Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Addison S Disease CONCEPT MAP
Addison S Disease CONCEPT MAP
Uploaded by
Master MastrikerCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Cholecystitis Concept MapDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (7)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Physiological ChangesDocument1 pagePhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Infertility Concept MapDocument1 pageInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocument1 pageSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocument1 pageNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocument1 pagePituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocument1 pageBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocument1 pageDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 AnswerDocument9 pagesQuiz 2 AnswerFelix Llamera50% (4)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 10 Physical EducationDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 10 Physical EducationKim Sheene Acero86% (7)
- The Art of TsukamakiDocument9 pagesThe Art of TsukamakiGrimm Cao100% (3)
- Mental Health Concept MapDocument2 pagesMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocument1 pagePathophysiology EmphysemaGil AswiguiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map BlankDocument2 pagesConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept Map TemplateDocument1 pageConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Hip FractureDocument3 pagesHip Fracturenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocument1 pageDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocument1 pageOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Fluids and Electrolytes IV FluidsDocument1 pageFluids and Electrolytes IV Fluidsnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept MapDocument1 pageCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Schizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFDocument19 pagesSchizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Reason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDDocument6 pagesReason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Principles 1Document13 pagesPrinciples 1RicaNo ratings yet
- 13 To 23 RizalDocument26 pages13 To 23 Rizalpaolo.canejaNo ratings yet
- CorrectionsDocument7 pagesCorrectionsJoshua AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Golden Cucumber Story TellingDocument4 pagesGolden Cucumber Story TellingDIMAS LSNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Severability and Doctrine of Eclipse Laws Inconsistent With or in Derogation of The Fundamental Rights (Article 13)Document19 pagesDoctrine of Severability and Doctrine of Eclipse Laws Inconsistent With or in Derogation of The Fundamental Rights (Article 13)kirti gargNo ratings yet
- ERDGEISTDocument73 pagesERDGEISTJorge RauberNo ratings yet
- 2-Effect of Claim of Adverse Possession - by B Mary Sara DanammaDocument5 pages2-Effect of Claim of Adverse Possession - by B Mary Sara DanammaJating JamkhandiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Ptosis: Evalution and Management DR - Tarakeswara Rao - MsDocument27 pagesCongenital Ptosis: Evalution and Management DR - Tarakeswara Rao - MsVikram Simha NagendlaNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument9 pagesTerm Papermaritthe moralesNo ratings yet
- Amphibia-Parental CareDocument4 pagesAmphibia-Parental CareAakash VNo ratings yet
- STB1093 Lect Schedule Sem 2 2018 - 2019Document3 pagesSTB1093 Lect Schedule Sem 2 2018 - 2019Alex XanderNo ratings yet
- The ST Jude PrayerDocument5 pagesThe ST Jude Prayerlex librisNo ratings yet
- Falling Worlds by Z0RUASDocument19 pagesFalling Worlds by Z0RUASGleneeveeNo ratings yet
- Yoruba and Benin Kingdom - Ile Ife The Final Resting Place of HistoryDocument5 pagesYoruba and Benin Kingdom - Ile Ife The Final Resting Place of HistoryugwakaluNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular Verbs With Meaning: Base Form Meaning Past 2 Form Past Participle 3 Form - Ing FORMDocument6 pagesList of Irregular Verbs With Meaning: Base Form Meaning Past 2 Form Past Participle 3 Form - Ing FORMShakeelAhmedNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving: Motion, Mixture, and Investment ProblemsDocument11 pagesProblem Solving: Motion, Mixture, and Investment ProblemsJelai TolejanoNo ratings yet
- China's Grand Strategy. Lukas K. Danner.Document219 pagesChina's Grand Strategy. Lukas K. Danner.LMNo ratings yet
- Dominum Et VivificantemDocument69 pagesDominum Et VivificantemIsaac Moro100% (1)
- SPM Biology NotesDocument32 pagesSPM Biology NotesAin Fza0% (1)
- MR NobodyDocument1 pageMR NobodyCatalina PricopeNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Belief Book Summary Bruce H Lipton PHDDocument9 pagesThe Biology of Belief Book Summary Bruce H Lipton PHDAyman ShetaNo ratings yet
