Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 14 Science Notes
Chapter 14 Science Notes
Uploaded by
Savannah MontelongoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 14 Science Notes
Chapter 14 Science Notes
Uploaded by
Savannah MontelongoCopyright:
Available Formats
Name Date
Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Before You Read
Before you read the chapter, respond to these statements.
1. Write an A if you agree with the statement.
2. Write a D if you disagree with the statement.
Before You
Read Solids, Liquids, and Gases
D • Solid, liquid, and gaseous states of matter
are determined only by temperature.
D • Plasma is the most abundant state of
matter in the universe.
A • Earth’s atmosphere is a fluid system.
D • Hydraulic lifts and toothpaste tubes both
apply Pascal’s principle.
A • Pressure and temperature are directly
proportional properties of a gas.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
Construct the Foldable as directed at the beginning of this chapter.
Science Journal
Identify examples of a solid, a liquid, and a gas in your classroom.
An example of a solid is crystalline. An example of a liquid is like drink such as water. An example of
a gas is the air.
Solids, Liquids, and Gases 171
Name Date
Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Section 1 Matter and Thermal Energy
Scan the headings, figures, and captions in Section 1 of your book.
Write four facts about kinetic theory you learned.
All matter is composed of tiny particals.
1.
These particals are in content, random motion.
2.
The particals collide with eachother, and with all the walls of a container.
3.
The amount of energy that the particals lose from the collision.
4.
Review
Vocabulary Define kinetic energy.
is an explanation of how particals in gases behave.
kinetic energy
New
Vocabulary Read the definitions below. Write the term that matches the
definition on the blank in the left column.
Kenetic energy
an explanation of how particles in matter behave
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
melting point
the temperature at which a solid begins to turn into a liquid
Thermal energy
the amount of energy needed to change a substance from a solid to
a liquid at its melting point
evaporation
the temperature at which the pressure of the vapor in a liquid is
equal to the external pressure acting on the surface of the liquid
heat of vaporation
the amount of energy needed for a liquid at its boiling point to
become a gas
Sublimation
the change from a solid to a gas without the liquid state
matter consisting of positively and negatively charged particles
thermal expansion
an increase in size of a substance when temperature is increased
Academic
Vocabulary Use a dictionary to define the term assumption.
a thing that is accepted as true or as certain to happen.
assumption
172 Solids, Liquids, and Gases
Name Date
Section 1 Matter and Thermal Energy (continued)
Kinetic Theory Complete the outline as you read about the states of matter.
States of Matter
I found this information A. Solid
on page . 1. Example:
2. Particle kinetic energy:
3. Particle behavior:
4. Other fact(s):
I found this information B. Liquid
on page . 1. Example:
2. Particle kinetic energy:
3. Particle behavior:
4. Other fact(s):
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
I found this information C. Gas
on page . 1. Example:
2. Particle kinetic energy:
3. Particle behavior:
4. Other fact(s):
I found this information D. Plasma
on page . 1. Example:
2. Particle kinetic energy:
3. Particle behavior:
4. Other fact(s):
Solids, Liquids, and Gases 173
Name Date
Section 1 Matter and Thermal Energy (continued)
Thermal Sequence the kinetic energy, temperature, and density of most
Expansion solids, liquids, and gases. Use 1 to represent the lowest amount and
I found this information 3 to represent the highest.
on page . Solid Liquid Gas
Kinetic energy
Temperature
Density
I found this information Compare the density of water’s solid state to that of other solid
on page . materials.
Copyright © Glencoe/McGraw-Hill, a division of The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.
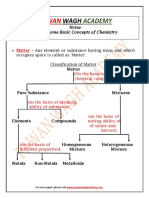
Solid or a Liquid? Organize the features and examples of other states of matter in
I found this information the following table.
on page . Amorphous Solid Liquid Crystal
Liquid
Solid
Examples
S YNTHESIZE I T Refer to the graph titled “State Changes of Water” in your
book. Imagine that you reverse the process to remove heat from water vapor. Describe
the changes to the temperature and energy at each level (a – d) in the reverse process.
