Professional Documents
Culture Documents
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 viewsClassification of Distribution Systems: Classification According To The Nature of The Current
Classification of Distribution Systems: Classification According To The Nature of The Current
Uploaded by
Sew KariyawasamThe document classifies distribution systems in three ways:
1. By the nature of current - AC distribution is more economical and simple than DC distribution.
2. By connection scheme - Radial, interconnected, and ring main systems are described.
3. By construction type - Underground and overhead systems are discussed, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You might also like
- Power Systems 1 Transmission Lines Hand Out Summer 2017Document13 pagesPower Systems 1 Transmission Lines Hand Out Summer 2017euler leoNo ratings yet
- Inductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive Circuits Inductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive CircuitsDocument51 pagesInductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive Circuits Inductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive CircuitsKareen Chua0% (1)
- Assignment #2 OnlineDocument6 pagesAssignment #2 OnlineSayed Nagy100% (1)
- Unsymmetrical FaultDocument32 pagesUnsymmetrical FaultPramod PathadeNo ratings yet
- Elmachi1 - Lecture18 - (Parallel Operation of Generators)Document16 pagesElmachi1 - Lecture18 - (Parallel Operation of Generators)Trisha SARMIENTO0% (1)
- EE Laws QuizDocument9 pagesEE Laws QuizJiever AustriaNo ratings yet
- e = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceDocument8 pagese = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceReniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- PS 1 - Unit 3 - PDFDocument20 pagesPS 1 - Unit 3 - PDFariel mentawanNo ratings yet
- College: Engineering Campus: Bambang: Instructional Module IM No.03: EE6-2S-2021-2022Document31 pagesCollege: Engineering Campus: Bambang: Instructional Module IM No.03: EE6-2S-2021-2022Andrea AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Induction Type Directional Over Current RelayDocument7 pagesInduction Type Directional Over Current Relayupendra3570% (10)
- DC Tutorial ProblemsDocument63 pagesDC Tutorial ProblemsKenneth Paul Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EPIRA (R.a 9136) - DOE - Department of Energy PortalDocument4 pagesEPIRA (R.a 9136) - DOE - Department of Energy PortalJc AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Example 8.27Document4 pagesExample 8.27Babasrinivas Guduru100% (1)
- Lec CH 17 Symmetric FaultsDocument16 pagesLec CH 17 Symmetric FaultsMajdi M. AbabnehNo ratings yet
- Guerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)Document22 pagesGuerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)John Nichol GuerraNo ratings yet
- EE ReviewerDocument13 pagesEE ReviewerZZROTNo ratings yet
- EE 435AL (6535) 3rd Exam, 2020-2021 - BERSABALDocument3 pagesEE 435AL (6535) 3rd Exam, 2020-2021 - BERSABALCegrow Ber BersabalNo ratings yet
- Circuits 3 Power Point NextDocument24 pagesCircuits 3 Power Point NextreyiNo ratings yet
- Reducing Ferranti Effect in Transmission Line Using Dynamic Voltage RestorerDocument6 pagesReducing Ferranti Effect in Transmission Line Using Dynamic Voltage RestorerDeptiranjan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Distribution - Lines-ConceptDocument17 pagesDistribution - Lines-ConceptAkd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDocument62 pagesZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanNo ratings yet
- CH3 Design Considerations of Primary Systems Mars 2020Document67 pagesCH3 Design Considerations of Primary Systems Mars 2020isra marabahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Symmetrical FaultsDocument46 pagesLecture 5 Symmetrical FaultsJoshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Circuits-2 Review B PDFDocument16 pagesCircuits-2 Review B PDFCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- CRKT 2 Module 1 Complex and AC CiruitDocument62 pagesCRKT 2 Module 1 Complex and AC CiruitArlie Laica BascoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines - Energy Regulatory CommissionDocument7 pagesRepublic of The Philippines - Energy Regulatory CommissionKhenan James NarismaNo ratings yet
