Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry
Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry
Uploaded by
Tanguy Pocquet0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageThe document describes the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that particles in solids are close together with a regular, fixed arrangement and shape. In liquids, particles are closer than gases but further apart than solids, with a random arrangement that takes the shape of its container. Gases have particles far apart with a random arrangement that fills its container. It also defines sublimation as the change from solid to gas without passing through liquid, and provides a table summarizing the properties of each state.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document describes the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that particles in solids are close together with a regular, fixed arrangement and shape. In liquids, particles are closer than gases but further apart than solids, with a random arrangement that takes the shape of its container. Gases have particles far apart with a random arrangement that fills its container. It also defines sublimation as the change from solid to gas without passing through liquid, and provides a table summarizing the properties of each state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pagePages de Cambridge IB Chemistry
Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry
Uploaded by
Tanguy PocquetThe document describes the three states of matter - solids, liquids, and gases. It explains that particles in solids are close together with a regular, fixed arrangement and shape. In liquids, particles are closer than gases but further apart than solids, with a random arrangement that takes the shape of its container. Gases have particles far apart with a random arrangement that fills its container. It also defines sublimation as the change from solid to gas without passing through liquid, and provides a table summarizing the properties of each state.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 1
嘔︱
Stoich iometric relationsh i ps
1.1 lntroduction to the particulate nature Learning objectives
of matter and chemical change Describe the three states of
matter
1.1.1 The particulate nature of matter understand the changes
involved when there is a change
The three states of rnatter are solid, liquid and gas and these differ
in state
in terms of the arrangement and movement of particles.The particles
making up a substance may be individual atoms or molecules or ions.
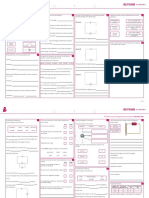
Simple diagrams of the three states of matter are shown in Figure 1.1 in
which the individual particles are represented by spheres.
Sublimation is the change of state when a substance goes directly
from the solid state to the gaseous state, without going through the
liquid state. Both iodine and solid carbon dioxide (dry ice) sublime at
atmospheric pressure.The reverse process (gas -+ solid) is often called
deposition (or sometim es desublimation, reuerse sublimation or occasionally just
sublimation).
The properties of the three states of matter are summarised inTable 1.1.
heating - energy is supplied
particles gain energy
-'::i:llltl'
sublimation +deposition
--9
particles vibrating particles moving particles moving at high
about mean positions around each other speeds in all diiections
particles lose energy
Figure 1.1 The arrangement of particles in solids, liquids and gases and the names
of the changes of state. Note that evaporation can occur at any temperature - boiling
occurs at a fixed temperature.
So:ids L10Ⅲ ids Gases
Dista,ce‐ between paFtiCieS close together close but further apart than in solids particles far apart
Arrangement regular random random
Shape fixed shape no fixed shape - take up the shape ofthe no fixed shape - fill the container
container
Vo:u饉 ● fixed fixed not fixed
illovement vibrate move around each other move around in all directions
Speedofmouement slowest faster fastest
Energy lowest higher highest
Forces10fattraction strongest weaker weakest
Table 1.1 The properties of the three states of matter.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- T SC 2549972 ks3 Electricity and Magnetism Foundation Revision Mat - Ver - 9Document4 pagesT SC 2549972 ks3 Electricity and Magnetism Foundation Revision Mat - Ver - 9Margarida SeromenhoNo ratings yet
- Huawei ICT Competition 2019-2020 Preliminary Examination Outline - PAkDocument5 pagesHuawei ICT Competition 2019-2020 Preliminary Examination Outline - PAkHamad KhanNo ratings yet
