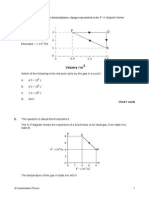
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Following Diagram Represents The Born Haber Cycle For The Formation of Compound MX
The Following Diagram Represents The Born Haber Cycle For The Formation of Compound MX
Uploaded by
Shaquille Dunkley0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views2 pagesThe document describes the Born Haber cycle for the formation of compound MX(s). It provides the following enthalpy changes in kJ/mol:
∆H M(s) = + 86; ∆H M(g) = + 408; ∆H (MX(s)) = – 431; ∆H X2 = + 122; ∆H X(g) = –372. It asks to define standard enthalpy of formation and lattice energy, and to identify the enthalpy values that correspond to stages I, III, and IV of the cycle. It also asks to calculate the lattice energy of MX(s) and account for differences in lattice energy between Mg
Original Description:
Original Title
The following diagram represents the Born Haber cycle for the formation of compound MX
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the Born Haber cycle for the formation of compound MX(s). It provides the following enthalpy changes in kJ/mol:
∆H M(s) = + 86; ∆H M(g) = + 408; ∆H (MX(s)) = – 431; ∆H X2 = + 122; ∆H X(g) = –372. It asks to define standard enthalpy of formation and lattice energy, and to identify the enthalpy values that correspond to stages I, III, and IV of the cycle. It also asks to calculate the lattice energy of MX(s) and account for differences in lattice energy between Mg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
57 views2 pagesThe Following Diagram Represents The Born Haber Cycle For The Formation of Compound MX
The Following Diagram Represents The Born Haber Cycle For The Formation of Compound MX
Uploaded by
Shaquille DunkleyThe document describes the Born Haber cycle for the formation of compound MX(s). It provides the following enthalpy changes in kJ/mol:
∆H M(s) = + 86; ∆H M(g) = + 408; ∆H (MX(s)) = – 431; ∆H X2 = + 122; ∆H X(g) = –372. It asks to define standard enthalpy of formation and lattice energy, and to identify the enthalpy values that correspond to stages I, III, and IV of the cycle. It also asks to calculate the lattice energy of MX(s) and account for differences in lattice energy between Mg
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
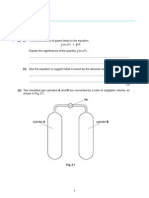
The following diagram represents the Born Haber cycle for the
formation of compound MX(s). The associated enthalpy changes in kJ
mol–1 for the cycle above are as follows: ∆H M(s) = + 86; ∆H M(g) = +
408; ∆H (MX(s)) = – 431; ∆H X2 = + 122; ∆H X(g) = –372 (i) State
Hess’ Law of heat
summation. .................................................................................................
................................ ....................................................................................
............................................. [1 mark] (ii) Define standard enthalpy
change of
formation. ...................................................................................................
............................. .......................................................................................
......................................... [1 mark] (iii) Which enthalpy values
correspond to EACH of the stages I, III and IV in the cycle
above? ........................................................................................................
......................... ...........................................................................................
...................................... [3 marks] (iv) Define lattice
energy. ........................................................................................................
......................... ...........................................................................................
...................................... [1 mark] - 7 - GO ON TO THE NEXT PAGE
02112020/CAPE/SPEC 2017 ‘‘*’’Barcode Area”*” Sequential Bar
Code DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS
AREA DO NOT WRITE IN THIS AREA (v) Calculate the lattice
energy of MX(s). [3 marks] (d) Account for the difference in the lattice
energy for MgCl2 (s) and
NaCl(s). ......................................................................................................
........................................ ............................................................................
.................................................................. ..................................................
........................................................................................... .........................
....................................................................................................................
.....................................................................................................................
......................... ...........................................................................................
.................................................. ..................................................................
