Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dayrit, Geoffrey C. Abm 11-B - Activity 1
Dayrit, Geoffrey C. Abm 11-B - Activity 1
Uploaded by
Accounting Materials0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pages1. The document discusses different types of nuclear reactions including fission, fusion, nuclear decay, and transmutation. Fission involves the splitting of a nucleus into smaller parts, fusion combines nuclei together. Nuclear decay involves unstable nuclei losing energy through radiation. Transmutation changes the number of protons in a nucleus.
2. Fission splits heavy nuclei into lighter ones, releasing energy. Fusion combines two light nuclei and releases vast amounts of energy.
3. Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from protons and neutrons. It occurred after the Big Bang and continues in stars through stellar and supernova nucleosynthesis, producing different elements.
Original Description:
Dayrit, Geoffrey c. Abm 11-B_activity 1
Original Title
Dayrit, Geoffrey c. Abm 11-B_activity 1
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. The document discusses different types of nuclear reactions including fission, fusion, nuclear decay, and transmutation. Fission involves the splitting of a nucleus into smaller parts, fusion combines nuclei together. Nuclear decay involves unstable nuclei losing energy through radiation. Transmutation changes the number of protons in a nucleus.
2. Fission splits heavy nuclei into lighter ones, releasing energy. Fusion combines two light nuclei and releases vast amounts of energy.
3. Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from protons and neutrons. It occurred after the Big Bang and continues in stars through stellar and supernova nucleosynthesis, producing different elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
16 views2 pagesDayrit, Geoffrey C. Abm 11-B - Activity 1
Dayrit, Geoffrey C. Abm 11-B - Activity 1
Uploaded by
Accounting Materials1. The document discusses different types of nuclear reactions including fission, fusion, nuclear decay, and transmutation. Fission involves the splitting of a nucleus into smaller parts, fusion combines nuclei together. Nuclear decay involves unstable nuclei losing energy through radiation. Transmutation changes the number of protons in a nucleus.
2. Fission splits heavy nuclei into lighter ones, releasing energy. Fusion combines two light nuclei and releases vast amounts of energy.
3. Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from protons and neutrons. It occurred after the Big Bang and continues in stars through stellar and supernova nucleosynthesis, producing different elements.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Dayrit, Geoffrey C.
ABM 11-B
ACTIVITY #1
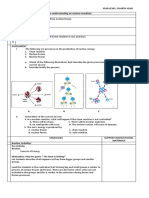
1. Constructing your own idea explains the types of Nuclear Reactions.
A. Fission : Fission means the division of single cell into two or multiple.
Fission can be of two types, namely, Binary fission and Multiple fission. In binary fission,
parent cell divides into two equal halves called daughter cells. Organisms like the amoeba,
bacteria, euglena, etc., exhibit binary fission. During multiple fission, organism divides itself into
numerous daughter cells.
Binary fission, asexual reproduction by a separation of the body into two new bodies. In the
process of binary fission, an organism duplicates its genetic material, or deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA), and then divides into two parts (cytokinesis), with each new organism receiving one
copy of DNA.
Example: Amoeba & Paramecium
Multiple fission is the process of reproduction in which many individuals are formed or
produced from the parent cell. In this process, the nucleus divides repeatedly to produce large
number of nuclei. ... Many daughter cells develop which on liberation grow into adult organism.
Example: Planaria
B. Fusion is the process that powers the sun and the stars. It is the reaction in which two atoms
of hydrogen combine together, or fuse, to form an atom of helium.
In nuclear physics, nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei and
combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles.
C. Nuclear decay or Radioactive decay is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus
loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three
of the most common types of decay are alpha decay, beta decay, and gamma decay, all of
which involve emitting one or more particles or photons.
D. Transmutation is a process in which nucleus changes in the number of protons to produce
an atom with a different atomic number.
The changing of one element into another by radioactive decay, Nuclear bombardment, or
similar processes.
2. Differentiate Nuclear Fusion to Nuclear Fission.
Both fission and fusion are nuclear reactions that produce energy, but the applications are not
the same.
