Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHAPTER 12 Management
CHAPTER 12 Management
Uploaded by
Michelle Ruth Abella0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views5 pagesHuman resource management involves attracting, developing, and maintaining an effective workforce. It includes hiring the right people, developing employees' skills to help the organization succeed, and retaining top talent. The changing social contract and legislation impact how employers manage human resources. Key aspects of human resource management are human resource planning, recruiting the best candidates, and using interviews and assessments during selection.
Original Description:
Business Management Chapter 12 NOTES
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentHuman resource management involves attracting, developing, and maintaining an effective workforce. It includes hiring the right people, developing employees' skills to help the organization succeed, and retaining top talent. The changing social contract and legislation impact how employers manage human resources. Key aspects of human resource management are human resource planning, recruiting the best candidates, and using interviews and assessments during selection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
285 views5 pagesCHAPTER 12 Management
CHAPTER 12 Management
Uploaded by
Michelle Ruth AbellaHuman resource management involves attracting, developing, and maintaining an effective workforce. It includes hiring the right people, developing employees' skills to help the organization succeed, and retaining top talent. The changing social contract and legislation impact how employers manage human resources. Key aspects of human resource management are human resource planning, recruiting the best candidates, and using interviews and assessments during selection.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 5
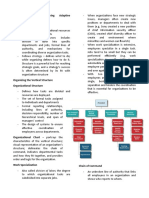
CHAPTER 12 – Human Resource Management Hiring the right people for improving
quality, innovation, and customer
Human Resource Management
service
- The design and application of formal Knowing the right people to retain after
systems in an organization to ensure the
effective and efficient use of human
talent to accomplish organization goals.
- Includes activities undertaken to attract,
develop, and maintain an effective
workforce.
- Managers have to find the right people,
place them in positions where they can
be most effective, and develop them so
they contribute to the company’s
success.
Human Capital
- Top factor in maintaining competitive
success, which reflects the critical role
of managing talent.
- The economic value of the combined mergers, acquisitions, or downsizing
knowledge, experience, skills, and Hiring the right people to apply new
capabilities of employees.
Three Key Elements in the Strategic
Approach to HRM
(1) All managers are involved in
managing human resources
(2) Employees are viewed as assets.
No strategy can be implemented
effectively without the right
people to put it into action.
Employees give a company its
competitive edge.
(3) HRM is a matching process,
integrating the organization’s
strategy and goals with the correct
approach to managing human
capital
Strategic Issues of Particular Concern to
Managers
Hiring the right people to become
more competitive on a global basis information technology for e-business
Building Human Capital to Drive Performance
The Changing Social Contract
Employer Brand: similar to a product brand
except that rather than promoting a specific
product, its aim is to make the organization
The Impact of Federal Legislation on HRM seem like a highly desirable place to work.
- HR managers have to understand and Contingent Worker: people who work for an
apply a variety of federal laws that organization but not on a permanent or full-
prohibit discrimination, establish safety time basis. Many of these workers are
standards, or require organizations to ‘involuntary’ temporary or part-time workers
provide certain benefits. who lost their jobs during the recession.
Discrimination: when hiring and promotion Telecommuting: using computers and
decisions are made based on criteria that are telecommunications equipment to do work
not job relevant; for example, refusing to hire a without going to an office.
black applicant for a job he is qualified to fill
and paying a woman a lower wage than a man
for the same work are discriminatory acts.
Affirmative Action: requires that an employer
take positive steps to guarantee equal
employment opportunities for people within
protected groups.
reflect the importance of
the human factor in the
organization’s success.
Many organizations use
internal recruiting or
promote-from-within
policies, to fill their high-
level positions.
Internal Recruiting – less
^ The Changing Social Contract ^ costly than an external
search, and generates higher employee
Matching Model – where the organization and commitment, development, and satisfaction
the individual attempt to match the needs, because it offers career advancement to
interests, and values that they offer each other. employees rather than outsiders.
External Recruiting –
recruiting newcomers from
outside the organization;
advantageous because
applicant are provided by a
variety of outside sources,
including advertising, state
employment services,
online recruiting services,
private employment
agencies (headhunters), job
fairs, and employee
referrals.