174 Solids, Liquids, and Gases
You might also like
- This Study Resource Was: 02.01 States of Matter Guided NotesDocument2 pagesThis Study Resource Was: 02.01 States of Matter Guided NotesRichelle Jane CaoresNo ratings yet
- Matter & Its CompositionDocument16 pagesMatter & Its CompositionVenkat100% (1)
- CH 14 Science Note BookDocument4 pagesCH 14 Science Note BookSavannah Montelongo100% (2)
- Chemistry 10 - 12 PDFDocument283 pagesChemistry 10 - 12 PDFRon ShamendeNo ratings yet
- CH 14 Science Note BookDocument4 pagesCH 14 Science Note BookSavannah Montelongo100% (2)
- Ch. 15 - Science Notebook Sec. 2Document4 pagesCh. 15 - Science Notebook Sec. 2Savannah MontelongoNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry Notes 123Document4 pagesGeneral Chemistry Notes 123Stephanie VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- 5 The Gaseous StateDocument14 pages5 The Gaseous StateArvin LiangdyNo ratings yet
- Solids, Liquids, and Gases: Presented by Kesler ScienceDocument23 pagesSolids, Liquids, and Gases: Presented by Kesler Scienced34dm4nNo ratings yet
- (L-1) - (JEE 3.0) - States of Matter - 13th May.Document50 pages(L-1) - (JEE 3.0) - States of Matter - 13th May.Mohith VenkateshNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Chemistry A - Notes Chapter 1 - The Particulate Nature of MaterDocument25 pagesIGCSE Chemistry A - Notes Chapter 1 - The Particulate Nature of MaterDhingra shellyNo ratings yet
- Physical Principles of Respiratory Care: Chapter ObjectivesDocument27 pagesPhysical Principles of Respiratory Care: Chapter ObjectivesMatthew SmileyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1Document16 pagesLecture 1wmemo42No ratings yet
- 1 States of Matter Changing States PowerpointDocument23 pages1 States of Matter Changing States PowerpointJoshua BermoyNo ratings yet
- 1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids AutosavedDocument16 pages1 Kinetic Molecular Model of Solid and Liquids Autosavedhinacay.jonNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Changing States PresentationDocument23 pagesStates of Matter Changing States PresentationAdonai David RaharjoNo ratings yet
- Genchem 2 Module 6Document34 pagesGenchem 2 Module 6Jessel TapelNo ratings yet
- MAT T Er in Our SurroundingDocument8 pagesMAT T Er in Our SurroundingBharathNo ratings yet
- States of Matter PracticeDocument10 pagesStates of Matter PracticeBenny AgassiNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 2: Quarter 1, Module 6 Phase Diagram of Water and Carbon DioxideDocument31 pagesGeneral Chemistry 2: Quarter 1, Module 6 Phase Diagram of Water and Carbon Dioxidekai luv100% (2)
- Week 2 Lec 1 Chem111: Inorganic and Organic Matter and Its PropertyDocument4 pagesWeek 2 Lec 1 Chem111: Inorganic and Organic Matter and Its PropertyJiean JohnNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Properties of Matter (Year 4)Document26 pages3.1 Properties of Matter (Year 4)reinaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Notes New SyllabusDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Notes New SyllabusMuhammad TaufiqueNo ratings yet
- Simple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - 1Document37 pagesSimple Kinetic Molecular Model of Matter - 1AbdullaahNo ratings yet
- Solid, Liquids, and GasesDocument27 pagesSolid, Liquids, and GasesHamass D MajdiNo ratings yet
- Solid, Liquids, and GasesDocument27 pagesSolid, Liquids, and Gasesleo markNo ratings yet
- Getting To Know Gases: Worksheet 4.1Document2 pagesGetting To Know Gases: Worksheet 4.1yunohahageNo ratings yet
- PHARM 121: Harmaceutical Norganic Hemistry: TitleDocument5 pagesPHARM 121: Harmaceutical Norganic Hemistry: TitleTrixie Anne FelicitasNo ratings yet
- L1 GasesDocument11 pagesL1 GasesNaeem ur RehmanNo ratings yet
