Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 viewsCh-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 07
Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 07
Uploaded by
Ayush KumarThis document contains 9 practice problems related to ray optics. The problems cover topics like refraction at an interface between two media, critical angles, total internal reflection, and calculating the area of a circle of light formed when light refracts through a liquid. The document provides the questions and space to show the answers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- HandWritten Notes PhyscisDocument18 pagesHandWritten Notes PhyscisvanshNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own CDIDocument14 pagesMake Your Own CDIrk-rex96% (28)
- Eletronics Lab Report - Rectifier CircuitDocument4 pagesEletronics Lab Report - Rectifier CircuitThan Lwin Aung93% (14)
- Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 08Document3 pagesCh-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 08Anmol KaushikNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios9 PDFDocument4 pagesEjercicios9 PDFapolo1711No ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Phys102 161 Second MajorDocument10 pagesPhys102 161 Second MajorAvneet Singh AroraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SET A - Model AnswerDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 SET A - Model Answershriramdhumal24744No ratings yet
- PHYSICS P2 To Be Done On 26th MarchDocument7 pagesPHYSICS P2 To Be Done On 26th MarchsykehanscyphaNo ratings yet
- DPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Document4 pagesDPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingNo ratings yet
- JEE Physics Solved Paper 2022Document5 pagesJEE Physics Solved Paper 2022Dhathree KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MT - Phys2 - Summer 23 - Version A - With AnswersDocument6 pagesMT - Phys2 - Summer 23 - Version A - With AnswersaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 23)Document3 pagesRay Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 23)Anmol KaushikNo ratings yet
- RAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12Document27 pagesRAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12AkankshaNo ratings yet
- Be - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2018 - December - Applied Physics II CbcgsDocument20 pagesBe - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2018 - December - Applied Physics II Cbcgsmahek guptaNo ratings yet
- HW 3solution PDFDocument6 pagesHW 3solution PDFanna.heeohNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Set-ADocument9 pagesXii Physics Set-AAshik Anamic ShimiyaNo ratings yet
- Ch-08 Electromagnetic Wave: Daily Practice Problem 02Document2 pagesCh-08 Electromagnetic Wave: Daily Practice Problem 02Chandrima Dola MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Be - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2019 - May - Applied Physics II CbcgsDocument20 pagesBe - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2019 - May - Applied Physics II Cbcgsnocap7884No ratings yet
- The Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics: Chapter OutlineDocument59 pagesThe Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics: Chapter OutlineTran Huy HauNo ratings yet
- Uace Physics Paper 2 2004 GuideDocument16 pagesUace Physics Paper 2 2004 GuideAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Physics MCQ Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument24 pagesCLASS XII Physics MCQ Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsilanchitraNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-12) - PaperDocument13 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-12) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument11 pagesWave OpticsNishi SinghalNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument38 pagesRay OpticsrajeshNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Wave Optics: Daily Practice Problem 03Document3 pagesCh-10 Wave Optics: Daily Practice Problem 03Harshit shuklaNo ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument3 pagesPhysics QPThemistocles AthensNo ratings yet
- Physics: AnswersDocument21 pagesPhysics: AnswersASRANo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (QB)Document12 pagesWave Optics (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 03 Jee Advanced PaperDocument20 pagesMock Test 03 Jee Advanced PaperGanesha Dattatraya Gaonkar CFALNo ratings yet
- KIET PhysicsDocument82 pagesKIET Physicsap cpianNo ratings yet
- 267229750-Sample Paper 4Document6 pages267229750-Sample Paper 4sithur2305No ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On Youtube: - Written Solution On WebsiteDocument4 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On Youtube: - Written Solution On WebsiteHrinmoy HusiyarNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL PROBLEMS ON FIBRE OPTICS - Image.Marked - 1Document4 pagesNUMERICAL PROBLEMS ON FIBRE OPTICS - Image.Marked - 1ANKURANNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION OF Lens, Mirror, RefractionDocument4 pagesSOLUTION OF Lens, Mirror, RefractionRumpa DasNo ratings yet
- Ioqjs (Part 1) 2020 SolutionDocument8 pagesIoqjs (Part 1) 2020 SolutionAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 7: Class XII 2023-24 PhysicsDocument6 pagesSample Paper 7: Class XII 2023-24 PhysicsBhaviniNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Answer Key SetbDocument21 pagesClass Xii Physics Answer Key Setbvarshanair2005No ratings yet
- NSEA 2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Document28 pagesNSEA 2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Pushpanjay Kumar100% (4)
- Ray Optics QuestionsDocument3 pagesRay Optics QuestionsBAAP ka papaNo ratings yet
- Cblephpu 20Document6 pagesCblephpu 20Mahadev SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tugas UAS Fisika Dasar TeknikDocument9 pagesTugas UAS Fisika Dasar TeknikNiko Rizaldi MshlNo ratings yet
