Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mallari Nervous Bsn1c
Mallari Nervous Bsn1c
Uploaded by
Keith Charlotte MallariCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Case Study On CVADocument22 pagesCase Study On CVAAgronaSlaughter100% (3)
- Lecture 9. Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesLecture 9. Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemJaime Japana III100% (2)
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous Systemjeni antonyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Nervous SystemDocument68 pagesAutomatic Nervous SystemEurika De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Update 2008Document4 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Update 2008Ali Obadi AlhalemyNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemSAGAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Kevin L. Villarante BSN-II Nur104 Parmacology 2 1. Describe How The Autonomic Nervous System Differ ANATOMICALLY From The Rest of The Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesKevin L. Villarante BSN-II Nur104 Parmacology 2 1. Describe How The Autonomic Nervous System Differ ANATOMICALLY From The Rest of The Nervous SystemKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Pharma LE EndoANSCardioRenalDocument69 pagesPharma LE EndoANSCardioRenalnibbles nibblesNo ratings yet
- ANS, Brainstem Cranial NervesDocument50 pagesANS, Brainstem Cranial NervesK SNo ratings yet
- Autonom NerveDocument27 pagesAutonom NerveMochammad Fariz AmsalNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 NotesDocument50 pagesExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNo ratings yet
- Assignment Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesAssignment Autonomic Nervous Systemahmad72 raza72No ratings yet
- Bio Unit 5 ArticleDocument20 pagesBio Unit 5 Articlemyacerlaptop15No ratings yet
- ANSDocument38 pagesANSrexef82757No ratings yet
- Exam 3 NotesDocument50 pagesExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesParasympathetic Nervous SystemAdeelBaigNo ratings yet
- Case Study Wearing On Her NervesDocument42 pagesCase Study Wearing On Her Nervesapi-460556390No ratings yet
- 7 - Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument98 pages7 - Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindCikgu Diana IbnoNo ratings yet
- Woreta Health Science and Business College Autonomic Nrevous SystemDocument37 pagesWoreta Health Science and Business College Autonomic Nrevous SystemEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- Ans Ny-Ncp Part 2Document11 pagesAns Ny-Ncp Part 2fatimasulaimanishereNo ratings yet
- ANS Anatomy PhysiologyDocument13 pagesANS Anatomy PhysiologyAnonymous pZ0XZwQNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Anatomy - LecturioDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Anatomy - LecturioAlfred ZhikNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemHyacinth CorralesNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesParasympathetic Nervous SystemKushagra GoyalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument10 pagesAnatomy, Autonomic Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfwood landerNo ratings yet
- Z (H) IV Chordata SHDocument3 pagesZ (H) IV Chordata SHalshareefsaadalshareefNo ratings yet
- 05 - 06 - 07.curs Farmacologie Speciala (SNV)Document108 pages05 - 06 - 07.curs Farmacologie Speciala (SNV)madalinaNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document8 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)202210034No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Systemanaliane azucenaNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychDocument2 pagesBio PsychMichaela Jeanyvieve L. TabanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Physiotherapy, Beauty S, Sport S II Sem 24.04.20Document18 pagesLecture Physiotherapy, Beauty S, Sport S II Sem 24.04.20Alexander VonPatrickNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The ANSDocument95 pagesDrugs Affecting The ANSKhalid OmarNo ratings yet
- Pns and CnsDocument3 pagesPns and Cnsjlcanja5No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Autonomic Nervous SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument61 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemHashir SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and TheDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and Theawele lauraNo ratings yet
- Biology of MindOK1Document120 pagesBiology of MindOK16130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document59 pagesNervous System 1Benner BagsterNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemHaris QurashiNo ratings yet
- 12 Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument39 pages12 Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemVinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- 08 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument0 pages08 Autonomic Nervous SystemjuniorebindaNo ratings yet
- 5 Psychology BiopsychologyDocument7 pages5 Psychology BiopsychologyKawthar MajedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.doc AnsDocument8 pagesLecture 5.doc AnsElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- ANS RevisedDocument31 pagesANS Revisedr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- The Cns and The Pns 1Document9 pagesThe Cns and The Pns 1angelaagbonze82No ratings yet
