Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 viewsCommunity Medicine 3.04 Andragogy - Dr. Zulueta
Community Medicine 3.04 Andragogy - Dr. Zulueta
Uploaded by
Joher MendezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Criminal Law Review-2020 Part 2 SyllabusDocument11 pagesCriminal Law Review-2020 Part 2 Syllabusrgtan3No ratings yet
- Pedagogy, AndraDocument1 pagePedagogy, AndraDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Andragogy of Learning Chapter 1Document29 pagesAndragogy of Learning Chapter 1Orapa Sarah GenNo ratings yet
- St. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Document5 pagesSt. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Cath TacisNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Educational PearlsDocument36 pagesTop Ten Educational Pearlsnad791No ratings yet
- Acfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3Document4 pagesAcfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3marcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document10 pagesChapter 7Luarez, Jessa S.No ratings yet
- The Learning CycleDocument19 pagesThe Learning Cyclehaddi awanNo ratings yet
- LP 100 Lesson 1 PEDAGOGY ANDRAGOGY AND HEUTAGOGYDocument18 pagesLP 100 Lesson 1 PEDAGOGY ANDRAGOGY AND HEUTAGOGYShania May100% (1)
- All NotesDocument205 pagesAll Notesjoseph mwizerwaNo ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument89 pagesPrinciples of TeachingAnne Anne Cabeltis-MañaboNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education: Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesNutrition Education: Learning OutcomesRay MondoNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Pedagogy, Andragogy and SynergonyDocument27 pagesConcepts of Pedagogy, Andragogy and SynergonyAvinash RambhursyNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Episode 16Document9 pagesFS 1 Episode 16jedshining4444No ratings yet
- Andragogy TheoryDocument5 pagesAndragogy Theoryjokovach11No ratings yet
- Adult LearningDocument19 pagesAdult LearningMaurisMilzaamANo ratings yet
- Adult Learning PrinciplesDocument2 pagesAdult Learning PrinciplesDonna AlteaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Training CycleDocument16 pagesTeaching Training CycleYESSENIANo ratings yet
- Module - Gonzales - Facilitating LearningDocument6 pagesModule - Gonzales - Facilitating Learningariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- GEE PMT Module 3Document4 pagesGEE PMT Module 3Ryan AmaroNo ratings yet
- Background On The Concept and The Educator: Knowles' 5 Assumptions of Adult LearnersDocument3 pagesBackground On The Concept and The Educator: Knowles' 5 Assumptions of Adult LearnersShiVani KoLashNo ratings yet
- Local Media2052876972954932851Document7 pagesLocal Media2052876972954932851Gennelle MacatangayNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Le16Document4 pagesFS 1 Le16Jorebell W. QuiminoNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesResearch MethodologyCharwayne DaitNo ratings yet
- Adult Learning and Learning NeedsDocument42 pagesAdult Learning and Learning NeedskrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- The Science of LearningDocument11 pagesThe Science of LearningSimpliciusNo ratings yet
- Advance Prin Modules ReviewDocument31 pagesAdvance Prin Modules ReviewKate ZylNo ratings yet
- The Paper Students' Characteristic and Teaching StrategisDocument12 pagesThe Paper Students' Characteristic and Teaching StrategisSMK MANBAUL MAARIFNo ratings yet
- LAC Nov. 18,2022 Strategies and Technique in Teaching ScienceDocument31 pagesLAC Nov. 18,2022 Strategies and Technique in Teaching ScienceCharm Vergara100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Educational Psychology A Tool For Effective TeachingDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Educational Psychology A Tool For Effective TeachingJay Mark CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ADULT LEARNINGDocument6 pagesChapter 5 ADULT LEARNINGJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- PragmatismDocument15 pagesPragmatismNizar Jan MhbNo ratings yet
