Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Worksheet On Wave Basics
Worksheet On Wave Basics
Uploaded by
khalisia francisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet On Wave Basics
Worksheet On Wave Basics
Uploaded by
khalisia francisCopyright:
Available Formats
Worksheet on Wave Basics
Name:Khalisia Francis Class: 505
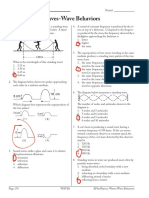
1. Label each part of the transverse wave in the space provided:
a
● Crest
c
● Trough
● Period
e d
● Amplitude f
● Wavelength b
Fill in the blanks:
2. In a wave, energy is carried from one place to another.
3.Medium is a substance/material that carries the wave.
4. The two types of waves are transverse waves and longitudinal waves.
5. In a longitudinal wave, the particles of the medium move in a direction parallel to the direction which the
wave moves.
6. In a transverse. wave, the particles of the medium move in a direction perpendicular to the direction
which the wave moves.
7. Sound waves is an example of longitudinal waves
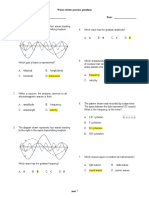
8. Label compression and rarefaction in the given figure:
compression rarefaction compression rarefaction compression rarefaction compression
9. Match the following:
a) Low pressure region in a longitudinal wave Ultrasonic (e)
b) Sound frequency less than 20 Hz
c) High pressure region in a longitudinal wave 20 Hz -20 KHz (g)
d) Low point in a transverse wave
e) Sound frequency more than 20 KHz crest (f)
f) High point in a transverse wave
g) Audible frequency Infrasonic (b)
Rarefaction (a)
Compression (c)
Trough (d)
10. Define:
a) Period: The time it takes a wavelength to go through one cycle,or the time it takes a point to go through
one phase of the wave.
b) Amplitude: The greatest distance from the equilibrium. The bigger the amplitude of the wave,the more
energy the wave has.
c) Wavelength: The shortest distance between points where the wave pattern repeats itself.
11. Give the mathematical relationship between:
a) Frequency, wavelength and speed of a wave:
Speed= wavelength x frequency , frequency= speed / wavelength , wavelength=speed/frequency
b) Frequency and period:
Period= 1/frequency frequency= 1/period
c) Wavelength and period:
12 a). What happens to the wavelength of a wave if you double the frequency?
When a frequency is doubled, the wavelength is halved.
b) What happens to the wavelength of a wave if you halve the frequency?
When a frequency is halved,the wavelength is doubled.
You might also like
- JSS 5855-11-2016Document28 pagesJSS 5855-11-2016Pooja sharma100% (1)
- Worksheet On Kinematics KeyDocument6 pagesWorksheet On Kinematics KeyelenaNo ratings yet
- WAVESDocument2 pagesWAVESJustus D ZatkalikNo ratings yet
- 14 Worksheet (AS) : 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveDocument4 pages14 Worksheet (AS) : 1 The Diagram Shows A Graph of The Displacement of A WaveNolawitNo ratings yet
- Fiber Optic Cable SplicingDocument62 pagesFiber Optic Cable SplicingKhawajaAyaz100% (2)
- Activity 3 - Parts of CameraDocument4 pagesActivity 3 - Parts of CameraPotpot Laceda33% (3)
- 11.6 Laws of Reflection WorksheetDocument6 pages11.6 Laws of Reflection WorksheetJojimar JulianNo ratings yet
- Speed and VelocityDocument3 pagesSpeed and Velocityteja eashanNo ratings yet
- C. C + v. C - v. V - C.: Ib Physics HL Multiple Choice Review Waves & Vibrations 1Document20 pagesC. C + v. C - v. V - C.: Ib Physics HL Multiple Choice Review Waves & Vibrations 1shammi nathanNo ratings yet
- Structure Questions Archimedes PrincipleDocument4 pagesStructure Questions Archimedes PrincipleEzra Loganathan Muniandi25% (4)
- Newtons Laws PacketDocument6 pagesNewtons Laws PacketWaleed AdnanNo ratings yet
- Experiment Number 2 Laws of MotionDocument10 pagesExperiment Number 2 Laws of MotionPatricia VagayNo ratings yet
- Tadamun Social Society Imamu-Nawawi Secondary Schools Bosaso-Puntland-Somalia Assignment: Subject Physics Classes: Form FourDocument13 pagesTadamun Social Society Imamu-Nawawi Secondary Schools Bosaso-Puntland-Somalia Assignment: Subject Physics Classes: Form FourIbrahim MohamedNo ratings yet
- Practice Questions in Projectile MotionDocument3 pagesPractice Questions in Projectile MotionMikai Trillanes ColloNo ratings yet
