Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ー Refuting evidence ー Research is correlational ー Too deterministic
ー Refuting evidence ー Research is correlational ー Too deterministic
Uploaded by
Kai KokoroOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ー Refuting evidence ー Research is correlational ー Too deterministic
ー Refuting evidence ー Research is correlational ー Too deterministic
Uploaded by
Kai KokoroCopyright:
Available Formats
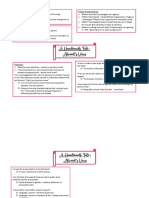
INFLUENCE OF EARLY ATTACHMENT
AO1:
Later childhood: Adulthood: Maternal deprivation (emotional and
The type of attachment formed is associated According to the internal working model, the intellectual):
with the quality of peer relationships within first relationship formed between an infant and
childhood caregiver will provide a mental representation Emotional effects
which is a template for future relationships Affectionless psychopathy and the difficulty to
Securely attached infants go on to form the form later relationships
best peer relationships/childhood friendships The quality of the child’s first attachment will
where as insecurely attached infants tend to determine the quality of their future Intellectual effects
have friendship difficulties relationships Mental retardation
(Goldforb) – institutionalised children have
(Smith et al.) – Bullying behaviour can also be A child’s who’s first experience us that of a lower IQs due to a lack of intellectual
linked to attachment type loving relationship will have a good template stimulation
for future relationships
Securely attached children are very unlikely to
be involved in any bullying Where as a child who’s first experience of
attachment is bad is going to have a bad
Insecure avoidant children were most likely to template for future relationships
be victims of bullying
Insecure resistant children were most likely to
be bullies
AO2/AO3:
Supporting evidence ー Refuting evidence ー Research is correlational ー Too deterministic
P A strength of research into early P A weakness of our understanding P A weakness of research on the P A weakness of the IWM as an
influence of attachment on adult of early attachment on later influence of early attachment on explanation of adult relationships
relationships is that there is development is there is refuting later relationships is that it is is that it is too deterministic
supporting research evidence for the internal working correlational E The internal working model
E For example, Hazan and Shaver model E For example, research linking suggests that early experiences
asked participants to take part in E For example, Fraley conducted a IWM and early attachment with have a fixed effect on later adult
a ‘Love Quiz’ which asked about review of 27 samples where later relationships is correlational relationships and children who
current relationship experiences, infants were assessed in infancy rather than experimental, thus are insecurely attached are
their attitudes towards ‘love’ and and reassessed later in childhood. we can’t claim that attachment certain not to experience
aimed to identify the participants’ He found correlations ranging quality causes relationship satisfactory relationships in their
childhood attachment types. The from 0.1 to 0.5. Such low experiences in later life to be adult life. However, Clarke and
found a positive correlation correlations indicate that the positive or negative. Moreover, Clarke have argued that problems
between the attachment type attachment type that infants factors like temperament may with attachment in early life do
and love experiences. Securely have may not be stable through affect the quality of childhood not guarantee difficult future
attached adults described their the course of their childhood and adult relationships. relationships, they just increase
love experiences as happy and E Therefore, this contradicts the According to Kagan, an infant’s the risk of them. Furthermore, an
trusting and they also have longer proposal that early attachments temperament is likely to individual who did not have a
