Professional Documents
Culture Documents
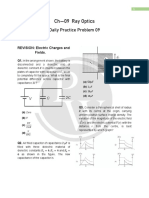
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.3
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.3
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriCopyright:
Available Formats
You might also like
- Geometrical Optics and Optical DesignDocument185 pagesGeometrical Optics and Optical DesignhuqedatoNo ratings yet
- (SPIE Vol. FG01) John E. Greivenkamp - Field Guide To Geometrical Optics (2003, SPIE Publications)Document132 pages(SPIE Vol. FG01) John E. Greivenkamp - Field Guide To Geometrical Optics (2003, SPIE Publications)Nikil Kumar100% (3)
- Light and Refraction Study Guide Answer KeysDocument5 pagesLight and Refraction Study Guide Answer Keyselvisfan777100% (1)
- RAY OPTICS DPP 1.2Document2 pagesRAY OPTICS DPP 1.2Dev KhattriNo ratings yet
- Test-25 Mains F2 QPDocument16 pagesTest-25 Mains F2 QPSejal KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssignmentDocument20 pagesRay Optics AssignmentApex Institute100% (1)
- 02 ExerciseDocument45 pages02 ExercisesocooltrishamNo ratings yet
- Optics 27 YearsDocument15 pagesOptics 27 YearssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- OPtics Notes IITDocument18 pagesOPtics Notes IITMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Optics SheetDocument6 pagesOptics SheetDarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument12 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics 1Document10 pagesGeometrical Optics 1S Prasad Shiva PulagamNo ratings yet
- DPP - DAY 1.pdf-75 PDFDocument32 pagesDPP - DAY 1.pdf-75 PDFYash bhartiNo ratings yet
- Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 09Document3 pagesCh-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 09Anmol KaushikNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Critical ThinkingDocument9 pagesRay Optics Critical Thinkingvishal_kalra100% (1)
- Test Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesTest Ray OpticsSarvesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument12 pagesGeometrical OpticsApex Institute100% (1)
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceDocument20 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceVivaan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Document5 pagesExercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Abhishek jainNo ratings yet
- Optics AssignmentDocument9 pagesOptics AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Geometrical OpticsDocument27 pagesExercise On Geometrical OpticssakshamamitagarwalNo ratings yet
- Go (Jee Main Online)Document19 pagesGo (Jee Main Online)balvantgk.hemant123No ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Document9 pagesCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Krupa Mariam BijuNo ratings yet
- Ca Opt 5 13Document4 pagesCa Opt 5 13Sunil DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics PG 1-20 (Rahul MCQS)Document69 pagesRay Optics PG 1-20 (Rahul MCQS)Anubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument4 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument8 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics TestDocument4 pagesRay Optics TestPaarth GulatiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Document7 pagesCBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)kumarisimon2No ratings yet
- 2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCDocument59 pages2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCazamchishty796No ratings yet
- Exercise-6: Fill in The BlanksDocument17 pagesExercise-6: Fill in The BlanksAbhishek jainNo ratings yet
- Optoelectrical PDFDocument25 pagesOptoelectrical PDFBala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics: PpendicesDocument27 pagesPhysics: PpendiceskankirajeshNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument28 pagesSolutionDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Entrance Questions HannDocument4 pagesRay Optics Entrance Questions HannPHYSCO BOT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 18 Geometrical OpticsDocument40 pages18 Geometrical OpticsSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII OpticDocument68 pagesChapter VII OpticDzaky Zakiyal FawwazNo ratings yet
- Test: Reflection and RefractionDocument8 pagesTest: Reflection and RefractionRabia MehraNo ratings yet
