Professional Documents
Culture Documents
cs394r Quiz Handout
cs394r Quiz Handout
Uploaded by
MikeCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Queuing Theory PDFDocument38 pagesQueuing Theory PDFNelson FicaNo ratings yet
- Hw2sol PDFDocument15 pagesHw2sol PDFPei JingNo ratings yet
- Steger Warming Flux Vector Splitting MethodDocument31 pagesSteger Warming Flux Vector Splitting Methodsanal_iitb100% (1)
- Keystone Formula Sheet-Algebra IDocument1 pageKeystone Formula Sheet-Algebra Iapi-234929154No ratings yet
- Write Your Solutions To Different Questions Beside Each OtherDocument6 pagesWrite Your Solutions To Different Questions Beside Each OtherHANSNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document5 pagesHW 4api-3716660No ratings yet
- Statisticsyear 1 DistributionsDocument3 pagesStatisticsyear 1 Distributionsapi-394057706No ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - Due October 18Document1 pageAssignment 4 - Due October 18Harsh Vardhan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Stat6201 ch3-1Document4 pagesStat6201 ch3-1BowenYangNo ratings yet
- Task2 22 23Document4 pagesTask2 22 23Pablo Martínez BordiuNo ratings yet
- The Convergence Acceleration of Two-Dimensional Fourier InterpolationDocument14 pagesThe Convergence Acceleration of Two-Dimensional Fourier InterpolationKate MossNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionDocument5 pagesRevision QuestionKeJeNo ratings yet
- امتحانات المعاصر - جبر لغات - 3 ع - ترم 2 - ذاكروليDocument177 pagesامتحانات المعاصر - جبر لغات - 3 ع - ترم 2 - ذاكروليmarcossimonammarNo ratings yet
- Higher Ordered DerivativesDocument7 pagesHigher Ordered DerivativesSukhdev satyamNo ratings yet
- Paper 69Document5 pagesPaper 69KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Problems: 0 0 N N I IDocument8 pagesPolynomial Problems: 0 0 N N I IAryan AbrolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Single Variable Functions: Lecturer: Do Trong HoangDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Single Variable Functions: Lecturer: Do Trong HoangNguyễn Sơn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document2 pagesHomework 2Laura MerchánNo ratings yet
- The Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5 c.ROC:0.5 - Z - 1Document2 pagesThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5 c.ROC:0.5 - Z - 1Engr Imran FirdosNo ratings yet
- Homework 10 - SolutionDocument8 pagesHomework 10 - SolutionAlaa SaadNo ratings yet
- S Election Internationale 2010 Scientific Test: MathematicsDocument3 pagesS Election Internationale 2010 Scientific Test: MathematicsKlevis KasoNo ratings yet
- University of NairobiDocument3 pagesUniversity of NairobiMary OgutaNo ratings yet
- 01 Function 1Document2 pages01 Function 1Kshitiz PandyaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Applied Mathematics-II: M L+M L M L M M L M M LDocument2 pagesMethods of Applied Mathematics-II: M L+M L M L M M L M M LJatin RamboNo ratings yet
- Second Exam Sheet: Taylor Polynomial ApproximationDocument2 pagesSecond Exam Sheet: Taylor Polynomial ApproximationSameer HmedatNo ratings yet
- HT2022 Inl 4Document2 pagesHT2022 Inl 4Jitender AhujaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exp and LogsDocument7 pagesPractice Exp and LogsTariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Jinx Katana MA-214-HW2Document3 pagesJinx Katana MA-214-HW2Sarah WiseNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivative Sheet Part (B)Document14 pagesApplication of Derivative Sheet Part (B)Premesh the greatNo ratings yet
- Ap P A P: N I I N I N I N IDocument38 pagesAp P A P: N I I N I N I N ItusharNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis: (MA214) : Instructor: Prof. Tony J. PuthenpurakalDocument29 pagesNumerical Analysis: (MA214) : Instructor: Prof. Tony J. PuthenpurakalRitwik KaduNo ratings yet
- Espacios de Frechet PDFDocument19 pagesEspacios de Frechet PDFelihu anastacioNo ratings yet
- Harare Institute of Technology: Bachelor of Technology Faculty of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyDocument2 pagesHarare Institute of Technology: Bachelor of Technology Faculty of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyDavid NyamasimeNo ratings yet
