Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Education Degree Fraud Detection and Student Certificate Verification Using Blockchain IJERTV9IS070156
Education Degree Fraud Detection and Student Certificate Verification Using Blockchain IJERTV9IS070156
Uploaded by
حسان فضل الشعيبيOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Education Degree Fraud Detection and Student Certificate Verification Using Blockchain IJERTV9IS070156
Education Degree Fraud Detection and Student Certificate Verification Using Blockchain IJERTV9IS070156
Uploaded by
حسان فضل الشعيبيCopyright:
Available Formats
Published by : International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
http://www.ijert.org ISSN: 2278-0181
Vol. 9 Issue 07, July-2020
Education Degree Fraud Detection and Student
Certificate Verification using Blockchain
Jayesh G. Dongre Dr.Kishore.T.Patil
Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering
Navi Mumbai, India Navi Mumbai, India
Sonali M. Tikam Vasudha B. Gharat
Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering Smt. Indira Gandhi College of Engineering
Navi Mumbai, India Navi Mumbai, India
Abstract— To verify the authenticity of an academic degree and same date as the alleged graduation or qualification,
certificates we propose a system which employs a digital technology does not offer a straightforward solution unless
signature scheme and timestamps using blockchain technology. the individual involved is in possession of the private keys
As the number of universities and tertiary education students, needed by a digital signature scheme. So if anyone wants to
the number of graduates is constantly increasing. Due to this
verification process of these degree certificates generates a lot of
prove who is not a graduate in the past, a remedy is to use a
new job opportunities. The sudden changes in the technology time mark next to each diploma's digital signature. Therefore,
and development of new technologies like blockchain is if a person claims to have received a university degree a
booming, the implementation of blockchain using blockcerts decade ago, then the digital signature with its timestamp must
software provides us a solution of plausible business models. In show that it was indeed ten years ago. In this way, modifying
this paper we showcase two financial models balancing where university records or databases avoids the creation of fake
the service rates is been balanced between graduates and degrees in the future. Besides its cost, the issue with
employer as to main stakeholders of that service. A proof check conventional timestamp technology is that it needs
of certificates for students is done at low cost and an easy check availability and faith in third parties (Time Stamping
of the authenticity of the certificate is done from and trustable
source while recruiting by the employer.
Authority) who validate the date. Then its legal use is not
universal but up to every jurisdiction, and the possibility of
Keywords— Blockcerts, Stakeholders, Tertiary, Recruiting bankruptcy, closure or negligence of who is certifying. On
the other hand, chaining timestamps can reduce the risk of
I. INTRODUCTION bankruptcy, closure or failure, but this additional complexity
Proving unambiguously that you have an academic certificate not only doesn't solve the problem at all (confidence is still
(university degree, doctorate, or any certification of studies) required), but also requires perpetual maintenance to maintain
is a process that changes in each country or institution of the validity of the certified timestamp. The use of
education. decentralized blockchain is a simpler, economical, and
Some academic centres allow a quick and simple online straightforward solution to correct the aforementioned
query to verify the authenticity of their certificates, without drawbacks. Although the time accuracy in many of today's
even asking who requires that information. Some assign the blockchains is far from ideal, it's more than enough where a
role to third parties (whether by default or as required by date is needed (not the exact minute or second the
regulations) or market the service. Finally, there are times certification was signed into). In this way there is no need for
when there is no alternative but to contact the office of the confidence or ongoing maintenance / payments to provide a
academic secretary at the educational institution directly, so clear timestamp. The method which uses a blockchain is the
that we can confirm if a diploma or qualification is valid or one already described. A cryptographic hash function is
not. While, academic credential fraud is a fact and comes applied to the diploma and recorded in the public blockchain
through counterfeiting, as well as through the involvement of with a transaction which the academic institution digitally
the authorities and employees of the institution. The signs. Given the decentralized nature of a blockchain, the
frequency of these events is also adequate to detect the date on which the information was recorded can not be
emergence of dedicated companies. changed and is publicly verifiable without our trust being
required by intermediaries.
