Professional Documents
Culture Documents
OrgMan - WEEK 4&5
OrgMan - WEEK 4&5
Uploaded by
Ji Pao0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views6 pagesThis document summarizes two major management theories: Scientific Management Theory and Administrative Management Theory. Scientific Management Theory, developed by Frederick Taylor, emphasizes efficiency and applying scientific principles to improve productivity. It focuses on analyzing work processes and using time-and-motion studies. Administrative Management Theory, introduced by Henri Fayol, focuses on overall organizational management and defines five functions and fourteen principles of management, such as division of work, authority, and discipline.
Original Description:
Organization and Management
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document summarizes two major management theories: Scientific Management Theory and Administrative Management Theory. Scientific Management Theory, developed by Frederick Taylor, emphasizes efficiency and applying scientific principles to improve productivity. It focuses on analyzing work processes and using time-and-motion studies. Administrative Management Theory, introduced by Henri Fayol, focuses on overall organizational management and defines five functions and fourteen principles of management, such as division of work, authority, and discipline.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
19 views6 pagesOrgMan - WEEK 4&5
OrgMan - WEEK 4&5
Uploaded by
Ji PaoThis document summarizes two major management theories: Scientific Management Theory and Administrative Management Theory. Scientific Management Theory, developed by Frederick Taylor, emphasizes efficiency and applying scientific principles to improve productivity. It focuses on analyzing work processes and using time-and-motion studies. Administrative Management Theory, introduced by Henri Fayol, focuses on overall organizational management and defines five functions and fourteen principles of management, such as division of work, authority, and discipline.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 6
processes to manufacture the greatest number of products in the shortest possible
JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc. time.
ACADEMIC EXCELLENCE.LEADERSHIP POTENTIAL. CHRISTIAN VALUES
Blk. 40 Lot 73 Road 1 Minuyan II, CSJDM Bulacan Scientific Management Theory
Organization and Management
2nd Semester – Week 4 & 5 Scientific management is a theory of
management which studies the
TOPIC: The Evolution of Management Theories application of scientific methods and
principles for the purpose of redesigning
The Development of Management
the work process to increase efficiency.
Ancient civilizations practiced management in organizing and implementing
various activities vital to their communities. In 1100 BC, the Chinese used the four It emphasizes the importance of labor in
basic management functions of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling to the production process and focuses on
carry out vast infrastructure projects and manage various parts of the expanding improving the efficiency of workers in
Chinese empire. The Greeks developed a scientific approach to work, and the Greek production. Among its important
philosophers Socrates and Plato discussed management concepts such as leadership advocates were Frederick W. Taylor,
and job specialization. The ancient Romans, meanwhile, practiced decentralized Henry Gantt, and Frank and Lillian
management to effectively manage their vast empire. During the medieval period,
Gilbreth.
Venetians improved production by standardizing the assembly line, using an
inventory system, and building warehouses. Leaders and managers often utilized trial Frederick W. Taylor, an American engineer, was the first to advocate scientific
and error in dealing with management problems before they could perfect operations. management. He pioneered several innovations during his tenure as foreman at
The Industrial Revolution of the 18th century introduced great changes in
management practices. The emphasis on production brought about by improved Midvale Steel Company in Philadephia. Taylor discussed in depth the scientific
industry generated a demand for new ways of ensuring efficiency and effectiveness in management in his book, the Principle of Scientific Management. He introduced the
factories and workplaces. By the 19th century, management has become an four principles of scientific management as follows:
established discipline and many entrepreneurs and academics sought new ideas and
approaches in improving the workplace. Manufacturing and industry soon become a 1. Replace rule-of-thumb methods with those that are scientifically proven.
core business in Europe and the United States, and many individuals sought to enter 2. Select, train, and develop each worker based on scientific methods.
the commercial world. By the 20th century, educational institutions were established 3. Cooperate with the workers to ensure that scientific methods are being
to focus on the study of business and management. The first business school in the observed and implemented in their work.
