Professional Documents
Culture Documents
B (Q1) B (Q2) e CQ Ceq (Q1) Ceq (Q2)
B (Q1) B (Q2) e CQ Ceq (Q1) Ceq (Q2)
Uploaded by
Miles GrubbsOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
B (Q1) B (Q2) e CQ Ceq (Q1) Ceq (Q2)
B (Q1) B (Q2) e CQ Ceq (Q1) Ceq (Q2)
Uploaded by
Miles GrubbsCopyright:
Available Formats
HW 20
Section 7– 2 The Class B and Class AB Push- Pull Amplifiers
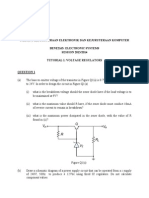
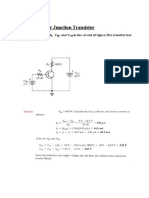
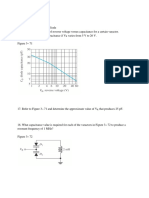
15. Refer to the class AB amplifier in Figure 7– 46 operating with a single power supply.
( a) Determine the dc parameters VB( Q1), VB( Q2), VE, ICQ, VCEQ( Q1), VCEQ( Q2).
( b) Assuming the input voltage is 10 V pp, determine the power delivered to the load resistor.
Figure 7– 46
16. Refer to the class AB amplifier in Figure 7– 46.
( a) What is the maximum power that could be delivered to the load resistor?
( b) Assume the power supply voltage is raised to 24 V. What is the new maximum power that
could be delivered to the load resistor?
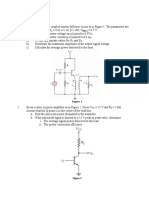
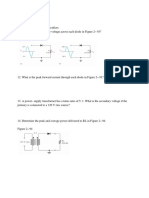
Section 7– 3 The Class C Amplifier
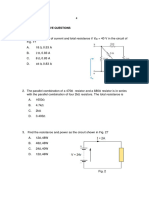
19. A certain class C amplifier transistor is on for 10 percent of the input cycle. If Vce(sat) = 0.18
V and Ic(sat) = 25 mA, what is the average power dissipation for maximum output?
20. What is the resonant frequency of a tank circuit with L = 10 mH and C = 0.001 uF?
21. What is the maximum peak-to-peak output voltage of a tuned class C amplifier with VCC =
12 V?
22. Determine the efficiency of the class C amplifier described in Problem 19 if VCC = 15 V and
the equivalent parallel resistance in the collector tank circuit is 50 Ω. Assume that the transistor
is on for 10% of the period.
Based upon:
FLOYD, THOMAS L., ELECTRONIC DEVICES (CONVENTIONAL CURRENT VERSION), 9th Ed., © 2012. Reprinted by
permission of Pearson Education, Inc., Upper Saddle River, NJ.
You might also like
- Tutorial C4 SEEU2012Document4 pagesTutorial C4 SEEU2012dukeNo ratings yet
- Problems-Chapter-4 - ContentsDocument7 pagesProblems-Chapter-4 - ContentsThiện NguyễnNo ratings yet
- HW 16Document3 pagesHW 16Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 6Document3 pagesHW 6Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 PDFDocument9 pagesTutorial 1 PDF马铃淑No ratings yet
- 153 - BEE107 - IEN00719 - 1612 - 12 - BEE107 Tutorial 7 HOMEWORKDocument2 pages153 - BEE107 - IEN00719 - 1612 - 12 - BEE107 Tutorial 7 HOMEWORKEcho WiieNo ratings yet
- Bipolar TransistorDocument9 pagesBipolar TransistorJitendra DubeyNo ratings yet
- Ans. (A) 0.32 W. (B) 2W, (C) 16%.: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman UEEA1333 Tutorial No: 6Document2 pagesAns. (A) 0.32 W. (B) 2W, (C) 16%.: Universiti Tunku Abdul Rahman UEEA1333 Tutorial No: 6y shuangNo ratings yet
- HW 15Document3 pagesHW 15Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4Document7 pagesAssignment 4Niraj Prasad YadavNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5 (Transistors)Document9 pagesAssignment 5 (Transistors)Rajesh PathakNo ratings yet
- BJT DC AnalysisDocument11 pagesBJT DC AnalysisShamganth KumarapandianNo ratings yet
- Important Questions For ExaminationDocument4 pagesImportant Questions For ExaminationSaurabh SinghNo ratings yet
- Bai Tap Ve BJT3Document23 pagesBai Tap Ve BJT3nguyenphuonghuy1979No ratings yet
- 4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetDocument19 pages4d8f8analog 1, Tut SheetmntykrNo ratings yet
- EN1802 Tutorial 2 PDFDocument4 pagesEN1802 Tutorial 2 PDFHashan ErandaNo ratings yet
- Taller01 FullDocument4 pagesTaller01 FullAlexander DitestaNo ratings yet
- HW 2Document10 pagesHW 2Kyto_oNo ratings yet
- Exercise Package 5Document4 pagesExercise Package 5Muhammad Sohaib ShahidNo ratings yet
- Assignment Electronics II.Document5 pagesAssignment Electronics II.lelisagetachew90No ratings yet
- SolutionDocument8 pagesSolutionPallavi SahuNo ratings yet
- Sheet 6 Electronics - AnswerDocument10 pagesSheet 6 Electronics - AnswerOla SamirNo ratings yet
- HW 19Document3 pagesHW 19Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial Sheet: = 10 Ω and V = 0.7 V. The load /N = 10/1. If the primary isDocument3 pagesTutorial Sheet: = 10 Ω and V = 0.7 V. The load /N = 10/1. If the primary isDaniel EkassiNo ratings yet
- Class C Amplifiers IntroDocument8 pagesClass C Amplifiers IntroTebogo SekgwamaNo ratings yet
- Class C Amplifier1Document8 pagesClass C Amplifier1qaisar ayubNo ratings yet
- 02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsDocument4 pages02 BJTs & BJT Amplifiers-ProblemsntldvlaiNo ratings yet