- LB APS ExperimentsDetails PhyIDocument37 pagesLB APS ExperimentsDetails PhyIMahesh YogamNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Geometrical Optics) Set-2Document10 pagesPHYSICS (Geometrical Optics) Set-2malani.swastikNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument5 pagesOPTICSNandan vadiNo ratings yet
- DPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Document4 pagesDPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 With solution-EP-IIDocument10 pagesAssignment-4 With solution-EP-IIadimeghaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics Jee-Main-Oline 2021 With AnswersDocument6 pagesGeometrical Optics Jee-Main-Oline 2021 With AnswersHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Optics RepDocument29 pagesOptics RepNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Light Olympiad 2Document4 pagesLight Olympiad 2nightbot.beastNo ratings yet
- OPTICS-07 - Subjective UnSolvedDocument4 pagesOPTICS-07 - Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument27 pagesOpticsSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Physics Exam Exercises For A-LEVEL/ STPM/ UEC/ PRE-UDocument13 pages2018 Physics Exam Exercises For A-LEVEL/ STPM/ UEC/ PRE-UKuen Jian LinNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Class 9 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 7 - Reflection of LightDocument40 pagesSelina Concise Physics Class 9 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 7 - Reflection of Lightfml5b9bd5No ratings yet
- Derivations (Optics) : 1. Mirror FormulaDocument24 pagesDerivations (Optics) : 1. Mirror FormulaHitesh Dua86% (44)
- 7 - Reflection of Light PDFDocument28 pages7 - Reflection of Light PDFprash_hingeNo ratings yet
- Group Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkDocument5 pagesGroup Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkMadhvi ShardaNo ratings yet
- Xiith PCB 02-06-2024 (MBR)Document18 pagesXiith PCB 02-06-2024 (MBR)Yashika NagNo ratings yet
- Excel SRG CT - 08 - (08-02-2024) FCDocument8 pagesExcel SRG CT - 08 - (08-02-2024) FCarnav BansalNo ratings yet
- Optics Mcq1Document7 pagesOptics Mcq1Manash SinghaNo ratings yet
- Test Optics 1Document4 pagesTest Optics 1Anant KumarNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics ResonanceDocument8 pagesGeometrical Optics ResonanceArush Nagpal50% (2)
- LAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesLAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightJose RizalNo ratings yet
- Pu2 Physics Part-2 Complete NotesDocument84 pagesPu2 Physics Part-2 Complete NotesRavindar Purohit100% (2)
- Brewster Angle and TIRDocument2 pagesBrewster Angle and TIRilg1No ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesReflection of LightBlesse Kathlyn LeoncioNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument31 pagesRay OpticsAnonymous a2kZINkNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties of LightDocument38 pagesWave Properties of LightMary Angelica Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Solutions Class 9 Chapter 7 Reflection of LightDocument30 pagesSelina Concise Physics Solutions Class 9 Chapter 7 Reflection of LightElite BrickmanNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of Plane WavesDocument36 pagesReflection and Refraction of Plane WavesJRonald85No ratings yet
- Ray Tracing in The Ionosphere: John M. KelsoDocument12 pagesRay Tracing in The Ionosphere: John M. KelsoASM AAS ASSASNo ratings yet
- From The Physics ClassroomDocument7 pagesFrom The Physics ClassroomA.Benson0% (1)
- Lab 8 Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesLab 8 Reflection and RefractionIKIARA K MERICHONo ratings yet
- Numerical With Answer2Document28 pagesNumerical With Answer2Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE TERM2 - Ray OpticsDocument132 pagesCBSE TERM2 - Ray Opticsvenom eNo ratings yet
- AberrationsDocument3 pagesAberrationsMansour AchaourNo ratings yet
- Television Production Handbook 11Th Edition Zettl Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument26 pagesTelevision Production Handbook 11Th Edition Zettl Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdarrenelliottzw310100% (11)
- Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesRefraction of LightMarilynTorreCameroNo ratings yet
- Grometrical Optics (With Solution)Document250 pagesGrometrical Optics (With Solution)Lalit Sharma100% (1)
- SIF1004 / SMES1203: Modern Physics: (2 Credit Hours)Document13 pagesSIF1004 / SMES1203: Modern Physics: (2 Credit Hours)J KNo ratings yet