- q1 SolnDocument4 pagesq1 SolnRajveer SandeepNo ratings yet
- Alternating Subsets Modulo: (1, 2, - . - , N) According To Parity Statistics Defined On Pairs of M 1. in Particular, WeDocument13 pagesAlternating Subsets Modulo: (1, 2, - . - , N) According To Parity Statistics Defined On Pairs of M 1. in Particular, We17. Nguyễn Gia BảoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Model Paper 03 Part B With Pass CodeDocument8 pages2021 Model Paper 03 Part B With Pass Codekjh yuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 TestDocument8 pagesChapter 5 TestkouriyoNo ratings yet
- Assignment I: (To Be Submitted in Tutorial Class by September 13, 2019)Document2 pagesAssignment I: (To Be Submitted in Tutorial Class by September 13, 2019)AnantaRajNo ratings yet
- Ass2019 Maths1 Single Variable PDFDocument2 pagesAss2019 Maths1 Single Variable PDFAnantaRajNo ratings yet
- 1011sem1 Ma2213Document4 pages1011sem1 Ma2213jlee970125No ratings yet
- A Constructive Method For Uniform Approximation On Two Dimensional IntervalDocument7 pagesA Constructive Method For Uniform Approximation On Two Dimensional IntervalSebestyén ZoltánNo ratings yet
- 1 Polynomial Approximation and Interpolation: 1.1 Jackson TheoremsDocument11 pages1 Polynomial Approximation and Interpolation: 1.1 Jackson TheoremsAurangZaib LaghariNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Approximation Theorems: Kunal Narayan ChaudhuryDocument4 pagesFundamental Approximation Theorems: Kunal Narayan Chaudhuryabd 01No ratings yet
- Tutorial1 SolnDocument3 pagesTutorial1 SolnLow Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- 2009 Continuous Random VariableDocument4 pages2009 Continuous Random Variablefabremil7472100% (2)
- Formula Sheet STAT1301Document3 pagesFormula Sheet STAT1301janeNo ratings yet
- The Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5Document1 pageThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5Engr Imran FirdosNo ratings yet
- E2 202 (Aug-Dec 2015) : Homework Assignment 3Document1 pageE2 202 (Aug-Dec 2015) : Homework Assignment 3Saptarshi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFalokNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFalokNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONSDocument5 pagesFUNCTIONS41 Rahul Anil AmrutsagarNo ratings yet
- BStat BMath UGB 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesBStat BMath UGB 2017 PDFarvind lakshmi ranjanNo ratings yet
- Bstat Bmath Ugb 2017Document2 pagesBstat Bmath Ugb 2017Manish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 22 May 2023Document17 pagesAdobe Scan 22 May 2023Youtube PremiumNo ratings yet
- Function Exercise-4 (Q)Document1 pageFunction Exercise-4 (Q)Aryan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PIB - Numerical Analysis I - Iserles (2010) 41pgDocument41 pagesPIB - Numerical Analysis I - Iserles (2010) 41pgfdsdsfsdfmgNo ratings yet
- 17-Soham APolynomialLemma FinalDocument3 pages17-Soham APolynomialLemma FinalUniversität BielefeldNo ratings yet
- Indian Association For The Cultivation of Science: Mathematical Physics PH-4103Document2 pagesIndian Association For The Cultivation of Science: Mathematical Physics PH-4103MANISH SINGHNo ratings yet
- NCM 2nd Ce 4a04b eDocument8 pagesNCM 2nd Ce 4a04b eapi-517118868No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)From EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)No ratings yet
- CS 394R, HW3ANS (Conditional Probability and Probability Mass Functions) 80 PtsDocument4 pagesCS 394R, HW3ANS (Conditional Probability and Probability Mass Functions) 80 PtsMikeNo ratings yet
- CS 394R, Worksheet1c (Counting # 2) NameDocument3 pagesCS 394R, Worksheet1c (Counting # 2) NameMikeNo ratings yet
- 1974 - Time-Domain Scattering From A Nonlinearly Loaded WireDocument3 pages1974 - Time-Domain Scattering From A Nonlinearly Loaded WireMikeNo ratings yet
- cs394r Hw2a Fs 18Document3 pagescs394r Hw2a Fs 18MikeNo ratings yet
- Soc Verif Udemy Lec 6 Directed CoverageDocument8 pagesSoc Verif Udemy Lec 6 Directed CoverageMikeNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification (Revised)Document2 pagesTable of Specification (Revised)karissa joyce eslaoNo ratings yet