- Core-Iii-558-32511301 - Oc-Electronic Circuits-17-12-2020Document2 pagesCore-Iii-558-32511301 - Oc-Electronic Circuits-17-12-2020Sachin KumarNo ratings yet
- Wa0002.Document1 pageWa0002.GauravNo ratings yet
- Analog Electronics Practice QuestionsDocument19 pagesAnalog Electronics Practice Questionssharma_rockstarNo ratings yet
- Expt No 7 8Document3 pagesExpt No 7 8c.bhavesh2709No ratings yet
- Sheet 3 With SoluDocument7 pagesSheet 3 With SoluAmr HatemNo ratings yet
- HW 17Document3 pagesHW 17Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 26 03 23Document9 pagesTutorial 26 03 23Venkata TejaNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 26 03 23Document9 pagesTutorial 26 03 23pennzoilonprowlNo ratings yet
- Power Amplifier (Part 1)Document45 pagesPower Amplifier (Part 1)Ahmad FadliNo ratings yet
- Be 108064Document7 pagesBe 108064khalidfarooq40No ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 EEE1016 2022-2023 2Document5 pagesTutorial 3 EEE1016 2022-2023 2j2yshjzzsxNo ratings yet
- Assignment I PDFDocument1 pageAssignment I PDFRam SharmaNo ratings yet
- Work SheetDocument4 pagesWork Sheetsm7526359No ratings yet
- EC I EC2205 University Ques BankDocument14 pagesEC I EC2205 University Ques Bankkamalsrec78No ratings yet
- UNIT 2: Bipolar Junction TransistorDocument14 pagesUNIT 2: Bipolar Junction TransistorWaleed HåšhįmNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 2Document5 pagesSem 3 Module 2shubhendra2No ratings yet
- Tutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)Document23 pagesTutorial Problems: Bipolar Junction Transistor (Basic BJT Amplifiers)vineetha nagahageNo ratings yet
- L10 BJT Applications and BiasingDocument23 pagesL10 BJT Applications and BiasingpojanopeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1b: BJT Bias Design BJT Bias DesignDocument24 pagesChapter 1b: BJT Bias Design BJT Bias DesignAl AidenNo ratings yet
- Sheet 4 ElectronicsDocument4 pagesSheet 4 ElectronicsAhmed Abo nNo ratings yet
- QUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22Document10 pagesQUIZ 3-NOV23 - CH-1-2-3 - Feb22MUHAMMAD NUR AMNI KHARIMANNo ratings yet
- Training Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010Document6 pagesTraining Questions in Electronics/F 6, Gths K'Bo Paper Two: January 2010NGOUNENo ratings yet
- Solved Problems On Transistor Biasing Excellent StuffDocument15 pagesSolved Problems On Transistor Biasing Excellent StuffStudent Helper100% (1)
- Bjts DC BiasingDocument89 pagesBjts DC BiasingVenugopal ReddyvariNo ratings yet
- HW 1Document9 pagesHW 1Kyto_oNo ratings yet
- Experiment #3 ReportDocument7 pagesExperiment #3 Reportdc22846No ratings yet
- Transistors: Transfer ResistorDocument75 pagesTransistors: Transfer ResistorMuhammadAfriNo ratings yet
- Transistors: Transfer ResistorDocument75 pagesTransistors: Transfer ResistorNagarajan RajaNo ratings yet
- Eee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentDocument6 pagesEee-III-Analog Electronic Circuits (15ee34) - AssignmentchaitanyaNo ratings yet
- Sem 3 Module 3Document5 pagesSem 3 Module 3Joshua HernandezNo ratings yet
- Numericals on tranistor configurationDocument27 pagesNumericals on tranistor configurationvaishaliNo ratings yet
- Module2 PDFDocument16 pagesModule2 PDFSrihari UttanurNo ratings yet
- Question Bank - Principles of ElectronicsDocument13 pagesQuestion Bank - Principles of ElectronicsADDELYN CYNTHIA ANAK TONYNo ratings yet
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsFrom EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsNo ratings yet
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)From EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)No ratings yet
- HW 12Document3 pagesHW 12Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 23Document2 pagesHW 23Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 22Document3 pagesHW 22Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 17Document3 pagesHW 17Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 15Document3 pagesHW 15Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 21Document2 pagesHW 21Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 19Document3 pagesHW 19Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 14Document4 pagesHW 14Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document3 pagesHW 4Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 11Document3 pagesHW 11Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 7Document3 pagesHW 7Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 9Document2 pagesHW 9Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 10Document3 pagesHW 10Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet
- HW 3Document3 pagesHW 3Miles GrubbsNo ratings yet