Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Experiment # 2: Capacitors and Capacitance
Experiment # 2: Capacitors and Capacitance
Uploaded by
Level ThreeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment # 2: Capacitors and Capacitance
Experiment # 2: Capacitors and Capacitance
Uploaded by
Level ThreeCopyright:
Available Formats
Experiment # 2: Capacitors and Capacitance
(Open and short circuited capacitors) Commented [wa1]:
Short-Circuited Capacitors:
OBJECTIVE In normal service, capacitors can become short-circuited
because the dielectric deteriorates with age, usually over a
period of years under the stress of charging voltage,
1. Ground / short test of a capacitor. especially at higher temperatures. This effect is more
2. Capacitance rating in mfds. common with paper and electrolytic capacitors. The
capacitor may become leaky gradually, indicating a partial
short circuit, or the dielectric may be punctured, causing a
short circuit.
APPARATUS
Open Capacitors:
1. Capacitor analyzer. In addition to the possibility of an open connection in any
2. Capacitor to be checked. type of capacitor, electrolytics develop high resistance in the
electrolyte with age, particularly at high temperatures. After
3. Testing leads. service of a few years, if the electrolyte dries up, the
4. Step-down Transformer capacitor will be partially open. Much of the capacitor action
is gone, and the capacitor should be replaced.
PROCEDURE
a) Connect the main leads of the analyzer to 110 v AC supply. Power may be checked by flashing
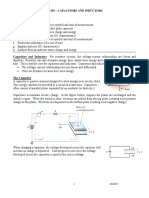
on the pilot light. Connect the capacitor terminals to the input jacks of the analyzer with the Commented [wa2]: Capacitance is the ability of a
help of testing leads. Place the selector switch of the analyzer (which is initially at center) to dielectric to hold or store an electric charge.
The more charge stored for a given voltage, the higher the
its left position and watch the light. capacitance. Capacitors are a common source of troubles
b) If it dose not flash, the capacitor is open. If it flashes brightly and dims down after a few because they can have either an open at the conductors or a
seconds, the capacitor is ok and is being charged. If the capacitor is open / short it should be short circuit through the dielectric.
The result is a device for storing charge in the dielectric.
discarded immediately without carrying further tests. Storage means that the charge remains even after the voltage
c) Now we shall check the capacitance of a charged capacitor. For this select the appropriate scale source is disconnected. The measure of how much charge
and place the selector switch to the right most position and note the mfds. Now compare the can be stored is the capacitance C. More charge stored for a
given amount of applied voltage means more capacitance
noted value with the rated one and if the noted is 20% less than the rated one, discard the
capacitor. ’ When one coulomb is stored in the dielectric with a
potential difference of one volt, the capacitance is one farad.’
GENERAL QUESTIONS Commented [wa3R2]: Dielectric types are air, ceramic,
mica, paper, film, and electrolytic capacitors.
Explain difference between starting and running capacitor. Commented [wa4]: Thinner Dielectric Increases
Capacitance:
What will be the result? The field between opposite plates can store more charge in
the dielectric. With less distance between the plates, the
a) If the area of the dielectric is increased. stored charge is greater for the same applied voltage, which
means that the capacitance is greater.
b) If the area of the plates is increased.
c) If the two capacitors are connected in parallel / series. Commented [wa5]: A larger plate area means that more of
the dielectric surface can contact each plate, allowing more
lines of force through the dielectric between the plates and
less flux leakage outside the dielectric. Then the field can
store more charge in the dielectric.
The result of larger plate area is more charge stored for the
same applied voltage, which means that the capacitance is
larger.
