Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice Set
MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice Set
Uploaded by
ArunasvaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- VTAMPS 5.0 Primary 3 Set 5Document9 pagesVTAMPS 5.0 Primary 3 Set 5Lance AlfantaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Hypergeometric Integrals PDFDocument160 pagesHandbook of Hypergeometric Integrals PDFYohansli Noya100% (3)
- Middle Grades Mathematics 5-9: Test Information GuideDocument39 pagesMiddle Grades Mathematics 5-9: Test Information GuideGina OakleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Downfall 1944-1945Document29 pagesChapter 8. Downfall 1944-1945ArunasvaNo ratings yet
- MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice SetDocument6 pagesMAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice SetArunasvaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1ArunasvaNo ratings yet
- Getting Started: Synchronous Vs Asynchronous CoursesDocument15 pagesGetting Started: Synchronous Vs Asynchronous CoursesArunasvaNo ratings yet
- Compass Rule and Transit RuleDocument14 pagesCompass Rule and Transit RuleRommel Dave TejanoNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation With ParameterDocument1 pageQuadratic Equation With ParameterPaulino AdaoNo ratings yet
- EC - 402-2nd MsDocument4 pagesEC - 402-2nd MspankajmadhuNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials (CH.2) - SolutionsDocument108 pagesMechanics of Materials (CH.2) - SolutionsGary Falanga33% (3)
- Half Yearly Test Paper - EconomicsDocument3 pagesHalf Yearly Test Paper - Economicslohiyadhrumil2007No ratings yet
- Dimensional Transformation, Subtractive, Additive Forms and Organization of Additive FormsDocument7 pagesDimensional Transformation, Subtractive, Additive Forms and Organization of Additive Formsvarshini100% (1)
- Subject: DSTC++: Unit-I: Above Average Questions Short QuestionsDocument7 pagesSubject: DSTC++: Unit-I: Above Average Questions Short QuestionsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentAbubakr KhanNo ratings yet
- Cours Acide-Base en English PDFDocument22 pagesCours Acide-Base en English PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneNo ratings yet
- Turbulent and Laminar FlowDocument4 pagesTurbulent and Laminar FlowMuhammadAliNo ratings yet
- Myers O ND DiferenceDocument16 pagesMyers O ND DiferenceObelix1789No ratings yet
- 133 4 6Document3 pages133 4 6劉星雨No ratings yet
- Whole NumbersDocument20 pagesWhole NumbersMaria Aleda LoquiasNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Mathematical Methods of Statistics Pms 9 Volume 9 Harald Cramer Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Mathematical Methods of Statistics Pms 9 Volume 9 Harald Cramer Online Ebook All Chapter PDFsonia.sproles459100% (18)
- MCA Mathematical Foundation For Computer Application 05Document25 pagesMCA Mathematical Foundation For Computer Application 05Kasaijja AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Answer Key - Module 2 - Using Visual Basic Programming ConstructsDocument42 pagesLab Answer Key - Module 2 - Using Visual Basic Programming ConstructsJoemarco BernabeNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics MCQ - Answer KeyDocument54 pagesCAPE Physics MCQ - Answer KeyShafiqueDeshongNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q3 w10Document7 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q3 w10Ramil GalidoNo ratings yet
- Source of Basic CalDocument14 pagesSource of Basic CalJohn Jeric SiguanNo ratings yet
- Mco 03 em PDFDocument8 pagesMco 03 em PDFFirdosh Khan80% (5)
- Physics 323 Term Project Fall 2017Document3 pagesPhysics 323 Term Project Fall 2017petermcleod117No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem Proofs From Spherical Standing Wave StructurDocument39 pagesPythagorean Theorem Proofs From Spherical Standing Wave StructurCIDNOVNo ratings yet
- Torque TestDocument25 pagesTorque TestYodaNo ratings yet
- MGT201 Chapter 6Document35 pagesMGT201 Chapter 6ImRanSaudNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Present Worth AnalysisDocument17 pagesCh5 Present Worth AnalysisAshley JuddNo ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan DM SampleDocument17 pages5E Lesson Plan DM SampleAWNo ratings yet
- Nalla Details: 1. Catchment Area 0.290 SQKM 71.659 Acres 0.112 SqmileDocument7 pagesNalla Details: 1. Catchment Area 0.290 SQKM 71.659 Acres 0.112 Sqmile98675No ratings yet
MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice Set
MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice Set
Uploaded by
ArunasvaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice Set
MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice Set
Uploaded by
ArunasvaCopyright:
Available Formats
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
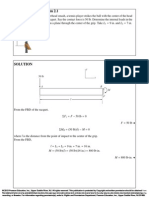
Q12. Consider the following system with six components. We say that it is
functional if there exists a path of functional components from left to right.
