Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Nursing Diagnosis and Drug Study Case Scenarion Dennis
Nursing Diagnosis and Drug Study Case Scenarion Dennis
Uploaded by
E.R.OCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Nursing Diagnosis and Drug Study Case Scenarion Dennis
Nursing Diagnosis and Drug Study Case Scenarion Dennis
Uploaded by
E.R.OCopyright:
Available Formats
Case Scenario:
Child Denis 9 year old boy playing with his friends outside their home stopped for a
while to void on a transparent container which he found inside the bathroom. His mother notice a
small amount and cola colored urine.
The next day, he informed his mother that he complains of mild headache and feels weak.
In addition, mother noticed that child Denis had no interest to eat. The condition became worse
when child Denis experienced shortness of breath the following day. This symptoms prompted
the mother to bring him to a Mandaluyong City Medical Center.
Question No. 1
Formulate three (3) nursing diagnosis, prioritize based on identified theory using the
template below. (6 points)
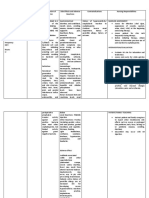
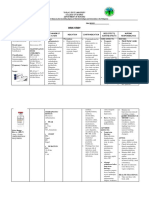
Prioritization Nursing Diagnosis Theory based explanation
1 Ineffective breathing pattern Maslow's Hierarchy ,
related to the inflammatory respiration which under the
process as evidenced by the biological and physiological
shortness of breath. needs was one of the highest
level of priority.
2 Excess Fluid Volume related Maslow's Hierarchy,
to compromised regulatory “Nutrition (elimination, skin
mechanisms (renal care)” Biological and
Insufficiency) as evidenced Physiological needs was one
by edema, pulmonary of the highest level of priority
congestion on x-ray, and next to respiration.
specific gravity changes.
3 Risk for infection related to Maslow's Hierarchy
renal impairment. “Protection/Free from
infection” which was under
the safety and security needs,
was one of the level 2 or
Moderately high priority next
to biological & physiological
needs.
Question No. 2
Based on the above scenario, formulate two (2) drug study using the suggested format.
(30 points)
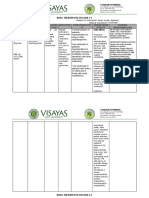
Drug Classific Mechani Indicati Contraindic Adverse Nursing
Data ation sm of ons ation Reaction Responsibilities
Action
Generic Pharma Inhibits Treatme Hyper Hyper Baseline assess
Name co bacterial nt of sensitivity to sensitivity ment
therapeu cell wall susceptib any reaction
Penicillin tic: synthesis le penicillin. ranging Question for
G Penicilli by infection from rash, history of
potassium n binding s Caution: fever, allergies,
to one or including chills to particularly
Brand Clinical: more of sepsis, Renal/heptic anaphylaxi penicillins,
Name Antibioti the meningit impairment, s occur cephalosporins.
c penicillin is, seizure occasional
Pfizerpen binding endocard disorder, ly. Intervention/eval
proteins itis, hypersensiti uation
Route and of pneumon vity to
frequency bacterial. ia. cephalospori Promptly report
Active ns, pts with rash
300, 000 Therape against asthma. (hypersensitivity)
units IM, utic gram diarrhea (with
o.d. Effect: positive fever, abdominal
organism pain,
Bacterici s (except mucus, or blood
dal S. in stool, may
aureus). indicate
Some antibiotic
gram- colitis). Monitor
negative I&O, urinalysis
organism electrolytes, renal
s (e.g. N. function tests for
gonorrho nephrotoxicity
eae) and
some
anaerobe
s and
spirochet
es.
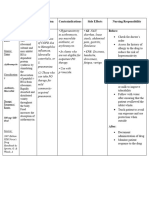
Generic Pharma Enhance Treatme Contraindic Vigorous Baseline
name co s nt of ations: diuresis assessment
Therape excretion edema may lead
Furosemid utic: of associate Hypersensiti to Check vital sign,
e sodium, d with vity to profound esp. B/P, pulse,
Loop chloride, HF and furosemide. water for hypotension
Brand diuretic. potassiu renal/hep Anuria. loss/electr before
Name m by atic olyte administration.
Clinical: direct disease: Caution: depletion,
Lasix Diuretic action at acute resulting Asses baseline
ascendin pulmona Hepatic in renal function,
Route & g limb of ry cirrhosis, hypokalem serum
frequency loop of edema. hepatic ia, electrolytes, esp.
Henle. Treatme coma, hyponatre serum sodium,
2 mg/kg nt of severe mia, potassium.
p.o. daily Therape hyperten electrolyte dehydratio
utic sion (not depletion, n. Assess skin
Effect: recomme prediabetes, turgor, mucous
nded as diabetes, Sudden membranes for
Produces initial systemic volume hydration status;
diuresis, treatment lupus depletion observe for
lower ). erythematos many edema.
