Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Demand Is Stable: P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5
Demand Is Stable: P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5
Uploaded by
Al BorjaCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Explanation: Step-By-Step ExplanationDocument1 pageExplanation: Step-By-Step ExplanationAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- P (F - High) 0.35 P (U - High) 0.65 P (F - Moderate) 0.45 P (U - Moderate) 0.55 P (F - Low) 0.20 P (U - Low) 0.80Document4 pagesP (F - High) 0.35 P (U - High) 0.65 P (F - Moderate) 0.45 P (U - Moderate) 0.55 P (F - Low) 0.20 P (U - Low) 0.80Al BorjaNo ratings yet
- P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5Document1 pageP (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5Al BorjaNo ratings yet
- s1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureDocument4 pagess1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- 1 Linear Programming ProblemDocument2 pages1 Linear Programming ProblemAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument2 pagesAnswerAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- s1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureDocument4 pagess1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- Facility Design and Management Handbook EricDocument6 pagesFacility Design and Management Handbook EricAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- Dealer Monthly Cost ($) Mileage Allowances Cost Per Additional Mile ($)Document2 pagesDealer Monthly Cost ($) Mileage Allowances Cost Per Additional Mile ($)Al BorjaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Biofuel ProducersDocument1 pagePhilippine Biofuel ProducersAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- SPBT2632C1A: Bluetooth Technology Class-1 ModuleDocument27 pagesSPBT2632C1A: Bluetooth Technology Class-1 ModuleAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Biofuels PDFDocument3 pagesPhilippine Biofuels PDFAl BorjaNo ratings yet
Demand Is Stable: P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5
Demand Is Stable: P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5
Uploaded by
Al BorjaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Demand Is Stable: P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5
Demand Is Stable: P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5
Uploaded by
Al BorjaCopyright:
Available Formats
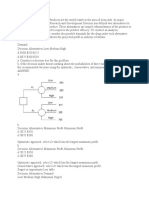
57.
A Manufacturing company introduces two product alternatives. The table below provides profit
payoffs in thousands of dollars.
?
?Bet onState of Nature (Demand)
?UpStableDown
?Product A1188
?Product B81012
?
?
?
The probabilities for the state of nature are P(Up) = 0.35, P(Stable) = 0.35, and P(Down) = 0.30.
A test market study of the potential demand for the product is expected to report either a favorable (F) or
unfavorable (U) condition. The relevant conditional probabilities are as follows:
P(F|Up) = 0.5; P(F|Stable) = 0.3; P(F|Down) = 0.2
P(U|Up) = 0.2; P(U|Stable) = 0.3; P(U|Down) = 0.5
Use Bayes’ theorem to compute the conditional probability of the demand being up, stable, or down,
given each market research outcome.
ANSWER:
Let s1 = Demand is up
s2 = Demand is stable
s3 = Demand is down
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5820)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1093)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (845)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (590)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (898)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (540)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (349)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (822)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Explanation: Step-By-Step ExplanationDocument1 pageExplanation: Step-By-Step ExplanationAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- P (F - High) 0.35 P (U - High) 0.65 P (F - Moderate) 0.45 P (U - Moderate) 0.55 P (F - Low) 0.20 P (U - Low) 0.80Document4 pagesP (F - High) 0.35 P (U - High) 0.65 P (F - Moderate) 0.45 P (U - Moderate) 0.55 P (F - Low) 0.20 P (U - Low) 0.80Al BorjaNo ratings yet
- P (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5Document1 pageP (F - Up) 0.5 P (F - Stable) 0.3 P (F - Down) 0.2 P (U - Up) 0.2 P (U - Stable) 0.3 P (U - Down) 0.5Al BorjaNo ratings yet
- s1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureDocument4 pagess1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- 1 Linear Programming ProblemDocument2 pages1 Linear Programming ProblemAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- AnswerDocument2 pagesAnswerAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- s1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureDocument4 pagess1 s2 s3 d1 d2: Decision Alternative State of NatureAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- Facility Design and Management Handbook EricDocument6 pagesFacility Design and Management Handbook EricAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- Dealer Monthly Cost ($) Mileage Allowances Cost Per Additional Mile ($)Document2 pagesDealer Monthly Cost ($) Mileage Allowances Cost Per Additional Mile ($)Al BorjaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Biofuel ProducersDocument1 pagePhilippine Biofuel ProducersAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- SPBT2632C1A: Bluetooth Technology Class-1 ModuleDocument27 pagesSPBT2632C1A: Bluetooth Technology Class-1 ModuleAl BorjaNo ratings yet
- Philippine Biofuels PDFDocument3 pagesPhilippine Biofuels PDFAl BorjaNo ratings yet