• Internal Fraud: Today's blockchain technology provides doors for
The fraud consists of applying to an educational institution 's implementing new business models on relatively
academic records individuals who did not actually concentrated markets. The use of blockchain in the education
successfully graduate or credential. Sometimes with the sector is one of the most challenging areas where mid- and
participation of someone who's part of the academic long-term results can be achieved. One of the areas where
institution, but not necessarily so. If the fraud occurs on the blockchain can provide a timely and solid solution thanks to
the use of widespread cryptocurrencies is the easy, trustable
IJERTV9IS070156 www.ijert.org 300
(This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)
Published by : International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
http://www.ijert.org ISSN: 2278-0181
Vol. 9 Issue 07, July-2020
and cheap verification of official documents, such as transactions, and it is virtually impossible to manipulate the
university degrees. Here the selection of a suitable public verification of a transaction, because it would require an
blockchain in terms of availability, versatility and cost is unreasonable amount of computing power in order to achieve
crucial to the creation of a top-up sustainable business model. the majority of the verification phase of the network.
Within this paper we discuss the question of finding an
economically viable solution to test university degrees
automatically. Has
Has
h h
• Blockchain Technology:
Blockchain is a ground breaking technology that enables new
types of distributed software architectures, where components BLOCK BLOCK
can find agreements on their shared states for decentralized
and transactional data sharing through a broad network of Ite Ite … Ite Ite …
untrusted users, without relying on a central point of m m m m
integration that should be trusted by any component within
the framework. The data structure blockchain is a time- Fig 1: Basic Blockchain Knowledge
stamped block list, which tracks and aggregates data about
transactions that have ever happened within the blockchain II. ANALYSIS
network. Thus, the blockchain provides an unchangeable The goal of this project is to solve the problems of the current
storage of data that only allows transactions to be inserted system of certificate verification and to stop user fraud and
without updating or deleting any existing transaction on the offer transparency in the education system by using
blockchain to prevent tampering and revision. Blockchain's blockchain technology. This project is designed to evaluate
most famous application are cryptocurrencies, which during the application of blockchain to implement distributed system
the last year was a huge phenomenon due to their promising as a service.
use of the technology. The largest and most popular of them The digital certificate, which adopts digital signature
is Bitcoin [6], and along with newer ones like Ethereum, they technology, provides the administrator with the authority to
are leading the cryptocurrency market at the 4-moment with confirm the administrator in the digital fields used to validate
more than 1,600 different currencies, with a market cap that the identity of a user and the authorisation to access the
last year was close to a trillion dollars, now over 300 billion network resources
dollars. Satoshi Nakamoto comments, as stated in the original (A) Objectives:
Bitcoin paper [6]: A purely peer-to - peer version of 1. Digital certificate that adopts digital signature technology
electronic cash would allow online payments to be sent provides the authority to validate the user himself in the
directly from one party to another without going through a digital fields used to validate the identity of a user and the
financial institution. Digital signatures offer part of the authorisation to access the network resources.
solution, but if a trustworthy third party is still needed to 2. This provides employers with clarity to check workers'
avoid double-spending, the key benefits are lost. Using a educational credentials during the recruiting process and
peer-to - peer network we offer a solution to the double- saves time for the review of educational documents
spending problem. The network timestamps transactions by (B) Scope:
hashing them into an ongoing proof-of - work hash-based 1. Blockchain technology is a growing field of interest
chain, forming a record that cannot be changed without for many European and other industries and universities. As a
redoing the proof-of-work, creating a record which cannot be fairly recent breakthrough in the field of computer science,
updated without proof-of - work redoing. The longest chain blockchain is a modern, cross-industry and disruptive
serves not only as evidence of the sequence of observed technology that is expected to drive global economic growth
occurrences, but also as evidence that it originated from the over the next few decades
largest pool of Computing power. So long so nodes that do 2. According to numerous researches around one
not collaborate to attack the network control a majority of million students passing out each year, the issuing authorities
CPU power, they can produce the longest chain and outpace of the certificate tend to be compromised for the student data
attackers. This requires minimal structure for the network protection credentials. Events which cause the graduation
itself. Messages are distributed on the best possible basis of certificate to be forged are often seen due to the lack of an
effort, and nodes can leave and re-joins the network at will, effective anti-forge mechanism. These systems are
embracing the longest proof-of - work chain as evidence of implemented to solve this problem while security problems
what happened when they left. Bitcoin incorporates and uses still exist. Blockchain is one of the latest Data Security
the Blockchain principle to allow transactions to be validated technology that can be adopted. The unalterable property of
by the majority of computing power in a network, ensuring the block chain helps to solve the problem of forgery of
that each transaction is checked and validated by the majority certificates.