- Elecdy Finals BrionesDocument5 pagesElecdy Finals BrionesJonathan Briones Mses MsphyNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer - 23Document29 pagesQuestion and Answer - 23meenakshisivarajNo ratings yet
- HCI 2022 Prelim P1 Guide PDFDocument6 pagesHCI 2022 Prelim P1 Guide PDFBrendanNo ratings yet
- Cluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)Document33 pagesCluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)manpreetsingh3458417No ratings yet
- Properties of Light: T E 15 MJ N 5.24Document17 pagesProperties of Light: T E 15 MJ N 5.24077 AgentNo ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On WebsiteDocument4 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On WebsiteHrinmoy HusiyarNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Physics 28 FebDocument4 pagesClass 12th Physics 28 FebPrem palaiyaNo ratings yet
- Part2 ch11Document9 pagesPart2 ch11api-3705610No ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Reading AssignmentDocument3 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Reading AssignmentDibyananda SahooNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 4 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document9 pagesSample Question Paper - 4 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22abcdNo ratings yet
- Homework No. 2: Fig. 1. Problem 1Document3 pagesHomework No. 2: Fig. 1. Problem 1victus0110No ratings yet
- Canadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesCanadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document7 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22satyam skNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10 Potential and Capacitance SolutionsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 10 Potential and Capacitance Solutionsreyessyrendaniel25No ratings yet
- UP3 - 1.4. Total Internal Reflection - pg19-24Document6 pagesUP3 - 1.4. Total Internal Reflection - pg19-24mohmmadaliawadNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Complete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDocument141 pagesComplete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDigvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - WEIGHT-VOLUME RELATIONSHIP PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - WEIGHT-VOLUME RELATIONSHIP PDFKasturi Letchumanan100% (1)
- Vapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11Document2 pagesVapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11MaykaMidreliDeandraLigutomNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMDocument5 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- M15 PDFDocument28 pagesM15 PDFMartha Escobar RojasNo ratings yet
- Transistor FAN431Document10 pagesTransistor FAN431Rodrigo AlencarNo ratings yet
- Grosse 1962Document10 pagesGrosse 1962Михаил ПарамоновNo ratings yet
- Boquillas Secas ABBDocument5 pagesBoquillas Secas ABBNoé Rafael Colorado SósolNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Paper 3 Section B ExperimentsDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experimentsjajabeans80% (5)
- Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageDatasheet PDFFrizkaZaskiaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 TransducerDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 3 TransducerDegaga KebedeNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 01 CompleteDocument26 pagesExercise # 01 CompleteRehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESDocument17 pages4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESJoebert SabidoNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Assignment Question Ii Year/Iii SemesterDocument2 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Assignment Question Ii Year/Iii SemesterMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- N 2023 Unit Test-1 - (11-July-21)Document25 pagesN 2023 Unit Test-1 - (11-July-21)QXnocMF5No ratings yet
- 3 Phase Motor CG CatalogueDocument74 pages3 Phase Motor CG CatalogueDiana Rose Tapel0% (2)
- MotorDocument10 pagesMotorsameer betalNo ratings yet
- Side Smart VRF - IND - CompressedDocument108 pagesSide Smart VRF - IND - CompressedVirga AnandaNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered AircraftDocument2 pagesSolar Powered AircraftQa LabNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP0403GHDocument5 pagesAdvanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP0403GHIulius CezarNo ratings yet
- Em Notes 20 Special RelativityDocument11 pagesEm Notes 20 Special RelativityHarshitNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Chapter ThreeDocument43 pagesFluid Mechanics - Chapter Threebiniyam mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Isochronous Vs Droop GenDocument4 pagesIsochronous Vs Droop GenInsan AzizNo ratings yet
- Q1 G.PHYSICS 1 L6 Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Document19 pagesQ1 G.PHYSICS 1 L6 Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Ms.Bangalando, S STEM 11-DNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Techniques in Applied ElectromagneticsDocument472 pagesAdvanced Computer Techniques in Applied Electromagneticssmaka_senadNo ratings yet
- Steca PF 166 240 Specification enDocument1 pageSteca PF 166 240 Specification en_at_to_No ratings yet
- CPC 100 PTM Quick Test Application Guide 2020 ENUDocument38 pagesCPC 100 PTM Quick Test Application Guide 2020 ENUNgoc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet
Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 07
Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 07
Uploaded by
Ayush Kumar0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesThis document contains 9 practice problems related to ray optics. The problems cover topics like refraction at an interface between two media, critical angles, total internal reflection, and calculating the area of a circle of light formed when light refracts through a liquid. The document provides the questions and space to show the answers.