United States, the Wharton School, was founded in Pennsylvania in 1881. In 1990, 4. Divide work between managers and workers to ensure the scientific
the Amos Tuck School was founded in New Hampshire and became distinguished as management principles are applied by the managers in planning tasks and by the
the first school to offer a master’s degree in business administration.
workers in performing their tasks.
The 20th century saw the development of modern management theories and
innovative methods that transformed production and led to the development of
modern industry and commerce. Various entrepreneurs applied scientific principles
in improving the level of productivity of their respective businesses. Businessmen
sought to establish the most efficient means of utilizing resources and production
Taylor emphasized efficiency in improving the production process. He 8. Centralization where the roles of all employees are clarified, with emphasis on
believed that analyzing the work process will enable the manager to identify the best the distinction between superior and subordinate roles.
way of doing things. His work, combined with the research of Frank and Lillian 9. Scalar Chain which means that communications should be open within the chain
of command.
Gilbreth on the same topic, led to the development of time and motion study.
10. Order where the organization of jobs and materials must be done in an orderly
Taylor is called the “Father of Scientific Management” because of his fashion.
contributions to the development of management. His ideas were also considered an 11. Equity which means that fairness and order must be practiced to maintain
important cornerstone of the Efficiency Movement, which improved industry and employee commitment.
production in Europe and the United States in the early 20th century. 12. Stability and tenure of personnel to actively promote employee loyalty to the
organization.
13. Initiative to encourage employees to act on their own in support of the
Administrative Management Theory. organization’s objectives.
Administrative management focuses on 14. Esprit de corps to promote teamwork and the unity of interest between the
the overall management of an organization, employees and the management.
emphasizing the role of managers as
administrators of the organization. This was
Max Weber, German sociologist, contributed to
introduced in the early 20th century by Henri
the development of administrative management
Fayol, a French industrialist.
through his studies on public administration and
Fayol identified five functions and fourteen bureaucracy. Weber considered bureaucracy as
principles of management. an important aspect of modern society, and its
emergence is an indication of people adopting a
The five functions are planning, organizing, communicating, coordinating, and
more rational and law-based view on leadership.
controlling. On the other hand, the fourteen principles of management are as follows:
Weber believed that bureaucratic structures
1. Division of work into specialized tasks, with specific duties and responsibilities allow for specialization of skills and enable
given to individuals. workers with different traits, skills, and goals to
2. Authority of managers to delegate work and tasks to the employees. The work together and contribute toward performing
employees, in turn, are expected to comply and exercise their tasks responsibly.
a common task.
3. Discipline where expectations should be clearly set and violators of rules must be
punished. Other contributors to the development of the administrative management
4. Unity of Command where an employee should only report to one supervisor. theory were Chester Barnard and Mary Parker Follet Barnard, a former president of
5. Unity of Direction which means that the efforts of the employees are guided the New Jersey Bell Telephone Co., wrote The Functions of the Executive, which
toward the attainment of organizational objectives. highlights the major functions of the senior executive, namely,
6. Predominance of general interest of the organization over the individual 1. to formulate the organization’s mission
interests of employees. 2. to hire key employees, and
7. Renumeration of the efforts of the employees which should be systematically
3. to maintain organizational communication
rewarded in line with the organization’s vision and mission.
Meanwhile, Follet wrote the Dynamic Organization, which emphasizes the described these needs according to an hierarchy where people try to satisfy their
ever-changing situations that managers have to deal with, In particular, Follet lower-level or basic needs first, such as food, clothing, and shelter, and then progress
recognized the human element in management and emphasized collaboration and upward to the higher-
level needs such as self-esteem
mutual cooperation in seeking solutions to problems.
and self-actualization. In 1970,
The views on administrative management acknowledged the need for Maslow revised his original
flexibility among managers and for them to recognize various ways of motivating 1954 pyramid and added two
groups and individuals. Also, the development of administrative management further more essential needs: cognitive
improved management methods and recognized management and business needs or the need to acquire
administration as significant and essential professions along with law and medicine. knowledge; and aesthetic needs
or the need to create and
Human Relations Theory experience beauty, balance and
structure.