B/P us. Pts with result in
prostatic increased Assess muscle
hyperplasia/ risk of strength, mental
urinary thrombosis status.
stricture. ,
circulatory Note skin
collapse temperature,
sudden moisture.
death.
Obtain baseline
Acute weight initiate
hypotensiv I&O monitoring.
e episodes
may occur, Auscultate lung
sometimes sounds
several
days after In pts with
beginning hepatic cirrhosis
therapy. and ascites,
consider giving
Ototoxicit initial doses in a
y hospital setting.
(deafness,
vertigo, Intervention/eval
tinnitus) uation
may occur,
esp in pts Monitor B/P,
with vital signs, serum
severe electrolytes,
renal weight
impairmen
t. Note extent of
diuresis
Can
exacerbate Watch for
diabetes symptoms of
mellitus, electrolyte
systemic imbalance
lupus hypokalemia may
erythemat result in changes
osus, in muscle
pancreatiti strength, tremor,
s muscle cramps,
altered mental
Blood status, cardiac
dyscrasias arrhythmias;
have been hyponatremia
reported. may result in
confusion, thirst,
cold/clammy
skin.
Consider
potassium
supplementation
if hypokalemia
occurs.
Patient/family
teaching
Expect increased
frequency,
volume of
urination.
Report
palpations, signs
of electrolyte
imbalances
(noted
previously),
hearing
abnormalities
(sense of fullness
in ears, tinnitus)
Eat foods high in
potassium such
as whole
grains(cereals),
legumes, meat,
bananas, apricots,
orange juice,
potatoes(white,
sweet) raisins.
Avoid sunlight,
sunlamps.
REFERENCES:
https://nursing.unboundmedicine.com/nursingcentral/view/Davis-Drug-
Guide/51345/all/furosemide
https://www.drugs.com/furosemide.html#:~:text=Furosemide%20is%20a%20loop
%20diuretic,disorder%20such%20as%20nephrotic%20syndrome.
https://nurseslabs.com/antibiotics/#penicillins_and_penicillinaseresistant_antibiotics
You might also like
- Cholecystitis Concept MapDocument4 pagesCholecystitis Concept Mapnursing concept maps100% (7)
- Small Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderDocument1 pageSmall Bowel Obstruction System - DisorderMarina Wasem Netzlaff0% (1)
- CASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesCASE STUDY Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de Castro86% (22)
- OKU 5 Orthopaedic Knowledge Update SpineDocument45 pagesOKU 5 Orthopaedic Knowledge Update SpinePubMed77100% (1)
- Pharmacology Mnemonics MNEMOMICSDocument14 pagesPharmacology Mnemonics MNEMOMICSE.R.O100% (1)
- YOUNG MIN LEE CASE STUDY Update 2Document7 pagesYOUNG MIN LEE CASE STUDY Update 2E.R.ONo ratings yet
- Piggery DocxdDocument7 pagesPiggery DocxdRamesiz Piad100% (2)
- Statement of Deficiencies and Plan of Correction For Andbe Home (Via DHHS)Document12 pagesStatement of Deficiencies and Plan of Correction For Andbe Home (Via DHHS)NTV NewsNo ratings yet
- S. Connolly Mini Guide Astral Temple ModifiedDocument31 pagesS. Connolly Mini Guide Astral Temple Modifiedbuddaofdestruction100% (10)
- Cefuroxime (Drug Study)Document2 pagesCefuroxime (Drug Study)Rosebel LaguraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RyDocument30 pagesDrug Study RyRyrey Abraham PacamanaNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAmoxicillin Drug StudyDUMANGENG ELLAINE D.No ratings yet
- Drug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaDocument6 pagesDrug Study Lab, NCP - Bronchial AsthmaRichelle Sandriel C. de CastroNo ratings yet
- 5drug StudyDocument7 pages5drug StudyPALEN, DONNA GRACE B.No ratings yet
- DS - Mod9Document2 pagesDS - Mod9designericlelynsoronioNo ratings yet
- Evangelista Drug-StudyDocument15 pagesEvangelista Drug-Studydinglasanerica57No ratings yet
- Case Study: Urinary Tract InfectionDocument21 pagesCase Study: Urinary Tract InfectionRania Sh AzzehNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyJIREH MAE NOTARTENo ratings yet
- Name: Ma Rupina B. Ponce Course: Bachelor of Science Major in Nursing Section: CDocument10 pagesName: Ma Rupina B. Ponce Course: Bachelor of Science Major in Nursing Section: CMaria Pina Barbado PonceNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument2 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Villamaria - Drug StudyDocument11 pagesVillamaria - Drug StudyHey LeunNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument14 pagesDrug StudyMary LyonNo ratings yet
- Rabia Drug StudyDocument6 pagesRabia Drug StudyMonmon BagarinaoNo ratings yet
- Kardex, Drug Study and CheckDocument12 pagesKardex, Drug Study and CheckJemina Rafanan RacadioNo ratings yet