Original Description:
Original Title
45310321-b292-48ac-8ca4-15ee45c1eda0
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document contains 9 practice problems related to ray optics. The problems cover topics like refraction at an interface between two media, critical angles, total internal reflection, and calculating the area of a circle of light formed when light refracts through a liquid. The document provides the questions and space to show the answers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
32 views3 pagesCh-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 07
Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 07
Uploaded by
Ayush KumarThis document contains 9 practice problems related to ray optics. The problems cover topics like refraction at an interface between two media, critical angles, total internal reflection, and calculating the area of a circle of light formed when light refracts through a liquid. The document provides the questions and space to show the answers.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as pdf or txt
You are on page 1of 3
1
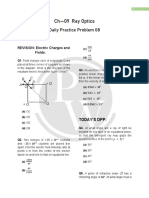
Ch—09 Ray Optics
Daily Practice Problem 07
REVISION: Electric Charges and (b) 5.62 × 107
Fields. (c) 562 × 107
(d) 0.0562 × 107
Q1. How many electrons should be removed
from a coin of mas 1.6 𝑔𝑔, so that it may float
in an electric field of intensity 109 N/C
directed upward?
TODAY’S DPP:
(a) 9.8 × 107
(b) 9.8 × 105 Q4. Determine the value of the angle of
incidence for a ray of light, travelling from a
(c) 9.8 × 103 medium of refractive index 𝜇𝜇1 = √2 into the
(d) 9.8 × 101 medium of refractive index 𝜇𝜇2 = 1, so that it
just grazes along the surface of separation.
[CBSE F 17]
Q2. The electric field in a region is radially
outward and at a point is given by 𝐸𝐸 =
250 𝑟𝑟 𝑉𝑉/𝑚𝑚 (where 𝑟𝑟 is the distance of the
Q5. The velocity of light in a liquid is
point from origin). Calculate the charge 1.5 × 108 𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −1 and in air, it is 3 × 108 𝑚𝑚𝑠𝑠 −1 .
contained in a sphere of radius 20 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 If a ray of light passes from this liquid into air,
centred at the origin calculate the value of critical angle. [Punjab
99]
(a) 2.22 × 10–6 𝐶𝐶
(b) 2.22 × 10–8 𝐶𝐶
Q6. A ray 𝑃𝑃𝑃𝑃 incident
(c) 2.22 × 10 –10
𝐶𝐶 normally on the refracting
face 𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵 is refracted in the
(d) Zero
prism 𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵𝐵 made of
material of refractive
index 1.5. A Complete the
Q3. An electron is rotating around an infinite path of ray through the
positive linear charge in a circle of radius prism. From which face
0.1 𝑚𝑚, if the linear charge density is 1 𝜇𝜇𝜇𝜇/𝑚𝑚, will the ray emerge? Justify your answer.
then the velocity of electron in 𝑚𝑚/𝑠𝑠 will be [CBSE OD 16]
(a) 0.562 × 107
Ray Optics 2
Q7. Find the maximum angle of refraction
when a ray of light is refracted from glass
Q9. A liquid of refractive index 1.5 is poured
(𝜇𝜇 = 1.5) to air.
into a cylindrical jar of radius 20 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐 upto a
height of 20 𝑐𝑐𝑐𝑐. A small bulb is lighted at the
centre of the bottom of the jar. Find the area
Q8. A luminous object 𝑆𝑆 is located at the of the liquid surface through which the light
bottom of a big pool of liquid of refractive of the bulb passes into air. [ISCE 98]
index 𝜇𝜇 and depth ℎ. The object 𝑆𝑆 emits rays
upwards in all directions, so that a circle of
light is formed at the surface of the liquid by
the rays which are refracted into the air. What
happens to the rays beyond the circle?