- Minutes of The 2Nd Homeroom Pta Meeting: Grade I2 - EINSTEINDocument2 pagesMinutes of The 2Nd Homeroom Pta Meeting: Grade I2 - EINSTEINShawie TabladaNo ratings yet
- Simple PastDocument25 pagesSimple PastAilyn Corpuz SamsonNo ratings yet
- Adriyanmahmoudi 168hourassignmentDocument3 pagesAdriyanmahmoudi 168hourassignmentapi-528485357No ratings yet
- Position Paper China MUN KosovoDocument2 pagesPosition Paper China MUN KosovoYllka KastratiNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Immovable PropertyDocument3 pagesRecovery of Immovable PropertyAzad SamiNo ratings yet
Addison S Disease CONCEPT MAP
Addison S Disease CONCEPT MAP
Uploaded by
Master MastrikerOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Addison S Disease CONCEPT MAP
Addison S Disease CONCEPT MAP
Uploaded by
Master MastrikerCopyright:
Available Formats
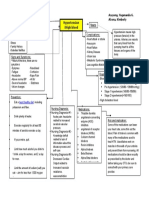
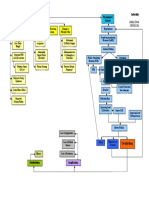
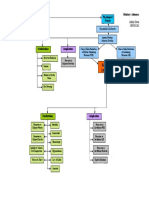
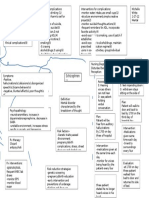
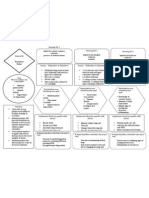
LEGEND
Disease
Definition
Etiology
Signs and symptoms
Nursing Interventions
Medical Management
Autoimmune Goal of Therapy
Idiopathic atrophy of the adrenal glands
Due to decreased cortisol/aldosterone
Iatrogenic – due to surgical removal of both glands
Infections (e.g.,TB/Histoplasmosis) Addison’s Disease
Secondary to hypofunctions of the pituitary gland Results when adrenal cortex function is
Sudden cessation of the exogenous adrenocortical hormone therapy inadequate to meet the patient’s need for
cortical hormones
Administration of medications Over secretion, exposure to cold,
a. Hydrocortisone (Solu- acute infections Prevention of infection
cortef) given thru IV
b. Vasopressor amine if Anorexia
hypotension persist
c. Antibiotics Gastrointestinal symptoms Restoring fluid balance
To combat shock
Monitor vital signs Severe/chronic dehydration
Muscular weakness Improving activity intolerance
Oral intake as tolerated to (Quiet and non-stressful
Emaciation (haggard
prevent hypovolemic shock activities)
To restore blood circulation looking/extreme leanness)
Administer fluids (5% dextrose in Monitoring for Addisonian
Mental status changes
NSS and corticosteroids) crisis’ s/sx :
(depression, apathy, emotional
a. Hypotension
Place patient in recumbent lability)
b. Rapid, weak
position with legs elevated respiratory rate
Addisonian crisis with disease
c. Extreme weakness
progression and acute
Supplementary dietary intake d. Pallor
hypotension
(i.e., pickles)
Dark pigmentation of the skin Promoting community and
home-based care
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5825)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (852)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (903)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (541)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (823)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (403)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Cholecystitis Concept MapDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (7)
- Hypertension Concept MapDocument1 pageHypertension Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Bipolar Concept MapDocument3 pagesBipolar Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (2)
- Physiological ChangesDocument1 pagePhysiological ChangesJilian McGuganNo ratings yet
- Coronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept MapDocument5 pagesCoronary Artery Bypass Graph Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Infertility Concept MapDocument1 pageInfertility Concept Mapnursing concept maps50% (2)
- Sleep Apnea Concept MapDocument1 pageSleep Apnea Concept Mapashleydean100% (2)
- Bronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesBronchial Asthma in Acute Exacerbation BAIAE Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramVictor Angelo VeraNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramDocument1 pageDiabetes Mellitus Type 2 Schematic DiagramJhe Lyn82% (11)
- Nursing Management Concept MapDocument1 pageNursing Management Concept MapXy-Za Roy Marie100% (1)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pituitary Adenoma Concept MapDocument1 pagePituitary Adenoma Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Bipolar Disorder Concept MapDocument1 pageBipolar Disorder Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Degenerative Disc Disease Concept MapDocument1 pageDegenerative Disc Disease Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 AnswerDocument9 pagesQuiz 2 AnswerFelix Llamera50% (4)
- A Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 10 Physical EducationDocument6 pagesA Detailed Lesson Plan For Grade 10 Physical EducationKim Sheene Acero86% (7)
- The Art of TsukamakiDocument9 pagesThe Art of TsukamakiGrimm Cao100% (3)
- Mental Health Concept MapDocument2 pagesMental Health Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology EmphysemaDocument1 pagePathophysiology EmphysemaGil AswiguiNo ratings yet