- Autonomic NSDocument9 pagesAutonomic NSsanyamana935No ratings yet
- Veterinary Neuropharmacology VPT 321 Lecture Notes TANUVASDocument101 pagesVeterinary Neuropharmacology VPT 321 Lecture Notes TANUVASSunil89% (18)
- Farmacologie CURS 5 MGDocument44 pagesFarmacologie CURS 5 MGIonescu SarahNo ratings yet
- Biology: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesBiology: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelAyesha GulzarNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - HandoutsDocument5 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - HandoutsKelly Trainor100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemroseNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervus System: Dr. Meida Sofyana, MbiomedDocument26 pagesAutonomic Nervus System: Dr. Meida Sofyana, MbiomedAyu Tiara FitriNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemVarsha Shende KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument27 pagesCoordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve Homeostasiskate corveraNo ratings yet
- Ajpe78 Faal PDFDocument11 pagesAjpe78 Faal PDFrangga_rspNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemRashmi SainiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Bms129 Lecture 15Document6 pagesBms129 Lecture 15Mirelle YousefNo ratings yet
- ENT SGD 1 Clinical History and ENT Physical ExaminationDocument51 pagesENT SGD 1 Clinical History and ENT Physical ExaminationEmerson QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Project - Aids and CancerDocument6 pagesProject - Aids and CancerMihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument16 pagesSpecial Senses Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsMark Lester DeocarisNo ratings yet
- B.SC Nursing 3rd Year SyllabusDocument53 pagesB.SC Nursing 3rd Year SyllabusSooraj Krishna sNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Pediatric Endocrinology A Clinical Handbook Dennis M Styne Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Pediatric Endocrinology A Clinical Handbook Dennis M Styne Online PDF All Chaptergilliganczbch100% (5)
- Importent NoteDocument54 pagesImportent Notekhaled.s.alformNo ratings yet
- Os 1Document3 pagesOs 1rizwanNo ratings yet
- Shock Pathophysiology: AbstractDocument9 pagesShock Pathophysiology: AbstractHernan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Tongue LesionDocument26 pagesOral Pathology - Tongue Lesionneji_murniNo ratings yet
- Surgery LMRP 2019Document65 pagesSurgery LMRP 2019skNo ratings yet
- ChronobiologieDocument16 pagesChronobiologieHouda LaatabiNo ratings yet
- Executive FunctionsDocument6 pagesExecutive FunctionsEri CkNo ratings yet
- MnemonicS in OphthaDocument22 pagesMnemonicS in Ophthaabuahmed&janaNo ratings yet
- Excretion MCQ For year-8-Term-4-Ass-1Document3 pagesExcretion MCQ For year-8-Term-4-Ass-1Jihan KhanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cranial Osteopathic Manipulative MedicinDocument8 pagesEffect of Cranial Osteopathic Manipulative MedicinGiovanniNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Venous ThrombosisDocument14 pagesCerebral Venous ThrombosisSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Test Nuro 2Document11 pagesTest Nuro 2Litsa XeimariouNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Medical Terminology Learning Through Practice Paula Manuel Bostwick Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Medical Terminology Learning Through Practice Paula Manuel Bostwick Online PDF All Chapterakadlegesa100% (8)
- 17 CSF Rhinorrhea FB Nose Myiasis Choanal AtresiaDocument82 pages17 CSF Rhinorrhea FB Nose Myiasis Choanal AtresiayasinoNo ratings yet
- Science 6: Let'S Work Together!Document26 pagesScience 6: Let'S Work Together!Xivaughn SebastianNo ratings yet
- Yagihashi, Mechanism Diabetic Neuropathy, 2011Document15 pagesYagihashi, Mechanism Diabetic Neuropathy, 2011elbueno21No ratings yet
- Hernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsDocument43 pagesHernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsFobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Cerebellar AtaxiaDocument2 pagesLec 2 - Cerebellar AtaxiaEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- Abstract 11Document2 pagesAbstract 11LarisjoursNo ratings yet
- Pneumoencephalography - WikipediaDocument14 pagesPneumoencephalography - Wikipediadr.pcd.sushantaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System TransDocument21 pagesEndocrine System TransMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Management of Epilepsy & SeizuresDocument9 pagesEmergency Management of Epilepsy & SeizuresDavid MendozaNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document1,362 pagesWa0006.HimanshuNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument99 pagesNeoplasiaNazma AkterNo ratings yet
Mallari Nervous Bsn1c
Mallari Nervous Bsn1c
Uploaded by
Keith Charlotte MallariOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mallari Nervous Bsn1c
Mallari Nervous Bsn1c
Uploaded by
Keith Charlotte MallariCopyright:
Available Formats
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
NAME: MALLARI, KEITH CHARLOTTE M
BSN 1-C
Activity 8.1
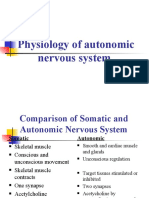
1. The Nervous System is classified into: Autom Nervous System, Parasympathetic Nervous System,
and Enteric Nervous System. In tabular form, differentiate each system.