Determine the radius and the area of the
circle.
Ray Optics 3
ANSWERS
1. a 4. 45° 8. Rays beyond the circle
are totally reflected into the
ℎ
liquid, 𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅𝑅 = 2 ,
2. c 5. 30° �𝜇𝜇 −1
𝜋𝜋ℎ2
𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴𝐴 =
𝜇𝜇 2 −1
3. b 7. 90°
9. 1004.8 𝑐𝑐𝑚𝑚2
You might also like
- HandWritten Notes PhyscisDocument18 pagesHandWritten Notes PhyscisvanshNo ratings yet
- Make Your Own CDIDocument14 pagesMake Your Own CDIrk-rex96% (28)
- Eletronics Lab Report - Rectifier CircuitDocument4 pagesEletronics Lab Report - Rectifier CircuitThan Lwin Aung93% (14)
- Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 08Document3 pagesCh-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 08Anmol KaushikNo ratings yet
- Ejercicios9 PDFDocument4 pagesEjercicios9 PDFapolo1711No ratings yet
- Ch-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Document3 pagesCh-04 Moving Charges and Magnetism: Daily Practice Problem 05Gurnaj Singh MannNo ratings yet
- Phys102 161 Second MajorDocument10 pagesPhys102 161 Second MajorAvneet Singh AroraNo ratings yet
- Quiz 1 SET A - Model AnswerDocument2 pagesQuiz 1 SET A - Model Answershriramdhumal24744No ratings yet
- PHYSICS P2 To Be Done On 26th MarchDocument7 pagesPHYSICS P2 To Be Done On 26th MarchsykehanscyphaNo ratings yet
- DPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Document4 pagesDPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingNo ratings yet
- JEE Physics Solved Paper 2022Document5 pagesJEE Physics Solved Paper 2022Dhathree KrishnaNo ratings yet
- MT - Phys2 - Summer 23 - Version A - With AnswersDocument6 pagesMT - Phys2 - Summer 23 - Version A - With AnswersaamerbolookiNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 23)Document3 pagesRay Optics - DPP 10 (Of Lecture 23)Anmol KaushikNo ratings yet
- RAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12Document27 pagesRAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12AkankshaNo ratings yet
- Be - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2018 - December - Applied Physics II CbcgsDocument20 pagesBe - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2018 - December - Applied Physics II Cbcgsmahek guptaNo ratings yet
- HW 3solution PDFDocument6 pagesHW 3solution PDFanna.heeohNo ratings yet
- Xii Physics Set-ADocument9 pagesXii Physics Set-AAshik Anamic ShimiyaNo ratings yet
- Ch-08 Electromagnetic Wave: Daily Practice Problem 02Document2 pagesCh-08 Electromagnetic Wave: Daily Practice Problem 02Chandrima Dola MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Be - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2019 - May - Applied Physics II CbcgsDocument20 pagesBe - First Year Engineering - Semester 2 - 2019 - May - Applied Physics II Cbcgsnocap7884No ratings yet
- The Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics: Chapter OutlineDocument59 pagesThe Nature of Light and The Principles of Ray Optics: Chapter OutlineTran Huy HauNo ratings yet
- Uace Physics Paper 2 2004 GuideDocument16 pagesUace Physics Paper 2 2004 GuideAinebyoona ChriscentNo ratings yet
- CLASS XII Physics MCQ Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsDocument24 pagesCLASS XII Physics MCQ Chapter 1 Electric Charges and FieldsilanchitraNo ratings yet
- Physics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-12) - PaperDocument13 pagesPhysics Advanced Level Problem Solving (ALPS-12) - PaperAnanmay ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Wave OpticsDocument11 pagesWave OpticsNishi SinghalNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument38 pagesRay OpticsrajeshNo ratings yet
- Ch-10 Wave Optics: Daily Practice Problem 03Document3 pagesCh-10 Wave Optics: Daily Practice Problem 03Harshit shuklaNo ratings yet
