Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Drug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Louise NTF0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views3 pagesCefuroxime is a second generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat mild to moderate bacterial infections. It works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. More serious adverse effects involve allergic reactions, hematologic issues, and colitis. Nursing responsibilities involve assessing for allergies, monitoring lab tests and symptoms, and educating patients about treatment and potential side effects. Dosing varies based on infection being treated, age, and renal function.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCefuroxime is a second generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat mild to moderate bacterial infections. It works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. More serious adverse effects involve allergic reactions, hematologic issues, and colitis. Nursing responsibilities involve assessing for allergies, monitoring lab tests and symptoms, and educating patients about treatment and potential side effects. Dosing varies based on infection being treated, age, and renal function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
66 views3 pagesDrug Study
Drug Study
Uploaded by
Louise NTFCefuroxime is a second generation cephalosporin antibiotic used to treat mild to moderate bacterial infections. It works by interfering with bacterial cell wall synthesis. Common side effects include gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea and nausea. More serious adverse effects involve allergic reactions, hematologic issues, and colitis. Nursing responsibilities involve assessing for allergies, monitoring lab tests and symptoms, and educating patients about treatment and potential side effects. Dosing varies based on infection being treated, age, and renal function.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 3
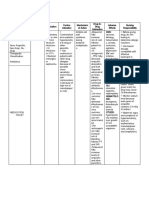
Name of Student: Ferrer, Nyree T.
Date: February 12,2021
Level/Block/Group: 2BSN-3 Hospital/Area: Clinical Instructor: Ma’am Amelita Dumaguin
NAME OF DRUG CONTRAINDICATIONS SIDE EFFECTS ADVERSE EFFECTS NURSING RESPONSIBILITIES
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Cephalosporins exert Hypersensitivity to GI: Vomiting Before:
GENERIC NAME
bactericidal activity by cefuroxime or to other Diarrhea, Abdominal pain Determine history
interfering with bacterial cephalosporins. nausea, antibiotic- Colitis of hypersensitivity rea
cell wall synthesis and associated colitis. Vaginal candidiasis ctions to
Cefuroxime inhibiting cross-linking of Toxic nephropathy cephalosporins,
the peptidoglycan. The Skin: Cholestasis penicillin, and history
cephalosporins are also Rash, pruritus, Aplastic anemia of allergies,
BRAND NAME thought to play a role in urticaria. Hemolytic anemia particularly to drugs,
the activation of bacterial Hemorrhage. before therapy is
cell autolysins which may Urogenital: initiated.
contribute to bacterial cell Increased serum Lab tests: Perform
Altoxime lysis. creatinine and culture and sensitivity
BUN, decreased tests before initiation
creatinine of therapy and
clearance. periodically during
CLASSIFICATION
therapy if indicated.
Therapeutic: Hematologic: Therapy may be
Anti-infectives Hemolytic anemia instituted pending test
results. Monitor
Pharmacologic: MISC: periodically BUN and
Second generation Anaphylaxis creatinine clearance.
Cephalosporins During:
Inspect IM and IV
injection sites
INDICATIONS frequently for signs of
phlebitis.
Susceptible mild to Monitor for
moderate infections manifestations
including of hypersensitivity (se
pharyngitis/tonsillitis, e Appendix F).
acute maxillary sinusitis, Discontinue drug and
chronic bronchitis, acute report their
otitis media, appearance promptly.
uncomplicated skin and Monitor I&O rates
skin structure, UTIs, and pattern: Especially
gonorrhea, early Lyme important in severely
disease. ill patients receiving
high doses. Report any
significant changes.
Report onset of
loose stools or
diarrhea. Although
pseudomembranous
DOSAGE & FREQUENCY colitis (see Signs &
Dosing in adults: Symptoms, Appendix
Acute exacerbation F) rarely occurs, this
of chronic potentially life-
bronchitis: 250mg to threatening
500mg PO q12h x 10 complication should
days be ruled out as the
Uncomplicated UTI: cause of diarrhea
125mg - 250mg PO during and after
q12h x 7-10 days antibiotic therapy.