The human relations theory grew out of
The application of Marlow’s
the human relations movement in the 1930s. If
theory in management requires
focuses on the social element in the workplace
managers to ensure that the
and considers the influence of interpersonal
essential needs of their workers
relationships, social conditioning, and group are being met in the workplace to
norms in determining the performance of guarantee their maximum
workers. performance.
The foundations of the human relations
movement were established in the 1920s with Quantitative Management Theory
the pioneering studies of Elton Mayo, an Quantitative management uses quantitative approaches such as statistical
Australian analyses and computer simulations to arrive at a management decision. The two main
psychologist who used his expertise to implement improvements in the workplace. branches of quantitative management are management science and operations
He and his colleagues embarked on a series of studies on workers in the Hawthorne management.
Works factory of the Western Electric Company. Among innovative outcomes of the Management science uses mathematics in problem solving and decision
Hawthorne studies were the introduction of a set number of work hours, the making. It seeks to create ideal models that will be the basis for improved business
implementation of break times for workers, improvements in lighting in work areas, operations and processes. On the other hand, operations management seeks to apply
and close supervision by managers. Managers were encouraged to be supportive of ideas and models from management science to the actual workplace in dealing with
managerial situations.
their workers and to actively involve them in management decisions. Mayo observed
Management information system, meanwhile, is a subfield of quantitative
that the introduction of these changes resulted in increased satisfaction among
management. It gathers past, present, and projected data from external and internal
workers which also resulted in their increased overall productivity.
sources and transforms them into usable information which managers use to select the
best alternatives and make decisions easily. The information is usually provided in
Another contributor of the field of human relations is Abraham Maslow. Maslow
easily accessible formats such as spreadsheets.
argued that individual behavior is primarily influenced by certain needs. He
closed systems, on the other hand, does not interact with its environment and
pays little attention to changes in its surroundings.
Systems Theory
The systems theory explains how interrelated parts operate to achieve a common Contingency Theory
purpose. With the advent of the Industrial Revolution and the increasing The contingency theory
requirements for increased efficiency and greater precision in production and argues that universal theories
operations, the system approach became the preferred model of business organization cannot be applied to
and management. It defines an organization as a system which is composed of organizations because each
four elements: organization has unique
characteristics and is confronted
by varied problems or
challenges. An organization’s
performance is also affected by
internal and external factors.
This perspective was introduced
in 1967 by Fred Fiedler, an
industrial and organizational
psychologist who studied the
relationship between leadership
and group effectiveness.
Fiedler’s contingency model states that the personality of the leader determines how
well he or she addresses situations in the workplace.
Quality Management Theory
1. Inputs (materials/human resources) Quality management emphasizes
2. Transformation processes (technology/managerial operations) consistency in an organization and
3. Outputs (products/services) minimal to no errors or defects in
production. This ensures quality products
4. Feedback (reaction from the environment)
and services that result in high customer
The contemporary systems theory analyses an organization according to
satisfaction and increased revenue.
the degree to which it is open or closed. An open system refers to an Managers and employees are both closely
organization that interacts closely with its environment and is fully aware of involved in quality management. The
what is going on in the environment as well as the changes it experiences. A quality management perspective emerged
after the Second World War, primarily
through the work of William Edwards
Deming. Deming conducted his work in
the 1950s in post-war Japan, as he helped
Japanese Industries improve production.
EVALUATION:
(Note: Write your answers in a separate sheet of paper. Write your FULL
NAME and SECTION at the top of the paper. USE AN INDIVIDUAL SHEET
OF PAPER PER SUBJECT.)
Instruction: Match each concept or example to its corresponding management
theory. Write the letter of your answer in the blank.
Identify the management principle by Fayol described by each statement. Write
_____ 1. Assembly line of Ford’s Model a. Administrative Management Theory
you answer in the blank.
T
_______________________ 1. Expectations and sanctions for violations are clearly
b. Human Relations Theory set.
_____ 2. Hawthorne studies
_______________________ 2. Efforts are systematically rewarded in line with the
c. Quantitative Management Theory organization’s vision and mission.