- Darkness Sensor CircuitDocument11 pagesDarkness Sensor CircuitBAKTHA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument24 pagesInduction MotorsJaniel MalitNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1: Three Phase Alternator: Open-And Short-Circuit CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesACTIVITY 1: Three Phase Alternator: Open-And Short-Circuit CharacteristicsKYLE LEIGHZANDER VICENTENo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument5 pagesCalculusAdi SkskNo ratings yet
- EE Resonance Handout 02 PDFDocument11 pagesEE Resonance Handout 02 PDFSangay NorbuNo ratings yet
- Pass 1Document13 pagesPass 1Jeffsquille YagisgamNo ratings yet
- The Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Document3 pagesThe Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Tim Picar100% (1)
- TransformerDocument25 pagesTransformerJerald SagusayNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Group 3Document10 pagesLab 4 Group 3AYESHA FAHEEMNo ratings yet
- EE 59D - Power System Analysis - Module 1Document17 pagesEE 59D - Power System Analysis - Module 1Mikhael angelo LabradorNo ratings yet
- Electronics Module 2Document13 pagesElectronics Module 2tirsollantadaNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta For Residential Electricity PDFDocument92 pagesMagna Carta For Residential Electricity PDFEmmanuel S. CaliwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDenisse Torizo Olan100% (1)
- 05 Voltage Drop PDFDocument20 pages05 Voltage Drop PDFaxl graceNo ratings yet
- DELMO - EE 023 - DC Machine Design v3Document16 pagesDELMO - EE 023 - DC Machine Design v3Hok HokNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Circuits 2Document1 pageProblem Set Circuits 2Vien Ysabel JasaNo ratings yet
- Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument33 pagesMesh and Nodal AnalysisBenjamin Konaya Makoni100% (1)
- 1Document6 pages1LuthekLudelAlfaroNo ratings yet
- HVDC SlidesDocument25 pagesHVDC SlidesAreeb ZulkifleNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterLemuel C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Problems in Gibilisco 1Document10 pagesProblems in Gibilisco 1Jessica YangNo ratings yet
- EE153 Homework 1Document2 pagesEE153 Homework 1Ivan Jonah CarpioNo ratings yet
- Impact of Electricity Theft On Power QualityDocument6 pagesImpact of Electricity Theft On Power QualitySachin Jose100% (1)
- AC Machines Alternators 2Document10 pagesAC Machines Alternators 2Vanvan BitonNo ratings yet
- TX Line AssignmentDocument9 pagesTX Line AssignmentShubham SarkarNo ratings yet
- Problems On Polyphase SystemsDocument1 pageProblems On Polyphase SystemsJunnel NegadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisDocument21 pagesChapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisHidayah KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)Document4 pagesBasic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)DARANo ratings yet
- Medium Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesMedium Transmission LinesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Edited-Course Outline & Learning OutcomeDocument9 pagesEdited-Course Outline & Learning OutcomeMalik AnasNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Lecture Series: Part Vii. Unsymmetrical Faults (Open Case)Document26 pagesPower Systems Lecture Series: Part Vii. Unsymmetrical Faults (Open Case)Joshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Distribution System: Topic 3Document54 pagesDistribution System: Topic 3hashim_mokhtar9286No ratings yet
- CHAPTER5Document10 pagesCHAPTER5Mukesh ParewaNo ratings yet
- EE17 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesEE17 Lecture NotesRoselyn MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering - Internal Actions - Problem Set & AnswersDocument11 pagesStructural Engineering - Internal Actions - Problem Set & AnswersSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Name: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi Index Number: 120608P Telephone Number: 0712737472 Project Title: Automatic Table LampDocument2 pagesName: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi Index Number: 120608P Telephone Number: 0712737472 Project Title: Automatic Table LampSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument1 pageProject ProposalSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Automatic Table Lamp: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi 120608PDocument9 pagesAutomatic Table Lamp: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi 120608PSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Construction Operation and Basic Control of VR, PM and Hybrid Type Stepper MotorsDocument5 pagesConstruction Operation and Basic Control of VR, PM and Hybrid Type Stepper MotorsSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Borsafe ™ He3490-Ls-H: PolyethyleneDocument3 pagesBorsafe ™ He3490-Ls-H: Polyethylenedeep patelNo ratings yet