NERVOUS SYSTEM
CLASSIFICATI DEFINITION FUNCTION PICTURES
ON
Autono Autonomic nervous The autonomic nervous
system, in vertebrates, system controls internal
mic the part of the nervous body processes such as the
Nervous system that controls following:
and regulates the Blood pressure
System internal organs without Heart and breathing rates
any conscious Body temperature
recognition or effort by Digestion
the organism. The Metabolism (thus affecting
autonomic nervous body weight)
system comprises two The balance of
antagonistic sets of water and electrolytes (suc
nerves, h as sodium and calcium)
the sympathetic and par The production of body
asympathetic nervous fluids (saliva, sweat, and
systems. tears)
Urination
The sympathetic Defecation
nervous Sexual response
system connects the
internal organs to
the brain by spinal
nerves. When
stimulated, these nerves
prepare the organism
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
for stress by increasing
the heart rate,
increasing blood flow to
the muscles, and
decreasing blood flow
to the skin. The nerve
fibres of
the parasympathetic
nervous system are
the cranial nerves,
primarily the vagus
nerve, and the lumbar
spinal nerves. When
stimulated, these nerves
increase digestive
secretions and reduce
the heartbeat.
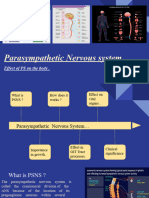
Parasympat Parasympathetic The functions of the PNS
hetic nervous system, division are commonly described as
Nervous of the nervous the “rest and
System system that primarily digest” response, since it is
modulates visceral orga involved in slowing down
ns such as glands. The the heart rate, relaxing the
parasympathetic system sphincter muscles in
is one of two the gastrointestinal and uri
antagonistic sets of nary tracts and increasing
nerves of the autonomic intestinal and gland
nervous system; the activity. The final result is
other conserving energy and
set comprises the sympa regulating basic bodily
thetic nervous system. functions such as digestion
While providing and urination. It is
important control of contrasted to the
many tissues, the sympathetic nervous
parasympathetic system system, which is described
is not crucial for the as the “fight and flight”
maintenance of life— response that occurs in
unlike the sympathetic stressful situations and has
system, which activates mainly opposite functions.
the so-called fight-or-
flight response. The
nerve fibres of the
parasympathetic
nervous system are
the cranial nerves,
primarily the vagus
nerve, and the
lumbar spinal nerves.
When stimulated, these
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
nerves increase
digestive secretions and
reduce the heartbeat.
Enteric The enteric nervous The enteric nervous
system (ENS) is a web system (ENS) controls
Nervous of sensory effector systems of
System neurons, motor the digestive tract,
neurons, consisting of the
and interneurons embe musculature, secretory
dded in the wall of the glands, and blood vessels.
gastrointesinal system, As in the central nervous
stretching from the system, circuits at the
lower third of the effector sites have evolved
esophagus right as an organized array of
through to the rectum. different kinds of neurons
The neurons of the ENS interconnected
are arranged in two by chemical synapses.
layers, the submucosal Function in the circuits is
and myenteric plexuses determined by generation
of the gut wall. It has of action potentials within
been estimated that the single neurons and
ENS actually contains chemical transmission of
more neurons than the information at the points
whole of the spinal of contact (i.e., synapses)
cord. The ENS processes between neurons. Action
a range of sensations, potentials transmit coded
such as the nature of information from one
gut contents and gut region of the neuron to
distension, and another.
integrates this
information with input
from the autonomic
nervous system.