- Concept Map BlankDocument2 pagesConcept Map Blanknursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept Map TemplateDocument1 pageConcept Map Templatenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- ESRD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesESRD Pathophysiologynursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- PathoPhysiology of Renal Failure OverviewDocument7 pagesPathoPhysiology of Renal Failure Overviewnursing concept maps100% (1)
- Hip FractureDocument3 pagesHip Fracturenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Diagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical ManifestationsDocument1 pageDiagnostics: Disorder & Basic Patho/Etiology: Clinical Manifestationsnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Osteoarthritis Concept MapDocument1 pageOsteoarthritis Concept Mapnursing concept maps0% (1)
- Fluids and Electrolytes IV FluidsDocument1 pageFluids and Electrolytes IV Fluidsnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Concept MapDocument1 pageConcept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 pagesAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Concept MapDocument1 pageCritical Care Concept Mapkonniep69100% (1)
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Schizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFDocument19 pagesSchizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Reason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDDocument6 pagesReason For Needing Health Care: Key Problem / ND: Noncompliance Key Problem / NDnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Hyponatremia Algorhythm Concept MapDocument2 pagesHyponatremia Algorhythm Concept Mapnursing concept mapsNo ratings yet
- Principles 1Document13 pagesPrinciples 1RicaNo ratings yet
- 13 To 23 RizalDocument26 pages13 To 23 Rizalpaolo.canejaNo ratings yet
- CorrectionsDocument7 pagesCorrectionsJoshua AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Golden Cucumber Story TellingDocument4 pagesGolden Cucumber Story TellingDIMAS LSNo ratings yet
- Doctrine of Severability and Doctrine of Eclipse Laws Inconsistent With or in Derogation of The Fundamental Rights (Article 13)Document19 pagesDoctrine of Severability and Doctrine of Eclipse Laws Inconsistent With or in Derogation of The Fundamental Rights (Article 13)kirti gargNo ratings yet
- ERDGEISTDocument73 pagesERDGEISTJorge RauberNo ratings yet
- 2-Effect of Claim of Adverse Possession - by B Mary Sara DanammaDocument5 pages2-Effect of Claim of Adverse Possession - by B Mary Sara DanammaJating JamkhandiNo ratings yet
- Congenital Ptosis: Evalution and Management DR - Tarakeswara Rao - MsDocument27 pagesCongenital Ptosis: Evalution and Management DR - Tarakeswara Rao - MsVikram Simha NagendlaNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument9 pagesTerm Papermaritthe moralesNo ratings yet
- Amphibia-Parental CareDocument4 pagesAmphibia-Parental CareAakash VNo ratings yet
- STB1093 Lect Schedule Sem 2 2018 - 2019Document3 pagesSTB1093 Lect Schedule Sem 2 2018 - 2019Alex XanderNo ratings yet
- The ST Jude PrayerDocument5 pagesThe ST Jude Prayerlex librisNo ratings yet
- Falling Worlds by Z0RUASDocument19 pagesFalling Worlds by Z0RUASGleneeveeNo ratings yet
- Yoruba and Benin Kingdom - Ile Ife The Final Resting Place of HistoryDocument5 pagesYoruba and Benin Kingdom - Ile Ife The Final Resting Place of HistoryugwakaluNo ratings yet
- List of Irregular Verbs With Meaning: Base Form Meaning Past 2 Form Past Participle 3 Form - Ing FORMDocument6 pagesList of Irregular Verbs With Meaning: Base Form Meaning Past 2 Form Past Participle 3 Form - Ing FORMShakeelAhmedNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving: Motion, Mixture, and Investment ProblemsDocument11 pagesProblem Solving: Motion, Mixture, and Investment ProblemsJelai TolejanoNo ratings yet
- China's Grand Strategy. Lukas K. Danner.Document219 pagesChina's Grand Strategy. Lukas K. Danner.LMNo ratings yet
- Dominum Et VivificantemDocument69 pagesDominum Et VivificantemIsaac Moro100% (1)
- SPM Biology NotesDocument32 pagesSPM Biology NotesAin Fza0% (1)
- MR NobodyDocument1 pageMR NobodyCatalina PricopeNo ratings yet
- The Biology of Belief Book Summary Bruce H Lipton PHDDocument9 pagesThe Biology of Belief Book Summary Bruce H Lipton PHDAyman ShetaNo ratings yet
- Minutes of The 2Nd Homeroom Pta Meeting: Grade I2 - EINSTEINDocument2 pagesMinutes of The 2Nd Homeroom Pta Meeting: Grade I2 - EINSTEINShawie TabladaNo ratings yet
- Simple PastDocument25 pagesSimple PastAilyn Corpuz SamsonNo ratings yet
- Adriyanmahmoudi 168hourassignmentDocument3 pagesAdriyanmahmoudi 168hourassignmentapi-528485357No ratings yet
- Position Paper China MUN KosovoDocument2 pagesPosition Paper China MUN KosovoYllka KastratiNo ratings yet
- Recovery of Immovable PropertyDocument3 pagesRecovery of Immovable PropertyAzad SamiNo ratings yet