Fission is the splitting of a heavy, unstable nucleus into two lighter nuclei, and Fusion is the
process where two light nuclei combine together releasing vast amounts of energy.
Dayrit, Geoffrey C. ABM 11-B
3. Explain the idea of Nucleosynthesis and give an example.
Nucleosynthesis is the process that creates new atomic nuclei from pre-existing nucleons,
primarily protons and neutrons. The first nuclei were formed about three minutes after the Big
Bang, through the process called Big Bang nucleosynthesis.
Example: Helium may burn via the triple alpha process.
- For example, some stable isotopes such as neon-21 and neon-22 are produced by several
routes of nucleonic synthesis, and thus only part of their abundance is primordial. Nuclear
reactions due to cosmic rays. ... One important example is carbon-14, produced from nitrogen-
14 in the atmosphere by cosmic rays.
Stellar Nucleosynthesis is the creation of chemical elements by nuclear fusion reactions within
stars. Stellar nucleosynthesis has occurred since the original creation of hydrogen, helium, and
lithium during the Big Bang. As a predictive theory, it yields accurate estimates of the observed
abundances of the elements.
Supernova Nucleosynthesis within exploding stars is largely responsible for the elements
between oxygen and rubidium: from the ejection of elements produced during stellar
nucleosynthesis; through explosive nucleosynthesis during the supernova explosion; and from
the r-process (absorption of multiple neutrons) during the explosion.
Big Bang Nucleosynthesis or Primordial Nucleosynthesis refers to the production of nuclei
other than H-1, the normal, light hydrogen, during the early phases of the universe, shortly after
the Big Bang.
You might also like
- SS3 Chemistry 2nd Term Lesson Note PDFDocument47 pagesSS3 Chemistry 2nd Term Lesson Note PDFAugustine Amaechi100% (1)
- 01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedDocument73 pages01 Chapter 01 How The Elements Found in The Universe Were FormedKyra Lim100% (1)
- Chapter 3 - IllustrationsDocument97 pagesChapter 3 - IllustrationsAccounting Materials0% (1)
- Definition of TermsDocument2 pagesDefinition of TermsJozzennie NarcisoNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Chemistry With Pen 1106Document63 pagesNuclear Chemistry With Pen 1106JOHN DAVE MOISES BALDRIASNo ratings yet
- The Nuclear Reactions Involved in The Synthesis of New ElementsDocument3 pagesThe Nuclear Reactions Involved in The Synthesis of New ElementsChristian Isip67% (3)
- Phy Sci NotesDocument8 pagesPhy Sci NotesReynalene ParagasNo ratings yet
- Ssci2 - Physical Science Lesson 1: Formation of Light and Heavy Elements in The UniverseDocument20 pagesSsci2 - Physical Science Lesson 1: Formation of Light and Heavy Elements in The UniverseMs. ArceñoNo ratings yet
- THE BIG BANG THEORY: Lecture and Supplemental Activity To The Lesson of Module-1Document6 pagesTHE BIG BANG THEORY: Lecture and Supplemental Activity To The Lesson of Module-1Bhea Bianca ReyesNo ratings yet
- Dalton's Atomic TheoryDocument2 pagesDalton's Atomic TheoryNath BongalonNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FusionDocument6 pagesNuclear FusionmokshNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Week 1Document15 pagesPhysical Science Week 1veive merlinNo ratings yet
- The Importance of The Formation of Light ElementsDocument2 pagesThe Importance of The Formation of Light ElementsAnnie BlanquezaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry - Nuclear - Physics - WebquestDocument6 pagesChemistry - Nuclear - Physics - Webquesto18.makiNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Component NotesDocument24 pagesChemistry Component NotescptilaonNo ratings yet
