Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 viewsIX Circular Motion
IX Circular Motion
Uploaded by
Yogy YThis document contains 20 physics problems related to circular motion. The problems involve calculating angular velocities, accelerations, time, angles rotated, speeds, tensions in strings, and other variables associated with objects moving in circular paths. The document provides the information needed to solve circular motion problems quantitatively through calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- AnswersDocument15 pagesAnswersjrence33% (3)
- Hand-Outs For Physics (Geo1-1 - EE1-1)Document2 pagesHand-Outs For Physics (Geo1-1 - EE1-1)janeth waminalNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument22 pagesPhysicsRed Crazy0% (1)
- Circular Motion 1Document5 pagesCircular Motion 1Moon WorldNo ratings yet
- Phyc 121 Week 1 10Document85 pagesPhyc 121 Week 1 10John Michael Cañero Maon80% (5)
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)John Michael Cañero MaonNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Circular MotionDocument22 pagesPhysics Project On Circular Motionishan67% (3)
- 08 Ansys Case Study Two Dimensional ElasticityDocument31 pages08 Ansys Case Study Two Dimensional ElasticityIsanda Ika DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Document3 pagesSaint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Nardos AlemayewNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Circular, Periodic and Rotational MotionDocument5 pagesCircular, Periodic and Rotational MotionMelissa A. BernardoNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion - Worksheet NewDocument3 pagesLaws of Motion - Worksheet Newzoombs1223No ratings yet
- Issa PraaaankDocument2 pagesIssa PraaaankAvelynHernandezNo ratings yet
- Tut 06 Circular Motion 2022Document2 pagesTut 06 Circular Motion 2022Brian MachachaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Circular MotionDocument1 pageAssignment On Circular MotiondivyanshgirivbpsNo ratings yet
- Geas Coaching 1Document3 pagesGeas Coaching 1Aaron Joseph SolanoNo ratings yet
- CircularMotion PCDocument18 pagesCircularMotion PCAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- A2讲义习题 (51) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesDocument1 pageA2讲义习题 (51) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesyanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- XI Physics Important ProblemsDocument2 pagesXI Physics Important ProblemsganeshblogsNo ratings yet
- Calculus Physics 1 Preexam 3Document3 pagesCalculus Physics 1 Preexam 3TylerNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION Modified 2022Document2 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION Modified 2022samarthmathur014No ratings yet
- Circular Motion Questions?Document29 pagesCircular Motion Questions?Muhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Questions 3Document2 pagesQuestions 3princeshirima290No ratings yet
- Assignment 11 Rotational MotionDocument1 pageAssignment 11 Rotational MotionMrinal TripathiNo ratings yet
- Std. XII Physics (Numericals) Question Bank PDFDocument34 pagesStd. XII Physics (Numericals) Question Bank PDFPaul Levis RioNo ratings yet
- Class9 Ncert NumericalsDocument5 pagesClass9 Ncert Numericalsananya workNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument18 pagesCircular MotionveereshgajwelNo ratings yet
- Name The Factor On Which The Coefficient of Friction DependsDocument2 pagesName The Factor On Which The Coefficient of Friction Dependsanannyaaa98No ratings yet
- Phy13 CompiledDocument10 pagesPhy13 CompiledJeremy RuizNo ratings yet
- Problems On Uniform Circular Motion Problem 1Document8 pagesProblems On Uniform Circular Motion Problem 1BK - 12KC 620995 Cawthra Park SSNo ratings yet
- Practice Assignment Work Energy and PowerDocument3 pagesPractice Assignment Work Energy and PowerAyush GogiaNo ratings yet
- 3 CircularMotion PCDocument21 pages3 CircularMotion PCsureshserious7226No ratings yet
- Tutorial Rotational MotionDocument5 pagesTutorial Rotational Motioneyfa firdausNo ratings yet
- A2讲义习题 (46) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesDocument1 pageA2讲义习题 (46) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesyanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum Problem SetDocument4 pagesEnergy and Momentum Problem SetPranjal DhamNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION 25 Imp McqsDocument4 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION 25 Imp Mcqskshitijchavan1018No ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics Exercise 2Document1 pageRotational Dynamics Exercise 2Chung Chee YuenNo ratings yet
- All ImpDocument48 pagesAll Impdevrarimanish72No ratings yet