You might also like
- A Review Paper On Supercapacitor UltraDocument21 pagesA Review Paper On Supercapacitor UltraShahzaib AhmadNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems For The Oil & Gas Industry Rev2Document89 pagesElectrical Systems For The Oil & Gas Industry Rev2Shola Daley100% (3)
- Informe Final DielectricosDocument9 pagesInforme Final DielectricosVanesa Alberto DamianNo ratings yet
- Tiger Emt 1Document30 pagesTiger Emt 1CharavanaNo ratings yet
- Let's Begin: Module 3. Capacitance, Current and Resistance Capacitors and CapacitanceDocument40 pagesLet's Begin: Module 3. Capacitance, Current and Resistance Capacitors and CapacitanceSam TabujaraNo ratings yet
- Chap10 CapacitorsDocument22 pagesChap10 Capacitorsbree789No ratings yet
- 1 Capacitor 2Document41 pages1 Capacitor 2muhamadhilalkhoidarNo ratings yet
- GENERAL PHYSICS 2 - Q3 - Capacitance and DielectricsDocument17 pagesGENERAL PHYSICS 2 - Q3 - Capacitance and DielectricsPrecious Leah MerluzaNo ratings yet
- Pbsedsci 009 Electricity and Magnetism - Module 3 - Capacitance and DielectricsDocument8 pagesPbsedsci 009 Electricity and Magnetism - Module 3 - Capacitance and DielectricsAlan BalilaNo ratings yet
- 9 CapacitancecapacitorDocument10 pages9 CapacitancecapacitorAbhijeet HotkarNo ratings yet
- Capacitor and CapacitanceDocument48 pagesCapacitor and CapacitanceDave Serapion67% (3)
- Types of Capacitors and Its ApplicationsDocument18 pagesTypes of Capacitors and Its ApplicationsRalph Justine Hernandez100% (1)
- Green White Watercolor Notes Blank Background A4 Document - 20231024 - 142406 - 0000Document20 pagesGreen White Watercolor Notes Blank Background A4 Document - 20231024 - 142406 - 0000gauthamdinesan218No ratings yet
- 10 - CapacitorsDocument5 pages10 - Capacitorschie CNo ratings yet
- Krati XII-B Physics ProjectDocument10 pagesKrati XII-B Physics ProjectKrati PandeyNo ratings yet
- ExtraDocument23 pagesExtradharshanbskNo ratings yet
- Learner's Activity Sheet (LAS) in GENERAL PHYSICS 2: Capacitance and DielectricsDocument5 pagesLearner's Activity Sheet (LAS) in GENERAL PHYSICS 2: Capacitance and DielectricsRae RedillasNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsDocument16 pagesLesson 4 Capacitors and InductorsBlueprint MihNo ratings yet
- 4-Capacitors and CapacitanceDocument24 pages4-Capacitors and CapacitanceJazzverNo ratings yet
- Superconductors and Supercapacitors Session 3 (Supercapacitors)Document6 pagesSuperconductors and Supercapacitors Session 3 (Supercapacitors)sanjivbadheNo ratings yet
- Supercapacitors: New Super Energy Storage Device: Nitin Kathuria, Assistant Professor Richa Sharma, LecturerDocument4 pagesSupercapacitors: New Super Energy Storage Device: Nitin Kathuria, Assistant Professor Richa Sharma, LecturerNitin Kathuria100% (1)
- Capacitors P.naren KarthyDocument18 pagesCapacitors P.naren KarthyAnitha PragasamNo ratings yet
- Eee3352 L4Document38 pagesEee3352 L4Desmond CheweNo ratings yet
- Chapter 26 CapacitanceDocument49 pagesChapter 26 Capacitancewaelabood51No ratings yet
- 04 CapacitanceDocument27 pages04 Capacitanceade saputraNo ratings yet
- Capacitors P.naren KarthyDocument17 pagesCapacitors P.naren KarthyAnitha PragasamNo ratings yet
- Capacitance and DielectricsDocument2 pagesCapacitance and DielectricsAnn Margarette MoralesNo ratings yet
- Phy ProjDocument19 pagesPhy Projselavathy1937No ratings yet
- Energy Storage Elements: Electrical and Electronic Technology (BNJ 10903)Document58 pagesEnergy Storage Elements: Electrical and Electronic Technology (BNJ 10903)Muhammad NaufalNo ratings yet
- Capacitor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument3 pagesCapacitor: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaPRincess ScarLetNo ratings yet
- How Do Dielectrics Affect Capacitance in Capacitors - QuoraDocument3 pagesHow Do Dielectrics Affect Capacitance in Capacitors - QuoraChandra PrakashNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument3 pagesCapacitorCHEE HONG CHANNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and Dielectrics With Calculations: For GENERAL PHYSICS 2/ Grade 12/ Quarter 3/ Week 3Document21 pagesCapacitors and Dielectrics With Calculations: For GENERAL PHYSICS 2/ Grade 12/ Quarter 3/ Week 3Sandro FloresNo ratings yet