Human Resource Planning
Job Analysis: a systematic process of gathering
- The forecasting of HR needs and the and interpreting information about the
projected matching of individuals with essential duties, tasks, and responsibilities of a
expected vacancies. job, as well as about the context within which
- What new technologies are emerging, the job is performed; managers or specialists
and how will these affect the work ask about the work activities and work flow, the
system? degree of supervision given and received in the
- What is the volume of the business job, knowledge and skills needed, performance
likely to be in the next five to ten years? standards, working conditions, and so forth.
- What is the turnover rate and how
Job Description: a clear and concise summary
much, if any, is avoidable?
of the specific tasks, duties, and responsibilities
Recruiting – activities or practices that define and;
the characteristics of applicant to whom
Job Specification: outlines the knowledge,
selection procedures are ultimately applied. It
skills, education, physical abilities, and other
is sometimes referred to as talent acquisition to
characteristics needed to perform the job concealed when answering structured
adequately questions.
- Panel interview: the candidate meets
Realistic Job Previews: gives applicants all
with several interviewers who take
pertinent and realistic information – positive
turns asking questions.
and negative – about the job and the
- Extreme interviewing: test job
organization
candidates’ ability to handle problems,
Internships: an arrangement whereby an cope with change, and work well with
intern, usually a high school or college student, others.
exchanges his or her services for the
opportunity to gain work experience
and see whether a particular career
is appealing.
Internships are an
increasingly popular approach to
recruiting because they provide a
way to ‘test-drive’ a potential
employee
Selection: process of assessing the
skills, abilities, and other attributes
of applicants in an attempt to
determine the fir between the job
and each applicant’s characteristics
Application Form: a selection device
that collects information about the
applicant’s education, previous work
experience, and other background
characteristics
Employment tests: assess candidates on
Interview various factors considered important for the
job to be performed and include cognitive
- Used as a selection technique in almost ability tests, physical ability tests, and
every job category in nearly every personality tests
organization.
- Structured interview: uses a set of Assessment center: used to select individuals
standardized questions that are asked of with high managerial potential based on their
every applicant so comparisons can be performance on a series of simulated
made easily. managerial tasks.
- Nondirective interview: the interviewer
Work sample tests: evaluate their performance
asks broad, open-ended questions and
in completing simulated tasks that are a part of
permits the applicant to talk freely with
the job
minimal interruption, in an attempt to
bring to light information, attitudes, and *One way in which HR managers gauge an
behavioral characteristics that might be applicant’s suitability for an open position is by
checking what the applicant says on social
media sites. Maryland was the first state to Behaviorally anchored rating scale (BARS):
pass a law making it illegal to ask job applicants performance evaluation technique that relates
for their social networking passwords. and employee’s performance to specific job-
related incidents.
Compensation: refers to all monetary
TRAINING AND DEVELOPMENT
payments and all nonmonetary goods or
Training and development programs represent benefits used to reward employees
a planned effort by an organization to facilitate
Job evaluation: process of determining the
employees’ learning of job-related skills and
value of jobs within an organization through an
behaviors. Training typically refers to teaching
examination of job content
people skills needed in their current job,
whereas development refers to teaching people Wage and salary surveys: show what other
broader career skills organizations pay incumbents in jobs that
match a sample of key jobs selected by the
On-the-job Training: most common method of
organization
training; in which an experienced employee is
asked to teach a new employee how to perform Pay-for-performance: also called incentive pay,
job duties. means tying at least a portion of compensation
to employee effort and performance benefits
Social learning: using social media tools to
make up a large portion of labor costs in the
network and lean informally
US. During recession, many organizations have
Corporate University: in-house training and cut benefits that are not required by law
development facility that offers broad-based
Rightsizing: also called downsizing, refers to
learning opportunities for employees
reducing the company’s workforce intentionally
Performance Appraisal: process of observing to the point where the number of employees is
and evaluating an employee’s performance, deemed right for the company’s current
recording the assessment, and providing situation. If not managed effectively and
feedback humanely, rightsizing can lead to decreased
morale and performance.
360-degree feedback: uses multiple raters,
including self-rating, to appraise employee Exit interview: interview conducted with
performance and guide development departing employees to determine reasons for
their departure and learn about potential
*Performance review ranking systems are problems in the organization.
increasingly being criticized because they tend
to pit employees against one another rather
than promoting cooperation and teamwork.