of nodes that actively compute network transactions. Then, III. LITERATURE SURVEY
the verified transactions are stacked in an unchangeable 1. Eductx: A Blockchain-Based Higher Education Credit
sequence. All computers which used computational resources Platform By (Muhamed Turkanović , Marko Hölbl ,
to verify a block of data receive some cryptocurrency as a Kristjan Košič, Marjan Heričko, Aida Kamišalić.) :
reward. In this way, a large number of computers verify all
IJERTV9IS070156 www.ijert.org 301
(This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)
Published by : International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
http://www.ijert.org ISSN: 2278-0181
Vol. 9 Issue 07, July-2020
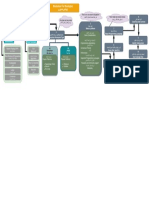
Blockchain technology enables the creation of a decentralized IV. DESIGN
environment, where transactions and data are not under the The design contains 3 Main components/ Model. They are
control of any third party organization. Any transaction ever to authentic details, Apply for new one, Check for
completed is recorded in a public ledger in a verifiable and authenticity. Here is the entire flow of the project in the form
permanent way. Based on the blockchain technology, we of flowchart.
propose a global higher education credit platform, named
eductx. This platform is based on the concept of the European Below are the mentioned tasks which is available in the
Credit Transfer and Accumulation System (ECTS). It system:
constitutes a globally trusted, decentralized higher education The system is such design as soon you open there is a
credit, and grading system that can offer a globally unified login/Registration option. Student / Employer can use this
viewpoint for students and higher education institutions software/portal to authenticate their certificates, apply for
(heis), as well as for other potential stakeholders, such as new certificates and for uploading new issued certificates if
companies, institutions, and organizations. As a proof of the university or the institution is new and not listed. As you
concept, we present a prototype implementation of the upload the certificates it creates a database for the respective
environment, based on the open-source Ark Blockchain new institution.
Platform. Based on a globally distributed peer-to-peer The Employer can use it for checking the authenticity of the
network, eductx will process, manage, and control ECTX certificate as a part of recruiting process and file action
tokens, which represent credits that students gain for against the fake one.
completed courses, such as ECTS. Heis are the peers of the
blockchain network. The platform is a first step toward a
more transparent and technologically advanced form of
higher education systems. The eductx platform represents the
basis of the eductx initiative, which anticipates that various
heis would join forces in order to create a globally efficient,
simplified, and ubiquitous environment in order to avoid
language and administrative barriers. Therefore, we invite
and encourage heis to join the eductx initiative and the eductx
blockchain network. INDEX TERMS Blockchain, higher
education, ECTS, tokens.
2. Blockchain, academic verification use case by (Federico
Bond, Franco Amati, Gonzalo Blousson):
To verify the authenticity of academic certificates we propose
employing a digital signature scheme and timestamps using
blockchain technology, because of its greater transparency,
less maintenance and lower cost than traditional alternatives.
Based on conversations held on July 31, 2015 on the stage of
the first Bitcoin forum organized by the government of
Ciudad de Buenos Aires.