relationships than those with set a long-lasting, stable template influence many aspects of a good relationship with their
resistant or avoidant attachment for future relationships person’s development, including caregiver or caregivers may make
types L This reduces the validity of their attachments an active effort to form better
E This suggests that childhood Bowlby’s internal working model E This is a problem as this indicates relationships in future
attachment type has some that early attachments are only E This indicates that individuals
influence over later relationships, part of the explanation of future have more conscious control over
with secure attachments relationships and should not be the success of future
associated with more successful seen as the cause of these relationships than according to
relationships relationships the internal working model
L These results therefore increase L As a result of the issues with the L Therefore, the IWM is overly
the validity of theories such as research, the validity of this deterministic in its perspective on
Bowlby’s internal working model, explanation is reduced adult relationships
as we can see early attachments
act as a template that affects
future relationships
NOTE: Only select the relevant AO1s (e.g. 2/3 points) and four evaluation points (AO2/AO3)
You might also like
- Risk For Loneliness NCPDocument2 pagesRisk For Loneliness NCPChloé Jane Hilario80% (10)
- The Handmaids Tale QuotesDocument33 pagesThe Handmaids Tale QuotesKai Kokoro100% (2)
- Step and Blended Families EssayDocument11 pagesStep and Blended Families EssayIlyssa YeNo ratings yet
- Bowlby - S Theory of AttachmentDocument1 pageBowlby - S Theory of AttachmentKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 Case StudyDocument6 pagesAssignment 2 Case Studyapi-427319867No ratings yet
- Laursen and Collins 2009 Handbook of Adolescent PsychologyDocument43 pagesLaursen and Collins 2009 Handbook of Adolescent PsychologyradityaadhitamaNo ratings yet
- Bowlby - S Theory of AttachmentDocument1 pageBowlby - S Theory of AttachmentKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- The Tempest - ALL ACTSDocument12 pagesThe Tempest - ALL ACTSKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- ー Studies do not tell us the ー There are problems with testing ー There is refuting evidence for theDocument1 pageー Studies do not tell us the ー There are problems with testing ー There is refuting evidence for theKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Rakocevic-Medojevic, D. - Rani Stilovi Afektivne Vezanosti Kao Prediktori Kvaliteta Partnerskih Veza I Razvoda BrakaDocument11 pagesRakocevic-Medojevic, D. - Rani Stilovi Afektivne Vezanosti Kao Prediktori Kvaliteta Partnerskih Veza I Razvoda BrakaSvetlana RadovanovicNo ratings yet
- Bullying Through Attchment TheoryDocument11 pagesBullying Through Attchment Theoryjasmine joyceNo ratings yet
- Allen & Miga, 2010Document10 pagesAllen & Miga, 2010Jada WoodNo ratings yet
- Punyanunt Carter 2006 Evaluating The Effects of Attachment Styles On Relationship Maintenance Behaviors in FatherDocument9 pagesPunyanunt Carter 2006 Evaluating The Effects of Attachment Styles On Relationship Maintenance Behaviors in FatherDafin CNo ratings yet
- Attchment TheoryDocument7 pagesAttchment Theoryjasmine joyceNo ratings yet
- 3 6 The Influence of Early Attachment On Childhood and Adult Relationships 12-02-16Document26 pages3 6 The Influence of Early Attachment On Childhood and Adult Relationships 12-02-16Adam BlackwellNo ratings yet
- Attachment Resource Booklet E BookDocument17 pagesAttachment Resource Booklet E BookMonika BobanacNo ratings yet
- Psychological Impact of Parent-Adolescent Communication: A Critical AnalysisDocument13 pagesPsychological Impact of Parent-Adolescent Communication: A Critical AnalysisIJPHSNo ratings yet
- Parent Child Relationships During AdolesDocument42 pagesParent Child Relationships During AdolesspellshreemNo ratings yet
- PSYCH 223 Assignment 1 Serena PENG Jan 27, 2024Document4 pagesPSYCH 223 Assignment 1 Serena PENG Jan 27, 2024Kyo learnNo ratings yet
- s10826-021-01979-3Document13 pagess10826-021-01979-3ayaasakura.kirihaNo ratings yet