- Nuclear FusionDocument11 pagesNuclear Fusiondo4 humanNo ratings yet
- Introduction: Nuclear Chemistry Is The Subfield of Chemistry Dealing With Radioactivity, NuclearDocument18 pagesIntroduction: Nuclear Chemistry Is The Subfield of Chemistry Dealing With Radioactivity, NuclearSmitaNo ratings yet
- Nu Cleo SynthesisDocument22 pagesNu Cleo SynthesisRaden Dave BaliquidNo ratings yet
- Physical Science 1Document25 pagesPhysical Science 1EJ RamosNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Module 1-2Document12 pagesReviewer Module 1-2Kathrina HuertoNo ratings yet
- LAS Physical-Science Week-1Document11 pagesLAS Physical-Science Week-1Shekaina Faith Cuizon LozadaNo ratings yet
- Pointers To ReviewDocument8 pagesPointers To Reviewhood64318No ratings yet
- BIG BANG 1st 2ndDocument33 pagesBIG BANG 1st 2ndangel coralesNo ratings yet
- 2nd Sem Module 1 Physical Science FINAL 1Document8 pages2nd Sem Module 1 Physical Science FINAL 1Arlyn BahinNo ratings yet
- Assignment Fusion and FissionDocument4 pagesAssignment Fusion and Fissionwymgraphics01No ratings yet
- 23 24 Q3 Physcie Week 1Document47 pages23 24 Q3 Physcie Week 1Aira GalacgacNo ratings yet
- Physical Science PowerpointDocument27 pagesPhysical Science PowerpointLucille Joy V. DadullaNo ratings yet
- Stellar NucleosynthesisDocument7 pagesStellar Nucleosynthesisclay adrianNo ratings yet
- Assignment : Meaning of TH FF 1. Star - 2Document3 pagesAssignment : Meaning of TH FF 1. Star - 2Allysa MendozaNo ratings yet
- Assignment : Meaning of TH FF 1. Star - 2Document3 pagesAssignment : Meaning of TH FF 1. Star - 2Angeline AcebucheNo ratings yet
- NucleosynthesisDocument4 pagesNucleosynthesisBerenice PantiiNo ratings yet
- Formation of The ElementsDocument1 pageFormation of The ElementsShyrine Sulit DalawampoNo ratings yet
- Topic One Physical ScienceDocument12 pagesTopic One Physical ScienceReynalie BotonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1.1 The Formation of The Light Elements in The Big Bang Theory - FacebookDocument10 pagesLesson 1.1 The Formation of The Light Elements in The Big Bang Theory - FacebookcedricNo ratings yet
- MODULES IN PHYSICAL SCIENCE WEEK OneDocument12 pagesMODULES IN PHYSICAL SCIENCE WEEK OneRODJHEN ANNE P. BARQUILLANo ratings yet
- Physical Science Module 1 For Students.Document10 pagesPhysical Science Module 1 For Students.YUH JBWDHGNo ratings yet
- Quipper Lecture Physical ScienceDocument279 pagesQuipper Lecture Physical ScienceLoren Marie Lemana AceboNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Nuclear Fusion and Fission Reading-1Document2 pagesDifference Between Nuclear Fusion and Fission Reading-1Tula RmahNo ratings yet
- NucleosynthesisDocument5 pagesNucleosynthesisJm FloresNo ratings yet
- NUCLEOSYNTHESISDocument20 pagesNUCLEOSYNTHESISchuryeonNo ratings yet
- Modern PhysicsDocument4 pagesModern PhysicsSamuel VivekNo ratings yet
- Nuclear Fusion: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchDocument3 pagesNuclear Fusion: Jump To Navigationjump To SearchMikko RamiraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1: S11/12Ps-Iiib-11Document8 pagesLesson 1: S11/12Ps-Iiib-11Maurice LanceNo ratings yet
- Physical Science Powerpoint 1Document40 pagesPhysical Science Powerpoint 1Jenezarie TarraNo ratings yet
- LP11 Fission and FusionDocument7 pagesLP11 Fission and FusionKeeyt KytheNo ratings yet
- Self-Check 1.1: OxygenDocument3 pagesSelf-Check 1.1: OxygenJustine AmarantoNo ratings yet
- Quipper Lecture Physical ScienceDocument326 pagesQuipper Lecture Physical ScienceLoren Marie Lemana AceboNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesPhysical ScienceRIALINE SACOPONNo ratings yet
- Module+1 +introduction+-1Document26 pagesModule+1 +introduction+-1Claire Justine100% (1)