- Conrady's Chromatic ConditionDocument7 pagesConrady's Chromatic ConditiondanyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Physics (Optics Notes)Document30 pagesBasics of Physics (Optics Notes)omkardashetwar100% (1)
- 01-Reflection of Light (MCQ) DifficultDocument10 pages01-Reflection of Light (MCQ) DifficultNarendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Pantulan Cahaya Pada Cermin SatahDocument4 pagesPantulan Cahaya Pada Cermin SatahHEHENo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6.2 A (Concept) Tutorial 6.2 B (Calculation) Tutorial 6.2 C (Problem Solving)Document3 pagesTutorial 6.2 A (Concept) Tutorial 6.2 B (Calculation) Tutorial 6.2 C (Problem Solving)naqibsyazaNo ratings yet
- RAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12Document27 pagesRAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12AkankshaNo ratings yet
- 1 Reflection and RefractionDocument27 pages1 Reflection and RefractionAl John Paz FiedalanNo ratings yet
- PHD Comprehensive Viva by Ayele Ossa LekaDocument151 pagesPHD Comprehensive Viva by Ayele Ossa Lekaayele ossaNo ratings yet
- The Critical AngleDocument8 pagesThe Critical AngleleonNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Learning Plan: General Physics 2Document28 pagesDynamic Learning Plan: General Physics 2lovj melNo ratings yet
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.3
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.3
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.3
RAY OPTICS DPP 1.3
Uploaded by
Dev KhattriCopyright:
Available Formats
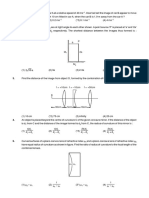
RAY OPTICS: REFRACTION CURVE SURFACE DPP 3
SUBJECTIVE TYPE
1. A parallel paraxial beam of light is incident on the arrangement as shown (μA = 3/2, μB =
4/3). The two spherical surfaces are very close and each has a radius of curvature. 10 cm.
Find the point where the rays are focussed. (w.r.t. point of entry)
SINGLE CORRECT ANSWER TYPE
2. A ray of light falls on the surface of a spherical glass paper weight making an angle α with the normal and is
refracted in the medium at an angle β. The angle of deviation of the emergent ray from the direction of the incident
ray
a. (α – β) b. 2(α – β) c. (α – β)/2 d. (β – α)
3. A point object O is placed in front of a glass rod having spherical end of radius of
curvature 30 cm. The image would be formed at
a.30 cm left b. Infinity c. 1 cm to the right d. 18 cm to the left
4. A glass hemisphere 0.04 m and R. I. of the material 1.6 is placed centrally over a cross mark on a paper,
i. with the flat face; ii. with the curved face in contact with the paper.
In each case the cross mark is viewed directly from above. The position of the images will be
a. i.0.04 m from the flat face; ii. 0.025 m from the flat face
b. i. At the same position of the cross mark; ii. 0.025 m below the flat face
c. i. 0.025 m from the flat face; ii. 0.04 m from the flat face
d. for both i. and ii. 0.025 m from the highest point of the hemisphere
5. An air bubble in sphere having 4 cm diameter appears 1 cm from surface nearest to eye when looked along
diameter. If 𝑎𝜇𝑔 = 1.5, the distance of bubble from refracting surface is
a. 1.2 cm b. 3.2 cm c. 2.8 cm d. 1.6 cm
6. The slab of a material of refractive index 2 shown in the figure has curved surface
APB of radius of curvature 10 cm and a plane surface CD. On the left of APB is air
and on the right of CD is water with refractive indices as given in the figure. An object
O is placed at a distance of 15 cm from pole P as shown. The distance of the final
image of O from P, as viewed from the left is
a.20 cm b. 30 cm c. 40 cm d. 50 cm
7. A parallel beam of light emerges from the opposite surface of the sphere when a point source of light lies at the
surface of the sphere. The refractive index of the sphere is
3 5 5
a. 2 b. 3 c. 2 d. 2
8. In a thin spherical fish bowl of radius 10 cm filled with water of refractive index 4/3 there is
a small fish at a distance of 4 cm from the centre C as shown in the figure. Where will the
image of fish appears, if seen from E.
a. 5.2 cm b. 7.2 cm c. 4.2 cm d. 3.2 cm
9. The observer ‘O’ sees the distance AB as infinitively large. If refractive index of liquid is
𝜇
𝜇1 and that of glass is 𝜇2 then 𝜇1 is:
2
a. 2 b. ½ c.4 d. None of these
ANISH SIR & TEAM LUCKNOW-ASHOK MARG - 9919495931
MULTIPLE CORRECT ANSWERS TYPE
10. The first factor length f1 for refraction at a spherical surface is defined as the
value of u corresponding to v = ∞ (as shown) with refractive indices of two
mediums, as n1 and n2. The second focal length f2 is defined as value of v for
u = ∞.