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
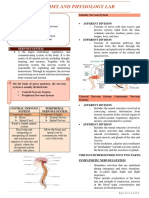
2. The Autonomic Nervous System is affected by the Sympathetic and Parasympathetic
Nervous System. In tabular form, differentiate the effects of sympathetics and
parasympathetics in various tissues and vital
organs in the body.
In the autonomic nervous system, a preganglionic neuron of
the CNS synapses with a postganglionic neuron of the PNS. The
postganglionic neuron, in turn, acts on a target organ.
Autonomic responses are mediated by the sympathetic and the
parasympathetic systems, which are antagonistic to one
another. The sympathetic system activates the “fight or flight”
response, while the parasympathetic system activates the “rest
and digest” response.
The sympathetic nervous system directs Once released, noradrenaline
the body's rapid involuntary response to and adrenaline bind adrenergic
dangerous or stressful situations. A flash receptors on peripheral tissues.
flood of hormones boosts the body's alertness Binding to adrenergic receptors
and heart rate, sending extra blood to the causes the effects seen during
muscles. the fight-or-flight response.
These include pupil dilation,
KIDNEY- when stimulated, have multitude of increased sweating, increased
heart rate, and increased blood
effects including increased renin secretion,
pressure.
decreased renal blood flow and increased
renal tubular sodium absorption[15]. These
changes contribute to the increased fluid
retention and sustenance of
vascular hypertension.
HEART- It releases the hormones
(catecholamines - epinephrine and
norepinephrine) to accelerate the heart rate.
LIVER- The sympathetic innervation to
the liver also influences ketone body
metabolism. In the
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
perfused liver model, sympathetic stimulation
inhibits hepatic ketogenesis, resulting in a
reduced ketone body output from the liver.
BLADDER- When the sympathetic nervous
system is active, it causes
the bladder to increase its capacity without
increasing detrusor resting pressure
(accommodation) and stimulates the
internal urinary sphincter to remain tightly
closed.
HEART- The parasympathetic nervous The parasympathetic activity
system (PNS) releases the hormone increases the contraction of
acetylcholine to slow the heart rate. smooth muscles present in
the wall of the gut. Thus, it
LIVER- Stimulation of several brain areas has promotes peristalsis and the
been shown to induce similar changes process of digestion.
in liver glucose metabolism as produced by The parasympathetic
direct stimulation of sympathetic system also promotes the
or parasympathetic nerves. These brain areas secretions of different glands
are either proposed or proven to be able associated with the
to affect liver glucose metabolism via alimentary tract.
their effect on autonomic neuronal output.
LUNGS- The lungs: Breathing slows down.
The bronchi (the tubes that bring air to
the lungs) also get narrower. The eyes: The
pupils get smaller. The digestive system:
Extra blood is sent to the stomach and
intestines.
BLADDER- When the bladder is full, afferent
activity conveying this information centrally
increases parasympathetic tone
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
Case Analysis 8.1.
A 53-year old male complained of left side body weakness associated with changes in
speech and sensorium. He was diagnosed as a case of Cerebrovascular Attack probably
Infarct vs. Bleed. You understand that thepathology is on the right side of the brain.
Discuss why this is so.
A pathologist is a medical doctor who specializes in
the classification and grading of tumors based on examining
tissue under the microscope and is responsible for the
management of various clinical laboratories.
Generally speaking, the left side of your brain controls the right
side of your body, and the right side of your brain
controls the left side of your body, according to the website
The Brain from Top to Bottom, which was written and
developed by Bruno Dubuc, a neuroscientist at McGill
University in Montreal.The brain has a commisure of both
sides of Brains . These commisures are crossing opposite to
each other making chyasmia. Thus making impulse travels
from right side of brain to left side of the bodily activities. if
you make across section through this chysmia then both sides
function will be lost. That is why we say right side of the brain
control left side of body & left side is control from right side of
the brain.