........................................................................... [4 marks] (e) Explain
why the molar enthalpy changes for the following reactions have
identical values. HCl (aq) + NaOH (aq) → NaCl (aq) + H2 O (l) H2 SO4
(aq) + 2KOH (aq) → K2 SO4 (aq) + 2H2 O
(l) ...............................................................................................
You might also like
- 2020 UST MBR BiochemistryDocument77 pages2020 UST MBR BiochemistryLorealLunaNo ratings yet
- Tasker-Milward School 1Document19 pagesTasker-Milward School 1Younes AlahmadNo ratings yet
- 4.2 Exam Questions EquilibriaDocument8 pages4.2 Exam Questions EquilibriaLeen JabbanNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 - Entropy QuestionsDocument49 pagesUnit 4 - Entropy Questionsareyouthere92100% (1)
- Hess Cycle QsDocument5 pagesHess Cycle QsJack SmitNo ratings yet
- Ideal GasesDocument37 pagesIdeal GasesEdgardo LeysaNo ratings yet
- WS A Level CHEMDocument57 pagesWS A Level CHEMPreet ShahNo ratings yet
- Kinetics QuestionsDocument9 pagesKinetics QuestionsridithaNo ratings yet
- 9702 Thermal Properties All Completed Upto May June 2011Document0 pages9702 Thermal Properties All Completed Upto May June 2011Ritwik KumarNo ratings yet
- Topic 4 TestDocument10 pagesTopic 4 TestRitik YadavNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Ws 2Document15 pagesIdeal Gas Ws 2daanish muftiNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes 4 QPDocument18 pagesEnthalpy Changes 4 QPnxgqyj4rwxNo ratings yet
- Grzesiek Relaxation TextDocument37 pagesGrzesiek Relaxation TextRigel_TNo ratings yet
- Q1. (A) State What Is Meant by The Term Activation Energy of A ReactionDocument85 pagesQ1. (A) State What Is Meant by The Term Activation Energy of A ReactionDaniyal HemaniNo ratings yet
- Explaining Hess' Law by Finding The Heat of ReactionDocument9 pagesExplaining Hess' Law by Finding The Heat of ReactionFanilo RazafindralamboNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes 3 QPDocument15 pagesEnthalpy Changes 3 QPnxgqyj4rwxNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1 Enthalpy ChangesDocument25 pages2.3.1 Enthalpy Changesp01084240882No ratings yet
- Oscillations & SHM 03-08 LQDocument5 pagesOscillations & SHM 03-08 LQAllyLauNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Past Paper Ch1.2Document18 pagesChemistry Past Paper Ch1.2Raymond Chan0% (1)
- t2 Chem Revision Ex 12Document16 pagest2 Chem Revision Ex 12Nicholas OwNo ratings yet
- 5.1 QuestionsDocument24 pages5.1 QuestionsHalil ZeybekogullariNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Energetics TestDocument8 pages2.1 Energetics TestLordie DlaNo ratings yet
- How Far QPDocument19 pagesHow Far QPsaadNo ratings yet
- Equilibria Part 1Document131 pagesEquilibria Part 1Raafi Mian Year 13No ratings yet
- Thermal and Statistical Physics - Mallett - BlumlerDocument27 pagesThermal and Statistical Physics - Mallett - BlumlerOswaldo Avalos QuispeNo ratings yet
- 5.1.2 Exam QuestionsDocument6 pages5.1.2 Exam QuestionsMaariya HasanNo ratings yet
- IB CHEMISTRY TEST KineticsDocument5 pagesIB CHEMISTRY TEST KineticsBeeta KhannaNo ratings yet
- A Group of Students Investigated The Effect of Concentration On The Rate of A ReactionDocument2 pagesA Group of Students Investigated The Effect of Concentration On The Rate of A ReactionMark FerdinandNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics WsDocument5 pagesThermodynamics Wsnturnaoglu25No ratings yet