- Wave PropertiesDocument2 pagesWave PropertiesAshok Kumar Dondati100% (1)
- Waves Revision MC TestDocument36 pagesWaves Revision MC Testlove_241No ratings yet
- Waves and Sound WorksheetDocument12 pagesWaves and Sound WorksheetprosenNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDocument21 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION JEE PracticeDev PatelNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions-1Document5 pagesMultiple Choice Questions-1Arushi100% (1)
- Directions: Choose The Best Answer For Each Multiple Choice Question. Write The Best Answer On The BlankDocument3 pagesDirections: Choose The Best Answer For Each Multiple Choice Question. Write The Best Answer On The BlankRanulfo MayolNo ratings yet
- Heat - MCQDocument16 pagesHeat - MCQMinuteBrain LearningNo ratings yet
- Sound, Waves & EchoDocument2 pagesSound, Waves & Echonewtonfogg123No ratings yet
- MCQs Physics Chap 6-9Document19 pagesMCQs Physics Chap 6-9Azka HaqNo ratings yet
- Speed Acceleration TestDocument8 pagesSpeed Acceleration Testapi-233777623No ratings yet
- Quiz On Work, Energy, and PowerDocument2 pagesQuiz On Work, Energy, and PowerNathaniel DimaocorNo ratings yet
- Usman Public School System: Pressure WorksheetDocument2 pagesUsman Public School System: Pressure Worksheetmarium khanNo ratings yet
- Question Bank of Sound PDFDocument21 pagesQuestion Bank of Sound PDFSwamy Nathan100% (2)
- Linear Motion and GraphDocument1 pageLinear Motion and GraphmydadawalfnNo ratings yet
- Standing Waves WorksheetDocument2 pagesStanding Waves WorksheetAdib HassanNo ratings yet
- Physics First Term Mid Exam Preparation QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhysics First Term Mid Exam Preparation QuestionsEnju ChipepeNo ratings yet
- The Doppler Effect - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument2 pagesThe Doppler Effect - Multiple Choice Questionsjonni sitorusNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion and Gravitation 2Document16 pagesCircular Motion and Gravitation 2martinNo ratings yet
- 9th Icse Pressure - Test LabzDocument48 pages9th Icse Pressure - Test Labzmanojboa100% (1)
- Examview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Document9 pagesExamview Waves and Sound Practice Test4Tajay Billings100% (1)
- Worksheet Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesWorksheet Ray OpticsYug GandhiNo ratings yet
- Kinematics Multiple Choice Questions 2Document15 pagesKinematics Multiple Choice Questions 2Nour FawazNo ratings yet
- Waves MCQDocument45 pagesWaves MCQkoeliaNo ratings yet
- Waves Review Practice Questions Name: DateDocument15 pagesWaves Review Practice Questions Name: DateShammany AlsuwaidiiNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresDocument17 pagesTest Bank For Introduction To Physical Science 14th Edition Shipman Wilson Higgins TorresaimeeNo ratings yet
- Physics (Class 9 Level Questions)Document2 pagesPhysics (Class 9 Level Questions)SahejNo ratings yet
- Chapter #06 GravitationDocument13 pagesChapter #06 GravitationSIR USMAN KHANNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1-A2 Physics - ADocument14 pagesLesson 1-A2 Physics - ACheng WLNo ratings yet
- 1.0 Test On Circular MotionDocument1 page1.0 Test On Circular Motionrsdiwane100% (1)
- 1 0wave1 11 2activityDocument10 pages1 0wave1 11 2activityNisa Hj MohamadNo ratings yet
- Phys 125 Pex 5Document9 pagesPhys 125 Pex 5Richard OuNo ratings yet
- Pressure NotesDocument11 pagesPressure NotesVaishnavi BannurNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 2 - WavesDocument1 pageWorksheet 2 - WavesMary BakhoumNo ratings yet
- Summative Test WaveDocument2 pagesSummative Test WaveMarian Anion-GauranoNo ratings yet
- Forces and Motion QuestionsDocument7 pagesForces and Motion Questionsleg kissingNo ratings yet
- Phase Difference (Final)Document7 pagesPhase Difference (Final)Muhammad ShahzebNo ratings yet
- HOOKES LAW - Docx MCQDocument4 pagesHOOKES LAW - Docx MCQfarogh hamid100% (2)
- Standing Waves QuestionsDocument3 pagesStanding Waves QuestionsEllen AbrigoNo ratings yet
- Mcq-1 (Work, Energy and Power)Document3 pagesMcq-1 (Work, Energy and Power)Fluorine ToxicNo ratings yet