- 04 - Tangent LinesDocument2 pages04 - Tangent LinesCss PursuerNo ratings yet
- 001 - Polar Form Multiplication and DivisionDocument13 pages001 - Polar Form Multiplication and DivisionKeri-ann MillarNo ratings yet
- Intro Examples Manual DRAFT PDFDocument229 pagesIntro Examples Manual DRAFT PDFEren KalayNo ratings yet
- JavaprogramsDocument3 pagesJavaprogramsVishal BhargavaNo ratings yet
- CHOO, Yan Min - H2 Mathematics PDFDocument1,384 pagesCHOO, Yan Min - H2 Mathematics PDFRaymond ChinNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 9Document12 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 9Zion Conrad FuentesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 TrigonometryDocument3 pagesWorksheet-1 Trigonometrysudhir singhNo ratings yet
- MR Lai Add Maths NotesDocument10 pagesMR Lai Add Maths Notesteng fsNo ratings yet
- MatLab Control System Toolbox ManualDocument64 pagesMatLab Control System Toolbox Manualluisgama22No ratings yet
- Erf TablesDocument2 pagesErf TablesaniNo ratings yet
- CFC - List - of - ElementsDocument188 pagesCFC - List - of - Elementsjhon omar100% (1)
- Maths Class 9TH Science 2023 1Document8 pagesMaths Class 9TH Science 2023 1SYED salman saeedNo ratings yet
- Expressions Dari QGIS USER DOCUMENTDocument9 pagesExpressions Dari QGIS USER DOCUMENTmona sihombingNo ratings yet
- AutMO03 PDFDocument2 pagesAutMO03 PDFAlfredo SarachoNo ratings yet
- Exercise WS11.1: Geoff Renshaw, 2016 All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesExercise WS11.1: Geoff Renshaw, 2016 All Rights ReservedmakedonisNo ratings yet
- X y X y X X N N X N: H2 FM 9649/2016 RI Year 5 Term 3 Common TestDocument4 pagesX y X y X X N N X N: H2 FM 9649/2016 RI Year 5 Term 3 Common TestYao Le Titanium ChenNo ratings yet
- Newman-Penrose FormalismDocument7 pagesNewman-Penrose FormalismAnonymous kg7YBMFHNo ratings yet
- Cal 2 70midterm Exam - Attempt ReviewDocument24 pagesCal 2 70midterm Exam - Attempt ReviewLor fighterNo ratings yet
- CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix ApproximationsDocument11 pagesCS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix ApproximationsOnkar PanditNo ratings yet
- MIT5 74s09 Lec01Document14 pagesMIT5 74s09 Lec01Sanjip Kumar SapkotaNo ratings yet
- 07 3DElasticity CompleteDocument45 pages07 3DElasticity CompleteSüleyman TüreNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction of Four-Dimensional Rotations Part I. Case of Four-Dimensional Euclidean SpaceDocument12 pagesGeometric Construction of Four-Dimensional Rotations Part I. Case of Four-Dimensional Euclidean SpaceShinya MinatoNo ratings yet
- Slides 4 (Routh, Root Locus)Document51 pagesSlides 4 (Routh, Root Locus)Felistus KavuuNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Analysis User's Manual (6 PDFDocument1 pageAbaqus Analysis User's Manual (6 PDFNguyen Ba DungNo ratings yet
- Deep Neural Network Approximation TheoryDocument80 pagesDeep Neural Network Approximation TheorynothardNo ratings yet
- On The Convergence of Bayesian Adaptive Filtering: Tayeb Sadiki, Dirk T.M. SlockDocument4 pagesOn The Convergence of Bayesian Adaptive Filtering: Tayeb Sadiki, Dirk T.M. SlockIulianNo ratings yet
- Classical and Multilinear Harmonic Analysis IIDocument342 pagesClassical and Multilinear Harmonic Analysis IIDavid PattyNo ratings yet
cs394r Quiz Handout
cs394r Quiz Handout
Uploaded by
MikeOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
cs394r Quiz Handout
cs394r Quiz Handout
Uploaded by
MikeCopyright:
Available Formats
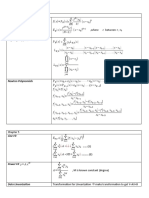
CS394r: Exam handout
Some common RVs
1. Discrete Uniform Random Variable
(a) Sample space {k = a, a + 1, . . . , b}
{
1
b−a+1 k = a, a + 1, . . . , b
(b) PMF pX (k) =
0 otherwise
a+b (b−a)(b−a+2)
(c) E[X] = 2 , VAR(X) = 12
esa (es(b−a+1) −1)
(d) MX (s) = (b−a+1)(es −1)
2. Bernoulli Random Variable
(a) Sample space {k = 0, 1}
{
1−p k =0
(b) PMF pX (k) =
p k=1
(c) E[X] = p, VAR(X) = p(1 − p)
(d) MX (s) = 1 − p + pes
3. Binomial Random Variable
(a) Sample space {0, 1, . . . n}
(n)
(b) PMF pk = k pk (1 − p)n−k , k = 0, 1, . . . , n
(c) E[X] = np, VAR(X) = np(1 − p)
(d) MX (s) = (1 − p + pes )n
4. Geometric Random Variable
(a) Version 1
i. Sample space [1, . . .]