- EnthalpyDocument5 pagesEnthalpydharmaraoNo ratings yet
- AQA Rates and Kinetics QP PDFDocument12 pagesAQA Rates and Kinetics QP PDFAhmad BustamiNo ratings yet
- Kinetics and EqulibriaDocument34 pagesKinetics and EqulibriaRimpa NagNo ratings yet
- Energetics: Q1. (A) State What Is Meant by The Term Mean Bond EnthalpyDocument95 pagesEnergetics: Q1. (A) State What Is Meant by The Term Mean Bond EnthalpyWeronika JRNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy ChangesDocument28 pagesEnthalpy Changesnxgqyj4rwxNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios de CiclosDocument20 pagesEjercicios de CiclosEkaterinNo ratings yet
- P4 EnergeticsDocument61 pagesP4 Energetics/ “Nu” /No ratings yet
- Jyoti EditedDocument10 pagesJyoti EditedheroNo ratings yet
- Energetics Question DatabaseDocument23 pagesEnergetics Question DatabaseKamrul Alam MasumNo ratings yet
- Course of Lectures On Magnetism of Lanthanide Ions Under Varying Ligand and Magnetic FieldsDocument92 pagesCourse of Lectures On Magnetism of Lanthanide Ions Under Varying Ligand and Magnetic FieldsuhramanNo ratings yet
- Topic Questions Qualitative AnalysisDocument26 pagesTopic Questions Qualitative Analysisjnf4krhk6bNo ratings yet
- Enthalpy Changes HWDocument13 pagesEnthalpy Changes HWChiwe Thando MatutaNo ratings yet
- Due: Mon March 14, 2022 @8am Weekend HomeworkDocument5 pagesDue: Mon March 14, 2022 @8am Weekend Homeworkade sianayNo ratings yet
- Energy Changes in Reactions Q1Document9 pagesEnergy Changes in Reactions Q1maryamhemed477No ratings yet
- Unit 2 1 A Energetics 2 Student NoteDocument5 pagesUnit 2 1 A Energetics 2 Student NoteshivashankaranrishiNo ratings yet
- Test Particle PhysicsDocument7 pagesTest Particle PhysicsAhmed HossainNo ratings yet
- Chem p4 TestDocument15 pagesChem p4 TestIbrahim MagayaNo ratings yet
- AS KineticsDocument41 pagesAS Kineticsvintu pvNo ratings yet
- FuelDocument80 pagesFuelalberth_carantónNo ratings yet
- Revision Unit 5Document63 pagesRevision Unit 5Mohammed Mohammed Al HassanNo ratings yet
- 680 KJ Mol +158 KJ Mol +715 KJ Mol: (Total 4 Marks)Document14 pages680 KJ Mol +158 KJ Mol +715 KJ Mol: (Total 4 Marks)baba23993No ratings yet
- Energetics Revision Exam QuestionsDocument13 pagesEnergetics Revision Exam QuestionsDulshan JayNo ratings yet
- A-Level Ap2 Paper 2Document13 pagesA-Level Ap2 Paper 2Just WadeNo ratings yet
- 2.3.1 Enthalpy ChangesDocument25 pages2.3.1 Enthalpy ChangesRobert EdwardsNo ratings yet
- WS 4 (18.07.22)Document4 pagesWS 4 (18.07.22)Micheelle JeannethNo ratings yet
- Logical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeFrom EverandLogical progression of twelve double binary tables of physical-mathematical elements correlated with scientific-philosophical as well as metaphysical key concepts evidencing the dually four-dimensional basic structure of the universeNo ratings yet
- The Admissible Dual of GL(N) via Compact Open Subgroups. (AM-129), Volume 129From EverandThe Admissible Dual of GL(N) via Compact Open Subgroups. (AM-129), Volume 129No ratings yet
- A Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsFrom EverandA Modern Course in Statistical PhysicsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- 55th International Mendeleev Olympiad 20Document6 pages55th International Mendeleev Olympiad 20Thành Lê MậuNo ratings yet