Gonorrhea: 1g PO x After:
1 dose Instruct patient to
Lower respiratory take medication
tract infection: around the clock at
750mg - 1.5g IV/IM evenly spaced times
q8h and to finish the
Bone/joint medication
infection: 1.5 g completely, even if
IV/IM q8h feeling better
Advise patient to
Dosing in pediatrics: report signs of
PO: 30mg/kg/day superinfection and
divided q12h allergy
IV/IM: 50- Instruct patient to
100mg/kg/day notify health
divided q6 to q8h professional if fever
and diarrhea develop
Disease state based
dosing:
Renal failure (IV dosing):
CrCl > 20mL/min:
Standard dosing
CrCl 10-20mL/min:
0.75g q12h
CrCl < 10mL/min:
0.75g q12h
You might also like
- PBCC Baseline SurveyDocument1 pagePBCC Baseline Surveylynore sandoval0% (1)
- Drug Study - CefuroximeDocument1 pageDrug Study - Cefuroximewindstruck88% (26)
- Ampicillin - Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmpicillin - Drug StudyLegendX100% (5)
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CEFAZOLINDocument6 pagesDrug Study CEFAZOLINAicelle Love Sampat LapenaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Drug Study ChanDocument5 pagesCefuroxime Drug Study Chanczeremar chanNo ratings yet
- DSREVISEDDocument8 pagesDSREVISEDamvNo ratings yet
- Co AmoxyclavDocument2 pagesCo AmoxyclavHaneulNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxomine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefuroxomine Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: AllopurinolDocument1 pageI. Drug Study: Allopurinolkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (IV)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (IV)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studystephanie valerioNo ratings yet
- Name of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionDocument1 pageName of Patient: E.J.P Ward/Room/Bed #: Pedia Ward/G.I./Bed 1 Age & Sex: 2 Y.o/ Female Diagnosis: Urinary Tract InfectionSALMA M. TUANONo ratings yet
- Drugsstudy Different ObDocument8 pagesDrugsstudy Different ObElvis DuotNo ratings yet
- Drug Study of OxytocinDocument4 pagesDrug Study of OxytocinNichole DancelNo ratings yet
- Drug Study FormatDocument7 pagesDrug Study FormatJane BautistaNo ratings yet
- Villamaria - Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVillamaria - Drug StudyHey LeunNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, CefuroximeDocument4 pagesDrug Study - Paracetamol Ambroxol, Ascorbic Acid, Cefuroximeapi-3701489100% (12)
- Drug Study - CefotaximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study - CefotaximeAngel laurestaNo ratings yet
- Case Pre Drug StudyDocument22 pagesCase Pre Drug StudyBenjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Drug/Classification Dose/Route Mechanism of Action Common Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesLiiza G-GsprNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Drugsss Study FinalDocument12 pagesGroup 3 Drugsss Study FinalRam EscaleraNo ratings yet
- Borres Drugstudy-M2w7Document3 pagesBorres Drugstudy-M2w7gnmalisaNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY Piptaz ClindamycinDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY Piptaz ClindamycinJAYMIE ROSE M. MANUELNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug AlgeDocument1 pageName of Drug Algealgerich_delacuestaNo ratings yet
- CEFUROXIMEDocument3 pagesCEFUROXIMEGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument9 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeRio Ramon HilarioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeDocument5 pagesDrug Study Paracetamol Ambroxol Ascorbic Acid CefuroximeCia TriiNo ratings yet
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 pagesDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyJamie Grace AbitNo ratings yet
- Drugs MaleDocument4 pagesDrugs MaleJb RosillosaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RyDocument30 pagesDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Banaag Antibacterial MedsDocument5 pagesBanaag Antibacterial MedsPrince JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem Drug StudyDocument3 pagesErtapenem Drug StudyBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Format and SampleDocument6 pagesDrug Study Format and SampleA.No ratings yet
- Drug-Study CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug-Study Cefuroximegervisrael.gonzales.twphosiNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyMary LyonNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyRisha Ethel BerondoNo ratings yet