The probability of each component functions is shown. Assume that the
components function or fail independently. What is the probability that the
system operates?
a)0.1815 b)0.8185 c) 0.6370 d)0.2046 e) none of
the preceding
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 26
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
Solution: let Box A consist of components 2, 3, 4, 5, Box B consist of
components 2, 3, 4, and Box C consist of components 2, 3. We will denote
the probability that Box j operates by P (j), j ∈ {A, B, C}.
We are interested in the probability P (S) that the system operates. Because
the components function or fail independently,
P (S) = P (component 1 and Box A and component 6 operate)
= P (1 operates) × P (A) × P (6 operates)
= 0.5 · P (A) · 0.5 = 0.52P (A).
There are two ways for Box A to operate: either component 5 operates
(with probability 0.5) or Box B operates:
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 27
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
P (A) = P (component 5 operates or Box B operates)
= P (5 operates) + P (B)
− P (component 5 operates and Box B operates)
= P (5 operates) + P (B) − P (5 operates)P (B)
= 0.5 + P (B) − 0.5P (B) = 0.5(1 + P (B)).
Thus,
P (S) = 0.52P (A) = 0.52 · 0.5(1 + P (B) = 0.53(1 + P (B)).
In order for Box B to operate, we need both Box C and component 4 to
operate, so that
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 28
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
P (B) = P (Box C operates and component 4 operates)
= P (4 operates)P (C) = 0.7P (C).
Thus,
P (S) = 0.53(1 + P (B)) = 0.53(1 + 0.7P (C)).
Finally, there are two ways for Box C to operate: either component
2 operates (with probability 0.7) or component 3 operates (also with
probability 0.7):
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 29
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
P (C) = P (component 2 operates or component 3 operates)
= P (2 operates) + P (3 operates)
− P (components 2 operates and component 3 operates)
= P (2 operates) + P (3 operates) − P (2 operates)P (3 operates)
= 0.7 + 0.7 − 0.7 · 0.7 = 0.7(2 − 0.7) = 0.7 · 1.3.
Thus,
P (S) = 0.53(1 + 0.7P (C)) = 0.53(1 + 0.7 · 0.7 · 1.3)
= 0.53(1 + 0.72 · 1.3) = 0.24046.
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 30
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
Q13. Three events are shown in the Venn diagram below.
Shade the region corresponding to the following events:
a)Ac b)(A ∩ B) ∪ (A ∩ B c)
c) (A ∩ B) ∪ C d)(B ∪ C)c
e) (A ∩ B)c ∪ C
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 31
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
Solution:
a) This is the set of all outcomes not in A:
b) We can rewrite (A ∩ B) ∪ (A ∩ B c) = A ∩ (B ∪ B c) = A ∩ S = A, so
this is the set of all outcomes in A:
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 32
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
c) This is the set all outcomes either in C or in the intersection of A and B:
d) This is the set of all outcomes that are not in either B or C (or that are
neither in B nor in C):
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 33
MAT 2377 – Probability and Statistics for Engineers Practice Set
e) Since C and A ∪ B are mutually exclusive (disjoint), C ⊆ (A ∩ B)c and
(A ∩ B)c ∪ C = (A ∩ B)c, so this is the set of all outcomes not in A ∩ B:
Based on course notes by Rafal Kulik 34
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5834)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (405)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- VTAMPS 5.0 Primary 3 Set 5Document9 pagesVTAMPS 5.0 Primary 3 Set 5Lance AlfantaNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Hypergeometric Integrals PDFDocument160 pagesHandbook of Hypergeometric Integrals PDFYohansli Noya100% (3)