- Bell PDFDocument8 pagesBell PDFlibraryNo ratings yet
- Presentation On GSMNetworDocument19 pagesPresentation On GSMNetworMohamed AbubackerNo ratings yet
- Time Price Research Astrofin - Blogspot.in Sun MarketsDocument16 pagesTime Price Research Astrofin - Blogspot.in Sun MarketsArudra RaoNo ratings yet
- Lec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumDocument13 pagesLec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumpvriiscNo ratings yet
- A Survey Paper Based On Image Encryption and Decryption TechniqueDocument9 pagesA Survey Paper Based On Image Encryption and Decryption TechniqueIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Temenos UXP Widget Developers GuideDocument45 pagesTemenos UXP Widget Developers GuideEngr Ebuka Orioha100% (1)
- 401LV100Document2 pages401LV100Carlos Zevallos VeraNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Using Temperature - BasedDocument6 pagesNon-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Using Temperature - BasedAl InalNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Floor FunctionDocument4 pagesProperties of The Floor FunctionSladjan StankovikNo ratings yet
- D HondtDocument14 pagesD HondtsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- HSPE-144M M6 HC Monofacial 450-460W Rev.00Document2 pagesHSPE-144M M6 HC Monofacial 450-460W Rev.00Alejandro Holguin QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration of LTMDocument18 pagesFree Vibration of LTMSourabhYadavNo ratings yet
- Similarity Review For Test PDFDocument6 pagesSimilarity Review For Test PDFJovito BuscasNo ratings yet
- Diagramas de Pourbaix 2018Document72 pagesDiagramas de Pourbaix 2018Leo RodgersNo ratings yet
- Geko Ansys CFD PDFDocument38 pagesGeko Ansys CFD PDFJulio Andrés Casal RamosNo ratings yet
- İng Us CG ExamDocument383 pagesİng Us CG ExamMustafaNo ratings yet
- Revit-MEP-FIRE FIGHTINGDocument68 pagesRevit-MEP-FIRE FIGHTINGRagul0042No ratings yet
- Saponins: Saponins Are in Glycosidic Structure. Mostly of Plant Originated, Give Stable Foams in WaterDocument39 pagesSaponins: Saponins Are in Glycosidic Structure. Mostly of Plant Originated, Give Stable Foams in WaterJetro NonanNo ratings yet
- PlanetDocument23 pagesPlanetBijendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stoian Gradinariu GinaDocument8 pagesStoian Gradinariu Ginapro_fiz_apNo ratings yet
- Preschool Teachers' Self-Efficacy, Classroom Process Quality, and Children's Social SkillsDocument10 pagesPreschool Teachers' Self-Efficacy, Classroom Process Quality, and Children's Social SkillsJose LuisNo ratings yet
- Creative Design Process PDFDocument21 pagesCreative Design Process PDFdanielNo ratings yet
- Instructions - FPMC 25 - LANGSATDocument8 pagesInstructions - FPMC 25 - LANGSATZaid Al Aris Md ArisNo ratings yet
- Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer Converter (Single-Channel Type) : Instruction ManualDocument27 pagesZirconia Oxygen Analyzer Converter (Single-Channel Type) : Instruction ManualArvind NangareNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : Gas LawDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : Gas Lawlui yangyangNo ratings yet
- Architectural Support For HLLDocument18 pagesArchitectural Support For HLLसुधांशु जनवाड़कर50% (2)
- User Manual: Channel ExplorerDocument58 pagesUser Manual: Channel ExplorerTenNo ratings yet
- Benchmarksql - 2.3.2 Installation and User Guide: EnvironmentDocument13 pagesBenchmarksql - 2.3.2 Installation and User Guide: Environmentpatrick_wangruiNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report For ART 203Document39 pagesThesis Report For ART 203Masum BillahNo ratings yet
Classification of Distribution Systems: Classification According To The Nature of The Current
Classification of Distribution Systems: Classification According To The Nature of The Current
Uploaded by
Sew Kariyawasam0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 views7 pagesThe document classifies distribution systems in three ways:
