Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Data Analytics, Basic Statistics, Machine Learning Exercise - Opie
Data Analytics, Basic Statistics, Machine Learning Exercise - Opie
Uploaded by
Opie SopyanOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Data Analytics, Basic Statistics, Machine Learning Exercise - Opie
Data Analytics, Basic Statistics, Machine Learning Exercise - Opie
Uploaded by
Opie SopyanCopyright:
Available Formats
Name : Opie Sopyan
Student ID : 20200130005
Class : Master Computer Science Nusa Putra University
Courses: Advanced Database
Lecture : Dr. DINI OKTARINA DWI HANDAYANI, S.T, M.Sc.
1. Describe your understanding about Data Analytics.
Data analytics is the science of analyzing raw data in order to make conclusions about
that information. Many of the techniques and processes of data analytics have been
automated into mechanical processes and algorithms that work over raw data for human
consumption.
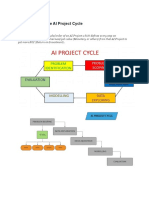
2. Explain Data Analytics as a Process and draw a diagram if necessary.
The data analysis process, or alternately, data analysis steps, involves gathering all the
information, processing it, exploring the data, and using it to find patterns and other
insights
3. What are the Data Analytics types? Describe each type and provide a relevant example
for each type?
There are 4 types of Data Analytics :
1. Diagnostic Analysis.
Diagnostic analysis answers the question, “Why did this happen?” Using insights gained
from statistical analysis (more on that later!), analysts use diagnostic analysis to identify
patterns in data. Ideally, the analysts find similar patterns that existed in the past, and
consequently, use those solutions to resolve the present challenges hopefully.
2. Predictive Analysis.
Predictive analysis answers the question, “What is most likely to happen?” By using
patterns found in older data as well as current events, analysts predict future events.
While there’s no such thing as 100 percent accurate forecasting, the odds improve if the
analysts have plenty of detailed information and the discipline to research it thoroughly.
3. Prescriptive Analysis.
Mix all the insights gained from the other data analysis types, and you have prescriptive
analysis. Sometimes, an issue can’t be solved solely with one analysis type, and instead
requires multiple insights.
4. Statistical Analysis.
Statistical analysis answers the question, “What happened?” This analysis covers data
collection, analysis, modeling, interpretation, and presentation using dashboards
4. Determine the following:
P(0 < Z < 1.57)= 0,4418 – 0 = 0,4418
P(Z > 1.57)= 0,5 - 0,4418 = 0,0582
P(1. 46 < Z)= 0,4279-0,5 = -0,0721
P(Z < -1. 46)= 0,5 +(- 0,4279) = 0,0721
5. Use a table or Excel, find interpret z0.07
a. P(Z > z0.07 ) = 0.07
So sory I’m afraid I Can’t explain anything
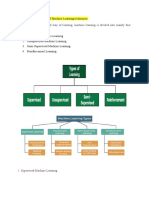
6. Write your understanding about different types of Machine Learning algorithms
Machine Learning is a domain of computer science with its base in computational
mathematics and statistics. The machine is shown a ton of data and it learns the pattern in
the data to make future predictions, recognise new patterns or suggest different classes to
the data. Broadly speaking, Machine Learning algorithms are of three types- Supervised
Learning, Unsupervised Learning, and Reinforcement Learning. A basic understanding of
the different types of algorithms will help you choose an algorithm for your project or will
simply help you appreciate the vast variety of problems AI can solve using Machine
Learning.
Supervised Learning
When the machine is supervised while it is “learning”, the training type is called
supervised learning. But what does supervising a machine really mean? It means
that we provide the machine with a ton of information about a case and also
provide it with the case outcome.
Unsupervised Learning
As the name suggests, in case of unsupervised learning, there is no help from the
user for the computer to learn. In the lack of labelled training sets, the machine
identifies patterns in the data that is not so obvious to the human eye.
Reinforcement Learning
Reinforcement learning is probably the closest to how we as humans learn. In this
case, the algorithm or the agent learns continually from its environment by
interacting with it. It gets a positive or a negative reward based on its action.