- BangkasDocument5 pagesBangkasJulianne BangkasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study ResumaDocument3 pagesDrug Study ResumaNicole Arriana ResumaNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDocument5 pagesCefuroxime and Ketorolac Drug StudyDeva HiyasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study EntecavirDocument4 pagesDrug Study EntecavirClarimae AwingNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesName of Drug Dosage, Route, Frequency and Timing Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Reactions Special Precautions Nursing ResponsibilitiesIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeDocument3 pagesDrug Name Indications Actions Contraindications and Cautions Adverse Effects Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities BeforeArdel LabadaNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsDocument20 pagesName of Drug: Ceftazidime Therapeutic Class: Pharmacologic Class: CephalosporinsianNo ratings yet
- Ertapenem Drug StudyDocument3 pagesErtapenem Drug StudyBea Dela CenaNo ratings yet
- Elsie Kho Ap300 Study NotesDocument36 pagesElsie Kho Ap300 Study Noteshanazawa_rui9878030No ratings yet
- Clinical Analysis: I. Patient's ProfileDocument19 pagesClinical Analysis: I. Patient's ProfileKathleen DimacaliNo ratings yet
- VILLAMIN - Drug StudyDocument4 pagesVILLAMIN - Drug StudyAzizah VillaminNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Adn Ncp-Case Pres.Document22 pagesDrug Study Adn Ncp-Case Pres.MaeNo ratings yet
- 4 Cefazolin Drug StudyDocument4 pages4 Cefazolin Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Pioquinto (Rot 2 Drug Study)Document8 pagesPioquinto (Rot 2 Drug Study)Ghianx Carlox PioquintoxNo ratings yet
- Amikacin 2Document2 pagesAmikacin 2Sian AsadaNo ratings yet
- Drugstudy 20Document9 pagesDrugstudy 20MahledJoy EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Peritonitis PDFDocument1 pagePeritonitis PDFHoney MacabuhayNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Cefaclor)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- NALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsDocument6 pagesNALAM 106 Ass. AntibioticsBeth100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudySierraSiwaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CefuroximeDocument2 pagesDrug Study CefuroximeTipey Segismundo100% (1)
- 5 Cefuroxime Drug StudyDocument4 pages5 Cefuroxime Drug Studyshadow gonzalezNo ratings yet
- Cefoxitin Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefoxitin Drug StudyBea Dela Cena100% (2)
- Drug Study ICUDocument14 pagesDrug Study ICUAndrea Isabel U. O'Dell100% (1)
- BIO 151 Congenital AspleniaDocument3 pagesBIO 151 Congenital AspleniaLance CarandangNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinDocument4 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study AzithromycinhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Med Ward)Document4 pagesDRUG STUDY (Med Ward)Kimberly Abellar LatoNo ratings yet
- RUG Tudy: College of NursingDocument3 pagesRUG Tudy: College of NursingYoko Mae YanoNo ratings yet
- Olores Drugstudy Cephalothin SodiumDocument7 pagesOlores Drugstudy Cephalothin SodiumTintin KingNo ratings yet
- NCM107 Lab Drug Study Manalo BSN 2BDocument4 pagesNCM107 Lab Drug Study Manalo BSN 2BBethrice MelegritoNo ratings yet
- Drug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesDocument3 pagesDrug Action Indications and Contraindications Nursing ResponsibilitesGino B. BulanaNo ratings yet
- AsncudDocument2 pagesAsncudJaylord VerazonNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument8 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesYamatoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CeftriaxioneDocument2 pagesDrug Study CeftriaxioneJulie LesmorasNo ratings yet
- Amoxicillin Drug StudyDocument1 pageAmoxicillin Drug StudyDivine LavaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Anti-InfectiveDocument8 pagesDrug Study: Anti-InfectiveTri ShaNo ratings yet
- Histopathology NotesDocument12 pagesHistopathology NotesLeandro Miguel TongolNo ratings yet
- Cefuroxomine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesCefuroxomine Drug StudyNiziu BearsNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY (Ceftriaxone)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY (Ceftriaxone)Avianna CalliopeNo ratings yet