- Pratt & Whitney Standard Practices Manual (PN 585005)Document22 pagesPratt & Whitney Standard Practices Manual (PN 585005)Paul FisherNo ratings yet
- Fco PTMMC Gar 42-40Document5 pagesFco PTMMC Gar 42-40mahendrarakasiwi631No ratings yet
- SAES-B-068 Editorial Revision (10-28-2021)Document17 pagesSAES-B-068 Editorial Revision (10-28-2021)Daniel MeanaNo ratings yet
- Coronary Stent DesignDocument79 pagesCoronary Stent DesignVickysh MevawalaNo ratings yet
- Macromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesMacromolecules. Monomers: Bio 11O Topic 5 - BiomoleculesYda TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Form 1 Term 1 Examination 2024Document97 pagesForm 1 Term 1 Examination 2024henryNo ratings yet
- Microbial Physiology LectureDocument88 pagesMicrobial Physiology LectureDaniNo ratings yet
- Fritz PakDocument159 pagesFritz PakTik TakNo ratings yet
- Course Syllabus - : Chem 1Document2 pagesCourse Syllabus - : Chem 1Janea PelpinosasNo ratings yet
- Sizing and Selection of HydrocyclonesDocument2 pagesSizing and Selection of HydrocyclonesaghilifNo ratings yet
- Experiment 18-SalivaDocument3 pagesExperiment 18-SalivaBismah SaeedNo ratings yet
- Nitrile Oxides A Key Intermediate in Organic SynthesisDocument12 pagesNitrile Oxides A Key Intermediate in Organic Synthesispopescu vasilicaNo ratings yet
- Angélica García-Quintero - 2021Document22 pagesAngélica García-Quintero - 2021sorinamotocNo ratings yet
- Cable Trench Installation Guide: 1.0 IndexDocument12 pagesCable Trench Installation Guide: 1.0 IndexThangarajan NagarajanNo ratings yet
- Blue Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsDocument22 pagesBlue Basic Concepts On Structure of SolidsME011Mohsin BilalNo ratings yet
- Glochem Industries Ltd. V/s Cadila Healthcare Ltd. & OthersDocument4 pagesGlochem Industries Ltd. V/s Cadila Healthcare Ltd. & OthersNaman MishraNo ratings yet
- 2022 - HULGAN and HARTEINK - Recent Advances in Collagen Mimetic Peptide Structure and DesignDocument15 pages2022 - HULGAN and HARTEINK - Recent Advances in Collagen Mimetic Peptide Structure and DesignCarlos FerreiraNo ratings yet
- Cleaning ProceduresDocument16 pagesCleaning ProceduresHữuĐầuĐấtNo ratings yet
- Wavin PPR Green Product GuideDocument24 pagesWavin PPR Green Product GuideGeorge Uche Anijah-obiNo ratings yet
- ZAID TS REM-2 MergedDocument35 pagesZAID TS REM-2 MergedSudip NeupaneNo ratings yet
- Injection Molding Reference Guide Inject PDFDocument96 pagesInjection Molding Reference Guide Inject PDFMario Allesina JuniorNo ratings yet
- Ibuprofen - Grupa 19Document6 pagesIbuprofen - Grupa 19Daniela PopaNo ratings yet
- Plant CellDocument112 pagesPlant CellAlfonso PlantillaNo ratings yet
- Zinc/Aluminum Corrosion Protective Coatings For FastenersDocument3 pagesZinc/Aluminum Corrosion Protective Coatings For FastenersDarwin DarmawanNo ratings yet
- 2019 ACJC Prelim H2 Chem P2 QPDocument22 pages2019 ACJC Prelim H2 Chem P2 QPYao Le Titanium ChenNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Questions Tnusrb S. I - 2010: Part - A': General KnowledgeDocument21 pagesPrevious Year Questions Tnusrb S. I - 2010: Part - A': General Knowledgemohamed AzathNo ratings yet
- MCQ On The Periodic TableDocument21 pagesMCQ On The Periodic TableIsabella EhizomohNo ratings yet