1. By the nature of current - AC distribution is more economical and simple than DC distribution.
2. By connection scheme - Radial, interconnected, and ring main systems are described.
3. By construction type - Underground and overhead systems are discussed, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Original Description:
machines and drive
Original Title
New Assign
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document classifies distribution systems in three ways:
1. By the nature of current - AC distribution is more economical and simple than DC distribution.
2. By connection scheme - Radial, interconnected, and ring main systems are described.
3. By construction type - Underground and overhead systems are discussed, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
136 views7 pagesClassification of Distribution Systems: Classification According To The Nature of The Current
Classification of Distribution Systems: Classification According To The Nature of The Current
Uploaded by
Sew KariyawasamThe document classifies distribution systems in three ways:
1. By the nature of current - AC distribution is more economical and simple than DC distribution.
2. By connection scheme - Radial, interconnected, and ring main systems are described.
3. By construction type - Underground and overhead systems are discussed, along with their advantages and disadvantages.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Download as docx, pdf, or txt
You are on page 1of 7
Classification of Distribution Systems
1. Classification according to the nature of the current
AC distribution - More economical than dc distribution. And also
simple than dc distribution. Therefore AC distribution is famous
than DC distribution.
DC distribution – Not simple as AC distribution.
2. Classification according to the scheme of connection
Radial systems
Interconnected systems
Ring Main systems
3. Classification according to the Type of Construction
Underground systems
Overhead Systems
Details of the above three classifications are given below,
AC distribution
As given above AC current is very popular. AC voltages can be converted to the
appropriate magnitudes by using transformers. So by taking this as an
advantage we can reduce currents in the transmission lines by using high
transmission voltages therefore the losses can be minimized.
Examples:
(a) AC distributors fed at one end (b) Ring type Ac distributers
DC distribution
(a) DC Distributor Fed at one End, Concentrated Loading
In here the system feds
at one end and different
currents are taken
from the different
point of the distributor. So the supply current is equal to the sum of all
concentrated currents.
(b) Uniformly Loaded Distributor Fed at One end
In this distribution the system feds at one end as before. But not like
previous case at every unit length of the distributor same loads are taken
out.
(c) Concentrated load distributor fed at both ends.
In here the supply is
feds at both ends.
Otherwise this is same
as the case one given
above. Here also different loads are taken from different places along the
distributor.
(d) Uniformly Loaded Distributor Fed at Both Ends
This is also identical to case
two given above. But the only
difference is in here the
distributor feds at both ends.
In here also same loads are
taken out at every unit length of the distributor.
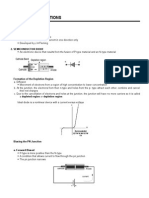
Radial systems
In radial systems separate feeders are radiate from a single substation.
And also the substation feeds the feeders at one end only. These radial
systems are employed only when the
power is generated at low voltage and
the substation is located at the centre
of the load.
The picture shows a diagram of a radial
distribution system.
Advantages of radial systems
Low initial cost.
Simple as it is fed only at one end.
More effective for the areas with lower population and lower load
requirement.
Low maintenance cost.
Preferred when the sub-station is located at the centre of the load.
More useful when the generation is at low voltage.
Disadvantages of radial systems
The feeding end of distributor gets heavily loaded.
As consumers are dependent on single feeder and distributor fault of any of
these two causes interruption in supply to all the consumers, who is at the
rest part of the distribution system.
According the demand of the subscriber’s, voltage at the distant end of the
distributor from the feeding end, subject to heavy fluctuation.
Ring systems
In this distribution
system we can see a loop. The
loop circuit begins with
substation bus bars and make
a loop through area which is
going to serve. These kind of
distribution systems can see
near to the urban or town
areas.
