou - 2007 - Simplified Procedure For Estimating EQ Slope DisplacementsAbdel KhediriNo ratings yet
- Student Exploration: IsotopesDocument3 pagesStudent Exploration: Isotopestmorales1726No ratings yet
- APFC Relay Catalogue - 12 StepDocument5 pagesAPFC Relay Catalogue - 12 SteparunNo ratings yet
- Zimsec Nov 2003 Paper 1 and 2-1Document9 pagesZimsec Nov 2003 Paper 1 and 2-1Emily Ncube0% (1)
- TechRef Series CapacitanceDocument14 pagesTechRef Series CapacitanceromulanecNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Molecules of Life Subtopic: 1.1 Water Learning OutcomeDocument20 pagesChapter 1: Molecules of Life Subtopic: 1.1 Water Learning Outcomemuhamad aqilhamdiNo ratings yet
- PROBLEM 4.45: SolutionDocument3 pagesPROBLEM 4.45: SolutionA CNo ratings yet
- схема и сервис мануал на английском LG CF-20F39 шасси MC-994ADocument17 pagesсхема и сервис мануал на английском LG CF-20F39 шасси MC-994AАндрій БілявськийNo ratings yet
- Test # 3 Redox RreactionsDocument2 pagesTest # 3 Redox RreactionsAzain CardenasNo ratings yet
- 5.03 Optical ActivityDocument4 pages5.03 Optical ActivityKartik RanaNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes Extra PracticeDocument2 pagesEnthalpy Changes Extra Practiceapi-210028385No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Statics 31Document27 pagesChapter 1 Statics 31ameena ameeraliNo ratings yet
- National Public School WhitefieldDocument2 pagesNational Public School WhitefieldSameera KurhekarNo ratings yet