3. Using blockchain as a tool for tracking and verification
of official degrees by (Miquel Oliver, Joan Moreno, Figure 2: System architecture
Gerson Prieto, David Benítez): While the number of
universities, tertiary education students and number of V. FUTURE MODIFICATIONS
graduates per year constantly increase, the need to easily In the future, we plan to test the prototype in a real-life
verify degree certificates generates new business environment, which would include HEIs, students and
opportunities. The irruption of blockchain, and its companies. In this way the presented concept could be further
implementation based in the blockcerts software, provides a validated. Additionally, we plan to adapt this system
straightforward solution that demands to explore plausible blockchain so that each course would be assigned with a
business models. In this paper we project two financial unique blockchain address and a pool of tokens. After
models balancing where the price for the service is balanced completing the course obligations, students would get tokens
between the graduate and the employer as the main from the course address and not directly from the institution.
stakeholders of that service. Students demand a proof-of- The course address would be a multi signature address
certification at low cost and easy to check, employers also between an institution and a professor
demand quick and trustable verification of degrees when
recruiting. Both models are projected for several geographic VI. CONCLUSIONS
markets and shares to explore plausible ways to develop that The proposed platform takes the advantage of the blockchain
business in the European Union in order to create a globally trusted higher education credit
and grading system. As a proof of concept, we presented a
prototype implementation of the system platform which is
IJERTV9IS070156 www.ijert.org 302
(This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)
Published by : International Journal of Engineering Research & Technology (IJERT)
http://www.ijert.org ISSN: 2278-0181
Vol. 9 Issue 07, July-2020
based on the open-source Ark blockchain platform. The [17] Lisha Chen-Wilson, Dr David Argles,”Towards a framework
of A Secure E-Qualification Certificate System.
proposed system platform addresses a globally unified
[18] Jiin-Chiou Cheng, Narn-Yih Lee, Chien Chi, and Yi-Hua
viewpoint for students and organizations. Students benefit Chen,” Blockchain and Smart Contract for Digital
from a single and transparent view of their completed Certificate”.
courses, while have access to up to date data regardless of a
student’s educational origins. Other beneficiaries of the
proposed system are potential employers, who can directly
validate the information provided by students. The proposed
solution is based on the distributed P2P network system. It
transfers the higher education grading system from the
current real-world physical records or traditional digital ones
(e.g. databases) to an efficient, simplified, ubiquitous version,
based on blockchain technology. It is anticipated that such a
system could potentially evolve into a unified, simplified and
globally ubiquitous higher education credit and grading
system.
REFERENCES
[1] C. K. Wong and S, S. Lam “Digital signatures for flows and
multicasts”, WEEE/ACM Transactions on Networking, 7(4):
502- 513, 1999.
[2] A. M. Antonopoulos, Mastering Bitcoin: Unlocking Digital.
Sebastopol, CA, USA: O’Reilly Media, 2015.
[3] Benyuan He, “An Empirical Study of Online Shopping Using
Blockchain Technology“, Department of Distribution
Management, Takming University of Science and
Technology, Taiwan, R.O.C., 2017.
[4] Chris Dannen, Introducing Ethereum and Solidity,
https://www.apress.com/br/book/9781484225349
[5] J. Clark and P. C. van Oorschot, “SoK: SSL and HTTPS:
Revisiting past challenges and evaluating certificate trust
model enhancements,” in proc. IEEE S&P’13, May 2013, pp.
511–525.
[6] L. Zhang, D. Choffnes, D. Levin,et al., “Analysis of SSL
certificate reissues and revocations in the wake of
Heartbleed,” in proc. ACMIMC’14, Nov 2014, pp. 489– 502.
[7] M. Carvalho and R. Ford, “Moving-target defenses for
computer networks,”IEEE Security & Privacy, vol. 12, no. 2,
pp. 73–76, Mar.-Apr.2014.
[8] Papazoglou, M., Service-Orientated Computing: Concepts,
Characteristics and Directions, in International Conference on
Web Information Systems Engineering. 2003, IEEE: Rome.
[9] D. Ferraiolo, R. Kuhn, and R. Sandhu, “Rbac standard
rationale: Comments on ”a critique of the ansi standard on
role-based access control”, ”IEEE Security Privacy, vol. 5,
no. 6, pp. 51–53, Nov 2007.
[10] A. Ouaddah, A. A. Elkalam, and A. A. Ouahman, “Towards a
novel privacy-preserving access control model based on
blockchain technology in iot,” in Europe and MENA
Cooperation Advances in Information and Communication
Technologies. Springer, 2017, pp. 523– 533.