- Physics QPDocument3 pagesPhysics QPThemistocles AthensNo ratings yet
- Physics: AnswersDocument21 pagesPhysics: AnswersASRANo ratings yet
- Wave Optics (QB)Document12 pagesWave Optics (QB)Raju SinghNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 03 Jee Advanced PaperDocument20 pagesMock Test 03 Jee Advanced PaperGanesha Dattatraya Gaonkar CFALNo ratings yet
- KIET PhysicsDocument82 pagesKIET Physicsap cpianNo ratings yet
- 267229750-Sample Paper 4Document6 pages267229750-Sample Paper 4sithur2305No ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On Youtube: - Written Solution On WebsiteDocument4 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On Website:-Video Solution On Youtube: - Written Solution On WebsiteHrinmoy HusiyarNo ratings yet
- NUMERICAL PROBLEMS ON FIBRE OPTICS - Image.Marked - 1Document4 pagesNUMERICAL PROBLEMS ON FIBRE OPTICS - Image.Marked - 1ANKURANNo ratings yet
- SOLUTION OF Lens, Mirror, RefractionDocument4 pagesSOLUTION OF Lens, Mirror, RefractionRumpa DasNo ratings yet
- Ioqjs (Part 1) 2020 SolutionDocument8 pagesIoqjs (Part 1) 2020 SolutionAnindita GhoshSatpathiNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper 7: Class XII 2023-24 PhysicsDocument6 pagesSample Paper 7: Class XII 2023-24 PhysicsBhaviniNo ratings yet
- Class Xii Physics Answer Key SetbDocument21 pagesClass Xii Physics Answer Key Setbvarshanair2005No ratings yet
- NSEA 2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Document28 pagesNSEA 2022-23 - (Answers & Solutions)Pushpanjay Kumar100% (4)
- Ray Optics QuestionsDocument3 pagesRay Optics QuestionsBAAP ka papaNo ratings yet
- Cblephpu 20Document6 pagesCblephpu 20Mahadev SharmaNo ratings yet
- Tugas UAS Fisika Dasar TeknikDocument9 pagesTugas UAS Fisika Dasar TeknikNiko Rizaldi MshlNo ratings yet
- Elecdy Finals BrionesDocument5 pagesElecdy Finals BrionesJonathan Briones Mses MsphyNo ratings yet
- Question and Answer - 23Document29 pagesQuestion and Answer - 23meenakshisivarajNo ratings yet
- HCI 2022 Prelim P1 Guide PDFDocument6 pagesHCI 2022 Prelim P1 Guide PDFBrendanNo ratings yet
- Cluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)Document33 pagesCluster Level Question Bank (Ahmedabad & Gandhinagar Cluster)manpreetsingh3458417No ratings yet
- Properties of Light: T E 15 MJ N 5.24Document17 pagesProperties of Light: T E 15 MJ N 5.24077 AgentNo ratings yet
- Hysicsaholics: Video Solution On WebsiteDocument4 pagesHysicsaholics: Video Solution On WebsiteHrinmoy HusiyarNo ratings yet
- Class 12th Physics 28 FebDocument4 pagesClass 12th Physics 28 FebPrem palaiyaNo ratings yet
- Part2 ch11Document9 pagesPart2 ch11api-3705610No ratings yet
- Massachusetts Institute of Technology: Reading AssignmentDocument3 pagesMassachusetts Institute of Technology: Reading AssignmentDibyananda SahooNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper - 4 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document9 pagesSample Question Paper - 4 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22abcdNo ratings yet
- Homework No. 2: Fig. 1. Problem 1Document3 pagesHomework No. 2: Fig. 1. Problem 1victus0110No ratings yet
- Canadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple ChoiceDocument5 pagesCanadian Association of Physicists 1999 Prize Exam Part A: Multiple Choiceelty TanNo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22Document7 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Sample Question Paper - 13 Physics (042) Class-XII, Session: 2021-22satyam skNo ratings yet
- Worksheet 10 Potential and Capacitance SolutionsDocument2 pagesWorksheet 10 Potential and Capacitance Solutionsreyessyrendaniel25No ratings yet