- Parental Bonding and Parent-Child Relationship Among Tertiary StudentsDocument17 pagesParental Bonding and Parent-Child Relationship Among Tertiary StudentsSunway UniversityNo ratings yet
- Parental Bonding and Parent-Child Relationship Among Tertiary StudentsDocument17 pagesParental Bonding and Parent-Child Relationship Among Tertiary StudentslaurahermosaNo ratings yet
- 03 Attachment Topic Essays Digital DownloadDocument25 pages03 Attachment Topic Essays Digital Downloadbasia100% (1)
- Attachment Model EssaysDocument25 pagesAttachment Model EssayslayomishoyemiNo ratings yet
- Parents and Child BehaviorDocument10 pagesParents and Child BehaviorCristina EneNo ratings yet
- Educ 1 - FinalsDocument9 pagesEduc 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Discussion 2Document3 pagesDiscussion 2cooper.ac.harrisNo ratings yet
- The Academic Effects of Romantic Relationships To K-12 Students in An Aeronautical School in Lombos Ave. S.Y. 2019-2020Document37 pagesThe Academic Effects of Romantic Relationships To K-12 Students in An Aeronautical School in Lombos Ave. S.Y. 2019-2020MV ANo ratings yet
- Parent-Adolescent ReciprocityDocument16 pagesParent-Adolescent ReciprocitypoopmanNo ratings yet
- Working IrbDocument19 pagesWorking Irbapi-539922879No ratings yet
- C2. Handbook of Attachment, 2008. 419-435Document17 pagesC2. Handbook of Attachment, 2008. 419-435Anonymous 2Oq2t3qNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0191886920306000 MainDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S0191886920306000 MainOana OrosNo ratings yet
- Content ServerDocument14 pagesContent ServerBenito CalasNo ratings yet
- Khan 2017 The Impact of Fathers On Child Mental HealthDocument14 pagesKhan 2017 The Impact of Fathers On Child Mental HealthDhiya HumairaNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Kecerdasan 4Document11 pagesJurnal Kecerdasan 4Nadzar AbdurrahmanNo ratings yet
- 2018 McCallDocument26 pages2018 McCallShabi EntertainerNo ratings yet
- Pbi 3Document17 pagesPbi 3Abi Nuri AnjaniNo ratings yet
- PR2 Chapter 1 Group 1Document19 pagesPR2 Chapter 1 Group 1Kyle Chloe BalistaNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Effects of Teenage Romantic Relationship in Academic PerformanceDocument6 pagesGroup 6 Effects of Teenage Romantic Relationship in Academic PerformanceKim Jendeuk HuxleyNo ratings yet
- The Advantages and Disadvantages of Preventing Students in Engaging Relationship at SFESDocument45 pagesThe Advantages and Disadvantages of Preventing Students in Engaging Relationship at SFESKnth Arhnfold Ugalde BonggoNo ratings yet
- Attachment Theory EvaluationDocument2 pagesAttachment Theory EvaluationEna Sion YsipNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Mecares YtacDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Mecares YtacDexter MecaresNo ratings yet
- PRDGHJJKKDocument11 pagesPRDGHJJKKrhiangidaNo ratings yet
- AdemolaDocument5 pagesAdemolaJohnNo ratings yet
- Attachment and Romantic RelationshipsDocument28 pagesAttachment and Romantic RelationshipsCatherine Masitsa OmondiNo ratings yet
- Ed101 The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument3 pagesEd101 The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesKenneth Herrera100% (2)
- Proposal PaperDocument7 pagesProposal Paperkate.mccandless14No ratings yet
- Perceptions Parents Intimate RelationshipsDocument23 pagesPerceptions Parents Intimate Relationshipslobont nataliaNo ratings yet
- BJDP 12445Document15 pagesBJDP 12445Susan KuriakoseNo ratings yet
- Attachment and Parenting Styles Influences On Adult RelationshipsDocument6 pagesAttachment and Parenting Styles Influences On Adult RelationshipsMaya MayaNo ratings yet
- Topic Essays AttachmentDocument25 pagesTopic Essays AttachmentShaty MohamedNo ratings yet
- Parental DisapprovalDocument24 pagesParental DisapprovalAirtonNo ratings yet
- Intimate 1Document9 pagesIntimate 1Josh RanceNo ratings yet
- Roles of AttachmentDocument5 pagesRoles of AttachmentNguyễn Thị Ngọc ÁnhNo ratings yet
- Fatima Tu Zahra 42-53Document12 pagesFatima Tu Zahra 42-53Mariem •.•No ratings yet