In this system the
distributor is tapped from
different places. The picture
shows the sketch of a ring system. There are some advantages and
disadvantages of this system.
Advantages
Voltage drop is less, along the distribution line.
Voltage fluctuation in high loaded areas of the distribution can be
minimized using a tie line.
Even though, there is a breakdown in one particular part of the ring
system, distribution can be done to all the customers without any
inconvenience.
Distribution can be provided through more subscribers than in a radial
distribution system.
Disadvantages
High initial cost for installation.
Comparatively complexity due to feeding at both ends.
Not much useful when the sub-station is located at the centre of the
load.
High maintenance cost.
According the demand of the subscriber’s, voltage at the distant end of
the distributor from the feeding end, subject to heavy fluctuation.
Interconnected Systems
Interconnected systems means when the systems which the feeders are
energized from two or more than substations. This is very suitable for urban
areas which has high power consumption.
These systems have few advantages than systems mentioned above.
In these type of systems reliability is high than other systems. Therefore
the service is much reliable than other systems
And also efficiency is high in this systems. Because an area fed from one
generating station during peak hours and other times can be fed from
other generating station.
. Underground Systems
A distribution system can be construct as an overhead system or
an underground system. In generally underground systems use cables,
conduits and manholes under the surface of sidewalks and streets. Several
factors are affected on selecting these systems. There are advantages and
disadvantages of these type of systems. Those things are given below.
Advantages
Underground systems are much safer than the overhead systems.
Underground systems are not exposed too much damage or bad
weather conditions.
Lifetimes of the underground systems are much higher than that of
overhead systems.
Underground systems have low interference with the communication
systems.
Under ground systems are cheaper.
Disadvantages
Difficulty in finding fault locations of underground systems.
Time taken to remedy the fault is much higher than that of overhead
systems.
Under ground systems are costly in setting up as having to use special
cables and weather proof equipment.
Underground systems cannot be used over long distance due to shunt
capacitance.
. Overhead Systems
In the overhead systems overhead lines are generally mount on
steel, concrete or wooden poles. In addition to the conductors these poles are
arraigned to carry distribution transformers. In Sri Lanka these systems are
very popular due to low cost and simplicity of these systems. There are many
advantages and disadvantage of this system also. So when choosing any
method among these two methods we have to consider about those factors.
Generally this method is not much popular in some western countries. This
systems are costly and complex.
The advantages and disadvantages of this system is given below.
Advantages
Low initial cost than the underground systems.
Much convenient in distributing to the houses than using underground
systems.
Low maintenance cost.
Can be used in long distance distribution due to the low shunt
capacitance.
Easy remedy in the case of faults.
Disadvantages
Not much safer like underground systems.
Have less life time compared to that of the underground cables.
Significant interference with the communication systems.
Overhead systems are exposed to damages and bad weather
conditions
You might also like
- Power Systems 1 Transmission Lines Hand Out Summer 2017Document13 pagesPower Systems 1 Transmission Lines Hand Out Summer 2017euler leoNo ratings yet
- Inductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive Circuits Inductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive CircuitsDocument51 pagesInductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive Circuits Inductance, Inductive Reactance, and Inductive CircuitsKareen Chua0% (1)
- Assignment #2 OnlineDocument6 pagesAssignment #2 OnlineSayed Nagy100% (1)
- Unsymmetrical FaultDocument32 pagesUnsymmetrical FaultPramod PathadeNo ratings yet
- Elmachi1 - Lecture18 - (Parallel Operation of Generators)Document16 pagesElmachi1 - Lecture18 - (Parallel Operation of Generators)Trisha SARMIENTO0% (1)
- EE Laws QuizDocument9 pagesEE Laws QuizJiever AustriaNo ratings yet
- e = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceDocument8 pagese = N (dΦ/dt) x 10: Generation of Alternating Electromotive ForceReniel MendozaNo ratings yet
- PS 1 - Unit 3 - PDFDocument20 pagesPS 1 - Unit 3 - PDFariel mentawanNo ratings yet
- College: Engineering Campus: Bambang: Instructional Module IM No.03: EE6-2S-2021-2022Document31 pagesCollege: Engineering Campus: Bambang: Instructional Module IM No.03: EE6-2S-2021-2022Andrea AlejandrinoNo ratings yet
- Induction Type Directional Over Current RelayDocument7 pagesInduction Type Directional Over Current Relayupendra3570% (10)
- DC Tutorial ProblemsDocument63 pagesDC Tutorial ProblemsKenneth Paul Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- EPIRA (R.a 9136) - DOE - Department of Energy PortalDocument4 pagesEPIRA (R.a 9136) - DOE - Department of Energy PortalJc AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Example 8.27Document4 pagesExample 8.27Babasrinivas Guduru100% (1)
- Lec CH 17 Symmetric FaultsDocument16 pagesLec CH 17 Symmetric FaultsMajdi M. AbabnehNo ratings yet
- Guerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)Document22 pagesGuerra, John Nichol N. Bsme 3C (Ac and DC Ass.2)John Nichol GuerraNo ratings yet
- EE ReviewerDocument13 pagesEE ReviewerZZROTNo ratings yet
- EE 435AL (6535) 3rd Exam, 2020-2021 - BERSABALDocument3 pagesEE 435AL (6535) 3rd Exam, 2020-2021 - BERSABALCegrow Ber BersabalNo ratings yet
- Circuits 3 Power Point NextDocument24 pagesCircuits 3 Power Point NextreyiNo ratings yet
- Reducing Ferranti Effect in Transmission Line Using Dynamic Voltage RestorerDocument6 pagesReducing Ferranti Effect in Transmission Line Using Dynamic Voltage RestorerDeptiranjan MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Distribution - Lines-ConceptDocument17 pagesDistribution - Lines-ConceptAkd DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- Zener Diode and Diode ApplicationDocument62 pagesZener Diode and Diode Applicationnibar dyllanNo ratings yet
- CH3 Design Considerations of Primary Systems Mars 2020Document67 pagesCH3 Design Considerations of Primary Systems Mars 2020isra marabahNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Symmetrical FaultsDocument46 pagesLecture 5 Symmetrical FaultsJoshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Circuits-2 Review B PDFDocument16 pagesCircuits-2 Review B PDFCristele Mae GarciaNo ratings yet
- CRKT 2 Module 1 Complex and AC CiruitDocument62 pagesCRKT 2 Module 1 Complex and AC CiruitArlie Laica BascoNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines - Energy Regulatory CommissionDocument7 pagesRepublic of The Philippines - Energy Regulatory CommissionKhenan James NarismaNo ratings yet
- Darkness Sensor CircuitDocument11 pagesDarkness Sensor CircuitBAKTHA SINGHNo ratings yet
- Induction MotorsDocument24 pagesInduction MotorsJaniel MalitNo ratings yet
- ACTIVITY 1: Three Phase Alternator: Open-And Short-Circuit CharacteristicsDocument17 pagesACTIVITY 1: Three Phase Alternator: Open-And Short-Circuit CharacteristicsKYLE LEIGHZANDER VICENTENo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument5 pagesCalculusAdi SkskNo ratings yet
- EE Resonance Handout 02 PDFDocument11 pagesEE Resonance Handout 02 PDFSangay NorbuNo ratings yet