_____ 3. Equal division of work among
managers and workers _______________________ 3. An employee is assigned to only one supervisor.
d. Systems Theory
_______________________ 4. Importance of superior and subordinate roles is
_____4. Kaizen determined.
e. Contingency Theory
_______________________ 5. Communication is kept open within the chain of
_____5. Input, transformation process,
output, and feedback
command.
f. Quality Management Theory
_______________________ 6. The practice of fairness and order promotes
_____ 6. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs employee commitment.
g. Scientific Management Theory
_______________________ 7. Employees are encouraged to act independently in
____ 7. Esprit de corps support of the company’s objectives.
_______________________ 8. The company must promote teamwork and the unity
_____ 8. Mathematics in problem of interest between employees and management.
solving and decision making
_______________________ 9. Loyalty is promoted in the organization.
_____9. Fiedler’s contingency model _______________________ 10. Individual interests are set aside and the general
interest of the company are prioritized.
____ 10. Open and closed system
You might also like
- Social Studies CXC SBADocument24 pagesSocial Studies CXC SBABlxck Hippie63% (38)
- Social Psyc 1Document71 pagesSocial Psyc 1Sumayya FatimaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Management Yesterday and TodayDocument9 pagesChapter 2 Management Yesterday and TodayCamille Phillips100% (4)
- Final Examination in Ed 107A: Assessment of Student LearningDocument2 pagesFinal Examination in Ed 107A: Assessment of Student LearningKarl Edrian Abendaño100% (1)
- Task 4 PpatDocument4 pagesTask 4 Ppatapi-176688637100% (1)
- Lesson 2 - Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument36 pagesLesson 2 - Evolution of Management TheoriesAppleCorpuzDelaRosaNo ratings yet
- The Schools of Management ThoughtDocument12 pagesThe Schools of Management ThoughtSatya Priya MishraNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document32 pagesLecture 4alialiibrahim05No ratings yet
- Weeks 5-7Document43 pagesWeeks 5-7Mohamed Bilal HamoushNo ratings yet
- C1 L2 0 Lecture Notes The Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument4 pagesC1 L2 0 Lecture Notes The Evolution of Management TheoriesLily Mar VinluanNo ratings yet
- History and Evolution of Management TheoryDocument4 pagesHistory and Evolution of Management TheoryDennis Brown MuremiNo ratings yet
- Organization and ManagementDocument11 pagesOrganization and ManagementNinia Cresil Ann JalagatNo ratings yet
- Principles of Management: Class Level: CS (1Document52 pagesPrinciples of Management: Class Level: CS (1RAF RAFNo ratings yet
- Evolution of Management ThoughtDocument10 pagesEvolution of Management ThoughtBhavya SreeNo ratings yet
- Unit 2Document31 pagesUnit 2HACHALU FAYENo ratings yet
- CH 2-Management History ModuleDocument21 pagesCH 2-Management History ModuleSiddique ali Siddique aliNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two Management TheoriesDocument55 pagesChapter Two Management TheoriesSAMMYNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 The Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument37 pagesChapter 2 The Evolution of Management TheoriesEshe EsmillarinNo ratings yet
- AVC - MGT Thought.2022 By. Yusuf A.Document133 pagesAVC - MGT Thought.2022 By. Yusuf A.tofikhassen56No ratings yet
- AzmerawfDocument31 pagesAzmerawfMaህNo ratings yet
- PPM PDFSDocument169 pagesPPM PDFSabhisrivastava7394No ratings yet
- 2 лекция менеджментDocument16 pages2 лекция менеджментАружанNo ratings yet
- Evolution of MGMTDocument31 pagesEvolution of MGMTSAMUEL GENENENo ratings yet
- MGT Lecture03Document8 pagesMGT Lecture03SARA AZIZNo ratings yet
- CH - 2Document37 pagesCH - 2TamiratNo ratings yet
- I. Topic: Development of Management Thought Ii. Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesI. Topic: Development of Management Thought Ii. Learning OutcomesArianne RecentesNo ratings yet
- MGT 2 HistoryDocument50 pagesMGT 2 Historysaifloki5No ratings yet