- The Learning Environment: Lesson 3Document3 pagesThe Learning Environment: Lesson 3Raymart SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Gtle Pedagogy SHS-1Document50 pagesGtle Pedagogy SHS-1piusdanaaNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate EducatorDocument14 pagesThe Ultimate EducatorAlexander Antonio Ortega AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Adult Learning Dr. Radhika KapurDocument7 pagesFacilitating Adult Learning Dr. Radhika KapurCaroline AquenNo ratings yet
- The Teaching Profession - Chapter 5Document7 pagesThe Teaching Profession - Chapter 5George Kevin TomasNo ratings yet
- 10 Learning PrinciplesDocument15 pages10 Learning PrinciplesAjeng HardinieNo ratings yet
- Phillips 66 - Chapter 1-3Document37 pagesPhillips 66 - Chapter 1-3Cindy GacutanNo ratings yet
- 4 Key Concepts of AndragogyDocument7 pages4 Key Concepts of AndragogyJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Towards Relevant Education For All: First ActivityDocument6 pagesTowards Relevant Education For All: First ActivityDarwin RosendeNo ratings yet
- KnowlesDocument6 pagesKnowlesMericar EsmedioNo ratings yet
- Andragogy and Learning TheoryDocument36 pagesAndragogy and Learning TheoryAyu AmbarwatiNo ratings yet
- Function of Group DiscussionDocument25 pagesFunction of Group DiscussionYogendra Patil100% (1)
- Principles of Learning: UNIT II - Chapter 1Document63 pagesPrinciples of Learning: UNIT II - Chapter 1Juodie Lee VaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2David MangawilNo ratings yet
- 0 Training TechniquesDocument22 pages0 Training TechniquesHani BoudiafNo ratings yet
- CM 4 PHDocument18 pagesCM 4 PHGeorgeNo ratings yet
- LEARNINGDocument7 pagesLEARNINGNYENTY PRIDE ASHU-CHINo ratings yet
- GEE-PMT Module 4 Week 6-7Document4 pagesGEE-PMT Module 4 Week 6-7TimothyLimNo ratings yet
- Activity 16.1 Analyzing Deped'S Philosophy of EducationDocument7 pagesActivity 16.1 Analyzing Deped'S Philosophy of EducationRay Allen FabroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Androgogy and PedagogyDocument17 pagesLecture 3 Androgogy and PedagogySajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- FLCTDocument7 pagesFLCTMissy GarciaNo ratings yet
- PED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Document18 pagesPED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Mary Antonette JalosjosNo ratings yet
- Principles of Adult Learning: Unit 2.3Document14 pagesPrinciples of Adult Learning: Unit 2.3Ronnie RicardelNo ratings yet
- Student Directed Learning StrategiesDocument36 pagesStudent Directed Learning Strategiesyhanne100% (17)
- Final Research Na DisDocument31 pagesFinal Research Na DisEarl SemblanteNo ratings yet
- 22 Teaching StrategiesDocument8 pages22 Teaching StrategiesArnyjoy RioNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document27 pagesGroup 3Random PersonNo ratings yet
- Lesson5 1Document16 pagesLesson5 1Ginalyn Fernandez DyangcoNo ratings yet
- Independent Thinking on Teaching and Learning: Developing independence and resilience in all teachers and learners (Independent Thinking On... series)From EverandIndependent Thinking on Teaching and Learning: Developing independence and resilience in all teachers and learners (Independent Thinking On... series)No ratings yet
- EPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesEPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- EPI 3.4 Outbreak Table Top ExerciseDocument5 pagesEPI 3.4 Outbreak Table Top ExerciseJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine 2.04 Public Health Administration Dr. AdversarioDocument5 pagesCommunity Medicine 2.04 Public Health Administration Dr. AdversarioJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-4.03 Public Health Administration and ManagementDocument5 pagesFCM3-4.03 Public Health Administration and ManagementJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-4.07 Precede-Proceed ModelDocument5 pagesFCM3-4.07 Precede-Proceed ModelJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine 3.02 BHW Open ForumDocument2 pagesCommunity Medicine 3.02 BHW Open ForumJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Philhealth: Coverage and ExclusionsDocument15 pagesPhilhealth: Coverage and ExclusionsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-4.04 Situational AnalysisDocument3 pagesFCM3-4.04 Situational AnalysisJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine 2.05 Health-Economics-Dr.-BrizuelaDocument7 pagesCommunity Medicine 2.05 Health-Economics-Dr.-BrizuelaJoher Mendez100% (1)