ii. PMF pX (k) = p(1 − p)k−1 , k = 1, 2, . . .
(1−p)
iii. E[X] = p1 , VAR(X) = p2
pe s
iv. MX (s) = 1−(1−p)e s
v. X is the number of trials until the first success in a sequence of independent Bernoulli
trials.
(b) Version 2
i. Sample space [0, . . .]
ii. PMF pX (k) = p(1 − p)k , k = 0, 1, . . .
1−p (1−p)
iii. E[X] = p , VAR(X) = p2
p
iv. MX (s) = 1−(1−p)e s
v. X is the number of failures before the first success in a sequence of independent
Bernoulli trials.
5. Poisson Random Variable
(a) Sample space [k = 0, 1, . . .]
αk −α
(b) PMF k! e ,k = 0, 1, . . . α>0
(c) E[X] = α, VAR(X) = α
s −1)
(d) MX (s) = eα(e
6. Uniform Random Variable
(a) Sample space [a, b]
1
(b) PDF fX (x) = b−a
a+b (b−a)2
(c) E[X] = 2 , VAR(X) = 12
sb −esa
(d) MX (s) = es(b−a)
7. Exponential Random Variable
(a) Sample space [0, ∞)
(b) CDF FX (x) = 1 − e−λx x ≥ 0, λ > 0
(c) PDF fX (x) = λe−λx x ≥ 0, λ > 0
1 1
(d) E[X] = λ, VAR(X) = λ2
λ
(e) MX (s) = λ−s , s<λ
Statistics
−nµ
Sn √
1. Zn = σ n
√
ϵ n
2. Z = σ
3. 95% confidence level is Z = 1.96
Counting
1. Permutation
n!
k-Permutations P (n, k) = (n−k)!
2. Combination
n!
k-Combinations C(n, k) = (n−k)!k!
3. Occupation (how many ways to choose a total of n items of m different types.) k-Occupation
(by partitioning) = C(n + k − 1, k − 1)
4. Conditional Probability
P [A|B] = P P[A∩B]
[B]
P [B|Ai ]P [Ai ]
5. Bayes’ Theorem P [Ai |B] = P [B|A1 ]P [A1 ]+...+P [B|An ]P [An ]
You might also like
- Queuing Theory PDFDocument38 pagesQueuing Theory PDFNelson FicaNo ratings yet
- Hw2sol PDFDocument15 pagesHw2sol PDFPei JingNo ratings yet
- Steger Warming Flux Vector Splitting MethodDocument31 pagesSteger Warming Flux Vector Splitting Methodsanal_iitb100% (1)
- Keystone Formula Sheet-Algebra IDocument1 pageKeystone Formula Sheet-Algebra Iapi-234929154No ratings yet
- Write Your Solutions To Different Questions Beside Each OtherDocument6 pagesWrite Your Solutions To Different Questions Beside Each OtherHANSNo ratings yet
- HW 4Document5 pagesHW 4api-3716660No ratings yet
- Statisticsyear 1 DistributionsDocument3 pagesStatisticsyear 1 Distributionsapi-394057706No ratings yet
- Assignment 4 - Due October 18Document1 pageAssignment 4 - Due October 18Harsh Vardhan DubeyNo ratings yet
- Stat6201 ch3-1Document4 pagesStat6201 ch3-1BowenYangNo ratings yet
- Task2 22 23Document4 pagesTask2 22 23Pablo Martínez BordiuNo ratings yet
- The Convergence Acceleration of Two-Dimensional Fourier InterpolationDocument14 pagesThe Convergence Acceleration of Two-Dimensional Fourier InterpolationKate MossNo ratings yet
- Revision QuestionDocument5 pagesRevision QuestionKeJeNo ratings yet
- امتحانات المعاصر - جبر لغات - 3 ع - ترم 2 - ذاكروليDocument177 pagesامتحانات المعاصر - جبر لغات - 3 ع - ترم 2 - ذاكروليmarcossimonammarNo ratings yet
- Higher Ordered DerivativesDocument7 pagesHigher Ordered DerivativesSukhdev satyamNo ratings yet
- Paper 69Document5 pagesPaper 69KaustubhNo ratings yet
- Polynomial Problems: 0 0 N N I IDocument8 pagesPolynomial Problems: 0 0 N N I IAryan AbrolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1: Single Variable Functions: Lecturer: Do Trong HoangDocument3 pagesChapter 1: Single Variable Functions: Lecturer: Do Trong HoangNguyễn Sơn ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Homework 2Document2 pagesHomework 2Laura MerchánNo ratings yet