Stereotyping: a performance evaluation error
that occurs when a manager places an
employee into a class or category based on one
or a few traits or characteristics
Halo effect: when a manager gives an
employee the same rating on all dimensions of
the job, even though performance may be good
on some and poor on others.
You might also like
- Organizational Behaviour PortfolioDocument13 pagesOrganizational Behaviour Portfolioapi-213064294No ratings yet
- Part 1Document1 pagePart 1wawanNo ratings yet
- The Usage of Social Media in The Workplace: An Argumentative EssayDocument8 pagesThe Usage of Social Media in The Workplace: An Argumentative EssayMichelle Ruth AbellaNo ratings yet
- (KMS1013) Assignment 2 by Group 19Document10 pages(KMS1013) Assignment 2 by Group 19Nur Sabrina AfiqahNo ratings yet
- Task 1 of Financial Management AssignmentDocument26 pagesTask 1 of Financial Management AssignmentWong Hui HuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: The Recording Process: Questions and AnswersDocument16 pagesChapter 2: The Recording Process: Questions and AnswersKarim KhaledNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Malaysian EconomyDocument15 pagesAssignment 1 Malaysian EconomyRoslyna khanNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3 (Marketing)Document12 pagesTutorial 3 (Marketing)P'NG RUI XUANNo ratings yet
- EPPM2033 W1 SEM2 20202021 - Introduction To International BusinessDocument45 pagesEPPM2033 W1 SEM2 20202021 - Introduction To International BusinessHaslindaNo ratings yet
- Company Law - Case Study 2Document7 pagesCompany Law - Case Study 2Diana Yong MeiChi100% (1)
- Strategic Management of Malaysian AirlineDocument7 pagesStrategic Management of Malaysian AirlineGeneisseNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Human Resource DDocument13 pagesThe Impact of Human Resource Dfareha riazNo ratings yet
- Assignment POM (AEON)Document4 pagesAssignment POM (AEON)maizatul athirahNo ratings yet
- Discussion Forum Assignment Help On Environmental Social GovernanceDocument9 pagesDiscussion Forum Assignment Help On Environmental Social GovernancejennifersmithsahNo ratings yet
- t8 - Abfa1153 Fa I (Tutor)Document3 pagest8 - Abfa1153 Fa I (Tutor)Wu kai AngNo ratings yet
- Administrative Reform ADS404Document13 pagesAdministrative Reform ADS404Eddie Edwansyah EidNo ratings yet
- MUET - Writing EssayDocument3 pagesMUET - Writing Essaywinn_07100% (1)
- Assignment Case Study SGHE5013Document27 pagesAssignment Case Study SGHE5013ctkhadeejaNo ratings yet
- Listening Practice Part 01Document7 pagesListening Practice Part 01Ernes Chia Nean ErnNo ratings yet
- ISDTDocument16 pagesISDTMohammad ArfanNo ratings yet
- Logica PEST Case StudyDocument4 pagesLogica PEST Case StudyMeltemNo ratings yet
- Acc406 Group AssignmentDocument16 pagesAcc406 Group AssignmentGladys DavidNo ratings yet
- LAW 309-Chapter 3Document11 pagesLAW 309-Chapter 3izatul294No ratings yet
- Case Study Ethical Dilemmas 2Document8 pagesCase Study Ethical Dilemmas 2AsiiyahNo ratings yet
- WRITING MuetDocument14 pagesWRITING MuetAhmad Ismail100% (2)
- Assignment May21 BDKM2103 Introductory Marketing CommunicationDocument10 pagesAssignment May21 BDKM2103 Introductory Marketing CommunicationSOBANAH A/P CHANDRAN STUDENTNo ratings yet
- OB - Chapter 14 - Case 1Document34 pagesOB - Chapter 14 - Case 1Vũ Hương ChiNo ratings yet
- Tuto5 BKAL DoneDocument8 pagesTuto5 BKAL DoneThe Four Incredible Hulks100% (1)
- Main Business and IFA IMPIANADocument7 pagesMain Business and IFA IMPIANAAlia NursyifaNo ratings yet