- FCM3-3.07 National Nutrition ProgramDocument24 pagesFCM3-3.07 National Nutrition ProgramJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-3.03 Renal Disease Control ProgramDocument10 pagesFCM3-3.03 Renal Disease Control ProgramJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- PDR 1.01 Code-of-EthicsDocument3 pagesPDR 1.01 Code-of-EthicsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- 4.01-PDR-Physician Communication SkillsDocument5 pages4.01-PDR-Physician Communication SkillsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-3.02 Philippine Cancer Control ProgramDocument11 pagesFCM3-3.02 Philippine Cancer Control ProgramJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Trans 3: Exam 2Document3 pagesTrans 3: Exam 2Joher MendezNo ratings yet
- Aspect That Make Adult Learner DifferentDocument3 pagesAspect That Make Adult Learner DifferentMohamed MansourNo ratings yet
- A Novel Viewpoint On Andragogy. Enabling Moments of CommunityDocument18 pagesA Novel Viewpoint On Andragogy. Enabling Moments of CommunitydarkbyronsNo ratings yet
- Professional Development and Ict in EducDocument131 pagesProfessional Development and Ict in EducHAN VLOGNo ratings yet
- Understanding Modular Learning - Developing A Strategic Plan To Embrace ChangeDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Modular Learning - Developing A Strategic Plan To Embrace ChangebabyyyyyyNo ratings yet
- Train-the-Trainer Manual:: Mentoring Adult LearnersDocument29 pagesTrain-the-Trainer Manual:: Mentoring Adult LearnersmuhammadkashikNo ratings yet
- WBSU PG SYLLABUS 2019 FinalDocument45 pagesWBSU PG SYLLABUS 2019 FinalDepartment of EducationNo ratings yet
- Midterm Serineh VartaniDocument6 pagesMidterm Serineh Vartaniapi-554373722No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Big Coaching ModelsDocument305 pagesThe Little Book of Big Coaching ModelsantarcticaNo ratings yet
- III Arvin Gwapo - PPTX 4.0Document32 pagesIII Arvin Gwapo - PPTX 4.0RoelNo ratings yet
- Instructional Strategies A-ZDocument78 pagesInstructional Strategies A-ZAlkaNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning TheoriesDocument5 pagesTeaching and Learning TheoriesJulie Ann Gerna100% (3)
- Sanchez Sebastian 2024 Integrating Affection Emotion and Aesthetics Into A General Theory of LearningDocument24 pagesSanchez Sebastian 2024 Integrating Affection Emotion and Aesthetics Into A General Theory of LearningZikri AhmadNo ratings yet
- Applications of Andragogy in Multi-Disciplined Teaching and Learning PDFDocument11 pagesApplications of Andragogy in Multi-Disciplined Teaching and Learning PDFtigresse123No ratings yet
- Principles of Adult Learning PDFDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Adult Learning PDFGangadharNo ratings yet
- JamaicaDocument21 pagesJamaicaChrismar SumayangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Andragogy How Adults LearnDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Andragogy How Adults LearnNicole M. MarshallNo ratings yet
- Emerging Pedagogies For Effective Adult Learning: From Andragogy To HeutagogyDocument6 pagesEmerging Pedagogies For Effective Adult Learning: From Andragogy To HeutagogyAnonymous GOUaH7FNo ratings yet
- Charecterstics of Adul LearnerDocument23 pagesCharecterstics of Adul LearnerFazila ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Learning SystemDocument56 pagesMathematics Learning SystemMajestyNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 5 and Others EditedDocument70 pagesChapters 1 5 and Others EditedJenica De Guzman GalvezNo ratings yet
- Ed203 Chapter 2 Young, Adolescent, Adult LearnersDocument23 pagesEd203 Chapter 2 Young, Adolescent, Adult Learnersjoedskie2801No ratings yet
