Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Typical House Emissions
Typical House Emissions
Uploaded by
morristranger aOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Typical House Emissions
Typical House Emissions
Uploaded by
morristranger aCopyright:
Available Formats
Typical House Emissions http://www.organicbuilding.com/index.mvc?
ArticleID=150
Home Typical House Emissions
Benefits
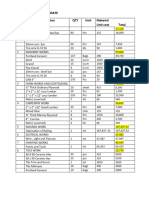
Contact Typical 93 square metre house with concrete floor, concrete block cladding, timber frame,
Printer Friendly aluminium window frames and iron roof. The following table shows the embodied energy and the
CO2 emissions for all the building materials.
Weight Energy Kg C Kg C
Materials Kgs Mj released stored
Wood Materials
Framing 1,990 5,254 97 995
Other Timber 300 204 4 150
Wood Products 1,170 3,197 59 586
Paper Products 159 5,430 99 57
Non Wood Materials
Plaster 2,310 18,150 347 0
Glass 500 17,325 336 0
Concrete 54,000 105,492 3,152 0
Clay Products 540 4,057 76 0
Plastics 271 44,884 823 0
Paints 96 15,752 294 0
Plumbing Steel 519 19,236 342 1
Other Steel 1,881 69,902 1,282 4
Aluminium 251 36,544 638 0
Copper/Alloys 102 4,867 89 0
Fibreglass Batts 100 15,010 287 0
Earthwork 16,000 6,982 134 0
Site Energy 23,752 475 0
Total 80,189 396,038 8,534 1,793
Total Wood 3,619 14,085 259 1,788
Wood %Total 4.5 3.6 3.0 99.7
From study of "Environmental Impacts of the New Zealand Building Industry" by Brian Honey and
Andrew Buchanan, Canterbury University 1992.
Note how little energy is required to make all the wood materials. This is less than the individual
totals for the fibreglass batts, the aluminium window frames, the glass, the paints and the plaster
board linings. By far the greatest amounts of energy are needed for the concrete and the steel.
1 of 1 06/02/2008 12:20 p.m.
You might also like
- Glass Wool Catalogue PDFDocument8 pagesGlass Wool Catalogue PDFThilan Senarathne100% (1)
- Deimos - Dead of Winter #1Document36 pagesDeimos - Dead of Winter #1Franny0% (2)
- Embodied Energy - TilesDocument13 pagesEmbodied Energy - TilesfakemasterkgpNo ratings yet
- B.O.Q Wacher Room MelsiripuraDocument17 pagesB.O.Q Wacher Room MelsiripuraChinthakaNo ratings yet
- Bills of MatirialsDocument2 pagesBills of MatirialsJessa AmidaNo ratings yet
- Properties of Nonmetals.: Temperature 10 Substance C W/M C KG/M KJ/KG C M /s Structural and Heat-Resistant MaterialsDocument3 pagesProperties of Nonmetals.: Temperature 10 Substance C W/M C KG/M KJ/KG C M /s Structural and Heat-Resistant MaterialsMalik Mohammad AsifNo ratings yet
- Bsce3203 Bom Group2Document5 pagesBsce3203 Bom Group2Eva Angel ManieboNo ratings yet
- Booch Fermentation Room EXT. MaterialsDocument1 pageBooch Fermentation Room EXT. MaterialssatejaNo ratings yet
- CMWPI WeightsDocument1 pageCMWPI WeightsSONNY BRYANNo ratings yet
- AAC Blocks Vs BWsDocument1 pageAAC Blocks Vs BWsAlaguNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 1 Thermal Conductivity of Insulating Material AIM: To Determine Thermal Conductivity of Insulating PowderDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 1 Thermal Conductivity of Insulating Material AIM: To Determine Thermal Conductivity of Insulating PowderVikas RathodNo ratings yet
- 2.1. Fundamentals of Heat Transfer and Thermodynamics 2.1.1. ThermodynamicsDocument5 pages2.1. Fundamentals of Heat Transfer and Thermodynamics 2.1.1. ThermodynamicsLeslie CatindigNo ratings yet
- BMC1.Basic Building MaterialsDocument44 pagesBMC1.Basic Building MaterialsMeenu Priya100% (1)
- Low Energy Building MaterialsDocument27 pagesLow Energy Building MaterialsKamalBhatia100% (2)
- 6TH ParklandsDocument6 pages6TH ParklandssatejaNo ratings yet
- Ds Torayca ClothDocument2 pagesDs Torayca ClothNoor MalakNo ratings yet
- Cement & Reinforcement Requirements-020608Document2 pagesCement & Reinforcement Requirements-020608Nagi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Recap ThermalDocument8 pagesRecap ThermalGunnerZedNo ratings yet