- The Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5 c.ROC:0.5 - Z - 1Document2 pagesThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5 c.ROC:0.5 - Z - 1Engr Imran FirdosNo ratings yet
- Homework 10 - SolutionDocument8 pagesHomework 10 - SolutionAlaa SaadNo ratings yet
- S Election Internationale 2010 Scientific Test: MathematicsDocument3 pagesS Election Internationale 2010 Scientific Test: MathematicsKlevis KasoNo ratings yet
- University of NairobiDocument3 pagesUniversity of NairobiMary OgutaNo ratings yet
- 01 Function 1Document2 pages01 Function 1Kshitiz PandyaNo ratings yet
- Methods of Applied Mathematics-II: M L+M L M L M M L M M LDocument2 pagesMethods of Applied Mathematics-II: M L+M L M L M M L M M LJatin RamboNo ratings yet
- Second Exam Sheet: Taylor Polynomial ApproximationDocument2 pagesSecond Exam Sheet: Taylor Polynomial ApproximationSameer HmedatNo ratings yet
- HT2022 Inl 4Document2 pagesHT2022 Inl 4Jitender AhujaNo ratings yet
- Practice Exp and LogsDocument7 pagesPractice Exp and LogsTariq MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Jinx Katana MA-214-HW2Document3 pagesJinx Katana MA-214-HW2Sarah WiseNo ratings yet
- Application of Derivative Sheet Part (B)Document14 pagesApplication of Derivative Sheet Part (B)Premesh the greatNo ratings yet
- Ap P A P: N I I N I N I N IDocument38 pagesAp P A P: N I I N I N I N ItusharNo ratings yet
- Numerical Analysis: (MA214) : Instructor: Prof. Tony J. PuthenpurakalDocument29 pagesNumerical Analysis: (MA214) : Instructor: Prof. Tony J. PuthenpurakalRitwik KaduNo ratings yet
- Espacios de Frechet PDFDocument19 pagesEspacios de Frechet PDFelihu anastacioNo ratings yet
- Harare Institute of Technology: Bachelor of Technology Faculty of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyDocument2 pagesHarare Institute of Technology: Bachelor of Technology Faculty of Engineering Sciences and TechnologyDavid NyamasimeNo ratings yet
- q1 SolnDocument4 pagesq1 SolnRajveer SandeepNo ratings yet
- Alternating Subsets Modulo: (1, 2, - . - , N) According To Parity Statistics Defined On Pairs of M 1. in Particular, WeDocument13 pagesAlternating Subsets Modulo: (1, 2, - . - , N) According To Parity Statistics Defined On Pairs of M 1. in Particular, We17. Nguyễn Gia BảoNo ratings yet
- 2021 Model Paper 03 Part B With Pass CodeDocument8 pages2021 Model Paper 03 Part B With Pass Codekjh yuiNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 TestDocument8 pagesChapter 5 TestkouriyoNo ratings yet
- Assignment I: (To Be Submitted in Tutorial Class by September 13, 2019)Document2 pagesAssignment I: (To Be Submitted in Tutorial Class by September 13, 2019)AnantaRajNo ratings yet
- Ass2019 Maths1 Single Variable PDFDocument2 pagesAss2019 Maths1 Single Variable PDFAnantaRajNo ratings yet
- 1011sem1 Ma2213Document4 pages1011sem1 Ma2213jlee970125No ratings yet
- A Constructive Method For Uniform Approximation On Two Dimensional IntervalDocument7 pagesA Constructive Method For Uniform Approximation On Two Dimensional IntervalSebestyén ZoltánNo ratings yet