Individuals who lead a more active lifestyle manifest increased
survival and fewer adverse health outcomes.1 Physical activity is
a complex behavior that depends on diverse physiologic
systems, including musculoskeletal structures, systemic
metabolism, and cardiopulmonary systems, as well as neural
systems that originate in the brain.2 Thus, degeneration and
the accumulation of age-related pathologies in the brain may
lead to lower levels of physical activity. The planning,
initiation, and execution of physical activity are under
volitional control. Thus, in addition to assessing an individual's
motor capacity for example grip strength and gait speed, it is
crucial to assess the quantity of how much an individual
actually moves during the course of the day. Previous studies in
this cohort have shown that higher levels of diverse brain
pathologies are associated with lower levels of motor capacity
in community-dwelling older adults proximate to death.3,–
5 However, it is not known to what extent brain pathologies are
related to objective metrics of the quantity of total daily
physical activity in community-dwelling older adults.
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology
Cabanatuan City, Nueva Ecija
REFERENCES:
https://www.britannica.com/science/autonomic-nervous-system
https://www.britannica.com/science/parasympathetic-nervous-system
https://www.livescience.com/65446-sympathetic-nervous-system.html
https://www.medscape.com/answers/453539-45917/what-is-the-role-of-the-sympathetic-nervous-system-
in-the-neuroanatomy-of-neurogenic-bladder
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S092544391000013X
You might also like
- Case Study On CVADocument22 pagesCase Study On CVAAgronaSlaughter100% (3)
- Lecture 9. Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument19 pagesLecture 9. Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemJaime Japana III100% (2)
- Nervous SystemDocument20 pagesNervous Systemjeni antonyNo ratings yet
- Automatic Nervous SystemDocument68 pagesAutomatic Nervous SystemEurika De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Update 2008Document4 pagesAutonomic Nervous System Anatomy and Physiology Update 2008Ali Obadi AlhalemyNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemSAGAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Kevin L. Villarante BSN-II Nur104 Parmacology 2 1. Describe How The Autonomic Nervous System Differ ANATOMICALLY From The Rest of The Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesKevin L. Villarante BSN-II Nur104 Parmacology 2 1. Describe How The Autonomic Nervous System Differ ANATOMICALLY From The Rest of The Nervous SystemKevin VillaranteNo ratings yet
- Pharma LE EndoANSCardioRenalDocument69 pagesPharma LE EndoANSCardioRenalnibbles nibblesNo ratings yet
- ANS, Brainstem Cranial NervesDocument50 pagesANS, Brainstem Cranial NervesK SNo ratings yet
- Autonom NerveDocument27 pagesAutonom NerveMochammad Fariz AmsalNo ratings yet
- Exam 3 NotesDocument50 pagesExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNo ratings yet
- Assignment Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesAssignment Autonomic Nervous Systemahmad72 raza72No ratings yet
- Bio Unit 5 ArticleDocument20 pagesBio Unit 5 Articlemyacerlaptop15No ratings yet
- ANSDocument38 pagesANSrexef82757No ratings yet
- Exam 3 NotesDocument50 pagesExam 3 NotesAnonymous C6g8uUmWGNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDocument6 pagesParasympathetic Nervous SystemAdeelBaigNo ratings yet
- Case Study Wearing On Her NervesDocument42 pagesCase Study Wearing On Her Nervesapi-460556390No ratings yet
- 7 - Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindDocument98 pages7 - Chapter 2 - The Biology of MindCikgu Diana IbnoNo ratings yet
- Woreta Health Science and Business College Autonomic Nrevous SystemDocument37 pagesWoreta Health Science and Business College Autonomic Nrevous SystemEyachew TewabeNo ratings yet