- Lecture Week 2Document30 pagesLecture Week 2Mukul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Capacitors and DielectricsDocument16 pagesCapacitors and DielectricsMahadi HasanNo ratings yet
- Omicron The Negative DF and The Interpretation of The Dielectric ResponseDocument6 pagesOmicron The Negative DF and The Interpretation of The Dielectric ResponseEduardo RogaNo ratings yet
- Capacitor AssignmentDocument3 pagesCapacitor Assignmentapi-2105647No ratings yet
- Examples of Dielectric Materials: Mica, Paper, Mylar, Electrolytic, CeramicDocument9 pagesExamples of Dielectric Materials: Mica, Paper, Mylar, Electrolytic, CeramicBerlin AlcaydeNo ratings yet
- Ee301 - Capacitors and InductorsDocument3 pagesEe301 - Capacitors and InductorsShahid RanaNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument1 pageCapacitorsJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- Oscillating-Circuits 0 PDFDocument31 pagesOscillating-Circuits 0 PDFjoseNo ratings yet
- College Physics 2: Capacitors, Electric Storage, and DielectricDocument24 pagesCollege Physics 2: Capacitors, Electric Storage, and DielectricJohn Christopher SibalNo ratings yet
- Application Note: CAPACITOR BASICS I - How Capacitors WorkDocument5 pagesApplication Note: CAPACITOR BASICS I - How Capacitors Workabdulyunus_amirNo ratings yet
- SUPERCAP Basic ConceptDocument145 pagesSUPERCAP Basic ConceptWaldyr Yassuo KamakuraNo ratings yet
- 1 CapacitorDocument37 pages1 CapacitorHeri Ardana SilaenNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5-Capacitive CircuitsDocument39 pagesLecture 5-Capacitive CircuitsMAENYA BRUCE OYONDINo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument86 pagesCapacitorsarunNo ratings yet
- Digital Quantum Batteries - Energy and Information Storage in Nanovacuum Tube Arrays (Complexity, Vol. 15, Issue 5) (2010)Document8 pagesDigital Quantum Batteries - Energy and Information Storage in Nanovacuum Tube Arrays (Complexity, Vol. 15, Issue 5) (2010)sepot24093No ratings yet
- Series ResonanceDocument11 pagesSeries Resonancegerald pradoNo ratings yet
- Grey Minimalist Business Project PresentationDocument19 pagesGrey Minimalist Business Project PresentationBeaver OrealNo ratings yet
- Capacitor Lab ReportDocument10 pagesCapacitor Lab ReportKarla MaalihanNo ratings yet
- CapacitorsDocument17 pagesCapacitorsWani SageerNo ratings yet
- 1937-Analysis of Series Capacitor Application ProblemsDocument14 pages1937-Analysis of Series Capacitor Application Problemssanela halidovic100% (1)
- Chapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. BoylestadDocument27 pagesChapter 10 - Capacitors: Introductory Circuit Analysis Robert L. Boylestadakankshag_13No ratings yet
- Charge Storing Tanks.: CapacitorsDocument19 pagesCharge Storing Tanks.: CapacitorsSweta VaishNo ratings yet
- Reporte 8Document4 pagesReporte 8Yaileen Ximena Aguilar MelendrezNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 AnswersDocument6 pagesLesson 2 AnswersAngelo Doldolea DerechoNo ratings yet
- Physics Pro.Document11 pagesPhysics Pro.thakurchenu742008No ratings yet
- Mexique 2013Document307 pagesMexique 2013Level ThreeNo ratings yet
- One Dimensional Convection: Interpolation Models For CFD: Gerald Recktenwald January 21, 2019Document24 pagesOne Dimensional Convection: Interpolation Models For CFD: Gerald Recktenwald January 21, 2019Level ThreeNo ratings yet
- Function: T Tridiag (A, B, C, D)Document13 pagesFunction: T Tridiag (A, B, C, D)Level ThreeNo ratings yet
- Level 3 Curriculum & ScheduleDocument5 pagesLevel 3 Curriculum & ScheduleLevel ThreeNo ratings yet
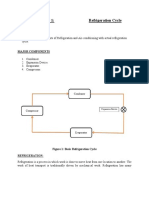
- Experiment # 1: Refrigeration Cycle: ObjectiveDocument2 pagesExperiment # 1: Refrigeration Cycle: ObjectiveLevel ThreeNo ratings yet
- Waste Heat Recovery and Flue Gas DesulphurizationDocument69 pagesWaste Heat Recovery and Flue Gas DesulphurizationLevel ThreeNo ratings yet