- Pass 1Document13 pagesPass 1Jeffsquille YagisgamNo ratings yet
- The Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Document3 pagesThe Equations of The Currents in Two Parallel Connected Electric Devices Are I1Tim Picar100% (1)
- TransformerDocument25 pagesTransformerJerald SagusayNo ratings yet
- Lab 4 Group 3Document10 pagesLab 4 Group 3AYESHA FAHEEMNo ratings yet
- EE 59D - Power System Analysis - Module 1Document17 pagesEE 59D - Power System Analysis - Module 1Mikhael angelo LabradorNo ratings yet
- Electronics Module 2Document13 pagesElectronics Module 2tirsollantadaNo ratings yet
- Magna Carta For Residential Electricity PDFDocument92 pagesMagna Carta For Residential Electricity PDFEmmanuel S. CaliwanNo ratings yet
- Experiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDocument4 pagesExperiment V Current Control of An SCR I. ObjectiveDenisse Torizo Olan100% (1)
- 05 Voltage Drop PDFDocument20 pages05 Voltage Drop PDFaxl graceNo ratings yet
- DELMO - EE 023 - DC Machine Design v3Document16 pagesDELMO - EE 023 - DC Machine Design v3Hok HokNo ratings yet
- Problem Set Circuits 2Document1 pageProblem Set Circuits 2Vien Ysabel JasaNo ratings yet
- Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument33 pagesMesh and Nodal AnalysisBenjamin Konaya Makoni100% (1)
- 1Document6 pages1LuthekLudelAlfaroNo ratings yet
- HVDC SlidesDocument25 pagesHVDC SlidesAreeb ZulkifleNo ratings yet
- Advantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Bridge Rectifier Circuit Over CenterLemuel C. FernandezNo ratings yet
- Problems in Gibilisco 1Document10 pagesProblems in Gibilisco 1Jessica YangNo ratings yet
- EE153 Homework 1Document2 pagesEE153 Homework 1Ivan Jonah CarpioNo ratings yet
- Impact of Electricity Theft On Power QualityDocument6 pagesImpact of Electricity Theft On Power QualitySachin Jose100% (1)
- AC Machines Alternators 2Document10 pagesAC Machines Alternators 2Vanvan BitonNo ratings yet
- TX Line AssignmentDocument9 pagesTX Line AssignmentShubham SarkarNo ratings yet
- Problems On Polyphase SystemsDocument1 pageProblems On Polyphase SystemsJunnel NegadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisDocument21 pagesChapter 03 - Mesh AnalysisHidayah KamaludinNo ratings yet
- Basic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)Document4 pagesBasic Principles of Signal Reproduction: Skirts Are The Sides of A Tuned Circuit Response Curve (See Figure 4.0)DARANo ratings yet
- Medium Transmission LinesDocument8 pagesMedium Transmission LinesJPR EEENo ratings yet
- Edited-Course Outline & Learning OutcomeDocument9 pagesEdited-Course Outline & Learning OutcomeMalik AnasNo ratings yet
- Power Systems Lecture Series: Part Vii. Unsymmetrical Faults (Open Case)Document26 pagesPower Systems Lecture Series: Part Vii. Unsymmetrical Faults (Open Case)Joshua Roberto GrutaNo ratings yet
- Distribution System: Topic 3Document54 pagesDistribution System: Topic 3hashim_mokhtar9286No ratings yet
- CHAPTER5Document10 pagesCHAPTER5Mukesh ParewaNo ratings yet
- EE17 Lecture NotesDocument10 pagesEE17 Lecture NotesRoselyn MatienzoNo ratings yet
- Structural Engineering - Internal Actions - Problem Set & AnswersDocument11 pagesStructural Engineering - Internal Actions - Problem Set & AnswersSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Name: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi Index Number: 120608P Telephone Number: 0712737472 Project Title: Automatic Table LampDocument2 pagesName: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi Index Number: 120608P Telephone Number: 0712737472 Project Title: Automatic Table LampSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument1 pageProject ProposalSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Automatic Table Lamp: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi 120608PDocument9 pagesAutomatic Table Lamp: K.M.G.Y. Sewwandi 120608PSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Construction Operation and Basic Control of VR, PM and Hybrid Type Stepper MotorsDocument5 pagesConstruction Operation and Basic Control of VR, PM and Hybrid Type Stepper MotorsSew KariyawasamNo ratings yet