- Kinematics WorksheetDocument3 pagesKinematics WorksheetDyanie PlummerNo ratings yet
- Ch.2 Kinematics WorksheetDocument11 pagesCh.2 Kinematics WorksheetShahroze AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 05Document6 pagesChapter 05Michelle HsiehNo ratings yet
- Physics Form 4 Introduction To PhysicsDocument4 pagesPhysics Form 4 Introduction To PhysicscikzafirahNo ratings yet
- R2019 49P1MSDocument29 pagesR2019 49P1MSSkruzdelyte MielaNo ratings yet
- All Kinematics WorksheetDocument5 pagesAll Kinematics Worksheetgrace_lo_10% (1)
- fIZIK 1Document14 pagesfIZIK 1AaronAlwynNo ratings yet
- Ultrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-3Document9 pagesUltrasonic Testing Ut Q Bank A-3kingstonNo ratings yet
- ch12 Test BDocument4 pagesch12 Test BAli AymanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document2 pagesChapter 1Jeng Mun SamNo ratings yet
- CH 08Document2 pagesCH 08shahNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolDocument3 pagesUnit 2 Worksheet 5 Aurora High SchoolシューゴNo ratings yet
- Psycology Assignment#2Document2 pagesPsycology Assignment#2Mirha FatimaNo ratings yet
- Measurement Systems: Application and Design by Ernest O. DoebelinDocument18 pagesMeasurement Systems: Application and Design by Ernest O. DoebelinAlhji AhmedNo ratings yet
- ICSE Physics Sem-1 Answer KeyDocument16 pagesICSE Physics Sem-1 Answer KeyPrithviraj GhoshNo ratings yet
- Electromagnetic Spectrum Project1Document5 pagesElectromagnetic Spectrum Project1RajKumarNo ratings yet
- P.F. Bernath Et Al - Spectroscopy of The CH Free RadicalDocument11 pagesP.F. Bernath Et Al - Spectroscopy of The CH Free RadicalUasnsdaNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Moment PDFDocument5 pagesMagnetic Moment PDFAnirudh Moza 16009No ratings yet
- Physics C: Superposition and Standing WavesDocument58 pagesPhysics C: Superposition and Standing WavesRanja JeNo ratings yet
- Organic Chemistry - lesson8-IIDocument6 pagesOrganic Chemistry - lesson8-IIKajal GuptaNo ratings yet
- 02a LASERs Session 1 (Spontaneous Emission, Stimulated Emission, Light Amplification)Document7 pages02a LASERs Session 1 (Spontaneous Emission, Stimulated Emission, Light Amplification)Bibaswan ChakmaNo ratings yet
- Atomic Line WidthDocument23 pagesAtomic Line WidthsadiaNo ratings yet
- Meade Product Catalog 2011Document36 pagesMeade Product Catalog 2011Paola AndreaNo ratings yet
- Physics Lecture Planner by Physics Wallah For Boards BoosterDocument1 pagePhysics Lecture Planner by Physics Wallah For Boards BoosterMr AnonymousNo ratings yet
- Energy Momentum TensorDocument3 pagesEnergy Momentum Tensorrgkelly62No ratings yet
- Transverse Wave Frequency of VibrationDocument7 pagesTransverse Wave Frequency of VibrationTreksha DC100% (2)
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 pagesScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- 26Document69 pages26physicsdocs78% (9)
- Flip-Chip III-V-To-Silicon Photonics Interfaces For Optical SensorDocument7 pagesFlip-Chip III-V-To-Silicon Photonics Interfaces For Optical Sensoranushpamathi SundararajanNo ratings yet
- Activity 01 The Microscope and MicrosDocument3 pagesActivity 01 The Microscope and MicrosRacquel BanaoNo ratings yet
- 1 - Coefficient of Linear Expension by Fizeau's MethodDocument6 pages1 - Coefficient of Linear Expension by Fizeau's MethodABHRANEIL BHATTACHARYANo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Photography: Camera Obscura (Latin, Literally Translating To "Dark Room") Had Been in ExistenceDocument25 pagesA Brief History of Photography: Camera Obscura (Latin, Literally Translating To "Dark Room") Had Been in ExistenceKalyan Ranjan100% (1)
- Exp. 1Document10 pagesExp. 1Rajat PandaNo ratings yet
- For MateDocument11 pagesFor Mateyash parmarNo ratings yet
- Atomic Force MicrosDocument18 pagesAtomic Force MicrosjgregueraNo ratings yet
- Physics - 61 - Week - 5 - Exercises and Solved Problems PDFDocument2 pagesPhysics - 61 - Week - 5 - Exercises and Solved Problems PDFSebastian SmytheNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Effect of Current PDFDocument45 pagesMagnetic Effect of Current PDFPuneet Kapoor100% (1)