- Assignment No. 1 Q. 1 Discuss Evolution of Management Theories in DetailDocument27 pagesAssignment No. 1 Q. 1 Discuss Evolution of Management Theories in DetailM Noaman Akbar100% (1)
- SClassical Schools of ThoughtsDocument3 pagesSClassical Schools of Thoughtsشکیل بن عبد الرحیمNo ratings yet
- Clearly Defined and Specialized Functions 2. Use of Legal AuthorityDocument3 pagesClearly Defined and Specialized Functions 2. Use of Legal AuthorityJane WambuiNo ratings yet
- Pocm SlideDocument193 pagesPocm Slidefaizun sekinNo ratings yet
- Development of Management ThoughtDocument53 pagesDevelopment of Management Thoughtemlyn ngwiriNo ratings yet
- Definition of Management: Peter DruckerDocument14 pagesDefinition of Management: Peter DruckerslayNo ratings yet
- Block-1 ECO-03 Unit-2 PDFDocument11 pagesBlock-1 ECO-03 Unit-2 PDFGowri PonprakashNo ratings yet
- A Review of The Evolution of Management Schools of Thought by Enyia Charles Daniel Department of Management, Faculty of Management Sciences, University of Port Harcourt +234 8165390560Document12 pagesA Review of The Evolution of Management Schools of Thought by Enyia Charles Daniel Department of Management, Faculty of Management Sciences, University of Port Harcourt +234 8165390560Nishi JangirNo ratings yet
- Management TheoryDocument32 pagesManagement TheoryHimansu NandaNo ratings yet
- Full Download Management 12th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual PDF Full ChapterDocument36 pagesFull Download Management 12th Edition Griffin Solutions Manual PDF Full Chaptersloppy.obsidian.v8ovu100% (20)
- Management 12th Edition Griffin Solutions ManualDocument21 pagesManagement 12th Edition Griffin Solutions Manualondogram.betulinpwl1gz100% (38)
- WK4 - Org. & Mgt. - MODULEDocument12 pagesWK4 - Org. & Mgt. - MODULEErick John SaymanNo ratings yet
- ManagmentDocument149 pagesManagmenttilanehmamuye4No ratings yet
- Evolution of Management TheoriesDocument18 pagesEvolution of Management Theoriesroy_prokash008No ratings yet
- Chapter Two: Development of Management ThoughtDocument70 pagesChapter Two: Development of Management Thoughttewodros bayisaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-Evolution of Management 1Document48 pagesUnit 1-Evolution of Management 1sambhussakshi3No ratings yet
- Principles of Management and OrganizationsDocument3 pagesPrinciples of Management and OrganizationsErichelle EspineliNo ratings yet
- 2 Beginning of 20thDocument8 pages2 Beginning of 20thMussie KebedeNo ratings yet
- School of Management ThoughtDocument13 pagesSchool of Management ThoughtShweta Sahni0% (1)
- Construction Management NotesDocument49 pagesConstruction Management NotesKay Cee GaneshNo ratings yet
- Development of Management1 Thought-1Document20 pagesDevelopment of Management1 Thought-1Jeremy OndoreNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - History of Management Learning OutcomesDocument9 pagesChapter 1 - History of Management Learning OutcomesFranselle GarciaNo ratings yet
- Assignment: TwentiethDocument7 pagesAssignment: Twentiethsonali soniNo ratings yet
- Si 01 Unit 01 Chapter 02Document13 pagesSi 01 Unit 01 Chapter 02nuzhatateeq272No ratings yet
- Unit 2 MGT TheoriesDocument37 pagesUnit 2 MGT TheoriessabynefaredNo ratings yet
- Managment and Administration (POM UNIT 1.2)Document14 pagesManagment and Administration (POM UNIT 1.2)Sunil ChinnuNo ratings yet
- ABM - Specialized Subject 1 Quarter - Module 1 Organization and ManagementDocument14 pagesABM - Specialized Subject 1 Quarter - Module 1 Organization and ManagementSir Jeh TungolNo ratings yet
- Part 2Document29 pagesPart 2amanray2604No ratings yet
- Organisation Theory and Management 112Document24 pagesOrganisation Theory and Management 112muna moonoNo ratings yet
- Topic Two Theories and History of ManagementDocument10 pagesTopic Two Theories and History of ManagementEli KagothoNo ratings yet
- Industrial Management Unit 1 NotesDocument33 pagesIndustrial Management Unit 1 Notesvgbharath80% (5)
- Management Concept and Practice: Chapter TwoDocument53 pagesManagement Concept and Practice: Chapter TwoBontu H AmeyaNo ratings yet