- Ans Ny-Ncp Part 2Document11 pagesAns Ny-Ncp Part 2fatimasulaimanishereNo ratings yet
- ANS Anatomy PhysiologyDocument13 pagesANS Anatomy PhysiologyAnonymous pZ0XZwQNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - Anatomy - LecturioDocument20 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - Anatomy - LecturioAlfred ZhikNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesSympathetic and Parasymphatetic Nervous SystemHyacinth CorralesNo ratings yet
- Parasympathetic Nervous SystemDocument18 pagesParasympathetic Nervous SystemKushagra GoyalNo ratings yet
- Anatomy, Autonomic Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI BookshelfDocument10 pagesAnatomy, Autonomic Nervous System - StatPearls - NCBI Bookshelfwood landerNo ratings yet
- Z (H) IV Chordata SHDocument3 pagesZ (H) IV Chordata SHalshareefsaadalshareefNo ratings yet
- 05 - 06 - 07.curs Farmacologie Speciala (SNV)Document108 pages05 - 06 - 07.curs Farmacologie Speciala (SNV)madalinaNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)Document8 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)202210034No ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument2 pagesThe Nervous Systemanaliane azucenaNo ratings yet
- Bio PsychDocument2 pagesBio PsychMichaela Jeanyvieve L. TabanoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Physiotherapy, Beauty S, Sport S II Sem 24.04.20Document18 pagesLecture Physiotherapy, Beauty S, Sport S II Sem 24.04.20Alexander VonPatrickNo ratings yet
- Drugs Affecting The ANSDocument95 pagesDrugs Affecting The ANSKhalid OmarNo ratings yet
- Pns and CnsDocument3 pagesPns and Cnsjlcanja5No ratings yet
- Anatomy of The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument27 pagesAnatomy of The Autonomic Nervous SystemKELVINNo ratings yet
- The Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument61 pagesThe Autonomic Nervous SystemHashir SiddiquiNo ratings yet
- Peripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and TheDocument3 pagesPeripheral Nervous System: Division of The PNS and Theawele lauraNo ratings yet
- Biology of MindOK1Document120 pagesBiology of MindOK16130019037 FATCHUR RIZQI HAMZAHNo ratings yet
- Nervous System 1Document59 pagesNervous System 1Benner BagsterNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument15 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemHaris QurashiNo ratings yet
- 12 Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument39 pages12 Physiology of Autonomic Nervous SystemVinod SharmaNo ratings yet
- 08 Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument0 pages08 Autonomic Nervous SystemjuniorebindaNo ratings yet
- 5 Psychology BiopsychologyDocument7 pages5 Psychology BiopsychologyKawthar MajedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5.doc AnsDocument8 pagesLecture 5.doc AnsElijah KamaniNo ratings yet
- ANS RevisedDocument31 pagesANS Revisedr74k8zgg8rNo ratings yet
- The Cns and The Pns 1Document9 pagesThe Cns and The Pns 1angelaagbonze82No ratings yet
- Autonomic NSDocument9 pagesAutonomic NSsanyamana935No ratings yet
- Veterinary Neuropharmacology VPT 321 Lecture Notes TANUVASDocument101 pagesVeterinary Neuropharmacology VPT 321 Lecture Notes TANUVASSunil89% (18)
- Farmacologie CURS 5 MGDocument44 pagesFarmacologie CURS 5 MGIonescu SarahNo ratings yet
- Biology: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelDocument4 pagesBiology: Pearson Edexcel International Advanced LevelAyesha GulzarNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous System - HandoutsDocument5 pagesAutonomic Nervous System - HandoutsKelly Trainor100% (1)
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument25 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemroseNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervus System: Dr. Meida Sofyana, MbiomedDocument26 pagesAutonomic Nervus System: Dr. Meida Sofyana, MbiomedAyu Tiara FitriNo ratings yet