- Desta Tesfay (Labour Cost)Document47 pagesDesta Tesfay (Labour Cost)Mehari GebreyohannesNo ratings yet
- Westbrook: Nickel Electrode For The Welding of Cast IronDocument1 pageWestbrook: Nickel Electrode For The Welding of Cast Ironmohamed AdelNo ratings yet
- MembraneDocument3 pagesMembraneer.sanjaysah2020No ratings yet
- Bill of Materials in BTDocument4 pagesBill of Materials in BTVINCE NIETONo ratings yet
- Desta Tesfay (Material Cost)Document49 pagesDesta Tesfay (Material Cost)Mehari GebreyohannesNo ratings yet
- Titan Indutril Materil Schaduil-474Document9 pagesTitan Indutril Materil Schaduil-474Kedir AmanNo ratings yet
- Price of KEL Agro Industry FinalDocument89 pagesPrice of KEL Agro Industry FinalMehari GebreyohannesNo ratings yet
- Pete 2 RevisedDocument4 pagesPete 2 Revisedcoffee addict 73No ratings yet
- Energy Saving Light Weight Bricks Using Waste News Paper-LibreDocument7 pagesEnergy Saving Light Weight Bricks Using Waste News Paper-LibreniuNo ratings yet
- Chloride Permeability and Impact Resista PDFDocument8 pagesChloride Permeability and Impact Resista PDFJulián MartínezNo ratings yet
- ClothDocument2 pagesClothRajulapati VinodkumarNo ratings yet
- Projec Location Owner Address Engineer Address Subject Item Description Unit Unit Cost Quantity AmountDocument6 pagesProjec Location Owner Address Engineer Address Subject Item Description Unit Unit Cost Quantity Amountroy richard macabodbodNo ratings yet
- Quantity (Final)Document20 pagesQuantity (Final)EyobNo ratings yet
- AAC Block - A New Eco-Friendly Material ForDocument8 pagesAAC Block - A New Eco-Friendly Material ForHanifhidayaNo ratings yet
- Subcontractors Progress Qtys To DateDocument373 pagesSubcontractors Progress Qtys To Datearchie_728No ratings yet
- Standard Coefficients For Building ProjectsDocument10 pagesStandard Coefficients For Building ProjectsnileshNo ratings yet
- 2015 GDP Formal and Informal Sector SplitDocument2 pages2015 GDP Formal and Informal Sector SplitTonye BakareNo ratings yet
- Uma Material Schedule 4Document1 pageUma Material Schedule 4Emmanuel OtienoNo ratings yet
- S.O (1) .R For Building Ahmedabad District 2015-16 PDFDocument426 pagesS.O (1) .R For Building Ahmedabad District 2015-16 PDFMehta MalayNo ratings yet
- Low Embodied Energy MaterialsDocument21 pagesLow Embodied Energy MaterialsAbishaTeslinNo ratings yet
- Zzz-1apdx33809 Apdx04 PDFDocument3 pagesZzz-1apdx33809 Apdx04 PDFJuriani AvinashNo ratings yet
- Total Amount $ 362,337.21: Payment TermsDocument34 pagesTotal Amount $ 362,337.21: Payment TermsmajoNo ratings yet
- NhungPham - Assigment 4Document2 pagesNhungPham - Assigment 4phamNo ratings yet
- Thermal Conductivity of Lagged PipeDocument17 pagesThermal Conductivity of Lagged PipeInzamamul HaqueNo ratings yet
- Stock Report For The Month of Feb. 2010Document9 pagesStock Report For The Month of Feb. 2010sivapomNo ratings yet
- Building Element Layer Current Number Layer'S Name Thickness (M) Density (Dan/MDocument3 pagesBuilding Element Layer Current Number Layer'S Name Thickness (M) Density (Dan/MFaeria20No ratings yet
- Embodied Energy CalculationDocument15 pagesEmbodied Energy CalculationSakshi AgarkarNo ratings yet
- An Experimental Investigation On Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete With Quarry Dust As A Partial Replacement of Fine AggregateDocument5 pagesAn Experimental Investigation On Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete With Quarry Dust As A Partial Replacement of Fine AggregateIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Rate Analysis SheetDocument5 pagesRate Analysis SheetGsUpretiNo ratings yet
- 5200FCDocument5 pages5200FCscribdme123No ratings yet
- ST Joseph College of EngineeringDocument27 pagesST Joseph College of EngineeringSandhiya saravananNo ratings yet
- 5200FCDocument5 pages5200FC夏斌No ratings yet
- Bill of MaterialsDocument2 pagesBill of MaterialsBrian Unciano100% (4)
- Guard HouseDocument31 pagesGuard HouseLelisa TarekegnNo ratings yet
- Buliding Material Transcript NPTELDocument441 pagesBuliding Material Transcript NPTELSUBHAM KumarNo ratings yet