- Thermal Boundary Conditions and Some Solutions For Laminar Duct Flow Forced ConvectionDocument7 pagesThermal Boundary Conditions and Some Solutions For Laminar Duct Flow Forced ConvectionLevel ThreeNo ratings yet
- Problem5, ThermodynamicsDocument2 pagesProblem5, ThermodynamicsLevel ThreeNo ratings yet
- Panama Renewable Energy PVT LTD: Standard Operating ProcedureDocument3 pagesPanama Renewable Energy PVT LTD: Standard Operating ProcedureAradhya SinghNo ratings yet
- HV Earthing, CME, EquipmentsDocument41 pagesHV Earthing, CME, EquipmentssamyuldarosaNo ratings yet
- Pembangkit Listrik Tenaga Panas Laut (Otec) Diusulkan OlehDocument9 pagesPembangkit Listrik Tenaga Panas Laut (Otec) Diusulkan OlehFebrianto WibowoNo ratings yet
- Modelling A Solar Charge Station For Electric Vehicle With Storage BackupDocument4 pagesModelling A Solar Charge Station For Electric Vehicle With Storage Backupankitabhu100% (1)
- EcoStruxure Power Advisor - TrainingDocument12 pagesEcoStruxure Power Advisor - TrainingFred Javier Melendez GarcíaNo ratings yet
- AAA - M. Pignataro, N. Rizzi and A. Luongo Auth. Stability, Bifurcation and Postcritical Behaviour of Elastic Structures 1991 PDFDocument362 pagesAAA - M. Pignataro, N. Rizzi and A. Luongo Auth. Stability, Bifurcation and Postcritical Behaviour of Elastic Structures 1991 PDFLuisFernandoMendietaElenaNo ratings yet
- Malitbog Geothermal Power StationDocument2 pagesMalitbog Geothermal Power StationdescataNo ratings yet
- Across The Line Magnetic Starter Is Applied To Motors Whose Locked RotorDocument4 pagesAcross The Line Magnetic Starter Is Applied To Motors Whose Locked RotorJames Adrian Abalde SaboNo ratings yet
- 22ESC142 Module 5Document9 pages22ESC142 Module 5Aditya Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Specification For Testing & CommissioningDocument7 pagesSpecification For Testing & CommissioningEric TaylorNo ratings yet
- School of Energy & Environmental Studies Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya IndoreDocument33 pagesSchool of Energy & Environmental Studies Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalaya IndoreSIVA NAGA SUDHEER SIDDANINo ratings yet
- Virgin Led Outdoor LightingDocument14 pagesVirgin Led Outdoor LightingVIRGIN SOLARNo ratings yet
- Engie Fy 2022 Databook PDFDocument90 pagesEngie Fy 2022 Databook PDFshyamagniNo ratings yet
- PSA Chapter 10Document78 pagesPSA Chapter 10Jorge Silva VelezNo ratings yet
- Normal Inverse IDMT Form 1.3/10 Relays Type 2TJM70: Easun ReyrolleDocument2 pagesNormal Inverse IDMT Form 1.3/10 Relays Type 2TJM70: Easun ReyrolleSasiKumar SivathangaveluNo ratings yet
- 100va TXR Leaflet Dec2020Document1 page100va TXR Leaflet Dec2020msbhasinNo ratings yet
- Performance of IC EnginesDocument30 pagesPerformance of IC Engines6 avinashNo ratings yet
- Lei BB-100Document6 pagesLei BB-100Ciprian PetruleNo ratings yet
- Review Questions Single Phase Circuits - v2 TestDocument4 pagesReview Questions Single Phase Circuits - v2 TestSri NisshaNo ratings yet
- Yamaha Virago 1100 Problems - You Need To Know ThisDocument3 pagesYamaha Virago 1100 Problems - You Need To Know ThisRodolfo Velasquez NaranjoNo ratings yet
- SDM630MCT-MA Three-Phase Smart Meter Quick Guide: Cut OffDocument2 pagesSDM630MCT-MA Three-Phase Smart Meter Quick Guide: Cut OffFrancisco GuerreroNo ratings yet
- CV Shambhu MehtoDocument3 pagesCV Shambhu MehtoShambhu MehtaNo ratings yet
- 4008TAG2A EngineDocument4 pages4008TAG2A EngineAnamta KhanNo ratings yet
- Wind TunnelsDocument2 pagesWind TunnelsSANARAHAMAT A KODAKERINo ratings yet
- 26 Jun 2019 18 - BERC Loading DetailsDocument31 pages26 Jun 2019 18 - BERC Loading DetailsChief Engineer TransOMNo ratings yet
- EV Charging Using Wireless Power TransmissionDocument8 pagesEV Charging Using Wireless Power Transmissionதளபதி PraveenNo ratings yet
- Smart Grid - WikipediaDocument48 pagesSmart Grid - WikipediaBablu VermaNo ratings yet
- Tidal EnergyDocument13 pagesTidal EnergyPrem sharmaNo ratings yet