- Phy 113 Past Question-1-1Document20 pagesPhy 113 Past Question-1-1Inalegwu EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument25 pagesPhysics QuestionsCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Physics 1Document1 pageAssignment For Physics 1Đặng Thị Hiếu LanNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument1 pageCircular Motionaishaalwin95No ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam For Review 2019Document2 pagesMechanics Exam For Review 2019John Derick LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 14Document6 pagesTutorial Week 14Chin Tiong LeeNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion MhtcetDocument2 pagesCircular Motion MhtcetUmesh PandeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies v2.0 - StudentDocument7 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies v2.0 - StudentLpt Ashley OlbinarNo ratings yet
- Rr320304 - Dynamics of MachinesDocument8 pagesRr320304 - Dynamics of MachinesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 5Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 5aidaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: A and A Wheel WeighingDocument1 pageAssignment: A and A Wheel WeighingIshfaqurNo ratings yet
- (Physics) AnswersDocument15 pages(Physics) AnswersLoraine Rose EstivaNo ratings yet
- DOM Model QuestionDocument2 pagesDOM Model QuestionSenthilkumar SubbiahNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument3 pagesRotational Motiononkar.kapuskari221No ratings yet
- 06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocument3 pages06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration and ForceDocument2 pagesCentripetal Acceleration and ForceRenor SagunNo ratings yet
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage Gen Physics1Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage Gen Physics1Valencia AngieNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Made by Ishan GuptaDocument22 pagesPhysics Project Made by Ishan GuptaishanNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- VageeswariDocument6 pagesVageeswariYogy YNo ratings yet
- Policy ClauseDocument14 pagesPolicy ClauseYogy YNo ratings yet
- Maths Iia (Em)Document4 pagesMaths Iia (Em)Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Final Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Physics Test Paper With SolutionDocument9 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Physics Test Paper With SolutionYogy YNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument3 pagesProposalYogy YNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 05-04-2021 15.12.45Document3 pagesCamScanner 05-04-2021 15.12.45Yogy YNo ratings yet
- 2 - Structure of Atom Work SheetDocument4 pages2 - Structure of Atom Work SheetYogy YNo ratings yet
- Final Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionDocument6 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionYogy YNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 01 Matter and Its CompositionDocument12 pagesICSE Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 01 Matter and Its CompositionYogy YNo ratings yet
- 07 07 2022 FT Xvi TD Jeem Key - SolDocument18 pages07 07 2022 FT Xvi TD Jeem Key - SolYogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 3Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 3Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 5Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 5Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 1Document5 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 1Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 4Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 4Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 2Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 2Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument14 pagesMotion in A Straight LineYogy YNo ratings yet
- 1.current ElectricityDocument147 pages1.current ElectricityYogy YNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 10 Redox Reactions: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesUNIT - 10 Redox Reactions: Multiple Choice QuestionsYogy YNo ratings yet
- Revised SR Inter (Bco, LX, ZX) Ipe SchedulesDocument5 pagesRevised SR Inter (Bco, LX, ZX) Ipe SchedulesYogy YNo ratings yet
- X - Biology Work Sheet - 1Document2 pagesX - Biology Work Sheet - 1Yogy YNo ratings yet
- English Work Sheet - 1Document4 pagesEnglish Work Sheet - 1Yogy YNo ratings yet
- గోరంత దీపాలు (ప్రక్రియ, ప్రశ్నలు)Document6 pagesగోరంత దీపాలు (ప్రక్రియ, ప్రశ్నలు)Yogy YNo ratings yet
- 7.nuclear Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry ExerciseDocument38 pages7.nuclear Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry ExerciseYogy YNo ratings yet
- SR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Yogy YNo ratings yet