- Acousteel Brochure Digital FINALDocument8 pagesAcousteel Brochure Digital FINALfahadullahNo ratings yet
- Glass Wool Insulation WorkDocument4 pagesGlass Wool Insulation WorkShakkik ZunaedNo ratings yet
- Shoe Shine CostDocument2 pagesShoe Shine CostmelkuNo ratings yet
- Laminate Wooden FlooringDocument1 pageLaminate Wooden Flooringsaddam.hussainNo ratings yet
- Manual For CPWDDocument56 pagesManual For CPWDabhay9411No ratings yet
- Construction of 2 Storey Residential Buildingrev2Document1 pageConstruction of 2 Storey Residential Buildingrev2Janlyn OrnosNo ratings yet
- RADocument141 pagesRAtnd tbecNo ratings yet
- Traditional To Modern Residential ArchitectureDocument11 pagesTraditional To Modern Residential ArchitectureRimsha AkramNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For Handrail ConstructionDocument13 pagesMethod Statement For Handrail Constructiondinidu3priyankara3saNo ratings yet
- How To Draw A Frog Icon in Adobe IllustratorDocument21 pagesHow To Draw A Frog Icon in Adobe IllustratorAleksandraNo ratings yet
- Irkutsk City MapDocument1 pageIrkutsk City MapohonestNo ratings yet
- Product CatalogDocument31 pagesProduct Catalogapi-309439120No ratings yet
- Art of Renaissance and Baroque PeriodDocument15 pagesArt of Renaissance and Baroque PeriodErvin John100% (1)
- Test Bank For Sensation and Perception Second EditionDocument19 pagesTest Bank For Sensation and Perception Second Editionmrssamanthagutierrezxwojrqntcg100% (26)
- Arts ReviewerDocument3 pagesArts ReviewerZENN MARIELLE TABAQUENo ratings yet
- What'S In: Visual Arts Literacy Arts Audio - Visual Arts Contemporary ArtDocument5 pagesWhat'S In: Visual Arts Literacy Arts Audio - Visual Arts Contemporary ArtRon Adrianne AsedillaNo ratings yet
- Appendix A Architectural Interior Finishes Requirments: Floor Base Wall CeilingDocument9 pagesAppendix A Architectural Interior Finishes Requirments: Floor Base Wall CeilingEr Bishwonath Shah100% (1)
- Sun Eater Vest GuideDocument4 pagesSun Eater Vest GuideallypeyrotNo ratings yet
- BIA-Subject Line Up Aug 2021Document2 pagesBIA-Subject Line Up Aug 2021CcNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Fernando Amorsolo's Painting (Readings in Phil. History)Document4 pagesAnalysis of Fernando Amorsolo's Painting (Readings in Phil. History)JeahannNo ratings yet
- Duo Pizza Party StratDocument7 pagesDuo Pizza Party Stratbence barabasNo ratings yet
- Death Eater Mask #1 - Half SizeDocument2 pagesDeath Eater Mask #1 - Half Sizep1n1n4No ratings yet
- Philippine Art History: I. Pre-Colonial Period 1. Burial JarDocument11 pagesPhilippine Art History: I. Pre-Colonial Period 1. Burial Jartoper cabzNo ratings yet
- Mona LisaDocument2 pagesMona LisaEdrian De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Milton Glaser: To Inform and DelightDocument4 pagesMilton Glaser: To Inform and DelightfrancisscribidNo ratings yet
- Ar. Chandni Thadani PortfolioDocument28 pagesAr. Chandni Thadani PortfolioChandni ThadaniNo ratings yet
- Contemporary Arts ReviewerDocument11 pagesContemporary Arts ReviewerArchessNo ratings yet
- RFQ For Building, Electricals and HardwareDocument3 pagesRFQ For Building, Electricals and HardwareSimbarashe KamudyariwaNo ratings yet
- EF4e Adv Filetest 07aDocument7 pagesEF4e Adv Filetest 07apolinaluk2109No ratings yet
- Group 3 NarraDocument18 pagesGroup 3 NarraMister RightNo ratings yet
- Black and White Portraits Cheat Sheet New2Document1 pageBlack and White Portraits Cheat Sheet New2Andy1C1No ratings yet
- Timeline of Philippine ArtsDocument2 pagesTimeline of Philippine ArtsJhonemar TejanoNo ratings yet
- Questions of Building Construction CourseDocument4 pagesQuestions of Building Construction CourseKhadar GuledNo ratings yet
- DLP in Technical Drafting Final Demo No IndicatorsDocument21 pagesDLP in Technical Drafting Final Demo No IndicatorsJERENI ARIELLE LABADANNo ratings yet
- MAPEH WHLP Q3 WK 5-6Document1 pageMAPEH WHLP Q3 WK 5-6sakunare senpaiNo ratings yet
- Djap Article p117 - 6Document19 pagesDjap Article p117 - 6Hadi Ja'afarNo ratings yet