You might also like
- ML Unit-1Document12 pagesML Unit-120-6616 Abhinay100% (1)
- Mitsubishi MT2100 - 210 - 2500 - 250 Parts Catalog EngineDocument64 pagesMitsubishi MT2100 - 210 - 2500 - 250 Parts Catalog EngineChristopher Anderson100% (1)
- KE13N Upload of COPA Offline PlanningDocument6 pagesKE13N Upload of COPA Offline PlanningMOORTHYNo ratings yet
- Loreal Case Study Managing The Diversity Describing The Ob Tools of A Successful Company 120304085031332 2Document27 pagesLoreal Case Study Managing The Diversity Describing The Ob Tools of A Successful Company 120304085031332 2Shreya Virmani100% (1)
- Crane PartsDocument931 pagesCrane Partstecnicomanel100% (3)
- Harddisk PCB Repairing PDFDocument18 pagesHarddisk PCB Repairing PDFmasood100% (1)
- Ai and Machine Learning For BusinessDocument114 pagesAi and Machine Learning For BusinessAditya KumarNo ratings yet
- Project Life CycleDocument14 pagesProject Life CycleDikshitha DNo ratings yet
- AI ProjectDocument14 pagesAI ProjectDikshitha DNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning FileDocument58 pagesDeep Learning FileAyush singhNo ratings yet
- Data Science Data Mathematical Model Algorithm Statistics Data Analysis Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine LearningDocument15 pagesData Science Data Mathematical Model Algorithm Statistics Data Analysis Artificial Intelligence (AI) Machine LearningLuiz FillipNo ratings yet
- Data Science Solutions IA 2Document16 pagesData Science Solutions IA 2Monesh RallapalliNo ratings yet
- Deep Learning FileDocument60 pagesDeep Learning FileAyush singhNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 NotesDocument29 pagesUnit 1 NotessakthiasphaltalphaNo ratings yet
- Data Science Interview Questions LeakedDocument12 pagesData Science Interview Questions Leakedkumar kumar100% (2)
- CCST9017 (2023-24lecture11printed Version) MachineLearningDocument55 pagesCCST9017 (2023-24lecture11printed Version) MachineLearningmeganyaptanNo ratings yet
- MLT Unit 1Document15 pagesMLT Unit 1sahil.utube2003No ratings yet
- Unit 1 (I)Document12 pagesUnit 1 (I)ayushNo ratings yet
- Terms in DSDocument6 pagesTerms in DSLeandro Rocha RímuloNo ratings yet
- InteligenceDocument19 pagesInteligenceMiraculous MiracleNo ratings yet
- AI Project Cycle: 2.1. Problem ScopingDocument6 pagesAI Project Cycle: 2.1. Problem ScopingAsmi AgnihotriNo ratings yet
- 02 Ai Project Cycle Revision NotesDocument4 pages02 Ai Project Cycle Revision NotesdevendrabanacNo ratings yet
- CS607Document18 pagesCS607Jamshed Ali67% (3)
- Machine Learning Project 1Document19 pagesMachine Learning Project 1Durga Prasad Reddy ChilukuriNo ratings yet
- Sentiment Analysis To Measure The Users Opinion by Using Machine Learning TechniquesDocument15 pagesSentiment Analysis To Measure The Users Opinion by Using Machine Learning TechniquesArthur AguilarNo ratings yet
- Data2 PDFDocument48 pagesData2 PDFYao magaoNo ratings yet
- Notes On AI and MLDocument10 pagesNotes On AI and MLsharvilNo ratings yet
- ML OL IntroductionDocument11 pagesML OL Introductionharrisc0909No ratings yet
- AI Project CycleDocument8 pagesAI Project Cyclesajanaka161No ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Predictive AnalysisDocument5 pagesChapter 6 Predictive AnalysisHiba AhmedNo ratings yet
- An Enlightenment To Machine Learning - RespDocument22 pagesAn Enlightenment To Machine Learning - RespIgorJalesNo ratings yet
- Survey of Machine Learning Algorithms For Disease DiagnosticDocument16 pagesSurvey of Machine Learning Algorithms For Disease DiagnosticRie TsuboiNo ratings yet