- MEC3076F - Stress Analysis and Materials (Part 1 Mechanics of Solids)Document202 pagesMEC3076F - Stress Analysis and Materials (Part 1 Mechanics of Solids)Sfiso FieNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument41 pagesUnit-II Second Law of Thermodynamicssamy gsNo ratings yet
- Science8 Pretest 1st QuarterDocument2 pagesScience8 Pretest 1st QuarterRAYMUND RODILLONo ratings yet
- CircularDocument3 pagesCircularJonathan SolimanNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear FEA of Base Plate Connections Used in Industrial Pallet Racking StructuresDocument9 pagesNon-Linear FEA of Base Plate Connections Used in Industrial Pallet Racking StructuressarbiniNo ratings yet
- CIVL6004 Advanced Soil Mechanics Assignment #1: CIVL6004 Prof. J. YangDocument3 pagesCIVL6004 Advanced Soil Mechanics Assignment #1: CIVL6004 Prof. J. YangZack FengNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- Jmse 08 00806 v2Document23 pagesJmse 08 00806 v2darlanbeckerNo ratings yet
- Advanced Heat Transfer Analysis of Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) PDFDocument9 pagesAdvanced Heat Transfer Analysis of Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) PDFDaniel Escobar100% (1)
- MCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationDocument6 pagesMCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationvishiNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure of Muff CouplingDocument2 pagesDesign Procedure of Muff CouplingSamuelshrly100% (2)
- Advance Structural Analysis (Internal Hinge) - Devdas MenomDocument42 pagesAdvance Structural Analysis (Internal Hinge) - Devdas MenomLuis MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Lamjed Hadj Taieb Med Amine Guidara Noura Bettaieb Sami El Aoud Ezzeddine Hadj Taieb Water-Hammer Control in An Actual Branched Cast Iron Network by Means of Polymeric PipesDocument10 pagesLamjed Hadj Taieb Med Amine Guidara Noura Bettaieb Sami El Aoud Ezzeddine Hadj Taieb Water-Hammer Control in An Actual Branched Cast Iron Network by Means of Polymeric PipesAli TrikiNo ratings yet
- Wpe PDFDocument47 pagesWpe PDFDewesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Pulse FormingDocument13 pagesMagnetic Pulse FormingUmesh KsNo ratings yet
- MCQ Units and MeasurementDocument9 pagesMCQ Units and MeasurementShreya Chakroverty ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- A Model For Cutting Forces Generated During Machining With Self-Propelled Rotary ToolsDocument7 pagesA Model For Cutting Forces Generated During Machining With Self-Propelled Rotary ToolsYashwanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Standards Pillars and Bushes2Document136 pagesStandards Pillars and Bushes2sansagithNo ratings yet
- DPP's Physics - Class-XI - 168 SolutionDocument106 pagesDPP's Physics - Class-XI - 168 SolutionEdumaaNo ratings yet
- MEC291 Dynamic Crank and Slider2Document9 pagesMEC291 Dynamic Crank and Slider2Amir ArsyadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Jacobians, Velocity, and Static Force: RoboticsDocument23 pagesChapter 4: Jacobians, Velocity, and Static Force: Roboticsbình nghuyễnNo ratings yet
- Scour Protection Bridge Piers: Yee-Meng Chiew, 1 Member, ASCEDocument10 pagesScour Protection Bridge Piers: Yee-Meng Chiew, 1 Member, ASCEAhmad HelmiNo ratings yet
- Natural Frequencies of Plates With Uniform PerforationsDocument7 pagesNatural Frequencies of Plates With Uniform Perforationsspider1970No ratings yet
- Sub Code: ME8292 Sub Name: Engineering Mechanics Max - Marks:100 Duration: 3 Hrs Branch: Mechanical Engg. Year/Sem: I / II Answer All QuestionsDocument3 pagesSub Code: ME8292 Sub Name: Engineering Mechanics Max - Marks:100 Duration: 3 Hrs Branch: Mechanical Engg. Year/Sem: I / II Answer All QuestionssivashanmugamNo ratings yet
- Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in CompressionDocument6 pagesStatic Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in CompressionnolanjcNo ratings yet
- SOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)Document39 pagesSOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)syafiqahdaudNo ratings yet
- Bernoullis EquationDocument45 pagesBernoullis EquationEuniceNo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit 7 Practice AssessmentDocument4 pagesPhysics: Unit 7 Practice AssessmentKaly CantongNo ratings yet
IX Circular Motion
IX Circular Motion
Uploaded by
Yogy Y0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesThis document contains 20 physics problems related to circular motion. The problems involve calculating angular velocities, accelerations, time, angles rotated, speeds, tensions in strings, and other variables associated with objects moving in circular paths. The document provides the information needed to solve circular motion problems quantitatively through calculations.