- How Adults LearnDocument3 pagesHow Adults LearnDamian MarreroNo ratings yet
- SWPP Online Final Coaching (Questionnaire)Document13 pagesSWPP Online Final Coaching (Questionnaire)salman arompacNo ratings yet
- Mapping Out The Research Field of Adult Education and LearningDocument228 pagesMapping Out The Research Field of Adult Education and LearningPetra Bajić100% (1)
- Theory of Distance Learning-2Document12 pagesTheory of Distance Learning-2api-264600724No ratings yet
- PED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Document18 pagesPED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Mary Antonette JalosjosNo ratings yet
- Religious Education: The Official Journal of The Religious Education AssociationDocument11 pagesReligious Education: The Official Journal of The Religious Education AssociationSENJA GULAMANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Adult Learning, OB ModDocument13 pagesLecture 6 - Adult Learning, OB ModPrashant Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Course Syllabus SuperLearner V2.0 UdemyDocument10 pages2018 - Course Syllabus SuperLearner V2.0 UdemyasdfsafdNo ratings yet
Community Medicine 3.04 Andragogy - Dr. Zulueta
Community Medicine 3.04 Andragogy - Dr. Zulueta
Uploaded by
Joher Mendez0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
10 views2 pagesCommunity Medicine 3.04 Andragogy - Dr. Zulueta
Community Medicine 3.04 Andragogy - Dr. Zulueta
Uploaded by
Joher MendezCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 2
Subject: Community Medicine
Topic: Andragogy
Lecturer: Dr. Zulueta
Date: February 9, 2016
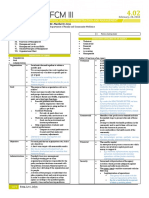
OUTLINE IV. CHARACTERISTICS OF ANDRAGOGY
I. Andragogy IV. Characteristics of Andragogy Goal oriented – All actions/activities must be directed towards
II. UERM Mission V. Principles of Andragogy achieving the set goal.
III. Andragogy vs. Pedagogy VI. Learning Strategies
o 2015B: Instructors must show adult learners how classes will
help them attain their goals which are said early in the course.
OBJECTIVES
At the end of the lecture, the learner will be able to: Respect ‑ as the lecturer, you show respect to your students by
1. Prepare a presentation applying the Principles of Adult Learning being on time
(Andragogy) o 2015B: Acknowledge the wealth of experiences; These adults
References: should be treated as equals in experience and knowledge and
1. Tuazon J., Dones L., Bonito S., A Training Manual for Health allowed to voice their opinions freely in class
Workers on Promoting Healthy Lifestyle, World Health Autonomous – independent or “adventurous” learning
Organization, 2003
2. Mencias, Cristina, Teacher Training Module on Adult Learning,
o 2015B: Teachers must actively involve adult participants in the
UERMMMCI, Jan. 2014 learning process and serve as facilitators for them
3. Zulueta, FM, Principles and Methods of Teaching, National Practical – when students see the use and purpose of the lesson,
Bookstore, Philippines, 2006 they tend to learn it better
o 2015B: They focus on the aspects of a lesson most useful to
I. ANDRAGOGY them in their work; NOT interested in knowledge for its own
Andragogy – the art and science of helping adults learn sake.
o Learning – modification of a behavioral tendency by Experience
experience (as exposure to conditioning) o 2015B: Accumulated a foundation of life experiences and
Develop outstanding professionals committed to lifelong learning knowledge that may include work--‐‑related activities, family
Provide equitable, holistic, and quality care responsibilities, and previous education.
Advance quality research relevant to education and practice of
health professionals Class Activity
Advocate causes and promote love of country, welfare of the A Question for You:
people, and preservation of the environment Who would you rather have?
Provide services relevant and responsive to the needs of the A teacher who is nice and friendly who allows you the
community liberty of doing everything you want a teacher who is strict
and demands outputs from you?