- UP3 - 1.4. Total Internal Reflection - pg19-24Document6 pagesUP3 - 1.4. Total Internal Reflection - pg19-24mohmmadaliawadNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Theoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1From EverandTheoretical Solid State Physics: International Series in Natural Philosophy, Volume 1Rating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- Electron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyFrom EverandElectron Beam-Specimen Interactions and Simulation Methods in MicroscopyNo ratings yet
- Problems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionFrom EverandProblems in Quantum Mechanics: Third EditionRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Complete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDocument141 pagesComplete General Science Notes by Anuj JindalDigvijay SinghNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - WEIGHT-VOLUME RELATIONSHIP PDFDocument44 pagesChapter 5 - WEIGHT-VOLUME RELATIONSHIP PDFKasturi Letchumanan100% (1)
- Vapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11Document2 pagesVapor Power Cycles Chapters 10 & 11MaykaMidreliDeandraLigutomNo ratings yet
- Science 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMDocument5 pagesScience 7 - Q3 - Episode 6 - SLMCaryll BaylonNo ratings yet
- M15 PDFDocument28 pagesM15 PDFMartha Escobar RojasNo ratings yet
- Transistor FAN431Document10 pagesTransistor FAN431Rodrigo AlencarNo ratings yet
- Grosse 1962Document10 pagesGrosse 1962Михаил ПарамоновNo ratings yet
- Boquillas Secas ABBDocument5 pagesBoquillas Secas ABBNoé Rafael Colorado SósolNo ratings yet
- F4 Physics Paper 3 Section B ExperimentsDocument7 pagesF4 Physics Paper 3 Section B Experimentsjajabeans80% (5)
- Datasheet PDFDocument1 pageDatasheet PDFFrizkaZaskiaNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 TransducerDocument18 pagesCHAPTER 3 TransducerDegaga KebedeNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 01 CompleteDocument26 pagesExercise # 01 CompleteRehan QureshiNo ratings yet
- 4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESDocument17 pages4 - Review Notes - MOTORS & ENGINESJoebert SabidoNo ratings yet
- Department of Civil Engineering Assignment Question Ii Year/Iii SemesterDocument2 pagesDepartment of Civil Engineering Assignment Question Ii Year/Iii SemesterMuthu LakshmiNo ratings yet
- N 2023 Unit Test-1 - (11-July-21)Document25 pagesN 2023 Unit Test-1 - (11-July-21)QXnocMF5No ratings yet
- 3 Phase Motor CG CatalogueDocument74 pages3 Phase Motor CG CatalogueDiana Rose Tapel0% (2)
- MotorDocument10 pagesMotorsameer betalNo ratings yet
- Side Smart VRF - IND - CompressedDocument108 pagesSide Smart VRF - IND - CompressedVirga AnandaNo ratings yet
- Solar Powered AircraftDocument2 pagesSolar Powered AircraftQa LabNo ratings yet
- Advanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP0403GHDocument5 pagesAdvanced Power Electronics Corp.: AP0403GHIulius CezarNo ratings yet
- Em Notes 20 Special RelativityDocument11 pagesEm Notes 20 Special RelativityHarshitNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics - Chapter ThreeDocument43 pagesFluid Mechanics - Chapter Threebiniyam mulugetaNo ratings yet
- Isochronous Vs Droop GenDocument4 pagesIsochronous Vs Droop GenInsan AzizNo ratings yet
- Q1 G.PHYSICS 1 L6 Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Document19 pagesQ1 G.PHYSICS 1 L6 Uniform Accelerated Motion 1Ms.Bangalando, S STEM 11-DNo ratings yet
- Advanced Computer Techniques in Applied ElectromagneticsDocument472 pagesAdvanced Computer Techniques in Applied Electromagneticssmaka_senadNo ratings yet
- Steca PF 166 240 Specification enDocument1 pageSteca PF 166 240 Specification en_at_to_No ratings yet
- CPC 100 PTM Quick Test Application Guide 2020 ENUDocument38 pagesCPC 100 PTM Quick Test Application Guide 2020 ENUNgoc Anh NguyenNo ratings yet