- Macro Environment and PESTL Analysis of Ford Car Manufacturing LTDDocument18 pagesMacro Environment and PESTL Analysis of Ford Car Manufacturing LTDShakeeb AhmedNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Determination of National IncomeDocument54 pagesChapter 3 - Determination of National IncomeHafizul Akmal100% (4)
- Hofstede in MalaysiaDocument3 pagesHofstede in MalaysiaWa Wa Jackson WongNo ratings yet
- Acc 116 - Chap 1Document12 pagesAcc 116 - Chap 1Azlie ArzimiNo ratings yet
- Vern's Company AnalysisDocument15 pagesVern's Company AnalysisShiqi Wang50% (2)
- Strategic Tactical and Operational Objectives - EditedDocument5 pagesStrategic Tactical and Operational Objectives - EditedAli RazaNo ratings yet
- AMIT 1703 IT Fundamentals and Application Tutorial 6 AnswersDocument3 pagesAMIT 1703 IT Fundamentals and Application Tutorial 6 AnswersWilliamLokNo ratings yet
- Macroeconomics Individual AssignmentDocument16 pagesMacroeconomics Individual AssignmentHafizul HelmyNo ratings yet
- Monopoly - Spec and Possible Essay QuestionsDocument2 pagesMonopoly - Spec and Possible Essay Questions詹堉梃No ratings yet
- Felda, Felcra Dan RisdaDocument3 pagesFelda, Felcra Dan RisdaasmawiNo ratings yet
- CHAP 2 Risk Magt ProDocument11 pagesCHAP 2 Risk Magt ProEbsa AdemeNo ratings yet
- Malaysia XportDocument14 pagesMalaysia XportNoly IthninNo ratings yet
- A143 Sqqs1013 Ga Group 10Document9 pagesA143 Sqqs1013 Ga Group 10Nurul Farhan IbrahimNo ratings yet
- Assignment Pad101Document4 pagesAssignment Pad101NURUL IZZATI AHMAD FERDAUSNo ratings yet
- TOPIC 2 ADS 465 HistoricalDocument23 pagesTOPIC 2 ADS 465 HistoricalAmylia IsmailNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management Exam 1 NotesDocument4 pagesPrinciples of Management Exam 1 Notestruckjones100% (1)
- Financial Analysis Nestle Malaysia Berhad For The Year 2019 A) Liquidity RatiosDocument13 pagesFinancial Analysis Nestle Malaysia Berhad For The Year 2019 A) Liquidity RatiosRawan NaderNo ratings yet
- Fsa FullDocument70 pagesFsa FullWai Kit WooNo ratings yet
- ADS 404 Chapter1Document14 pagesADS 404 Chapter1Damon CopelandNo ratings yet
- IMC 402 - Chapter 3Document67 pagesIMC 402 - Chapter 3Suzaini SupingatNo ratings yet
- BPMN1013 Chapter 6 MCQDocument14 pagesBPMN1013 Chapter 6 MCQNzw BbaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4.determinants of National Advantage, CompetitivenesDocument78 pagesChapter 4.determinants of National Advantage, CompetitivenesMarlon BoucaudNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Planning ProcessDocument3 pagesHuman Resource Planning ProcessG & E Apparel100% (1)
- PFP Group Assignment - 17032019Document38 pagesPFP Group Assignment - 17032019Chuah Chong AnnNo ratings yet
- Why Do Workers Join Trade Unions: - Economic NeedsDocument20 pagesWhy Do Workers Join Trade Unions: - Economic NeedsPayal Parmar100% (1)
- Griffin 9e PPT ch03Document44 pagesGriffin 9e PPT ch03Ngọc DươngNo ratings yet
- Group Assignment 2 (Report) HRM554 - Group 3Document9 pagesGroup Assignment 2 (Report) HRM554 - Group 3Mohd Rozi AmbranNo ratings yet
- Planning Organizing: The 5 Basic Functions of The Management Process AreDocument27 pagesPlanning Organizing: The 5 Basic Functions of The Management Process AreKamal AkzNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management - S3-2Document25 pagesHuman Resource Management - S3-2Aeimei JojiNo ratings yet
- Recruitment and SelectionDocument9 pagesRecruitment and Selectioneislaine.babylovesNo ratings yet
- Cbmec 2 ModuleDocument4 pagesCbmec 2 ModuleJacqueline Acera BalingitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14 ManagementDocument6 pagesChapter 14 ManagementMichelle Ruth AbellaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 10 ManagementDocument9 pagesCHAPTER 10 ManagementMichelle Ruth AbellaNo ratings yet