- ABM 7 Module 3rd Quarter 2Document38 pagesABM 7 Module 3rd Quarter 2Pacito Sto TomasNo ratings yet
- Theories of OrganizationsDocument21 pagesTheories of Organizations1921 Pallav Pali100% (1)
- Human Resource ManagementDocument43 pagesHuman Resource ManagementSneha PriyadarshiniNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document4 pagesWeek 2Anabel BahintingNo ratings yet
- Management at a Glance: For Top, Middle and Lower ExecutivesFrom EverandManagement at a Glance: For Top, Middle and Lower ExecutivesNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M02 - L02 - L03 - WEEK 4Document9 pagesEarth Science - M02 - L02 - L03 - WEEK 4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M02 - L01 - WEEK 3Document6 pagesEarth Science - M02 - L01 - WEEK 3Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Energy Resources (Part 1)Document11 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Energy Resources (Part 1)Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M02 - L02 - WEEK 4Document5 pagesEarth Science - M02 - L02 - WEEK 4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
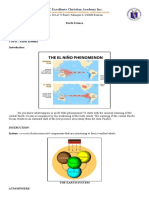
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Quarter 2 - WEEK 5Document3 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Quarter 2 - WEEK 5Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M01 - L03 - WEEK 2Document4 pagesEarth Science - M01 - L03 - WEEK 2Ji PaoNo ratings yet
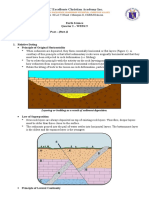
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Endogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) - Part 3Document8 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Endogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition) - Part 3Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science M05 L01 01 W4Document2 pagesEarth Science M05 L01 01 W4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Blk. 40 Lot 73 Road 1 Minuyan II, CSJDM BulacanDocument4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Blk. 40 Lot 73 Road 1 Minuyan II, CSJDM BulacanJi PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M01 - L02 - WEEK 2Document4 pagesEarth Science - M01 - L02 - WEEK 2Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Document4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M04 - L01 - Q2 - W1Document3 pagesEarth Science - M04 - L01 - Q2 - W1Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M04 - L02 - Q2 - W2Document2 pagesEarth Science - M04 - L02 - Q2 - W2Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M04 - L03 - Q2 - W3Document4 pagesEarth Science - M04 - L03 - Q2 - W3Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Soil Resources InstructionDocument4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Soil Resources InstructionJi PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Document7 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 7Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 6Document5 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Earth Science Week 6Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Exogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition)Document4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Exogenic Processes (Erosion and Deposition)Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Exogenic Processes (Weathering)Document7 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Exogenic Processes (Weathering)Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Human Activity and The EnvironmentDocument4 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Human Activity and The EnvironmentJi PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Soil ResourcesDocument2 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Soil ResourcesJi PaoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science - M02 - L03 - WEEK 4Document4 pagesEarth Science - M02 - L03 - WEEK 4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
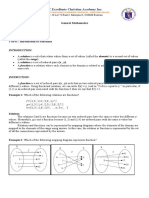