Original Description:
Original Title
IX circular motion
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 20 physics problems related to circular motion. The problems involve calculating angular velocities, accelerations, time, angles rotated, speeds, tensions in strings, and other variables associated with objects moving in circular paths. The document provides the information needed to solve circular motion problems quantitatively through calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views2 pagesIX Circular Motion
IX Circular Motion
Uploaded by
Yogy YThis document contains 20 physics problems related to circular motion. The problems involve calculating angular velocities, accelerations, time, angles rotated, speeds, tensions in strings, and other variables associated with objects moving in circular paths. The document provides the information needed to solve circular motion problems quantitatively through calculations.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Dr. K.K.R’s GOWTHAM [E.
M] HIGH SCHOOL :: GUDIVADA
Class : IX –CBSE ( Topic : CIRCULAR MOTION) Marks : 100
Sub : Physics
1. Starting from rest the fly wheel of a motor attains an angular velocity of 30 rad/s in 5 seconds. The
angular acceleration attained is ------- rad/s2
2. An engine increases its angular speed 300 rpm to 600 rpm in 5 seconds. Number of revolutions made
during this time by the engine is -------
3. A fly wheel is revolving at the rate of 600 rpm on applying a retarding torque, it slows down at the rate
of 2 rad/s2. The time in which it comes to rest is ------ sec.
4 A particle ravels in a circle of radius 10 cm at a speed that uniformly increases. If the speed changes
from 5.0 m/s to 7.0 m/s in 2.0 s, find the angular acceleration.
5. The wheel of a motor, accelerated uniformly from rest, rotates through 2 radian during the first second.
Find the angle rotated during the next two seconds.
6. A wheel is making revolutions about its axis with uniform angular acceleration. Starting from rest, it
reaches 50 rev/sec in 2 seconds. Find the angle rotated during these four seconds.
7. A wheel starting from rest is uniformly accelerated at 2 rad/s2 for 10 seconds. It is allowed to rotate
uniformly for the next 10 seconds and is finally brought to rest in the next 10 seconds. Find the total
angle rotated by the wheel.
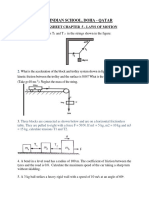
8. A string can sustain a maximum force of 300 N without breaking. A mass of 1kg is tied to one end of the
string 3 metre long and the mass is rotated in a horizontal circular path on a smooth horizontal surface.
The other end of the string is fixed on the table. The maximum linear speed of the mass is ------ m/s.
9. A body moves along a circular path of radius 25cm. The coefficient of friction between the surface of the
path and body is 0.4. The angular velocity in radians/sec, with which the both should move so that it
does not leave the path is (g=10 ms-2)
10. A coin is placed on a rotating turn table slips if it is placed at a minimum distance of 32cm from the
cenrtre. If the angular velocity of the turn table is quadrapled, it will just slip if the distance from the
centre is --- cm.
11. A cyclist riding the bicycle at a speed of 14 m/s takes a turn around a circular road of radius 20 m
without skidding. Given g=9.8ms-2 what is his inclination to the vertical?
12. A circular road of radius 5 m has the angle of banking equal to 450. At what speed should a vehicle go
on this road so that the friction is not used ?