- T SC 2550160 Ks2 Year 5 Properties and Changes of Materials Revision Activity Mat Ver 4Document6 pagesT SC 2550160 Ks2 Year 5 Properties and Changes of Materials Revision Activity Mat Ver 4khushbakhtNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 ClassDocument30 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 ClassAnn MichelleNo ratings yet
- Unit 1.1 - States of Matter and Mixtures - Student NotesDocument20 pagesUnit 1.1 - States of Matter and Mixtures - Student Notesjaniel2027No ratings yet
- The Gaseous StateDocument28 pagesThe Gaseous Stateevermorenicole42No ratings yet
- Phases of MatterDocument35 pagesPhases of MatterAngel MoranNo ratings yet
- 13 - States of MatterDocument5 pages13 - States of MatterdodoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - States of Matter (Chemistry AS - Level)Document6 pagesChapter 4 - States of Matter (Chemistry AS - Level)Mohamed AkkashNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (AS-Level) : Solid Liquid GasDocument6 pagesChapter 4 (AS-Level) : Solid Liquid GashoNo ratings yet
- Physics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)Document28 pagesPhysics Chapter 9 (Chel, NIa, Sal)salma salNo ratings yet
- States of Matter: BIG IdeaDocument40 pagesStates of Matter: BIG IdeaJay Ar GalangNo ratings yet
- Describe Ways On Proper Use Handling Solid, Liquid, Gas Found at Home and in SchoolDocument7 pagesDescribe Ways On Proper Use Handling Solid, Liquid, Gas Found at Home and in SchoolShanel Silvano100% (2)
- Fluids Unit Review - AnswersDocument4 pagesFluids Unit Review - Answersisele1977No ratings yet
- Q4 Science 10 Week2Document3 pagesQ4 Science 10 Week2Edison Caringal50% (2)
- Class 11 Physics Kinetic Theory of Gases NotesDocument32 pagesClass 11 Physics Kinetic Theory of Gases NotesMath AddaNo ratings yet
- Matter:: It's What The World's Made ofDocument18 pagesMatter:: It's What The World's Made ofmarisexerta2850100% (3)
- CHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsDocument23 pagesCHAPTER 1 Matter, MeasurementsRusher SigueNo ratings yet
- 08 - Particles and PurificationDocument20 pages08 - Particles and PurificationDaniel IciousNo ratings yet
- Chemistry 10 - 12Document333 pagesChemistry 10 - 12Théé Néw SåmûNo ratings yet
- Properties of Fluids: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsDocument27 pagesProperties of Fluids: Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and ApplicationsAhmedalaal LotfyNo ratings yet
- Sle 2Document7 pagesSle 2Abdulrahman DesoukyNo ratings yet
- Booklet 2 Particles LWi ANSWERSDocument45 pagesBooklet 2 Particles LWi ANSWERS18811301255No ratings yet
- 02 Phase ChangeDocument5 pages02 Phase ChangebadhriNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - ThermodynamicsDocument73 pagesLecture 1 - ThermodynamicsNgọc ĐàoNo ratings yet
- Ncert Mole Concept PDFDocument25 pagesNcert Mole Concept PDFRavi TripathiNo ratings yet
- Pravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225511125526807058Document228 pagesPravindra Singh PWSFAC75824 20225511125526807058jkNo ratings yet
- ME3310 - Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument55 pagesME3310 - Properties of Pure SubstancesRenjith SinghNo ratings yet
- States of MatterDocument27 pagesStates of MatterEstelito Tamonan AmarNo ratings yet
- Some Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11th NotesDocument10 pagesSome Basic Concepts of Chemistry 11th NotesRʌĸɘsʜ GɘʜɭotNo ratings yet
- Booklet 2 ParticlesDocument43 pagesBooklet 2 Particles18811301255No ratings yet
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of MatterRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Practice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersFrom EverandPractice Makes Perfect in Chemistry: The Physical Behavior of Matter with AnswersNo ratings yet
- Children Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeFrom EverandChildren Encyclopedia Chemistry: The World of KnowledgeRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- Fahrenheit 451 Background Mini Research Project (Eng I)Document2 pagesFahrenheit 451 Background Mini Research Project (Eng I)Savannah MontelongoNo ratings yet