- Borsafe ™ He3490-Ls-H: PolyethyleneDocument3 pagesBorsafe ™ He3490-Ls-H: Polyethylenedeep patelNo ratings yet
- Bell PDFDocument8 pagesBell PDFlibraryNo ratings yet
- Presentation On GSMNetworDocument19 pagesPresentation On GSMNetworMohamed AbubackerNo ratings yet
- Time Price Research Astrofin - Blogspot.in Sun MarketsDocument16 pagesTime Price Research Astrofin - Blogspot.in Sun MarketsArudra RaoNo ratings yet
- Lec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumDocument13 pagesLec14-Cross Product, Torque, and Angular MomentumpvriiscNo ratings yet
- A Survey Paper Based On Image Encryption and Decryption TechniqueDocument9 pagesA Survey Paper Based On Image Encryption and Decryption TechniqueIJRASETPublicationsNo ratings yet
- Temenos UXP Widget Developers GuideDocument45 pagesTemenos UXP Widget Developers GuideEngr Ebuka Orioha100% (1)
- 401LV100Document2 pages401LV100Carlos Zevallos VeraNo ratings yet
- Non-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Using Temperature - BasedDocument6 pagesNon-Invasive Blood Glucose Measurement Using Temperature - BasedAl InalNo ratings yet
- Properties of The Floor FunctionDocument4 pagesProperties of The Floor FunctionSladjan StankovikNo ratings yet
- D HondtDocument14 pagesD HondtsakuraleeshaoranNo ratings yet
- HSPE-144M M6 HC Monofacial 450-460W Rev.00Document2 pagesHSPE-144M M6 HC Monofacial 450-460W Rev.00Alejandro Holguin QuinteroNo ratings yet
- Free Vibration of LTMDocument18 pagesFree Vibration of LTMSourabhYadavNo ratings yet
- Similarity Review For Test PDFDocument6 pagesSimilarity Review For Test PDFJovito BuscasNo ratings yet
- Diagramas de Pourbaix 2018Document72 pagesDiagramas de Pourbaix 2018Leo RodgersNo ratings yet
- Geko Ansys CFD PDFDocument38 pagesGeko Ansys CFD PDFJulio Andrés Casal RamosNo ratings yet
- İng Us CG ExamDocument383 pagesİng Us CG ExamMustafaNo ratings yet
- Revit-MEP-FIRE FIGHTINGDocument68 pagesRevit-MEP-FIRE FIGHTINGRagul0042No ratings yet
- Saponins: Saponins Are in Glycosidic Structure. Mostly of Plant Originated, Give Stable Foams in WaterDocument39 pagesSaponins: Saponins Are in Glycosidic Structure. Mostly of Plant Originated, Give Stable Foams in WaterJetro NonanNo ratings yet
- PlanetDocument23 pagesPlanetBijendra SharmaNo ratings yet
- Stoian Gradinariu GinaDocument8 pagesStoian Gradinariu Ginapro_fiz_apNo ratings yet
- Preschool Teachers' Self-Efficacy, Classroom Process Quality, and Children's Social SkillsDocument10 pagesPreschool Teachers' Self-Efficacy, Classroom Process Quality, and Children's Social SkillsJose LuisNo ratings yet
- Creative Design Process PDFDocument21 pagesCreative Design Process PDFdanielNo ratings yet
- Instructions - FPMC 25 - LANGSATDocument8 pagesInstructions - FPMC 25 - LANGSATZaid Al Aris Md ArisNo ratings yet
- Zirconia Oxygen Analyzer Converter (Single-Channel Type) : Instruction ManualDocument27 pagesZirconia Oxygen Analyzer Converter (Single-Channel Type) : Instruction ManualArvind NangareNo ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : Gas LawDocument5 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1 (Grade 11-STEM) : Gas Lawlui yangyangNo ratings yet
- Architectural Support For HLLDocument18 pagesArchitectural Support For HLLसुधांशु जनवाड़कर50% (2)
- User Manual: Channel ExplorerDocument58 pagesUser Manual: Channel ExplorerTenNo ratings yet
- Benchmarksql - 2.3.2 Installation and User Guide: EnvironmentDocument13 pagesBenchmarksql - 2.3.2 Installation and User Guide: Environmentpatrick_wangruiNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report For ART 203Document39 pagesThesis Report For ART 203Masum BillahNo ratings yet