[11] L. Y. Chen and H. P. Reiser, “Distributed applications and
interoperable systems, 17th ifip wg 6.1 international
conference, dais 2017, held as part of the 12th international
federated conference on distributed computing techniques,
discotec 2017, neuchtel, switzerland, june 1922, 2017.”
Springer, 2017.
[12] Q. Xia, E. B. Sifah, K. O. Asamoah, J. Gao, X. Du, and M.
Guizani, “Medshare: Trust-less medical data sharing among
cloud service providers via blockchain,” IEEE Access, vol. 5,
pp. 14 757–14 767, 2017.
[13] M. Warasart and P. Kuacharoen, “Paper-based Document
Authentication using Digital Signature and QR Code,” no.
Iccet, 2012.
[14] J. van Beusekom, F. Shafait, and T. M. Breuel,“Text-line
examination for document forgery detection,” Int. J. Doc.
Anal. Recognit., vol. 16, no. 2, pp. 189–207, 2013.
[15] Mahamat, M. B. (2016), A Web Service Based Database
Access for Nigerian Universities’ Certificate Verification
System.
[16] Osman Ghazali, Omar S. Saleh, “Cloud Based Graduation
Certificate Verification Model”.
IJERTV9IS070156 www.ijert.org 303
(This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.)
You might also like
- Journal of Retailing and Consumer Services: Mengmeng Song, Xinyu Xing, Yucong Duan, Jason Cohen, Jian MouDocument17 pagesJournal of Retailing and Consumer Services: Mengmeng Song, Xinyu Xing, Yucong Duan, Jason Cohen, Jian MouDavid OvallosNo ratings yet
- Business Finance: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Different Types of InvestmentsDocument22 pagesBusiness Finance: Quarter 4 - Module 1 The Different Types of Investmentsrandy magbudhi71% (7)
- Ubisoft Swot AnalysisDocument10 pagesUbisoft Swot AnalysisAkash MandalNo ratings yet
- Israel KirznerDocument2 pagesIsrael KirznerJohn Brian Cali100% (1)
- La Presse BDocument7 pagesLa Presse BSitara QadirNo ratings yet
- Cyberoam Release Notes V 10 CR15wi, CR15i & CR25iDocument17 pagesCyberoam Release Notes V 10 CR15wi, CR15i & CR25ijyothivzgNo ratings yet
- Ethicalhacking NdaDocument6 pagesEthicalhacking NdaraviNo ratings yet
- H. Steyerl - If You Don't Have Bread, Eat Art!Document8 pagesH. Steyerl - If You Don't Have Bread, Eat Art!CarmenjonesNo ratings yet
- Indian Business Environment Foreign Trade Policy of IndiaDocument28 pagesIndian Business Environment Foreign Trade Policy of IndiaReshma RavichandranNo ratings yet
- Detailed PH.D ReportDocument27 pagesDetailed PH.D ReportCHETSUNNo ratings yet
- Memoire MasterDocument75 pagesMemoire MasterFranck HenryNo ratings yet
- Theme 1 ReportDocument9 pagesTheme 1 ReportLusajo Lazarus MwaisakaNo ratings yet
- 3MGTG Up Front and Personal ReportDocument48 pages3MGTG Up Front and Personal ReportbinkomerNo ratings yet
- Indicium Business PlanDocument21 pagesIndicium Business PlanAnonymous hjyc5oPAc100% (1)
- BITCOIN - The Final Piece of The Protocol PuzzleDocument17 pagesBITCOIN - The Final Piece of The Protocol PuzzleeliforuNo ratings yet
- Weekend Media Blast: and Now For Something Completely Different..Document11 pagesWeekend Media Blast: and Now For Something Completely Different..krrajanNo ratings yet
- FINTECHDocument21 pagesFINTECHshamira haqueNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document28 pagesChapter 1bugima1No ratings yet
- Flux Tutorial MS2DDocument42 pagesFlux Tutorial MS2DAlexandre BourrieauNo ratings yet
- Authenticating Social Media EvidenceDocument11 pagesAuthenticating Social Media EvidenceMehar VermaNo ratings yet
- Cyber Attack Modelling Thesis SampleDocument177 pagesCyber Attack Modelling Thesis Samplebalestier235No ratings yet
- INFOTONICS MEDIA Company Profile...Document32 pagesINFOTONICS MEDIA Company Profile...Shally AhujaNo ratings yet