𝑛2 𝑅 𝑛2 𝑅
a.f2 is equal to (𝑛 b. f1 is equal to (𝑛
2 −𝑛1 ) 2−𝑛1)
𝑛1 𝑅 𝑛1 𝑅
c. f2 is equal to (–) (𝑛 d. f1 is equal to (–) (𝑛
2 −𝑛1 ) 2 −𝑛1 )
COMPREHENSION TYPE
Figure shows a point object placed in front of a transparent sphere of radius 20 cm and
refractive index 1.5. The sphere forms an image due to refraction at surface I followed
by refraction at surface II. The sphere is kept in air and the object is located at distance
x from P1. It is found that for x > x1, the formed due to refraction at surface I is real,
the final image formed by the sphere is also real and forms to the right of P2. For x2 <
x < x1, the image formed by surface I is virtual while the final image formed by the
sphere is real and forms to the right of P2. However, for x < x2, the image formed by
the sphere are virtual.
It is also found that the final image is virtual if the distance of image formed by surface I from P2 is less than y. The
object is now moved away from the sphere so that x becomes large and say, x → ∞. In this case, the final image is
formed at distance y1 from P2. If the given sphere is replaced by another one of the same radius but of refractive
index. 2.5, the final image is formed at distance y2 from P2.
11. Distance x1 such that for x > x1, the image formed by surface I and also the final image are real, is
a.60 cm b. 40 cm c. 20 cm d. 10 cm
12. Distance x2 such that for x2 <x <x1, the image formed by surface I is virtual but the final image is real, is
a.10 cm b. 25 cm c. 40 cm d. 32.5 cm
13. As stated above, if the distance of image formed by surface 1 from P2 is less than y, the final image is virtual.
Then, y will be
a. 40 cm b. 60 cm c. 80 cm d. 100 cm
14. For the object place at x → ∞, the given sphere of refractive index 1.5 forms an image at distance y1 from P2.
a. this image is real and y1 = 12.5 cm right of P2 b. this image is real and y1 = 10 cm right of P2
c. this image is real and y1 = 20 cm right of P2 d. this image is virtual and y1 = 12 cm left of P2
15. For the object place at x → ∞, a sphere of the same radius but of refractive index 2.5 forms an image at distance y 2
from P2
a.this image is real and y2 = 6.67 cm right of P2 b. this image is virtual and y2 = 6.67 cm left of P2
c. this image is virtual and y2 = 3.33 cm left of P2 d. this image is real and y2 = 2.5 cm left of P2
ANSWERS KEY
Subjective type 1.17.5 cm
Single correct answer type
2.b 3.a 4.b 5.a 6.b 7.c 8. a 9. a
Multiple correct answers type 10.(a, b)
Comprehension type 11. b 12. a 13.b 14.b 15.c
ANISH SIR & TEAM LUCKNOW-ASHOK MARG - 9919495931
You might also like
- Geometrical Optics and Optical DesignDocument185 pagesGeometrical Optics and Optical DesignhuqedatoNo ratings yet
- (SPIE Vol. FG01) John E. Greivenkamp - Field Guide To Geometrical Optics (2003, SPIE Publications)Document132 pages(SPIE Vol. FG01) John E. Greivenkamp - Field Guide To Geometrical Optics (2003, SPIE Publications)Nikil Kumar100% (3)
- Light and Refraction Study Guide Answer KeysDocument5 pagesLight and Refraction Study Guide Answer Keyselvisfan777100% (1)
- RAY OPTICS DPP 1.2Document2 pagesRAY OPTICS DPP 1.2Dev KhattriNo ratings yet
- Test-25 Mains F2 QPDocument16 pagesTest-25 Mains F2 QPSejal KhandelwalNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics AssignmentDocument20 pagesRay Optics AssignmentApex Institute100% (1)
- 02 ExerciseDocument45 pages02 ExercisesocooltrishamNo ratings yet
- Optics 27 YearsDocument15 pagesOptics 27 YearssmrutirekhaNo ratings yet
- OPtics Notes IITDocument18 pagesOPtics Notes IITMoni KakatiNo ratings yet
- Optics SheetDocument6 pagesOptics SheetDarsh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument12 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFAnonymous vRpzQ2BLNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics 1Document10 pagesGeometrical Optics 1S Prasad Shiva PulagamNo ratings yet