II. UERM - MISSION
Develop outstanding professionals committed to lifelong learning
Provide equitable, holistic, and quality care. V. PRINCIPLES OF ANDRAGOGY
Advance quality research relevant to education and practice of Malcolm Shepherd Knowles (1913-1997)
health professionals A pioneer in the study of adult learning
Advocate causes and promote love of country, welfare of the “Who would you rather have: a teacher who is nice and friendly
people, and preservation of the environment who allows you the liberty of doing everything you want or a
Provide services relevant and responsive to the needs of the teacher who is strict and demands outputs from you?”
community – one of the needs is health education Teacher as facilitator of learning: they make learning easier for
students; no room for terror teachers
Adults are capable of making their own decisions once they have
Class Activity
information they need
Recall something that you learned well.
Adults learn best when learning is focused on them, not the
This could be an idea, skill, or an attitude.
teacher
Describe the condition in which you learned it. When, where,
Ex: student seminars in DPC
how and from whom or with whom did you learn it?
Why do you think you learned it well? Principles
1. They understand why something is important to know or do.
2. They have the freedom to learn in their own way.
III. ANDRAGOGY VS. PEDAGOGY 3. Learning is experiential.
2015B: PEDAGOGY: TEACHER‑CENTERED learning. 4. The time is right for them to learn.
Sit in a classroom 5. The process is positive and encouraging.
Job was to be quiet, listen to the teacher
And do what they were told VI. LEARNING STRATEGIES
ANDRAGOGY: The process of HELPING ADULTS LEARN Discussion – most widely used teaching method in the
Adults are capable of making their own decisions once they have community setting
the information they need. Laboratory
Adults learn best when learning is focused on them, not the Simulation
teacher. Field Experiences – one must not learn by watching, but by
Trans Group: 2 – John, Steph, Lara, Boss Page 1 of 2
Edited By: Alex
doing. Theories mean nothing if you cannot apply them.
Team Projects
Action Learning – active learning with participation.
Use a variety of teaching materials and methods (to take into
account differences in style, time, types, and pace of learning)
Page 2 of 2
You might also like
- Criminal Law Review-2020 Part 2 SyllabusDocument11 pagesCriminal Law Review-2020 Part 2 Syllabusrgtan3No ratings yet
- Pedagogy, AndraDocument1 pagePedagogy, AndraDANA ISABELLE PILAPILNo ratings yet
- Andragogy of Learning Chapter 1Document29 pagesAndragogy of Learning Chapter 1Orapa Sarah GenNo ratings yet
- St. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Document5 pagesSt. Louis College of Bulanao: Purok 6, Bulanao, Tabuk City, Kalinga 3800Cath TacisNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Educational PearlsDocument36 pagesTop Ten Educational Pearlsnad791No ratings yet
- Acfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3Document4 pagesAcfrogbd Sdxinp0mtk2gcuyb-Aktoxoi5yge0qmcajqwgu2wgajquml Jfzfxsqk3x5fuakcja3adjjlzddkuio7wh1lhnu65aneq0k Htid v8 Ac8cyh2xtxgozuwrfgruozl-Kl5d1o2p3c3marcNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7Document10 pagesChapter 7Luarez, Jessa S.No ratings yet
- The Learning CycleDocument19 pagesThe Learning Cyclehaddi awanNo ratings yet
- LP 100 Lesson 1 PEDAGOGY ANDRAGOGY AND HEUTAGOGYDocument18 pagesLP 100 Lesson 1 PEDAGOGY ANDRAGOGY AND HEUTAGOGYShania May100% (1)
- All NotesDocument205 pagesAll Notesjoseph mwizerwaNo ratings yet