13. A small block of mass 200 g moves with uniform speed in a horizontal circular groove, with vertical side
walls, of radius 25 cm. If the block takes 1.0 s to completes one round, find the normal contact force by
the side wall of the groove. (π2=10}
14. A motor cyclist rides on a cylindrical wall of a velodrome (hollow metal cylinder kept with the axis
vertical) of radius ‘r’ rotating about its axis at the rate f rev/s. The least coefficient of friction necessary so
that he does not step down is
15. A bob of mass 100 gm tied at the end of a string of length 50 cm is revolved in a vertical circle with a
constant speed 1 ms-1. When the tension in the string is 0.8N, the angle made by the string with the
vertical is, (g = 10 ms-2)
16. A mass 0.9 kg is suspended from a string of length 0.5 m at rest. Another body of mass 100 gm. moving
horizontally strikes the mass and sticks to it. If the combined mass just able to complete the circle, initial
velocity of the body is ----- m/s. (g = 10 ms-2)
17. 2 kg stone is swung in a vertical circle by attaching it at the end of a string of length 2m. If the string can
withstand a tension of 163.6 N, the maximum speed with which the stone can be rotated is ---- m/s.
18. A 5 kg body is rotated in a vertical circle with a speed 4 ms-1 using a string of length 1m. When the
tension in the string is 80 N, then the body will be at -------.
19. A body of mass m is rotating in a vertical circle of radius ‘r’ with critical speed. the difference in its K.E. at
the top and the bottom is nmgr. n = ------.
20. A 1kg ball is rotated in a vertical circle by using a thread of radius 0.1 m. If the tension in the string at
lowest point is 24.2N, its angular velocity at that position is --------.
You might also like
- AnswersDocument15 pagesAnswersjrence33% (3)
- Hand-Outs For Physics (Geo1-1 - EE1-1)Document2 pagesHand-Outs For Physics (Geo1-1 - EE1-1)janeth waminalNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument22 pagesPhysicsRed Crazy0% (1)
- Circular Motion 1Document5 pagesCircular Motion 1Moon WorldNo ratings yet
- Phyc 121 Week 1 10Document85 pagesPhyc 121 Week 1 10John Michael Cañero Maon80% (5)
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage (Gen. Physics)John Michael Cañero MaonNo ratings yet
- Physics Project On Circular MotionDocument22 pagesPhysics Project On Circular Motionishan67% (3)
- 08 Ansys Case Study Two Dimensional ElasticityDocument31 pages08 Ansys Case Study Two Dimensional ElasticityIsanda Ika DamayantiNo ratings yet
- Saint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Document3 pagesSaint Joseph Catholic School-Adama: Grade 11 Physics Worksheet April 2012 (2020)Nardos AlemayewNo ratings yet
- Sheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Document5 pagesSheet Exercise 2 - Circular Motion - S - L-1 1668503345455Gaurav KumarNo ratings yet
- Circular, Periodic and Rotational MotionDocument5 pagesCircular, Periodic and Rotational MotionMelissa A. BernardoNo ratings yet
- Laws of Motion - Worksheet NewDocument3 pagesLaws of Motion - Worksheet Newzoombs1223No ratings yet
- Issa PraaaankDocument2 pagesIssa PraaaankAvelynHernandezNo ratings yet
- Tut 06 Circular Motion 2022Document2 pagesTut 06 Circular Motion 2022Brian MachachaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On Circular MotionDocument1 pageAssignment On Circular MotiondivyanshgirivbpsNo ratings yet
- Geas Coaching 1Document3 pagesGeas Coaching 1Aaron Joseph SolanoNo ratings yet
- CircularMotion PCDocument18 pagesCircularMotion PCAaryan KeshanNo ratings yet
- A2讲义习题 (51) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesDocument1 pageA2讲义习题 (51) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesyanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- XI Physics Important ProblemsDocument2 pagesXI Physics Important ProblemsganeshblogsNo ratings yet