- Unit 1-1Document12 pagesUnit 1-1kirangayke1122No ratings yet
- Nuclear Fission: By: SaaiDocument4 pagesNuclear Fission: By: SaaiSaaiNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Confucius Pointers For Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesGrade 11 Confucius Pointers For Physical ScienceSuzette Ann MantillaNo ratings yet
- Origin of ElementsDocument27 pagesOrigin of ElementsJoanna Ruth SeproNo ratings yet
- Physical Sciences Lesson 1 NucleosynthesisDocument14 pagesPhysical Sciences Lesson 1 NucleosynthesisJustin BirdNo ratings yet
- Concepts in Physical Science Q3 Week 1 To 8 2023 2024Document68 pagesConcepts in Physical Science Q3 Week 1 To 8 2023 2024lydi ibiezaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Explain - Ionizing RadiationDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Explain - Ionizing Radiationapi-344880038No ratings yet
- Shs Module v2020 #m1.2Document6 pagesShs Module v2020 #m1.2Peter Anton RoaNo ratings yet
- Essay English IV Third PartialDocument4 pagesEssay English IV Third PartialCarmen Elizabeth Cabrera AvaloNo ratings yet
- Phy SciDocument55 pagesPhy SciMALOU ELEVERANo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument30 pagesUntitledKrizalyn Salvador LopezNo ratings yet
- What's the Difference Between Fission and Fusion? | Children's Physics of EnergyFrom EverandWhat's the Difference Between Fission and Fusion? | Children's Physics of EnergyNo ratings yet
- A333 Group 2 Case Study 1Document12 pagesA333 Group 2 Case Study 1Accounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- SUMMARY - Working Capital ManagementDocument4 pagesSUMMARY - Working Capital ManagementAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Terms in This SetDocument3 pagesTerms in This SetAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Case 1 - Accounted Separately Case 2 - Not Accounted SeparatelyDocument40 pagesCase 1 - Accounted Separately Case 2 - Not Accounted SeparatelyAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Buscom 2ND Sem Prelims and Midterms Reviewer 1Document13 pagesBuscom 2ND Sem Prelims and Midterms Reviewer 1Accounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Cooperative CodeDocument58 pagesCooperative CodeAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- January 1Document1 pageJanuary 1Accounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- 20 Direct Costing - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument28 pages20 Direct Costing - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- CVP AssignmentDocument5 pagesCVP AssignmentAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Advacc Midterm AssignmentsDocument11 pagesAdvacc Midterm AssignmentsAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Auditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsDocument6 pagesAuditing Theory 2nd Sem PrelimsAccounting MaterialsNo ratings yet
- Economic Valuation of Ecosystem Services PDFDocument43 pagesEconomic Valuation of Ecosystem Services PDFNaturrAllNo ratings yet
- Group 4 - M9 Pre-TaskDocument4 pagesGroup 4 - M9 Pre-TaskRR LajadaNo ratings yet
- Cell Cycle and Cancer ReviewDocument5 pagesCell Cycle and Cancer ReviewEivor LynNo ratings yet
- Slide Lipide PDFDocument37 pagesSlide Lipide PDFMrr Kva Rmx Music-ProducerNo ratings yet
- (Download PDF) Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15Th Edition Cecie Starr Online Ebook All Chapter PDFDocument42 pages(Download PDF) Biology The Unity and Diversity of Life 15Th Edition Cecie Starr Online Ebook All Chapter PDFmartha.schwartz443100% (10)
- Minimum Important Learning ChemistryDocument3 pagesMinimum Important Learning ChemistrySubbiahNo ratings yet