- National Economic Report of BermudaDocument33 pagesNational Economic Report of BermudaAnonymous UpWci5No ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Support at and Around Inria As of August 2021Document73 pagesEntrepreneurship Support at and Around Inria As of August 2021Herve LebretNo ratings yet
- E-Cheque in E-CommerceDocument22 pagesE-Cheque in E-CommerceSaran KumarNo ratings yet
- Essay Benefits of Social Media For Business EnterprisesDocument1 pageEssay Benefits of Social Media For Business EnterprisesQuraisy AmriNo ratings yet
- GEMMA Pitch Deck V5.3Document67 pagesGEMMA Pitch Deck V5.3Guillaume VingtcentNo ratings yet
- Cheating in Building ConstructionDocument18 pagesCheating in Building ConstructionJihad TámímíNo ratings yet
- Accommodation Operation ManagementDocument14 pagesAccommodation Operation ManagementJether IgnacioNo ratings yet
- EntrepriseDocument16 pagesEntrepriseIdir BenferhatNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Web ArchivingDocument15 pagesThe Evolution of Web ArchivingMadNo ratings yet
- Bring Your Own Computer: Why Should We Have Separate Devices For Home and Work?Document7 pagesBring Your Own Computer: Why Should We Have Separate Devices For Home and Work?api-232672640No ratings yet
- Effects of Cryptocurrency To Entertainment, Media, and CommunicationDocument19 pagesEffects of Cryptocurrency To Entertainment, Media, and CommunicationLouise GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Artificial Intelligence Smart Contract and IslamicDocument10 pagesArtificial Intelligence Smart Contract and IslamicTuqir BaabayNo ratings yet
- Launchpad Development Services - MobiloitteDocument1 pageLaunchpad Development Services - MobiloitteMobiloitte TechnologiesNo ratings yet
- Cypheme Deep Tracing PresentationDocument25 pagesCypheme Deep Tracing PresentationArifullah HussainiNo ratings yet
- Title:: Cyberwar: M.A.D 2.0-SummaryDocument3 pagesTitle:: Cyberwar: M.A.D 2.0-SummaryAhmed AminNo ratings yet
- Ioana Vasiu Computer ForensicsDocument71 pagesIoana Vasiu Computer ForensicsTarhon AncaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To e Business Project ReportDocument32 pagesIntroduction To e Business Project ReportBikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Impact of Digital Currency in E-CommerceDocument3 pagesImpact of Digital Currency in E-CommerceGRD JournalsNo ratings yet
- Real-World Asset Tokenization STM 2023 - 230412 - 131023Document28 pagesReal-World Asset Tokenization STM 2023 - 230412 - 131023Emilien ErcolaniNo ratings yet
- Swole Doge Whitepaper v1.0Document33 pagesSwole Doge Whitepaper v1.0Swole DogeNo ratings yet
- BUSINESS PROBLEM STATEMENT On UnemploymentDocument8 pagesBUSINESS PROBLEM STATEMENT On UnemploymentAkash MathewsNo ratings yet
- Sec18-Reverse Engineering EthereumDocument16 pagesSec18-Reverse Engineering EthereumShuixin ChenNo ratings yet
- DUP BlockchainDocument20 pagesDUP Blockchainjesus_yustasNo ratings yet
- #1 - Social's Growth ContinuesDocument14 pages#1 - Social's Growth ContinueschanNo ratings yet
- Crowdfunding in FintechDocument6 pagesCrowdfunding in FintechhukaNo ratings yet
- DissertationDocument93 pagesDissertationAppy ThianhlunNo ratings yet
- A Strategic Partnership PresentationDocument21 pagesA Strategic Partnership Presentationfarooq_bhattiNo ratings yet
- One United Properties - Residential PortfolioDocument10 pagesOne United Properties - Residential PortfoliosubsoniqueNo ratings yet
- WiFi Penetration Testing Guide 1691371226Document11 pagesWiFi Penetration Testing Guide 1691371226LevelupNo ratings yet