- AI STUDY MetarialDocument9 pagesAI STUDY MetarialArohan BuddyNo ratings yet
- Artificial Neural NertworkDocument52 pagesArtificial Neural NertworkNachtlicht MondlichtNo ratings yet
- What Is Data Analysis GRP 4Document7 pagesWhat Is Data Analysis GRP 4wilson philipoNo ratings yet
- An Enlightenment To Machine LearningDocument16 pagesAn Enlightenment To Machine LearningAnkur Singh100% (1)
- Federal University of Lafia: Department of Computer ScienceDocument6 pagesFederal University of Lafia: Department of Computer ScienceKc MamaNo ratings yet
- Six Weeks Summer Training ReportpdfDocument26 pagesSix Weeks Summer Training ReportpdfVikas Gupta100% (1)
- Theories, Detection Methods, and Opportunities of Fake News DetectionDocument4 pagesTheories, Detection Methods, and Opportunities of Fake News DetectionadityaNo ratings yet
- Name: Sujit Rajbhar Roll No: 81 Div: A UID: 120CP1206A Essay On Engineer'S DayDocument13 pagesName: Sujit Rajbhar Roll No: 81 Div: A UID: 120CP1206A Essay On Engineer'S DaySujitNo ratings yet
- CSC 413 AssDocument7 pagesCSC 413 AssKc MamaNo ratings yet
- A18 Cu6051np CW1 18028985Document17 pagesA18 Cu6051np CW1 18028985urja tech academyNo ratings yet
- Machine Learning Based Model-13122022-3Document7 pagesMachine Learning Based Model-13122022-3akshatguptaec20.rvitmNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Detection Using Machine LearningDocument31 pagesMental Health Detection Using Machine LearninggvarshithavarshiNo ratings yet
- Importany Questions Unit 3 4Document30 pagesImportany Questions Unit 3 4Mubena HussainNo ratings yet
- ML ReportDocument13 pagesML Reportyukta sachdevNo ratings yet
- AI Assignment 2Document5 pagesAI Assignment 2Abraham Onyedikachi OguduNo ratings yet
- ML Chapter 1Document37 pagesML Chapter 1mikiNo ratings yet
- Statistical Modeling For Data AnalysisDocument24 pagesStatistical Modeling For Data Analysisfisha adaneNo ratings yet
- Helsenki - Intro To MLDocument35 pagesHelsenki - Intro To MLAjwad Abrar Mostofa 190042106No ratings yet
- Module 6 Analytics-Making Sense of DataDocument9 pagesModule 6 Analytics-Making Sense of DataNoe AgubangNo ratings yet
- There Are Key Areas in The Process of Machine Learning, LikeDocument45 pagesThere Are Key Areas in The Process of Machine Learning, LikeYashiNo ratings yet
- Disease Prediction Using Machine LearningDocument10 pagesDisease Prediction Using Machine LearningIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Data Science Interview Questions 1599708768Document54 pagesData Science Interview Questions 1599708768aalto faltoNo ratings yet
- DL Unit-1Document25 pagesDL Unit-1Kalpana MNo ratings yet
- L01 - Introduction-to-MLDocument10 pagesL01 - Introduction-to-MLsayali sonavaneNo ratings yet
- Python UNIT-5Document67 pagesPython UNIT-5Chandan Kumar100% (1)
- Analytics Data PDFDocument9 pagesAnalytics Data PDFErica Mae BorromeoNo ratings yet
- Colloquium Evaluation: Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering To:Kanika Gupta Ma'Am Bhavya Sethi 16csu082Document12 pagesColloquium Evaluation: Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering To:Kanika Gupta Ma'Am Bhavya Sethi 16csu082CHIRAGNo ratings yet
- DataScience Unit1 (+notes)Document56 pagesDataScience Unit1 (+notes)110 Krishna KumarNo ratings yet
- Mental Health PredictionDocument14 pagesMental Health Predictionvanitamane1No ratings yet
- Introductrory NotesDocument13 pagesIntroductrory Notesaumar moctarNo ratings yet