- Tragedy of The Commons - ArticleDocument13 pagesTragedy of The Commons - ArticleAguasNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Ghee (Clarified Butter) On Serum Lipid Levels and Microsomal Lipid PeroxidationDocument16 pagesThe Effect of Ghee (Clarified Butter) On Serum Lipid Levels and Microsomal Lipid PeroxidationBoicu VioletaNo ratings yet
- Recent Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Drug Delivery SystemsDocument18 pagesRecent Advances in Natural Polymer-Based Drug Delivery SystemsTelmoNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of FloweringDocument40 pagesMechanism of FloweringIrdatul WardahNo ratings yet
- Work 1Document12 pagesWork 1Islem MannaiNo ratings yet
- Lecture Planner - Botany (Alpha) - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025Document4 pagesLecture Planner - Botany (Alpha) - Yakeen NEET 2.0 2025kashyapabhinav62No ratings yet
- Notes For Jest & PST Preparation (Part-1 General Science) : By: Muntazir ChandioDocument4 pagesNotes For Jest & PST Preparation (Part-1 General Science) : By: Muntazir ChandioQasim RafiqueNo ratings yet
- Succession of Arthropods On White Rat Carcasses in Ile Ife, Southwestern NigeriaDocument5 pagesSuccession of Arthropods On White Rat Carcasses in Ile Ife, Southwestern NigeriaEditor IJTSRDNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Treatment FAQsDocument4 pagesAerobic Treatment FAQsvince6111No ratings yet
- 10 Nomina ConservandaDocument13 pages10 Nomina ConservandaFernando FariasNo ratings yet
- Classics of Tea - Ming DynastyDocument64 pagesClassics of Tea - Ming DynastyZX LeeNo ratings yet
- Cultivation of Rice in IndiaDocument65 pagesCultivation of Rice in IndiarishabhNo ratings yet
- Reishi MushroomDocument5 pagesReishi MushroomBrij Mohan SinghNo ratings yet
- Amyloidosis: Marwa Bawab - SP 10Document51 pagesAmyloidosis: Marwa Bawab - SP 10Marrouch Ba100% (1)
- Faisal 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 557 012074Document11 pagesFaisal 2019 IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 557 012074manushaNo ratings yet
- OB-Blanchard-Fields, F. (2007) - Everyday Problem Solving and Emotion. An Adult Developmental PerspectiveDocument6 pagesOB-Blanchard-Fields, F. (2007) - Everyday Problem Solving and Emotion. An Adult Developmental Perspectivemilan3zxNo ratings yet
- Dog Coat Colour Genetics - A Review, Saif Et Al. 2020Document11 pagesDog Coat Colour Genetics - A Review, Saif Et Al. 2020Emmanuel A. Sessarego Dávila100% (1)
- Cats Claw Ethnopharmacology 1999Document12 pagesCats Claw Ethnopharmacology 1999Jency SamNo ratings yet
- 100 Clot Signature Curves and The ACL AdvanceDocument50 pages100 Clot Signature Curves and The ACL AdvancedinumolNo ratings yet
- D.G.C.F.S Iusse30 Reality Based CombatDocument18 pagesD.G.C.F.S Iusse30 Reality Based CombatMr.TraylorNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam SUBJECT: Science 5Th Grade Teacher: A-B-C-D Name: Average: DateDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam SUBJECT: Science 5Th Grade Teacher: A-B-C-D Name: Average: DateByed Pedroza VivesNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)Document7 pagesAnaPhy - Reviewer (Final)HyvieNo ratings yet
- Capillary ElectrophoresisDocument44 pagesCapillary ElectrophoresisLestari TiaNo ratings yet
- Comparative-Analysis-of-Water-Extracts-from-Roselle-Hibiscus-sabdariffa-L-Plants-and-Callus-Cells-Constituents-Effects-on-Human-Skin-Cells-and-Transcriptome-Profiles_2023_Multidisciplinary-Digital-Publishing-InstitDocument21 pagesComparative-Analysis-of-Water-Extracts-from-Roselle-Hibiscus-sabdariffa-L-Plants-and-Callus-Cells-Constituents-Effects-on-Human-Skin-Cells-and-Transcriptome-Profiles_2023_Multidisciplinary-Digital-Publishing-InstitFabruwo pajoveNo ratings yet