- Anodot Cloud Cost Survey Report 2023Document19 pagesAnodot Cloud Cost Survey Report 2023Serigne Modou NDIAYENo ratings yet
- Crowdfunding Using Blockchain by Aishwarya and KavinDocument7 pagesCrowdfunding Using Blockchain by Aishwarya and KavinAishwarya RajeshNo ratings yet
- Using OSS For Forensic PurposesDocument7 pagesUsing OSS For Forensic PurposesManuel DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Internship Cover LetterDocument1 pageInternship Cover LetterrvwassupNo ratings yet
- Emerging Juris Business 10Document21 pagesEmerging Juris Business 10Jai ShreeramNo ratings yet
- Competitive Intelligence: An IntroductionDocument21 pagesCompetitive Intelligence: An IntroductionManu GargNo ratings yet
- RTP Audit CapiiiDocument33 pagesRTP Audit CapiiiMaggie HartonoNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Cryptography For The Internet of ThingsDocument13 pagesLightweight Cryptography For The Internet of ThingsmoonimaNo ratings yet
- Phishing Detection Using Machine LearningDocument9 pagesPhishing Detection Using Machine LearningbhattajagdishNo ratings yet
- Apple Arcade LawsuitDocument39 pagesApple Arcade LawsuitMikey CampbellNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 - Time Value of MoneyDocument38 pagesChapter 2 - Time Value of Moneyحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Chapterfivehomework Scanner Scanner System String FilenotfoundexceptionDocument6 pagesChapterfivehomework Scanner Scanner System String Filenotfoundexceptionحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- 2019 08 08 OriginStamp Blockchain Technology PresentationDocument12 pages2019 08 08 OriginStamp Blockchain Technology Presentationحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Car Number Plate Detection Using MATLAB and Image ProcessingDocument29 pagesCar Number Plate Detection Using MATLAB and Image Processingحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- المستندDocument5 pagesالمستندحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Iot Key FeaturesDocument4 pagesIot Key Featuresحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Project Final Report: FP7-317862-COMPOSE Collaborative Open Market To Place Objects at Your ServiceDocument66 pagesProject Final Report: FP7-317862-COMPOSE Collaborative Open Market To Place Objects at Your Serviceحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Blockchain: Fundamentals & Opportunities: A Primer On Its Evolution, Technological Functionality & Potential Use CasesDocument23 pagesBlockchain: Fundamentals & Opportunities: A Primer On Its Evolution, Technological Functionality & Potential Use Casesحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- خارطة طريق بلوكتشينDocument1 pageخارطة طريق بلوكتشينحسان فضل الشعيبي100% (1)
- Blockchain Technology:: Implications For Operations and Supply Chain ManagementDocument34 pagesBlockchain Technology:: Implications For Operations and Supply Chain Managementحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- An Overview of Blockchain Technology Based On A Study of Public AwarenessDocument9 pagesAn Overview of Blockchain Technology Based On A Study of Public Awarenessحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Blockchain For Developers: @aliaalzubaidi Ali-AlzubaidiDocument1 pageBlockchain For Developers: @aliaalzubaidi Ali-Alzubaidiحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- خارطة طريق بلوكتشينDocument1 pageخارطة طريق بلوكتشينحسان فضل الشعيبيNo ratings yet
- Editors' Picks Market Summary: More IndicesDocument16 pagesEditors' Picks Market Summary: More IndiceschandraNo ratings yet