- Calculus Physics 1 Preexam 3Document3 pagesCalculus Physics 1 Preexam 3TylerNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION Modified 2022Document2 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION Modified 2022samarthmathur014No ratings yet
- Circular Motion Questions?Document29 pagesCircular Motion Questions?Muhammad RafayNo ratings yet
- Questions 3Document2 pagesQuestions 3princeshirima290No ratings yet
- Assignment 11 Rotational MotionDocument1 pageAssignment 11 Rotational MotionMrinal TripathiNo ratings yet
- Std. XII Physics (Numericals) Question Bank PDFDocument34 pagesStd. XII Physics (Numericals) Question Bank PDFPaul Levis RioNo ratings yet
- Class9 Ncert NumericalsDocument5 pagesClass9 Ncert Numericalsananya workNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument18 pagesCircular MotionveereshgajwelNo ratings yet
- Name The Factor On Which The Coefficient of Friction DependsDocument2 pagesName The Factor On Which The Coefficient of Friction Dependsanannyaaa98No ratings yet
- Phy13 CompiledDocument10 pagesPhy13 CompiledJeremy RuizNo ratings yet
- Problems On Uniform Circular Motion Problem 1Document8 pagesProblems On Uniform Circular Motion Problem 1BK - 12KC 620995 Cawthra Park SSNo ratings yet
- Practice Assignment Work Energy and PowerDocument3 pagesPractice Assignment Work Energy and PowerAyush GogiaNo ratings yet
- 3 CircularMotion PCDocument21 pages3 CircularMotion PCsureshserious7226No ratings yet
- Tutorial Rotational MotionDocument5 pagesTutorial Rotational Motioneyfa firdausNo ratings yet
- A2讲义习题 (46) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesDocument1 pageA2讲义习题 (46) -Equilibrium of a rigid body under coplanar forcesyanghaoyi1985No ratings yet
- Energy and Momentum Problem SetDocument4 pagesEnergy and Momentum Problem SetPranjal DhamNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR MOTION 25 Imp McqsDocument4 pagesCIRCULAR MOTION 25 Imp Mcqskshitijchavan1018No ratings yet
- Rotational Dynamics Exercise 2Document1 pageRotational Dynamics Exercise 2Chung Chee YuenNo ratings yet
- All ImpDocument48 pagesAll Impdevrarimanish72No ratings yet
- Phy 113 Past Question-1-1Document20 pagesPhy 113 Past Question-1-1Inalegwu EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- Physics QuestionsDocument25 pagesPhysics QuestionsCarlos KasambiraNo ratings yet
- Assignment For Physics 1Document1 pageAssignment For Physics 1Đặng Thị Hiếu LanNo ratings yet
- Circular MotionDocument1 pageCircular Motionaishaalwin95No ratings yet
- Mechanics Exam For Review 2019Document2 pagesMechanics Exam For Review 2019John Derick LacsamanaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Week 14Document6 pagesTutorial Week 14Chin Tiong LeeNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion MhtcetDocument2 pagesCircular Motion MhtcetUmesh PandeNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Rigid Bodies v2.0 - StudentDocument7 pagesDynamics of Rigid Bodies v2.0 - StudentLpt Ashley OlbinarNo ratings yet
- Rr320304 - Dynamics of MachinesDocument8 pagesRr320304 - Dynamics of MachinesSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Tutorial Topic 5Document3 pagesTutorial Topic 5aidaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: A and A Wheel WeighingDocument1 pageAssignment: A and A Wheel WeighingIshfaqurNo ratings yet
- (Physics) AnswersDocument15 pages(Physics) AnswersLoraine Rose EstivaNo ratings yet
- DOM Model QuestionDocument2 pagesDOM Model QuestionSenthilkumar SubbiahNo ratings yet
- Rotational MotionDocument3 pagesRotational Motiononkar.kapuskari221No ratings yet
- 06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesDocument3 pages06 Rotation of Rigid BodiesJerico LlovidoNo ratings yet