- CefoxitinDocument1 pageCefoxitinDaryl PaglinawanNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn Care ChecklistDocument2 pagesImmediate Newborn Care ChecklistE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Reflection Improving's Maternal HealthDocument1 pageReflection Improving's Maternal HealthE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Case Study Analysis On Nanotechnology STSDocument4 pagesCase Study Analysis On Nanotechnology STSE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Group 6 Group Case Study DONEDocument5 pagesGroup 6 Group Case Study DONEE.R.ONo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY: Pre Labor Infant With Respiratory Distress SyndromeDocument4 pagesCASE STUDY: Pre Labor Infant With Respiratory Distress SyndromeE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Bag Technique and Dressing Care WoundDocument3 pagesBag Technique and Dressing Care WoundE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Genes and Human Disease: Monogenic DiseasesDocument8 pagesGenes and Human Disease: Monogenic DiseasesE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Poemheal The WorldDocument1 pagePoemheal The WorldE.R.ONo ratings yet
- FINAL FNCP (CHN) ResearchDocument50 pagesFINAL FNCP (CHN) ResearchE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Salicylates: 1.1. Drug Classification DefinitionDocument6 pagesSalicylates: 1.1. Drug Classification DefinitionE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Roger Case Study and Nursing Process 2Document9 pagesRoger Case Study and Nursing Process 2E.R.ONo ratings yet
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Dorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryDocument3 pagesDorothea Elizabeth Orem: Self-Care TheoryE.R.ONo ratings yet
- Genes and Human Disease: Monogenic DiseasesDocument8 pagesGenes and Human Disease: Monogenic DiseasesE.R.ONo ratings yet
- MMH Gastro98Document7 pagesMMH Gastro98TanveerNo ratings yet
- Topical Immunomodulators in DermatologyDocument9 pagesTopical Immunomodulators in DermatologyRifky Budi TriyatnoNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEMISTRY 2nd SessionDocument116 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY 2nd SessionShane CoquillaNo ratings yet
- Hematology PPT 1Document287 pagesHematology PPT 1TarishiMalikNo ratings yet
- OlivierDocument481 pagesOlivierVetriSelvan Nagarajan0% (1)
- Microbiology Lab ManualDocument78 pagesMicrobiology Lab ManualDrMd IdrisNo ratings yet
- RGKSU 1st Proff 10 YearsDocument115 pagesRGKSU 1st Proff 10 YearsAranya BhandaryNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis and Management of Renal Failure and Replacement Therapy For Stage V Chronic Renal DiseaseDocument30 pagesPathogenesis and Management of Renal Failure and Replacement Therapy For Stage V Chronic Renal DiseaseByzantine Wulandari ParubakNo ratings yet
- 28.physical EducationDocument11 pages28.physical EducationVikram SinghNo ratings yet
- Relapse PreventionDocument1 pageRelapse PreventionAnonymous nYp4sSNo ratings yet
- Synthesis of Volume 1, 2 and 3Document399 pagesSynthesis of Volume 1, 2 and 3W Montague Cobb LabNo ratings yet
- Pneumonia (Overview Journal)Document12 pagesPneumonia (Overview Journal)Ayu Baitul MNo ratings yet
- Chemotherapy - Alkylating AgentsDocument33 pagesChemotherapy - Alkylating AgentsNolan100% (1)
- 4007 6537 1 PBDocument13 pages4007 6537 1 PBDian Gita RamadaniNo ratings yet
- Hematopoiesis (HEMA)Document12 pagesHematopoiesis (HEMA)April Lady Faith P. PaundogNo ratings yet
- Cardiotonics & Inotropic Drugs PDFDocument10 pagesCardiotonics & Inotropic Drugs PDFZehra AmirNo ratings yet
- NeuroQuantology Publication June 2022 Vol 20 Issue 6 AU Category B JournalDocument7 pagesNeuroQuantology Publication June 2022 Vol 20 Issue 6 AU Category B JournalNARESHNo ratings yet
- Grade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14Document26 pagesGrade 4 PPT - Science - Q2 - Lesson 14John Benedict CruzNo ratings yet
- The One Minute PreceptorDocument8 pagesThe One Minute PreceptorRannia ShehrishNo ratings yet
- Tes TLMDocument16 pagesTes TLMAmelia RosyidaNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Postural Control For Feeding. REVIEW PDFDocument5 pagesThe Importance of Postural Control For Feeding. REVIEW PDFViviana SalazarNo ratings yet
- Slide Microteaching MM Iqbal 2Document40 pagesSlide Microteaching MM Iqbal 2RAJA HARAHAPNo ratings yet
- The Breast: Kristoff Armand E. Tan Hannah Lois Kangleon-TanDocument30 pagesThe Breast: Kristoff Armand E. Tan Hannah Lois Kangleon-TanKenneth NuñezNo ratings yet
- Practical PhysiologyDocument436 pagesPractical Physiologyaastha212002100% (1)
- Care PlanDocument1 pageCare PlanFahim AhmedNo ratings yet
- YearDocument95 pagesYearBasil KuriakoseNo ratings yet