- It Iat 1642Document8 pagesIt Iat 1642Liya FathimaNo ratings yet
- The State of Crypto - Corporate Adoption - CoinbaseDocument14 pagesThe State of Crypto - Corporate Adoption - CoinbaseKoloNo ratings yet
- BidWell Report V003Document2 pagesBidWell Report V003Brooks CliffordNo ratings yet
- Dark Web and The Onion Routing (TOR)Document125 pagesDark Web and The Onion Routing (TOR)Neeraj GargNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Attack Surface of Blockchain: A Systematic OverviewDocument30 pagesExploring The Attack Surface of Blockchain: A Systematic Overviewhassan husseinNo ratings yet
- Chart Pteern CryptocurrencyDocument227 pagesChart Pteern CryptocurrencyImn HmtiNo ratings yet
- Q3 2023 PitchBook Analyst Note 17 Takeaways From FinovateFallDocument23 pagesQ3 2023 PitchBook Analyst Note 17 Takeaways From FinovateFallmikeNo ratings yet
- Basic Crypto Currency TradingDocument34 pagesBasic Crypto Currency TradingANo ratings yet
- Bitcoin Black Whitepaper 2.0Document29 pagesBitcoin Black Whitepaper 2.0zagab bryanNo ratings yet
- 2019 Ransomware Hostage Rescue ManualDocument20 pages2019 Ransomware Hostage Rescue ManualVlad OlteanNo ratings yet
- FuturePaymentsNon FungibleTokensDocument46 pagesFuturePaymentsNon FungibleTokensPetraNo ratings yet
- #1 Bitcoin Mining Calculator - ACCURATE! (2021 Updated)Document1 page#1 Bitcoin Mining Calculator - ACCURATE! (2021 Updated)Ahmad FajrihNo ratings yet
- A Scalable Verification Solution For BlockchainsDocument50 pagesA Scalable Verification Solution For BlockchainsJosé IgnacioNo ratings yet
- Easy Ways How To Get BitcoinDocument3 pagesEasy Ways How To Get Bitcoingo nikNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Blockchain Technology On Business Financial AuditoDocument57 pagesThe Impact of Blockchain Technology On Business Financial AuditoIan KwepuNo ratings yet
- Formal Verification of Fraud Resilience in A Crowdsourci - 2023 - Computers - SeDocument26 pagesFormal Verification of Fraud Resilience in A Crowdsourci - 2023 - Computers - SeAkashah ArshadNo ratings yet
- A Survey On Characteristics of Top CryptocurrenciesDocument9 pagesA Survey On Characteristics of Top CryptocurrenciesIJAR JOURNALNo ratings yet
- Holy Angel University School of Business and Accountancy Angeles City, PampangaDocument39 pagesHoly Angel University School of Business and Accountancy Angeles City, PampangaAlyssa QuiambaoNo ratings yet
- Application of The VAR Model in Examining The Determinants of Returns of Selected CryptocurrenciesDocument10 pagesApplication of The VAR Model in Examining The Determinants of Returns of Selected CryptocurrenciesSanja StojanovicNo ratings yet
- Ey Digital Asset EcosystemDocument11 pagesEy Digital Asset EcosystemEnrico Lentini SantoNo ratings yet
- Osint Chatgpt: Prompt IdeasDocument124 pagesOsint Chatgpt: Prompt IdeasPedrito OrangeNo ratings yet
- IBPS SO AFO - IT - HR Prelims 2023 Memory Based PaperDocument115 pagesIBPS SO AFO - IT - HR Prelims 2023 Memory Based Paperruha28665No ratings yet
- 2024 Crypto Investment OutlookDocument4 pages2024 Crypto Investment OutlookIvan DoriNo ratings yet
- Play Dice Casino Game Online - Dice Betting at Stake CasinoDocument1 pagePlay Dice Casino Game Online - Dice Betting at Stake Casinolkate5299No ratings yet
- Profile Paycec 2022Document20 pagesProfile Paycec 2022rino pradityaNo ratings yet
- Gravity Finance White PaperDocument14 pagesGravity Finance White PaperMichael WongNo ratings yet
- Thank You For Purchasing My Private Method, Price-400$: Get Free BitcoinsDocument5 pagesThank You For Purchasing My Private Method, Price-400$: Get Free BitcoinsCLARA ANGELINANo ratings yet