- 1 Polynomial Approximation and Interpolation: 1.1 Jackson TheoremsDocument11 pages1 Polynomial Approximation and Interpolation: 1.1 Jackson TheoremsAurangZaib LaghariNo ratings yet
- Fundamental Approximation Theorems: Kunal Narayan ChaudhuryDocument4 pagesFundamental Approximation Theorems: Kunal Narayan Chaudhuryabd 01No ratings yet
- Tutorial1 SolnDocument3 pagesTutorial1 SolnLow Jia HuiNo ratings yet
- 2009 Continuous Random VariableDocument4 pages2009 Continuous Random Variablefabremil7472100% (2)
- Formula Sheet STAT1301Document3 pagesFormula Sheet STAT1301janeNo ratings yet
- The Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5Document1 pageThe Islamia University of Bahawalpur: a.ROC: - Z - 1 b.ROC: - Z - 0.5Engr Imran FirdosNo ratings yet
- E2 202 (Aug-Dec 2015) : Homework Assignment 3Document1 pageE2 202 (Aug-Dec 2015) : Homework Assignment 3Saptarshi ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFalokNo ratings yet
- 1 PDFDocument2 pages1 PDFalokNo ratings yet
- FUNCTIONSDocument5 pagesFUNCTIONS41 Rahul Anil AmrutsagarNo ratings yet
- BStat BMath UGB 2017 PDFDocument2 pagesBStat BMath UGB 2017 PDFarvind lakshmi ranjanNo ratings yet
- Bstat Bmath Ugb 2017Document2 pagesBstat Bmath Ugb 2017Manish ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Adobe Scan 22 May 2023Document17 pagesAdobe Scan 22 May 2023Youtube PremiumNo ratings yet
- Function Exercise-4 (Q)Document1 pageFunction Exercise-4 (Q)Aryan SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- PIB - Numerical Analysis I - Iserles (2010) 41pgDocument41 pagesPIB - Numerical Analysis I - Iserles (2010) 41pgfdsdsfsdfmgNo ratings yet
- 17-Soham APolynomialLemma FinalDocument3 pages17-Soham APolynomialLemma FinalUniversität BielefeldNo ratings yet
- Indian Association For The Cultivation of Science: Mathematical Physics PH-4103Document2 pagesIndian Association For The Cultivation of Science: Mathematical Physics PH-4103MANISH SINGHNo ratings yet
- NCM 2nd Ce 4a04b eDocument8 pagesNCM 2nd Ce 4a04b eapi-517118868No ratings yet
- Analytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageFrom EverandAnalytic Geometry: Graphic Solutions Using Matlab LanguageNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Cohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)From EverandCohomology Operations (AM-50), Volume 50: Lectures by N. E. Steenrod. (AM-50)No ratings yet
- CS 394R, HW3ANS (Conditional Probability and Probability Mass Functions) 80 PtsDocument4 pagesCS 394R, HW3ANS (Conditional Probability and Probability Mass Functions) 80 PtsMikeNo ratings yet
- CS 394R, Worksheet1c (Counting # 2) NameDocument3 pagesCS 394R, Worksheet1c (Counting # 2) NameMikeNo ratings yet
- 1974 - Time-Domain Scattering From A Nonlinearly Loaded WireDocument3 pages1974 - Time-Domain Scattering From A Nonlinearly Loaded WireMikeNo ratings yet
- cs394r Hw2a Fs 18Document3 pagescs394r Hw2a Fs 18MikeNo ratings yet
- Soc Verif Udemy Lec 6 Directed CoverageDocument8 pagesSoc Verif Udemy Lec 6 Directed CoverageMikeNo ratings yet
- Table of Specification (Revised)Document2 pagesTable of Specification (Revised)karissa joyce eslaoNo ratings yet