- Middle Grades Mathematics 5-9: Test Information GuideDocument39 pagesMiddle Grades Mathematics 5-9: Test Information GuideGina OakleyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8. Downfall 1944-1945Document29 pagesChapter 8. Downfall 1944-1945ArunasvaNo ratings yet
- MAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice SetDocument6 pagesMAT 2377 - Probability and Statistics For Engineers Practice SetArunasvaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1ArunasvaNo ratings yet
- Getting Started: Synchronous Vs Asynchronous CoursesDocument15 pagesGetting Started: Synchronous Vs Asynchronous CoursesArunasvaNo ratings yet
- Compass Rule and Transit RuleDocument14 pagesCompass Rule and Transit RuleRommel Dave TejanoNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equation With ParameterDocument1 pageQuadratic Equation With ParameterPaulino AdaoNo ratings yet
- EC - 402-2nd MsDocument4 pagesEC - 402-2nd MspankajmadhuNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials (CH.2) - SolutionsDocument108 pagesMechanics of Materials (CH.2) - SolutionsGary Falanga33% (3)
- Half Yearly Test Paper - EconomicsDocument3 pagesHalf Yearly Test Paper - Economicslohiyadhrumil2007No ratings yet
- Dimensional Transformation, Subtractive, Additive Forms and Organization of Additive FormsDocument7 pagesDimensional Transformation, Subtractive, Additive Forms and Organization of Additive Formsvarshini100% (1)
- Subject: DSTC++: Unit-I: Above Average Questions Short QuestionsDocument7 pagesSubject: DSTC++: Unit-I: Above Average Questions Short QuestionsNaveen KumarNo ratings yet
- AssignmentDocument9 pagesAssignmentAbubakr KhanNo ratings yet
- Cours Acide-Base en English PDFDocument22 pagesCours Acide-Base en English PDFالغزيزال الحسن EL GHZIZAL HassaneNo ratings yet
- Turbulent and Laminar FlowDocument4 pagesTurbulent and Laminar FlowMuhammadAliNo ratings yet
- Myers O ND DiferenceDocument16 pagesMyers O ND DiferenceObelix1789No ratings yet
- 133 4 6Document3 pages133 4 6劉星雨No ratings yet
- Whole NumbersDocument20 pagesWhole NumbersMaria Aleda LoquiasNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Mathematical Methods of Statistics Pms 9 Volume 9 Harald Cramer Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Mathematical Methods of Statistics Pms 9 Volume 9 Harald Cramer Online Ebook All Chapter PDFsonia.sproles459100% (18)
- MCA Mathematical Foundation For Computer Application 05Document25 pagesMCA Mathematical Foundation For Computer Application 05Kasaijja AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Answer Key - Module 2 - Using Visual Basic Programming ConstructsDocument42 pagesLab Answer Key - Module 2 - Using Visual Basic Programming ConstructsJoemarco BernabeNo ratings yet
- CAPE Physics MCQ - Answer KeyDocument54 pagesCAPE Physics MCQ - Answer KeyShafiqueDeshongNo ratings yet
- DLL Mathematics 6 q3 w10Document7 pagesDLL Mathematics 6 q3 w10Ramil GalidoNo ratings yet
- Source of Basic CalDocument14 pagesSource of Basic CalJohn Jeric SiguanNo ratings yet
- Mco 03 em PDFDocument8 pagesMco 03 em PDFFirdosh Khan80% (5)
- Physics 323 Term Project Fall 2017Document3 pagesPhysics 323 Term Project Fall 2017petermcleod117No ratings yet
- Pythagorean Theorem Proofs From Spherical Standing Wave StructurDocument39 pagesPythagorean Theorem Proofs From Spherical Standing Wave StructurCIDNOVNo ratings yet
- Torque TestDocument25 pagesTorque TestYodaNo ratings yet
- MGT201 Chapter 6Document35 pagesMGT201 Chapter 6ImRanSaudNo ratings yet
- Ch5 Present Worth AnalysisDocument17 pagesCh5 Present Worth AnalysisAshley JuddNo ratings yet
- 5E Lesson Plan DM SampleDocument17 pages5E Lesson Plan DM SampleAWNo ratings yet
- Nalla Details: 1. Catchment Area 0.290 SQKM 71.659 Acres 0.112 SqmileDocument7 pagesNalla Details: 1. Catchment Area 0.290 SQKM 71.659 Acres 0.112 Sqmile98675No ratings yet