- DPP - DAY 1.pdf-75 PDFDocument32 pagesDPP - DAY 1.pdf-75 PDFYash bhartiNo ratings yet
- Ch-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 09Document3 pagesCh-09 Ray Optics: Daily Practice Problem 09Anmol KaushikNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Critical ThinkingDocument9 pagesRay Optics Critical Thinkingvishal_kalra100% (1)
- Test Ray OpticsDocument4 pagesTest Ray OpticsSarvesh Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometrical OpticsDocument12 pagesGeometrical OpticsApex Institute100% (1)
- Part - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceDocument20 pagesPart - I: Subjective Questions: ResonanceVivaan AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Exercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Document5 pagesExercise-01: MCQ (Single Choice Correct)Abhishek jainNo ratings yet
- Optics AssignmentDocument9 pagesOptics AssignmentShiva Ram Prasad PulagamNo ratings yet
- Exercise On Geometrical OpticsDocument27 pagesExercise On Geometrical OpticssakshamamitagarwalNo ratings yet
- Go (Jee Main Online)Document19 pagesGo (Jee Main Online)balvantgk.hemant123No ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Document9 pagesCBSE Test Paper-02 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Krupa Mariam BijuNo ratings yet
- Ca Opt 5 13Document4 pagesCa Opt 5 13Sunil DeshpandeNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics PG 1-20 (Rahul MCQS)Document69 pagesRay Optics PG 1-20 (Rahul MCQS)Anubhav SinghNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics PDFDocument4 pagesGeometrical Optics PDFTarun GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument8 pagesRay Optics and Optical InstrumentsKoyal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics TestDocument4 pagesRay Optics TestPaarth GulatiNo ratings yet
- CBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)Document7 pagesCBSE Test Paper-04 Class - 12 Physics (Ray Optics and Optical Instruments)kumarisimon2No ratings yet
- 2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCDocument59 pages2 - GO Sheet - Exc - PCazamchishty796No ratings yet
- Exercise-6: Fill in The BlanksDocument17 pagesExercise-6: Fill in The BlanksAbhishek jainNo ratings yet
- Optoelectrical PDFDocument25 pagesOptoelectrical PDFBala KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Physics: PpendicesDocument27 pagesPhysics: PpendiceskankirajeshNo ratings yet
- SolutionDocument28 pagesSolutionDebayanbasu.juNo ratings yet
- Ray Optics Entrance Questions HannDocument4 pagesRay Optics Entrance Questions HannPHYSCO BOT GAMINGNo ratings yet
- 18 Geometrical OpticsDocument40 pages18 Geometrical OpticsSamsul BahriNo ratings yet
- Chapter VII OpticDocument68 pagesChapter VII OpticDzaky Zakiyal FawwazNo ratings yet
- Test: Reflection and RefractionDocument8 pagesTest: Reflection and RefractionRabia MehraNo ratings yet
- LB APS ExperimentsDetails PhyIDocument37 pagesLB APS ExperimentsDetails PhyIMahesh YogamNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS (Geometrical Optics) Set-2Document10 pagesPHYSICS (Geometrical Optics) Set-2malani.swastikNo ratings yet
- OPTICSDocument5 pagesOPTICSNandan vadiNo ratings yet
- DPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247Document4 pagesDPP - 07 - Geometrical Optics NJ - 247gaurankkingNo ratings yet
- Assignment-4 With solution-EP-IIDocument10 pagesAssignment-4 With solution-EP-IIadimeghaNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics Jee-Main-Oline 2021 With AnswersDocument6 pagesGeometrical Optics Jee-Main-Oline 2021 With AnswersHarsh SinghNo ratings yet
- Optics RepDocument29 pagesOptics RepNikhil KumarNo ratings yet
- Light Olympiad 2Document4 pagesLight Olympiad 2nightbot.beastNo ratings yet