- Centripetal Acceleration and ForceDocument2 pagesCentripetal Acceleration and ForceRenor SagunNo ratings yet
- Mga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage Gen Physics1Document4 pagesMga Sagot Ni Ashe Montage Gen Physics1Valencia AngieNo ratings yet
- Physics Project Made by Ishan GuptaDocument22 pagesPhysics Project Made by Ishan GuptaishanNo ratings yet
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersFrom EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- VageeswariDocument6 pagesVageeswariYogy YNo ratings yet
- Policy ClauseDocument14 pagesPolicy ClauseYogy YNo ratings yet
- Maths Iia (Em)Document4 pagesMaths Iia (Em)Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Final Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Physics Test Paper With SolutionDocument9 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Physics Test Paper With SolutionYogy YNo ratings yet
- ProposalDocument3 pagesProposalYogy YNo ratings yet
- CamScanner 05-04-2021 15.12.45Document3 pagesCamScanner 05-04-2021 15.12.45Yogy YNo ratings yet
- 2 - Structure of Atom Work SheetDocument4 pages2 - Structure of Atom Work SheetYogy YNo ratings yet
- Final Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionDocument6 pagesFinal Jee-Main Examination - July, 2022: Chemistry Test Paper With SolutionYogy YNo ratings yet
- ICSE Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 01 Matter and Its CompositionDocument12 pagesICSE Class 9 Chemistry Chapter 01 Matter and Its CompositionYogy YNo ratings yet
- 07 07 2022 FT Xvi TD Jeem Key - SolDocument18 pages07 07 2022 FT Xvi TD Jeem Key - SolYogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 3Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 3Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 5Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 5Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 1Document5 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 1Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 4Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 4Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Krishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 2Document6 pagesKrishna Reddy'S Sri Chaitanya: Week End - 2Yogy YNo ratings yet
- Motion in A Straight LineDocument14 pagesMotion in A Straight LineYogy YNo ratings yet
- 1.current ElectricityDocument147 pages1.current ElectricityYogy YNo ratings yet
- UNIT - 10 Redox Reactions: Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument9 pagesUNIT - 10 Redox Reactions: Multiple Choice QuestionsYogy YNo ratings yet
- Revised SR Inter (Bco, LX, ZX) Ipe SchedulesDocument5 pagesRevised SR Inter (Bco, LX, ZX) Ipe SchedulesYogy YNo ratings yet
- X - Biology Work Sheet - 1Document2 pagesX - Biology Work Sheet - 1Yogy YNo ratings yet
- English Work Sheet - 1Document4 pagesEnglish Work Sheet - 1Yogy YNo ratings yet
- గోరంత దీపాలు (ప్రక్రియ, ప్రశ్నలు)Document6 pagesగోరంత దీపాలు (ప్రక్రియ, ప్రశ్నలు)Yogy YNo ratings yet
- 7.nuclear Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry ExerciseDocument38 pages7.nuclear Chemistry and Environmental Chemistry ExerciseYogy YNo ratings yet
- SR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Document8 pagesSR - Iit - Incomming-Cosaprk&Spark, Ic Ncert - Jee Main Model: Physics MAX - MARKS: 100Yogy YNo ratings yet
- MEC3076F - Stress Analysis and Materials (Part 1 Mechanics of Solids)Document202 pagesMEC3076F - Stress Analysis and Materials (Part 1 Mechanics of Solids)Sfiso FieNo ratings yet
- Unit-II Second Law of ThermodynamicsDocument41 pagesUnit-II Second Law of Thermodynamicssamy gsNo ratings yet
- Science8 Pretest 1st QuarterDocument2 pagesScience8 Pretest 1st QuarterRAYMUND RODILLONo ratings yet
- CircularDocument3 pagesCircularJonathan SolimanNo ratings yet