- DS - Mod9Document2 pagesDS - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyJoseph Angelo Fortuna CarmonaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!Document3 pagesDrug Study Ko BFF Pa-Print Pls Thanks Much Mwa!shasheeeeyNo ratings yet
- I. Drug Study: Denosuma B Natalizuma B, RoflumilastDocument2 pagesI. Drug Study: Denosuma B Natalizuma B, Roflumilastkimglaidyl bontuyanNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument3 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- MEROPENEMDocument1 pageMEROPENEMJust now0% (1)
- Drug Study: Nursing DepartmentDocument1 pageDrug Study: Nursing Departmentgiselle chloeNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime Axetil (Oral)Document2 pagesCefuroxime Axetil (Oral)STORAGE FILENo ratings yet
- Antimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineFrom EverandAntimicrobial Therapy in Veterinary MedicineSteeve GiguèreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Untoward Effects of Drugs - A Pharmacological and Clinical ManualFrom EverandThe Untoward Effects of Drugs - A Pharmacological and Clinical ManualNo ratings yet
- Tropical Diseases: An Overview of Major Diseases Occurring in the AmericasFrom EverandTropical Diseases: An Overview of Major Diseases Occurring in the AmericasNo ratings yet
- 01 Diseases - Guess What It IsDocument11 pages01 Diseases - Guess What It IsRahmania PamungkasNo ratings yet
- CellulitisDocument6 pagesCellulitisjadeNo ratings yet
- Literature Review On BacteriaDocument9 pagesLiterature Review On Bacteriaea83xjp7100% (1)
- 8C Microbes and DiseaseDocument31 pages8C Microbes and Diseasefmk2005No ratings yet
- Noma Cancrum Oris Gangrenous GingivitisDocument3 pagesNoma Cancrum Oris Gangrenous GingivitisSuprit Sn100% (2)
- FlagellatesDocument64 pagesFlagellatesRandy BerryNo ratings yet
- ImmunopharmacologyDocument19 pagesImmunopharmacologyMaaz Uddin Siddiqui100% (2)
- Wang 2017Document10 pagesWang 2017vania adheliaNo ratings yet
- 2020 Anaphylaxis JACI 2020Document42 pages2020 Anaphylaxis JACI 2020Peter Albeiro Falla CortesNo ratings yet
- Microbiology SBA For MRCOG Part 1Document42 pagesMicrobiology SBA For MRCOG Part 1Mohamed Rikarz Ahamed Rikarz100% (1)
- Final Project: Be Vaccinated For Covid-19?" What Can Be Design That Will Make 100% of Citizen in India ToDocument23 pagesFinal Project: Be Vaccinated For Covid-19?" What Can Be Design That Will Make 100% of Citizen in India ToSaiAditya MeesalaNo ratings yet
- Agglutination-Reactions Agglutination - ReactionsDocument4 pagesAgglutination-Reactions Agglutination - Reactionsrenato renatoNo ratings yet
- Immunology ModuleDocument42 pagesImmunology ModuleAhmed KerAtyNo ratings yet
- Lufthansa Travel RegulationsDocument5 pagesLufthansa Travel RegulationsmNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Innate ImmunityDocument26 pagesLecture 3 Innate ImmunitytimcarasNo ratings yet
- Maklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsDocument1 pageMaklumat Vaksinasi: Vaccination DetailsSyamin FarhanimNo ratings yet
- Blood - Chapter 11 Functions of Blood HematopoiesisDocument8 pagesBlood - Chapter 11 Functions of Blood HematopoiesisLol lolNo ratings yet
- Chapter XI FinalDocument12 pagesChapter XI FinalFadNo ratings yet
- Pneumonii PedDocument19 pagesPneumonii PedVeronica NefiruNo ratings yet
- DR Brownstein A Novel Approach To Treating Cornavirus Using Nutritional and Oxidative TherapiesDocument19 pagesDR Brownstein A Novel Approach To Treating Cornavirus Using Nutritional and Oxidative Therapiessame shitNo ratings yet
- TUBERCULOSIS (Lec Community Medicine)Document24 pagesTUBERCULOSIS (Lec Community Medicine)wanderer_1010No ratings yet
- Tuberculosis: Kristine SuguitanDocument10 pagesTuberculosis: Kristine SuguitanKish SuguitanNo ratings yet
- Alcantara, Charmine Swab PDFDocument1 pageAlcantara, Charmine Swab PDFJohnmar AquinoNo ratings yet
- Global TB Report 2022 FactsheetDocument2 pagesGlobal TB Report 2022 FactsheetKao YokoboriNo ratings yet
- Literature ReviewDocument2 pagesLiterature ReviewericNo ratings yet
- Soal Hematologi 2014Document3 pagesSoal Hematologi 2014Muhammad Faza NaufalNo ratings yet
- Major Histocompatibility Complex (Aka HumanDocument5 pagesMajor Histocompatibility Complex (Aka HumanDarwin AlejosNo ratings yet
- ISBB CompilationDocument6 pagesISBB CompilationElla SalesNo ratings yet
- Blood SmearsDocument4 pagesBlood SmearsAmor KourdouliNo ratings yet