- R20 ML - Unit-1Document23 pagesR20 ML - Unit-1ssamatha8811No ratings yet
- AIUnit IIDocument47 pagesAIUnit IIomkar dhumalNo ratings yet
- UENR90610001Document58 pagesUENR90610001wrya hussainNo ratings yet
- Micro 133 Midterm Lecture 2 - IO Interfacing With 8255 & Assembly Language - EditedDocument10 pagesMicro 133 Midterm Lecture 2 - IO Interfacing With 8255 & Assembly Language - EditedKeilla Romabiles LeopandoNo ratings yet
- Six Sigma Green Belt New PDFDocument9 pagesSix Sigma Green Belt New PDFAshwani KumarNo ratings yet
- Name - Phet Simulation - Forces and Motion: BasicsDocument3 pagesName - Phet Simulation - Forces and Motion: Basicsnatalie goodjoinesNo ratings yet
- Simulado 7 AnoDocument6 pagesSimulado 7 AnoAnny LimaNo ratings yet
- Text As Connected DiscourseDocument69 pagesText As Connected DiscourseIvy Mae SagangNo ratings yet
- Sources of Problems For Investigation: What Makes A Good Research Statement?Document3 pagesSources of Problems For Investigation: What Makes A Good Research Statement?Darlen Daileg SantianezNo ratings yet
- Gazette SSC A2023 UpdatedDocument1,705 pagesGazette SSC A2023 UpdatedRoman SadiqNo ratings yet
- 1memo Physics, NmuDocument63 pages1memo Physics, NmuHlulo WyntonNo ratings yet
- HHM - Unit-I-Uniform FlowDocument25 pagesHHM - Unit-I-Uniform Flow032 HarshithNo ratings yet
- ELEC 3200 Advanced Digital Circuit Design Lab 7Document5 pagesELEC 3200 Advanced Digital Circuit Design Lab 7ZebNo ratings yet
- Andriani.2022.Key Determinants of Intention To Visit Halal Tourism in MaduraDocument12 pagesAndriani.2022.Key Determinants of Intention To Visit Halal Tourism in MaduraAhmad Zulfikar AliNo ratings yet
- 100 SeriesDocument5 pages100 Seriesfathur2107No ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets English 7 Quarter 4 Week 4 Determining Truthfulness and Accuracy of The Materials Viewed or ReadDocument6 pagesWeekly Learning Activity Sheets English 7 Quarter 4 Week 4 Determining Truthfulness and Accuracy of The Materials Viewed or ReadSha JeszhamNo ratings yet
- Worksheet in InquiryDocument4 pagesWorksheet in Inquirynhel armstrongNo ratings yet
- Soil Comp Action FinalDocument7 pagesSoil Comp Action FinalNam-Jo KimNo ratings yet
- Cytology MCQ 01: MCQ On Mitochondria: Cytology MCQ: 01 Print Less Save Paper Save TreesDocument7 pagesCytology MCQ 01: MCQ On Mitochondria: Cytology MCQ: 01 Print Less Save Paper Save TreesMalaya Kumar BhoiNo ratings yet
- Infosys Case StudyDocument12 pagesInfosys Case StudyvaisakhgokulNo ratings yet
- Cambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62Document12 pagesCambridge IGCSE: PHYSICS 0625/62AdilNo ratings yet
- Psychopathy Checklist Revised PCL RDocument7 pagesPsychopathy Checklist Revised PCL Rb02814591No ratings yet
- Lot 38, Block 1, PCS-07-003726 TCT No. T-144386Document16 pagesLot 38, Block 1, PCS-07-003726 TCT No. T-144386Ivan JamesNo ratings yet
- 5e Lesson PlanDocument16 pages5e Lesson Planapi-289454387No ratings yet
- Case 4Document2 pagesCase 4Harnam RainuNo ratings yet
- Urbanpromise Honduras: Urbanpromise History Urbanpromise Ministries Started in CamdenDocument1 pageUrbanpromise Honduras: Urbanpromise History Urbanpromise Ministries Started in Camdenapi-67779196No ratings yet
- Penyebab Perbedaan Tarif Ina-Cbgs Pada Kasus Sectio Caesarean Dengan Indikasi Malpresentasi Di Rsud Tugurejo Kota Semarang Tahun 2018Document15 pagesPenyebab Perbedaan Tarif Ina-Cbgs Pada Kasus Sectio Caesarean Dengan Indikasi Malpresentasi Di Rsud Tugurejo Kota Semarang Tahun 2018Nasrul WahdiNo ratings yet