- Principles of TeachingDocument89 pagesPrinciples of TeachingAnne Anne Cabeltis-MañaboNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Education: Learning OutcomesDocument6 pagesNutrition Education: Learning OutcomesRay MondoNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Pedagogy, Andragogy and SynergonyDocument27 pagesConcepts of Pedagogy, Andragogy and SynergonyAvinash RambhursyNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Episode 16Document9 pagesFS 1 Episode 16jedshining4444No ratings yet
- Andragogy TheoryDocument5 pagesAndragogy Theoryjokovach11No ratings yet
- Adult LearningDocument19 pagesAdult LearningMaurisMilzaamANo ratings yet
- Adult Learning PrinciplesDocument2 pagesAdult Learning PrinciplesDonna AlteaNo ratings yet
- Teaching Training CycleDocument16 pagesTeaching Training CycleYESSENIANo ratings yet
- Module - Gonzales - Facilitating LearningDocument6 pagesModule - Gonzales - Facilitating Learningariannerose gonzalesNo ratings yet
- GEE PMT Module 3Document4 pagesGEE PMT Module 3Ryan AmaroNo ratings yet
- Background On The Concept and The Educator: Knowles' 5 Assumptions of Adult LearnersDocument3 pagesBackground On The Concept and The Educator: Knowles' 5 Assumptions of Adult LearnersShiVani KoLashNo ratings yet
- Local Media2052876972954932851Document7 pagesLocal Media2052876972954932851Gennelle MacatangayNo ratings yet
- FS 1 Le16Document4 pagesFS 1 Le16Jorebell W. QuiminoNo ratings yet
- Research MethodologyDocument5 pagesResearch MethodologyCharwayne DaitNo ratings yet
- Adult Learning and Learning NeedsDocument42 pagesAdult Learning and Learning NeedskrishnasreeNo ratings yet
- The Science of LearningDocument11 pagesThe Science of LearningSimpliciusNo ratings yet
- Advance Prin Modules ReviewDocument31 pagesAdvance Prin Modules ReviewKate ZylNo ratings yet
- The Paper Students' Characteristic and Teaching StrategisDocument12 pagesThe Paper Students' Characteristic and Teaching StrategisSMK MANBAUL MAARIFNo ratings yet
- LAC Nov. 18,2022 Strategies and Technique in Teaching ScienceDocument31 pagesLAC Nov. 18,2022 Strategies and Technique in Teaching ScienceCharm Vergara100% (1)
- Lesson 1 Educational Psychology A Tool For Effective TeachingDocument8 pagesLesson 1 Educational Psychology A Tool For Effective TeachingJay Mark CabreraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 ADULT LEARNINGDocument6 pagesChapter 5 ADULT LEARNINGJulius FrondaNo ratings yet
- PragmatismDocument15 pagesPragmatismNizar Jan MhbNo ratings yet
- The Learning Environment: Lesson 3Document3 pagesThe Learning Environment: Lesson 3Raymart SantiagoNo ratings yet
- Gtle Pedagogy SHS-1Document50 pagesGtle Pedagogy SHS-1piusdanaaNo ratings yet
- The Ultimate EducatorDocument14 pagesThe Ultimate EducatorAlexander Antonio Ortega AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Facilitating Adult Learning Dr. Radhika KapurDocument7 pagesFacilitating Adult Learning Dr. Radhika KapurCaroline AquenNo ratings yet
- The Teaching Profession - Chapter 5Document7 pagesThe Teaching Profession - Chapter 5George Kevin TomasNo ratings yet
- 10 Learning PrinciplesDocument15 pages10 Learning PrinciplesAjeng HardinieNo ratings yet
- Phillips 66 - Chapter 1-3Document37 pagesPhillips 66 - Chapter 1-3Cindy GacutanNo ratings yet
- 4 Key Concepts of AndragogyDocument7 pages4 Key Concepts of AndragogyJoshuaNo ratings yet
- Towards Relevant Education For All: First ActivityDocument6 pagesTowards Relevant Education For All: First ActivityDarwin RosendeNo ratings yet
- KnowlesDocument6 pagesKnowlesMericar EsmedioNo ratings yet
- Andragogy and Learning TheoryDocument36 pagesAndragogy and Learning TheoryAyu AmbarwatiNo ratings yet
- Function of Group DiscussionDocument25 pagesFunction of Group DiscussionYogendra Patil100% (1)
- Principles of Learning: UNIT II - Chapter 1Document63 pagesPrinciples of Learning: UNIT II - Chapter 1Juodie Lee VaelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document9 pagesChapter 2David MangawilNo ratings yet