- Autonomic Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesAutonomic Nervous SystemVarsha Shende KhobragadeNo ratings yet
- Coordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve HomeostasisDocument27 pagesCoordination of Nervous System and Endocrine System To Achieve Homeostasiskate corveraNo ratings yet
- Ajpe78 Faal PDFDocument11 pagesAjpe78 Faal PDFrangga_rspNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument48 pagesNervous SystemRashmi SainiNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument3 pagesNervous SystemCUESCANO, CRISTEL G. BSMT 2-ANo ratings yet
- Bms129 Lecture 15Document6 pagesBms129 Lecture 15Mirelle YousefNo ratings yet
- ENT SGD 1 Clinical History and ENT Physical ExaminationDocument51 pagesENT SGD 1 Clinical History and ENT Physical ExaminationEmerson QuimbaNo ratings yet
- Project - Aids and CancerDocument6 pagesProject - Aids and CancerMihir SagarNo ratings yet
- Special Senses Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsDocument16 pagesSpecial Senses Anatomy and Physiology - NurseslabsMark Lester DeocarisNo ratings yet
- B.SC Nursing 3rd Year SyllabusDocument53 pagesB.SC Nursing 3rd Year SyllabusSooraj Krishna sNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Pediatric Endocrinology A Clinical Handbook Dennis M Styne Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Pediatric Endocrinology A Clinical Handbook Dennis M Styne Online PDF All Chaptergilliganczbch100% (5)
- Importent NoteDocument54 pagesImportent Notekhaled.s.alformNo ratings yet
- Os 1Document3 pagesOs 1rizwanNo ratings yet
- Shock Pathophysiology: AbstractDocument9 pagesShock Pathophysiology: AbstractHernan GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Oral Pathology - Tongue LesionDocument26 pagesOral Pathology - Tongue Lesionneji_murniNo ratings yet
- Surgery LMRP 2019Document65 pagesSurgery LMRP 2019skNo ratings yet
- ChronobiologieDocument16 pagesChronobiologieHouda LaatabiNo ratings yet
- Executive FunctionsDocument6 pagesExecutive FunctionsEri CkNo ratings yet
- MnemonicS in OphthaDocument22 pagesMnemonicS in Ophthaabuahmed&janaNo ratings yet
- Excretion MCQ For year-8-Term-4-Ass-1Document3 pagesExcretion MCQ For year-8-Term-4-Ass-1Jihan KhanNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cranial Osteopathic Manipulative MedicinDocument8 pagesEffect of Cranial Osteopathic Manipulative MedicinGiovanniNo ratings yet
- Cerebral Venous ThrombosisDocument14 pagesCerebral Venous ThrombosisSrinivas PingaliNo ratings yet
- Test Nuro 2Document11 pagesTest Nuro 2Litsa XeimariouNo ratings yet
- Full Ebook of Medical Terminology Learning Through Practice Paula Manuel Bostwick Online PDF All ChapterDocument69 pagesFull Ebook of Medical Terminology Learning Through Practice Paula Manuel Bostwick Online PDF All Chapterakadlegesa100% (8)
- 17 CSF Rhinorrhea FB Nose Myiasis Choanal AtresiaDocument82 pages17 CSF Rhinorrhea FB Nose Myiasis Choanal AtresiayasinoNo ratings yet
- Science 6: Let'S Work Together!Document26 pagesScience 6: Let'S Work Together!Xivaughn SebastianNo ratings yet
- Yagihashi, Mechanism Diabetic Neuropathy, 2011Document15 pagesYagihashi, Mechanism Diabetic Neuropathy, 2011elbueno21No ratings yet
- Hernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsDocument43 pagesHernia: Inguinal - Surgical Anatomy, Presentation, Treatment, ComplicationsFobin VargheseNo ratings yet
- Lec 2 - Cerebellar AtaxiaDocument2 pagesLec 2 - Cerebellar AtaxiaEmily MurrayNo ratings yet
- Abstract 11Document2 pagesAbstract 11LarisjoursNo ratings yet
- Pneumoencephalography - WikipediaDocument14 pagesPneumoencephalography - Wikipediadr.pcd.sushantaNo ratings yet
- Endocrine System TransDocument21 pagesEndocrine System TransMa. Mil Adrianne PamaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Management of Epilepsy & SeizuresDocument9 pagesEmergency Management of Epilepsy & SeizuresDavid MendozaNo ratings yet
- Wa0006.Document1,362 pagesWa0006.HimanshuNo ratings yet
- NeoplasiaDocument99 pagesNeoplasiaNazma AkterNo ratings yet