- 04 - Tangent LinesDocument2 pages04 - Tangent LinesCss PursuerNo ratings yet
- 001 - Polar Form Multiplication and DivisionDocument13 pages001 - Polar Form Multiplication and DivisionKeri-ann MillarNo ratings yet
- Intro Examples Manual DRAFT PDFDocument229 pagesIntro Examples Manual DRAFT PDFEren KalayNo ratings yet
- JavaprogramsDocument3 pagesJavaprogramsVishal BhargavaNo ratings yet
- CHOO, Yan Min - H2 Mathematics PDFDocument1,384 pagesCHOO, Yan Min - H2 Mathematics PDFRaymond ChinNo ratings yet
- Math 9 Q1 Week 9Document12 pagesMath 9 Q1 Week 9Zion Conrad FuentesNo ratings yet
- Worksheet-1 TrigonometryDocument3 pagesWorksheet-1 Trigonometrysudhir singhNo ratings yet
- MR Lai Add Maths NotesDocument10 pagesMR Lai Add Maths Notesteng fsNo ratings yet
- MatLab Control System Toolbox ManualDocument64 pagesMatLab Control System Toolbox Manualluisgama22No ratings yet
- Erf TablesDocument2 pagesErf TablesaniNo ratings yet
- CFC - List - of - ElementsDocument188 pagesCFC - List - of - Elementsjhon omar100% (1)
- Maths Class 9TH Science 2023 1Document8 pagesMaths Class 9TH Science 2023 1SYED salman saeedNo ratings yet
- Expressions Dari QGIS USER DOCUMENTDocument9 pagesExpressions Dari QGIS USER DOCUMENTmona sihombingNo ratings yet
- AutMO03 PDFDocument2 pagesAutMO03 PDFAlfredo SarachoNo ratings yet
- Exercise WS11.1: Geoff Renshaw, 2016 All Rights ReservedDocument2 pagesExercise WS11.1: Geoff Renshaw, 2016 All Rights ReservedmakedonisNo ratings yet
- X y X y X X N N X N: H2 FM 9649/2016 RI Year 5 Term 3 Common TestDocument4 pagesX y X y X X N N X N: H2 FM 9649/2016 RI Year 5 Term 3 Common TestYao Le Titanium ChenNo ratings yet
- Newman-Penrose FormalismDocument7 pagesNewman-Penrose FormalismAnonymous kg7YBMFHNo ratings yet
- Cal 2 70midterm Exam - Attempt ReviewDocument24 pagesCal 2 70midterm Exam - Attempt ReviewLor fighterNo ratings yet
- CS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix ApproximationsDocument11 pagesCS168: The Modern Algorithmic Toolbox Lecture #9: The Singular Value Decomposition (SVD) and Low-Rank Matrix ApproximationsOnkar PanditNo ratings yet
- MIT5 74s09 Lec01Document14 pagesMIT5 74s09 Lec01Sanjip Kumar SapkotaNo ratings yet
- 07 3DElasticity CompleteDocument45 pages07 3DElasticity CompleteSüleyman TüreNo ratings yet
- Geometric Construction of Four-Dimensional Rotations Part I. Case of Four-Dimensional Euclidean SpaceDocument12 pagesGeometric Construction of Four-Dimensional Rotations Part I. Case of Four-Dimensional Euclidean SpaceShinya MinatoNo ratings yet
- Slides 4 (Routh, Root Locus)Document51 pagesSlides 4 (Routh, Root Locus)Felistus KavuuNo ratings yet
- Abaqus Analysis User's Manual (6 PDFDocument1 pageAbaqus Analysis User's Manual (6 PDFNguyen Ba DungNo ratings yet
- Deep Neural Network Approximation TheoryDocument80 pagesDeep Neural Network Approximation TheorynothardNo ratings yet
- On The Convergence of Bayesian Adaptive Filtering: Tayeb Sadiki, Dirk T.M. SlockDocument4 pagesOn The Convergence of Bayesian Adaptive Filtering: Tayeb Sadiki, Dirk T.M. SlockIulianNo ratings yet
- Classical and Multilinear Harmonic Analysis IIDocument342 pagesClassical and Multilinear Harmonic Analysis IIDavid PattyNo ratings yet