- 0 Training TechniquesDocument22 pages0 Training TechniquesHani BoudiafNo ratings yet
- CM 4 PHDocument18 pagesCM 4 PHGeorgeNo ratings yet
- LEARNINGDocument7 pagesLEARNINGNYENTY PRIDE ASHU-CHINo ratings yet
- GEE-PMT Module 4 Week 6-7Document4 pagesGEE-PMT Module 4 Week 6-7TimothyLimNo ratings yet
- Activity 16.1 Analyzing Deped'S Philosophy of EducationDocument7 pagesActivity 16.1 Analyzing Deped'S Philosophy of EducationRay Allen FabroNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Androgogy and PedagogyDocument17 pagesLecture 3 Androgogy and PedagogySajida Bibi NoonariNo ratings yet
- FLCTDocument7 pagesFLCTMissy GarciaNo ratings yet
- PED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Document18 pagesPED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Mary Antonette JalosjosNo ratings yet
- Principles of Adult Learning: Unit 2.3Document14 pagesPrinciples of Adult Learning: Unit 2.3Ronnie RicardelNo ratings yet
- Student Directed Learning StrategiesDocument36 pagesStudent Directed Learning Strategiesyhanne100% (17)
- Final Research Na DisDocument31 pagesFinal Research Na DisEarl SemblanteNo ratings yet
- 22 Teaching StrategiesDocument8 pages22 Teaching StrategiesArnyjoy RioNo ratings yet
- Group 3Document27 pagesGroup 3Random PersonNo ratings yet
- Lesson5 1Document16 pagesLesson5 1Ginalyn Fernandez DyangcoNo ratings yet
- Independent Thinking on Teaching and Learning: Developing independence and resilience in all teachers and learners (Independent Thinking On... series)From EverandIndependent Thinking on Teaching and Learning: Developing independence and resilience in all teachers and learners (Independent Thinking On... series)No ratings yet
- EPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchDocument5 pagesEPI 3.6 Qualitative ResearchJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- EPI 3.4 Outbreak Table Top ExerciseDocument5 pagesEPI 3.4 Outbreak Table Top ExerciseJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine 2.04 Public Health Administration Dr. AdversarioDocument5 pagesCommunity Medicine 2.04 Public Health Administration Dr. AdversarioJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-4.03 Public Health Administration and ManagementDocument5 pagesFCM3-4.03 Public Health Administration and ManagementJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-4.07 Precede-Proceed ModelDocument5 pagesFCM3-4.07 Precede-Proceed ModelJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine 3.02 BHW Open ForumDocument2 pagesCommunity Medicine 3.02 BHW Open ForumJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Philhealth: Coverage and ExclusionsDocument15 pagesPhilhealth: Coverage and ExclusionsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-4.04 Situational AnalysisDocument3 pagesFCM3-4.04 Situational AnalysisJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Community Medicine 2.05 Health-Economics-Dr.-BrizuelaDocument7 pagesCommunity Medicine 2.05 Health-Economics-Dr.-BrizuelaJoher Mendez100% (1)
- FCM3-3.07 National Nutrition ProgramDocument24 pagesFCM3-3.07 National Nutrition ProgramJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-3.03 Renal Disease Control ProgramDocument10 pagesFCM3-3.03 Renal Disease Control ProgramJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- PDR 1.01 Code-of-EthicsDocument3 pagesPDR 1.01 Code-of-EthicsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- 4.01-PDR-Physician Communication SkillsDocument5 pages4.01-PDR-Physician Communication SkillsJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- FCM3-3.02 Philippine Cancer Control ProgramDocument11 pagesFCM3-3.02 Philippine Cancer Control ProgramJoher MendezNo ratings yet
- Trans 3: Exam 2Document3 pagesTrans 3: Exam 2Joher MendezNo ratings yet
- Aspect That Make Adult Learner DifferentDocument3 pagesAspect That Make Adult Learner DifferentMohamed MansourNo ratings yet