- Penguin ClassicsDocument1 pagePenguin ClassicsTanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-18Document1 pagePages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-18Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-16Document1 pagePages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-16Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-11Document1 pagePages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-11Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Pages de Cambridge IB ChemistryDocument1 pagePages de Cambridge IB ChemistryTanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Pages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-2Document1 pagePages de Cambridge IB Chemistry-2Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Ciszak, T. Josel, S.F. Multiphonic Aggregates On The Electric Guitar (2019)Document25 pagesCiszak, T. Josel, S.F. Multiphonic Aggregates On The Electric Guitar (2019)Tanguy Pocquet100% (1)
- Sabat, M. The Harmonic Series 1-64 (2005)Document1 pageSabat, M. The Harmonic Series 1-64 (2005)Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Sabat, M. Helmholtz-Ellis Accidentals Full Legend (2005)Document2 pagesSabat, M. Helmholtz-Ellis Accidentals Full Legend (2005)Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Sabat, M. The Harmonic Series 1-64 (2005)Document1 pageSabat, M. The Harmonic Series 1-64 (2005)Tanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- Bonet, N. Musical Borrowing in Sonification (2019) PDFDocument11 pagesBonet, N. Musical Borrowing in Sonification (2019) PDFTanguy PocquetNo ratings yet
- V Rep2Document37 pagesV Rep2ANANo ratings yet
- Motores de Combustion Interna A DieselDocument2 pagesMotores de Combustion Interna A DieselAlex Francisco Santillán QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Physical and Chemical Adsorption and Its Applications: December 2021Document9 pagesPhysical and Chemical Adsorption and Its Applications: December 2021Virat KholiNo ratings yet
- EE ProblemsDocument33 pagesEE ProblemsSaied Aly SalamahNo ratings yet
- NX Open ProgrammingDocument5 pagesNX Open ProgramminggsgsureshNo ratings yet
- ISTQB Latest Sample Paper 7Document7 pagesISTQB Latest Sample Paper 7Shadaab QureshiNo ratings yet
- Digital 262Document4 pagesDigital 262directNo ratings yet
- Os NotesDocument17 pagesOs NotesAshish KadamNo ratings yet
- Manual EP200 enDocument42 pagesManual EP200 enJose AguirreNo ratings yet
- TSJ Transportation Frame General NotesDocument1 pageTSJ Transportation Frame General NotesBhuvan GanesanNo ratings yet
- ANTAM Datasheet 10LAD21AA121 00Document1 pageANTAM Datasheet 10LAD21AA121 00heviNo ratings yet
- CoreJava NotesDocument25 pagesCoreJava Notesnikita thombreNo ratings yet
- Barsha Pump MK5 Technical SpecificationsDocument9 pagesBarsha Pump MK5 Technical SpecificationsAndrés PerezNo ratings yet
- Process Integration Scenario in SAP PI 7.1Document19 pagesProcess Integration Scenario in SAP PI 7.1Durga Prasad Anagani100% (1)
- Technical Specs PDFDocument12 pagesTechnical Specs PDFcsolanki6586100% (1)
- Programming With SIMD-instructionsDocument10 pagesProgramming With SIMD-instructionsMahipal YadavNo ratings yet
- Tank Design APIDocument63 pagesTank Design APIBSK entertainmentNo ratings yet
- Word TutorialDocument12 pagesWord TutorialMuahamad MusaNo ratings yet
- The Blue Wool StandardsDocument3 pagesThe Blue Wool StandardsWilli De Barros GonçalvesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Dry Etching PDFDocument7 pagesIntroduction To Dry Etching PDFp.designNo ratings yet
- Report of Comparing 5 Classification Algorithms of Machine Learning PDFDocument4 pagesReport of Comparing 5 Classification Algorithms of Machine Learning PDFabhinavNo ratings yet
- 4. VLF Hipot Tester-User Manual(按键款)Document9 pages4. VLF Hipot Tester-User Manual(按键款)Mạnh Nguyễn VănNo ratings yet
- Whole Number 3Document1 pageWhole Number 3hyunckellNo ratings yet
- UCF Computer Science Electives 2012Document2 pagesUCF Computer Science Electives 2012patpatpats3No ratings yet
- Allen Chemistry Class 10-Pages-45-55-CompressedDocument11 pagesAllen Chemistry Class 10-Pages-45-55-CompressedSaismita ParidaNo ratings yet
- Sensor Lect7Document42 pagesSensor Lect7morton1472No ratings yet
- Structural Tubing Square Dimensions and PropertiesDocument11 pagesStructural Tubing Square Dimensions and Propertiesnando riskyNo ratings yet
- 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument6 pages3V FM Transmitter CircuitMahmood AhmedNo ratings yet