- General Mathematics - M02 - L01 - WEEK 2Document2 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M02 - L01 - WEEK 2Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Water ResourcesDocument7 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: TOPIC: Water ResourcesJi PaoNo ratings yet
- JC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Science - 8 4 Quarter - Week 4Document5 pagesJC Excellente Christian Academy Inc.: Science - 8 4 Quarter - Week 4Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics - M01 - L01 - WEEK 1Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M01 - L01 - WEEK 1Ji PaoNo ratings yet
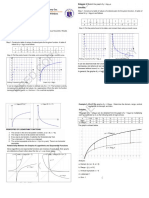
- General Mathematics - M05 - L05 - WEEK 5&6Document5 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M05 - L05 - WEEK 5&6Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- General Mathematics - M04 - L04 - WEEK 1Document4 pagesGeneral Mathematics - M04 - L04 - WEEK 1Ji PaoNo ratings yet
- Illness Anxiety DisorderDocument2 pagesIllness Anxiety DisorderPrince AroraNo ratings yet
- A Thematic Look at Selected Cases of Marital Nullity in The PhilippinesDocument23 pagesA Thematic Look at Selected Cases of Marital Nullity in The PhilippinesJesus MenguriaNo ratings yet
- Introduction of CPDDocument6 pagesIntroduction of CPDMaizatul Akmar IbrahimNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Students Curiosity and Imagination On Overall Classroom AchievementDocument5 pagesThe Effect of Students Curiosity and Imagination On Overall Classroom AchievementInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Kuya Irvin EssayDocument2 pagesKuya Irvin EssaySHIENNA MAE ALVISNo ratings yet
- Unit 4: The Human ActDocument43 pagesUnit 4: The Human ActTajuna, Mitzui JerlaineNo ratings yet
- MINDFULNESS Design by TunmiseDocument10 pagesMINDFULNESS Design by Tunmiseadeiyiebook tobiNo ratings yet
- Level of Academic Motivation and Interpersonal Dependency of Nursing Students in The University of San AgustinDocument11 pagesLevel of Academic Motivation and Interpersonal Dependency of Nursing Students in The University of San AgustinWayne Patrick Emmanuel WuthrichNo ratings yet
- Course Book Evaluation CheckListDocument1 pageCourse Book Evaluation CheckListNebiye Mesut Kartal AslanNo ratings yet
- ALP Chat-1 TEACHEXCELSDocument6 pagesALP Chat-1 TEACHEXCELSJerry Barad SarioNo ratings yet
- Group 5: Lesson 2 and 3Document18 pagesGroup 5: Lesson 2 and 3JOMELYN MIAONo ratings yet
- ALL 16 Marks SI Attach Mem Approach 2024Document60 pagesALL 16 Marks SI Attach Mem Approach 2024rufuskollerNo ratings yet
- Tour GuidingDocument3 pagesTour GuidingKrista ZeyNo ratings yet
- Teacher Characteristics and ADHD Intervention Outcomes in SchoolsDocument21 pagesTeacher Characteristics and ADHD Intervention Outcomes in SchoolsfgfddNo ratings yet
- Academic Procrastination of StudentsDocument10 pagesAcademic Procrastination of StudentsMiroNo ratings yet
- Different Types of Dogs Lesson PlanDocument4 pagesDifferent Types of Dogs Lesson Planapi-216944187No ratings yet
- Gen Ed 6 Art Apprection Module P.1 7Document8 pagesGen Ed 6 Art Apprection Module P.1 7Rose Anne MartinNo ratings yet
- HR - IOCL ProjectDocument92 pagesHR - IOCL Projectguptamahek0% (1)
- Uganda PSS ManualDocument188 pagesUganda PSS ManualGlenn Kenneth Esguerra IINo ratings yet
- Definisi DisleksiaDocument2 pagesDefinisi DisleksiaOOIJOUFENNo ratings yet
- Intention of Words Used in Propaganda TechniquesDocument5 pagesIntention of Words Used in Propaganda TechniquesDianne Permejo del PradoNo ratings yet
- 5 Principles of Constructivist Teaching 2 - Transcript PDFDocument3 pages5 Principles of Constructivist Teaching 2 - Transcript PDFMohammad FaazilNo ratings yet
- Advanced Educatioal Psychology - Term Paper..Document19 pagesAdvanced Educatioal Psychology - Term Paper..Hania KhaanNo ratings yet
- KAP Questionnaire For Nodal OfficersDocument3 pagesKAP Questionnaire For Nodal OfficersDharma Reddy PashapuNo ratings yet
- Kristeva - Some Observations On Female SexualityDocument11 pagesKristeva - Some Observations On Female SexualityLady MosadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Managing Non-Verbal CommunicationDocument11 pagesChapter 6: Managing Non-Verbal CommunicationJin Hui TanNo ratings yet