- Practical Research Chapter 4&5Document18 pagesPractical Research Chapter 4&5Michelle Ruth AbellaNo ratings yet
- Assignment Public Finance and Taxation - 2022-ExtensionDocument3 pagesAssignment Public Finance and Taxation - 2022-ExtensionMesfin YohannesNo ratings yet
- Capital Structure TheoriesDocument47 pagesCapital Structure Theoriesamol_more37No ratings yet
- Audit of Construction CompaniesDocument2 pagesAudit of Construction Companiesnicole bancoroNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Income From House PropertyDocument15 pagesChapter 2 - Income From House PropertyPuran GuptaNo ratings yet
- Oppurtunities On A Business - Swot AnalysisDocument3 pagesOppurtunities On A Business - Swot AnalysisMj AustriaNo ratings yet
- Modul Implementasi StrategiDocument44 pagesModul Implementasi StrategiPutri VioNo ratings yet
- Intrinsic Value Calculator. Book Value and Dividend GrowthDocument4 pagesIntrinsic Value Calculator. Book Value and Dividend GrowthrmilhoriniNo ratings yet
- Operating CostingDocument15 pagesOperating CostingBishnuNo ratings yet
- Problem StatementDocument6 pagesProblem StatementSyed Bilal AliNo ratings yet
- Solution Manual For Modern Advanced Accounting in Canada 9th Edition Darrell Herauf Murray HiltonDocument35 pagesSolution Manual For Modern Advanced Accounting in Canada 9th Edition Darrell Herauf Murray Hiltoncravingcoarctdbw6wNo ratings yet
- Total Financial RatiosDocument2 pagesTotal Financial RatioshoangsubaxdNo ratings yet
- SHRM Module 1 Topic 3Document10 pagesSHRM Module 1 Topic 3Aaron Christopher SungaNo ratings yet
- Aqa 80352 QP Jun22 CRDocument41 pagesAqa 80352 QP Jun22 CRratnam55369No ratings yet
- CH 12Document45 pagesCH 12Pulkit AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Non-Executive Director-Chairman: Type Traded AsDocument3 pagesNon-Executive Director-Chairman: Type Traded AsAyman KhalidNo ratings yet
- CIR Vs Team SualDocument2 pagesCIR Vs Team SualKim Patrick DayosNo ratings yet
- Organization of Petroleum Exporting CountriesDocument17 pagesOrganization of Petroleum Exporting CountriesTushar AtreyNo ratings yet
- Compliances Under Labour LawDocument15 pagesCompliances Under Labour LawSudhakar GanjikuntaNo ratings yet
- Mivumba in Kampala/Used Clothes TradeDocument49 pagesMivumba in Kampala/Used Clothes TradeMegan GarnerNo ratings yet
- AS-Solved Past Paper Business 9609 P1 2023-2022Document51 pagesAS-Solved Past Paper Business 9609 P1 2023-2022TheOfficialTitaniumNo ratings yet
- U.S. Individual Income Tax Return: Standard DeductionDocument15 pagesU.S. Individual Income Tax Return: Standard Deductionchantel100% (2)
- Ethic Assigment No 1Document32 pagesEthic Assigment No 1Sania ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 SHRMDocument75 pagesUnit 1 SHRMpinky Nath100% (1)
- Helmet Manufacturing Industry-293269 PDFDocument68 pagesHelmet Manufacturing Industry-293269 PDFJaydeep MoharanaNo ratings yet
- Plus One Business StudiesDocument8 pagesPlus One Business StudiesSHAHIN SNo ratings yet
- Actividad D1. Final Term Paper Maria FigueroaDocument6 pagesActividad D1. Final Term Paper Maria FigueroaEdith MezaNo ratings yet
- AL Brothers Prakashan: 7. Outcomes of DemocracyDocument7 pagesAL Brothers Prakashan: 7. Outcomes of DemocracyVino AldrinNo ratings yet
- 08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, InflationDocument3 pages08 Business Cycles, Unemployment, Inflationcatherine tucayNo ratings yet
- Surplus, Salvage & Scrap DisposalDocument5 pagesSurplus, Salvage & Scrap DisposalJoju Johny100% (1)
- India Strategy - InCred - 28 AugDocument37 pagesIndia Strategy - InCred - 28 AugDeepul WadhwaNo ratings yet