- Untitled Document 29Document11 pagesUntitled Document 29fatinadrihammryNo ratings yet
- RelationshipDocument2 pagesRelationshipalyNo ratings yet
- Socialization in The Context of The Family - Parent-Child Interaction-5Document1 pageSocialization in The Context of The Family - Parent-Child Interaction-5HoàngKimNgânNo ratings yet
- Intra-And Inter-Individual Differences in Adolescent Depressive Mood: The Role of Relationships With Parents and FriendsDocument14 pagesIntra-And Inter-Individual Differences in Adolescent Depressive Mood: The Role of Relationships With Parents and FriendsIsabella SánchezNo ratings yet
- Couple Empathy - The Mediator of Attachment Styles For PartnersDocument14 pagesCouple Empathy - The Mediator of Attachment Styles For PartnersddvruddhiNo ratings yet
- Case Studies 02Document8 pagesCase Studies 02russu52No ratings yet
- Children's Representations of Attachment and Positive Teacher-Child RelationshipsDocument19 pagesChildren's Representations of Attachment and Positive Teacher-Child RelationshipsLissette CampbellNo ratings yet
- Running Head: Parental Conflict and Infidelity 1Document11 pagesRunning Head: Parental Conflict and Infidelity 1Angelica NicholeNo ratings yet
- CSP 500 Resilience Paper DraftpdfDocument24 pagesCSP 500 Resilience Paper Draftpdfapi-741762310No ratings yet
- Anxious Preoccupied Attachment: Break the Cycle of Anxiety, Jealousy, Looming Fear, Abandonment of Nurture, Lack of Trust and Connection with Your Partner Without Feeling Unworthy of LoveFrom EverandAnxious Preoccupied Attachment: Break the Cycle of Anxiety, Jealousy, Looming Fear, Abandonment of Nurture, Lack of Trust and Connection with Your Partner Without Feeling Unworthy of LoveNo ratings yet
- Working Memory ModelDocument1 pageWorking Memory ModelKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Memory and The Multistore ModelDocument1 pageMemory and The Multistore ModelKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Consistent Findings From Laboratory Research Application To The Real WorldDocument1 pageConsistent Findings From Laboratory Research Application To The Real WorldKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Ainsworth Strange SituationDocument1 pageAinsworth Strange SituationKai Kokoro100% (1)
- Cognitive InterviewDocument1 pageCognitive InterviewKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Misleading InformationDocument1 pageMisleading InformationKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Animal Studies of AttachmentDocument1 pageAnimal Studies of AttachmentKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- ー Studies do not tell us the ー There are problems with testing ー There is refuting evidence for theDocument1 pageー Studies do not tell us the ー There are problems with testing ー There is refuting evidence for theKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- ー Biased sample ー Problems studying asocial stage ー Refuting evidence on multipleDocument1 pageー Biased sample ー Problems studying asocial stage ー Refuting evidence on multipleKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Learning Theory of AttachmentDocument1 pageLearning Theory of AttachmentKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Research Methods - Mega BookletDocument100 pagesResearch Methods - Mega BookletKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Theme Scene One Scene Two Scene Three Verbal Dominance Visual ComedyDocument3 pagesTheme Scene One Scene Two Scene Three Verbal Dominance Visual ComedyKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Research Methods - Mega Booklet - Mark SchemeDocument101 pagesResearch Methods - Mega Booklet - Mark SchemeKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- The Tempest Revision2Document36 pagesThe Tempest Revision2Kai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Holism and ReductionismDocument1 pageHolism and ReductionismKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Idiographic and NomotheticDocument1 pageIdiographic and NomotheticKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- ADHROS