- A Novel Viewpoint On Andragogy. Enabling Moments of CommunityDocument18 pagesA Novel Viewpoint On Andragogy. Enabling Moments of CommunitydarkbyronsNo ratings yet
- Professional Development and Ict in EducDocument131 pagesProfessional Development and Ict in EducHAN VLOGNo ratings yet
- Understanding Modular Learning - Developing A Strategic Plan To Embrace ChangeDocument13 pagesUnderstanding Modular Learning - Developing A Strategic Plan To Embrace ChangebabyyyyyyNo ratings yet
- Train-the-Trainer Manual:: Mentoring Adult LearnersDocument29 pagesTrain-the-Trainer Manual:: Mentoring Adult LearnersmuhammadkashikNo ratings yet
- WBSU PG SYLLABUS 2019 FinalDocument45 pagesWBSU PG SYLLABUS 2019 FinalDepartment of EducationNo ratings yet
- Midterm Serineh VartaniDocument6 pagesMidterm Serineh Vartaniapi-554373722No ratings yet
- The Little Book of Big Coaching ModelsDocument305 pagesThe Little Book of Big Coaching ModelsantarcticaNo ratings yet
- III Arvin Gwapo - PPTX 4.0Document32 pagesIII Arvin Gwapo - PPTX 4.0RoelNo ratings yet
- Instructional Strategies A-ZDocument78 pagesInstructional Strategies A-ZAlkaNo ratings yet
- Teaching and Learning TheoriesDocument5 pagesTeaching and Learning TheoriesJulie Ann Gerna100% (3)
- Sanchez Sebastian 2024 Integrating Affection Emotion and Aesthetics Into A General Theory of LearningDocument24 pagesSanchez Sebastian 2024 Integrating Affection Emotion and Aesthetics Into A General Theory of LearningZikri AhmadNo ratings yet
- Applications of Andragogy in Multi-Disciplined Teaching and Learning PDFDocument11 pagesApplications of Andragogy in Multi-Disciplined Teaching and Learning PDFtigresse123No ratings yet
- Principles of Adult Learning PDFDocument22 pagesPrinciples of Adult Learning PDFGangadharNo ratings yet
- JamaicaDocument21 pagesJamaicaChrismar SumayangNo ratings yet
- Understanding Andragogy How Adults LearnDocument5 pagesUnderstanding Andragogy How Adults LearnNicole M. MarshallNo ratings yet
- Emerging Pedagogies For Effective Adult Learning: From Andragogy To HeutagogyDocument6 pagesEmerging Pedagogies For Effective Adult Learning: From Andragogy To HeutagogyAnonymous GOUaH7FNo ratings yet
- Charecterstics of Adul LearnerDocument23 pagesCharecterstics of Adul LearnerFazila ShafiqueNo ratings yet
- Mathematics Learning SystemDocument56 pagesMathematics Learning SystemMajestyNo ratings yet
- Chapters 1 5 and Others EditedDocument70 pagesChapters 1 5 and Others EditedJenica De Guzman GalvezNo ratings yet
- Ed203 Chapter 2 Young, Adolescent, Adult LearnersDocument23 pagesEd203 Chapter 2 Young, Adolescent, Adult Learnersjoedskie2801No ratings yet
- How Adults LearnDocument3 pagesHow Adults LearnDamian MarreroNo ratings yet
- SWPP Online Final Coaching (Questionnaire)Document13 pagesSWPP Online Final Coaching (Questionnaire)salman arompacNo ratings yet
- Mapping Out The Research Field of Adult Education and LearningDocument228 pagesMapping Out The Research Field of Adult Education and LearningPetra Bajić100% (1)
- Theory of Distance Learning-2Document12 pagesTheory of Distance Learning-2api-264600724No ratings yet
- PED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Document18 pagesPED 12 - Facilitating Learning in Diverse Contexts - Unit 1Mary Antonette JalosjosNo ratings yet
- Religious Education: The Official Journal of The Religious Education AssociationDocument11 pagesReligious Education: The Official Journal of The Religious Education AssociationSENJA GULAMANNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 - Adult Learning, OB ModDocument13 pagesLecture 6 - Adult Learning, OB ModPrashant Kumar GuptaNo ratings yet
- 2018 - Course Syllabus SuperLearner V2.0 UdemyDocument10 pages2018 - Course Syllabus SuperLearner V2.0 UdemyasdfsafdNo ratings yet