- Polly Sits Tight Text and QuestionsDocument3 pagesPolly Sits Tight Text and QuestionsSavannah Montelongo0% (1)
- DMR - Multiplying PolynomialsDocument1 pageDMR - Multiplying PolynomialsSavannah MontelongoNo ratings yet
- The Pedestrian Pre-Reading QuestionsDocument1 pageThe Pedestrian Pre-Reading QuestionsSavannah MontelongoNo ratings yet
- Magnetism and SupercoductivityDocument49 pagesMagnetism and SupercoductivityAbdo HusseinNo ratings yet
- EFP - MISO 100-250 750USGPM @110mDocument5 pagesEFP - MISO 100-250 750USGPM @110mRahmanu AribowoNo ratings yet
- Details of KO DrumDocument7 pagesDetails of KO Drumnishank soniNo ratings yet
- Heater Treater SeparatorDocument2 pagesHeater Treater SeparatorMurat KalfaNo ratings yet
- Crystalgrowth PDFDocument84 pagesCrystalgrowth PDFBhaskar AnandNo ratings yet
- How Does Rain HappenDocument2 pagesHow Does Rain HappenAndrewNo ratings yet
- Petroleum HandbookDocument28 pagesPetroleum HandbookVinoth100% (1)
- Fluid Coupling Fusible PlugDocument1 pageFluid Coupling Fusible Plug최승원No ratings yet
- Answer All Questions. Each Question Carries 2 Marks.: Sixth Semester B.Tech Degree ExaminationDocument3 pagesAnswer All Questions. Each Question Carries 2 Marks.: Sixth Semester B.Tech Degree ExaminationKrishna YadavNo ratings yet
- Dinosaur Charleslaw RorDocument25 pagesDinosaur Charleslaw RorFaith Renzel RoxasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 2 CHM207 Intermediate Organic Chemistry Distillation Technique and To Determine The Boiling Point of A LiquidDocument3 pagesExperiment 2 CHM207 Intermediate Organic Chemistry Distillation Technique and To Determine The Boiling Point of A LiquidWan ZulkifliNo ratings yet
- Chemical BondingDocument30 pagesChemical BondingAnsh AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Crystallization PDFDocument9 pagesCrystallization PDFonly. starNo ratings yet
- Code No: 43011/43012Document7 pagesCode No: 43011/43012SRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- CHEN 623 Problems Old Examination Problems: 1.: (P + A /V) (V B) RTDocument34 pagesCHEN 623 Problems Old Examination Problems: 1.: (P + A /V) (V B) RTZohaib Ali0% (1)
- Compressor Api617 LMC BMC 311f Maintenance ManualDocument6 pagesCompressor Api617 LMC BMC 311f Maintenance ManualAvishek HazraNo ratings yet
- Flow RegimesDocument5 pagesFlow RegimesSri Varshini PrathaNo ratings yet
- SuggestedAnswers 08 EDocument12 pagesSuggestedAnswers 08 ERaiNo ratings yet
- Modelling Plasma Arcs For Electrical SimulationsDocument4 pagesModelling Plasma Arcs For Electrical Simulationsadmatama221100% (1)
- Llano Restrepo2011Document13 pagesLlano Restrepo2011Gefersson Ochoa VelandiaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics 1 Mark QuestionsDocument81 pagesFluid Mechanics 1 Mark QuestionsYashwant RajeshirkeNo ratings yet
- Intro Natural Gas ProcessingDocument12 pagesIntro Natural Gas ProcessingVishalIndrapuriNo ratings yet
- Joule Thomson ExpansionDocument2 pagesJoule Thomson ExpansiondndudcNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Gases PDFDocument6 pagesBehaviour of Gases PDFdliteddlitedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of FluidsDocument64 pagesMechanics of FluidsShiva U100% (2)
- Surface Production Operations 7Document108 pagesSurface Production Operations 7Сергей Вельдяксов100% (1)
- Fluid Mechncs by McdonaldDocument116 pagesFluid Mechncs by McdonaldSneha SolankiNo ratings yet
- Tutorials ChE314Document12 pagesTutorials ChE314Nagwa MansyNo ratings yet
- Chemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HDocument7 pagesChemical Bonding Board Level Assignment: 1. Which of The Following Has Maximum Bond Angle? HLightNo ratings yet
- Magneto HydrodynamicsDocument7 pagesMagneto HydrodynamicsTintu Philip0% (1)