InfoDocument16 pagesADHROS InfoKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- AS Research Methods - Mark Scheme PackDocument33 pagesAS Research Methods - Mark Scheme PackKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- ReligionDocument2 pagesReligionKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- A Handmaids Tale: Atwood S ViewsDocument2 pagesA Handmaids Tale: Atwood S ViewsKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- In Dystopian Literature, Female Characters Are Presented UnfavourableDocument2 pagesIn Dystopian Literature, Female Characters Are Presented UnfavourableKai KokoroNo ratings yet
- Family ActDocument76 pagesFamily ActteicayNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument4 pagesProject ProposalPUTIAN, REYNA MARIE ANTONETTE S.100% (2)
- Final Proposal - Olivia MccarthyDocument9 pagesFinal Proposal - Olivia Mccarthyapi-541668778No ratings yet
- Case Summary TemplateDocument4 pagesCase Summary TemplateRonn SerranoNo ratings yet
- Sexualised Portrayal of Women in Men's Magazines: A SynopsisDocument5 pagesSexualised Portrayal of Women in Men's Magazines: A Synopsisriajethi12No ratings yet
- Junior High Department: Maria Salud F. Lerum College InstructorDocument6 pagesJunior High Department: Maria Salud F. Lerum College InstructorMary PedrezuelaNo ratings yet
- My DocumentDocument26 pagesMy Documentvipul skpNo ratings yet
- Advanced Counseling SkillsDocument14 pagesAdvanced Counseling SkillsabcdNo ratings yet
- Development Through The Lifespan 7th Edition Berk Solutions ManualDocument16 pagesDevelopment Through The Lifespan 7th Edition Berk Solutions Manualjosephrodriguez04121993gbm100% (23)
- Tracing Family Traits Using A GenogramDocument3 pagesTracing Family Traits Using A GenogramArvin VelascoNo ratings yet
- 30 Topics For English Conversation PDFDocument25 pages30 Topics For English Conversation PDFtinita stoessel100% (1)
- Biblical Sexual MoralityDocument5 pagesBiblical Sexual Moralityapi-231781675100% (1)
- The 6 Primary Types of BullyingDocument2 pagesThe 6 Primary Types of BullyingMaria Angela JuganasNo ratings yet
- Review of Related Literature: (Chapter 2) - 1Document5 pagesReview of Related Literature: (Chapter 2) - 1Julienne AquinoNo ratings yet
- Bullies Are CriminalsDocument1 pageBullies Are CriminalsHoney Grace Liwanag NicasioNo ratings yet
- Genograma - Convenciones. McGoldrick PDFDocument1 pageGenograma - Convenciones. McGoldrick PDFLarry Hardy100% (1)
- Early Marriage in Ethiopia: Causes and Health Consequences: Bogalech AlemuDocument3 pagesEarly Marriage in Ethiopia: Causes and Health Consequences: Bogalech Alemumadilshahzad217No ratings yet
- Communication Issues in MarriageDocument11 pagesCommunication Issues in Marriageoyinoje2004No ratings yet
- Extended FamiliesDocument13 pagesExtended Familiesapi-385995156No ratings yet
- Love, Courtship, and MarriageDocument73 pagesLove, Courtship, and MarriageAsher WayneNo ratings yet
- Adoption Domestic & Inter-Country: ADOPTION (Ra 8552 and Ra 8043)Document28 pagesAdoption Domestic & Inter-Country: ADOPTION (Ra 8552 and Ra 8043)Rhaegar Targaryen100% (1)
- Univerzitet U Kragujevcu Učiteljski Fakultet U Užicu: (Among Students)Document12 pagesUniverzitet U Kragujevcu Učiteljski Fakultet U Užicu: (Among Students)Тамара Д. ЈанковићNo ratings yet
- MassTPC Trans Rights Bill FactsheetDocument1 pageMassTPC Trans Rights Bill FactsheetNat'l Center for Transgender EqualityNo ratings yet
- Family Registration CardDocument3 pagesFamily Registration Cardapi-253357730No ratings yet
- 3 Main Reasons Why People Stop Being FriendsDocument1 page3 Main Reasons Why People Stop Being Friendspta26.hdNo ratings yet
- History of Human Marriage. Westermack - Vol.1Document606 pagesHistory of Human Marriage. Westermack - Vol.1JulianNo ratings yet
- Domestic Release Approval (Form B)Document10 pagesDomestic Release Approval (Form B)Sazali SaadNo ratings yet
- Literature Review: Pengaplikasian Teori Penetrasi Sosial Pada Aplikasi Online DatingDocument10 pagesLiterature Review: Pengaplikasian Teori Penetrasi Sosial Pada Aplikasi Online DatingNadhirah AmaniNo ratings yet