- Non-Linear FEA of Base Plate Connections Used in Industrial Pallet Racking StructuresDocument9 pagesNon-Linear FEA of Base Plate Connections Used in Industrial Pallet Racking StructuressarbiniNo ratings yet
- CIVL6004 Advanced Soil Mechanics Assignment #1: CIVL6004 Prof. J. YangDocument3 pagesCIVL6004 Advanced Soil Mechanics Assignment #1: CIVL6004 Prof. J. YangZack FengNo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagesFluid MechanicsVivek MishraNo ratings yet
- Jmse 08 00806 v2Document23 pagesJmse 08 00806 v2darlanbeckerNo ratings yet
- Advanced Heat Transfer Analysis of Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) PDFDocument9 pagesAdvanced Heat Transfer Analysis of Continuously Variable Transmissions (CVT) PDFDaniel Escobar100% (1)
- MCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationDocument6 pagesMCQ Questions With Answers Class 9 Chapter 10 GravitationvishiNo ratings yet
- Design Procedure of Muff CouplingDocument2 pagesDesign Procedure of Muff CouplingSamuelshrly100% (2)
- Advance Structural Analysis (Internal Hinge) - Devdas MenomDocument42 pagesAdvance Structural Analysis (Internal Hinge) - Devdas MenomLuis MontoyaNo ratings yet
- Lamjed Hadj Taieb Med Amine Guidara Noura Bettaieb Sami El Aoud Ezzeddine Hadj Taieb Water-Hammer Control in An Actual Branched Cast Iron Network by Means of Polymeric PipesDocument10 pagesLamjed Hadj Taieb Med Amine Guidara Noura Bettaieb Sami El Aoud Ezzeddine Hadj Taieb Water-Hammer Control in An Actual Branched Cast Iron Network by Means of Polymeric PipesAli TrikiNo ratings yet
- Wpe PDFDocument47 pagesWpe PDFDewesh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Magnetic Pulse FormingDocument13 pagesMagnetic Pulse FormingUmesh KsNo ratings yet
- MCQ Units and MeasurementDocument9 pagesMCQ Units and MeasurementShreya Chakroverty ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- A Model For Cutting Forces Generated During Machining With Self-Propelled Rotary ToolsDocument7 pagesA Model For Cutting Forces Generated During Machining With Self-Propelled Rotary ToolsYashwanth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Standards Pillars and Bushes2Document136 pagesStandards Pillars and Bushes2sansagithNo ratings yet
- DPP's Physics - Class-XI - 168 SolutionDocument106 pagesDPP's Physics - Class-XI - 168 SolutionEdumaaNo ratings yet
- MEC291 Dynamic Crank and Slider2Document9 pagesMEC291 Dynamic Crank and Slider2Amir ArsyadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4: Jacobians, Velocity, and Static Force: RoboticsDocument23 pagesChapter 4: Jacobians, Velocity, and Static Force: Roboticsbình nghuyễnNo ratings yet
- Scour Protection Bridge Piers: Yee-Meng Chiew, 1 Member, ASCEDocument10 pagesScour Protection Bridge Piers: Yee-Meng Chiew, 1 Member, ASCEAhmad HelmiNo ratings yet
- Natural Frequencies of Plates With Uniform PerforationsDocument7 pagesNatural Frequencies of Plates With Uniform Perforationsspider1970No ratings yet
- Sub Code: ME8292 Sub Name: Engineering Mechanics Max - Marks:100 Duration: 3 Hrs Branch: Mechanical Engg. Year/Sem: I / II Answer All QuestionsDocument3 pagesSub Code: ME8292 Sub Name: Engineering Mechanics Max - Marks:100 Duration: 3 Hrs Branch: Mechanical Engg. Year/Sem: I / II Answer All QuestionssivashanmugamNo ratings yet
- Static Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in CompressionDocument6 pagesStatic Modulus of Elasticity and Poisson's Ratio of Concrete in CompressionnolanjcNo ratings yet
- SOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)Document39 pagesSOW MCO F4 Physics 2020 (LATEST 17OGOS2020)syafiqahdaudNo ratings yet
- Bernoullis EquationDocument45 pagesBernoullis EquationEuniceNo ratings yet
- Physics: Unit 7 Practice AssessmentDocument4 pagesPhysics: Unit 7 Practice AssessmentKaly CantongNo ratings yet