- OPTICS-07 - Subjective UnSolvedDocument4 pagesOPTICS-07 - Subjective UnSolvedRaju SinghNo ratings yet
- OpticsDocument27 pagesOpticsSiddharth AcharyaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Physics Exam Exercises For A-LEVEL/ STPM/ UEC/ PRE-UDocument13 pages2018 Physics Exam Exercises For A-LEVEL/ STPM/ UEC/ PRE-UKuen Jian LinNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Class 9 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 7 - Reflection of LightDocument40 pagesSelina Concise Physics Class 9 ICSE Solutions For Chapter 7 - Reflection of Lightfml5b9bd5No ratings yet
- Derivations (Optics) : 1. Mirror FormulaDocument24 pagesDerivations (Optics) : 1. Mirror FormulaHitesh Dua86% (44)
- 7 - Reflection of Light PDFDocument28 pages7 - Reflection of Light PDFprash_hingeNo ratings yet
- Group Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkDocument5 pagesGroup Bohr's Optics Section A: One MarkMadhvi ShardaNo ratings yet
- Xiith PCB 02-06-2024 (MBR)Document18 pagesXiith PCB 02-06-2024 (MBR)Yashika NagNo ratings yet
- Excel SRG CT - 08 - (08-02-2024) FCDocument8 pagesExcel SRG CT - 08 - (08-02-2024) FCarnav BansalNo ratings yet
- Optics Mcq1Document7 pagesOptics Mcq1Manash SinghaNo ratings yet
- Test Optics 1Document4 pagesTest Optics 1Anant KumarNo ratings yet
- Geometrical Optics ResonanceDocument8 pagesGeometrical Optics ResonanceArush Nagpal50% (2)
- LAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument4 pagesLAB MANUAL DATA SHEET Experiment 10. Reflection and Refraction of LightJose RizalNo ratings yet
- Pu2 Physics Part-2 Complete NotesDocument84 pagesPu2 Physics Part-2 Complete NotesRavindar Purohit100% (2)
- Brewster Angle and TIRDocument2 pagesBrewster Angle and TIRilg1No ratings yet
- Reflection of LightDocument21 pagesReflection of LightBlesse Kathlyn LeoncioNo ratings yet
- Ray OpticsDocument31 pagesRay OpticsAnonymous a2kZINkNo ratings yet
- Wave Properties of LightDocument38 pagesWave Properties of LightMary Angelica Dela PazNo ratings yet
- Selina Concise Physics Solutions Class 9 Chapter 7 Reflection of LightDocument30 pagesSelina Concise Physics Solutions Class 9 Chapter 7 Reflection of LightElite BrickmanNo ratings yet
- Reflection and Refraction of Plane WavesDocument36 pagesReflection and Refraction of Plane WavesJRonald85No ratings yet
- Ray Tracing in The Ionosphere: John M. KelsoDocument12 pagesRay Tracing in The Ionosphere: John M. KelsoASM AAS ASSASNo ratings yet
- From The Physics ClassroomDocument7 pagesFrom The Physics ClassroomA.Benson0% (1)
- Lab 8 Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesLab 8 Reflection and RefractionIKIARA K MERICHONo ratings yet
- Numerical With Answer2Document28 pagesNumerical With Answer2Rahul KumarNo ratings yet
- CBSE TERM2 - Ray OpticsDocument132 pagesCBSE TERM2 - Ray Opticsvenom eNo ratings yet
- AberrationsDocument3 pagesAberrationsMansour AchaourNo ratings yet
- Television Production Handbook 11Th Edition Zettl Test Bank Full Chapter PDFDocument26 pagesTelevision Production Handbook 11Th Edition Zettl Test Bank Full Chapter PDFdarrenelliottzw310100% (11)
- Refraction of LightDocument44 pagesRefraction of LightMarilynTorreCameroNo ratings yet
- Grometrical Optics (With Solution)Document250 pagesGrometrical Optics (With Solution)Lalit Sharma100% (1)
- SIF1004 / SMES1203: Modern Physics: (2 Credit Hours)Document13 pagesSIF1004 / SMES1203: Modern Physics: (2 Credit Hours)J KNo ratings yet
- Conrady's Chromatic ConditionDocument7 pagesConrady's Chromatic ConditiondanyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Physics (Optics Notes)Document30 pagesBasics of Physics (Optics Notes)omkardashetwar100% (1)
- 01-Reflection of Light (MCQ) DifficultDocument10 pages01-Reflection of Light (MCQ) DifficultNarendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Pantulan Cahaya Pada Cermin SatahDocument4 pagesPantulan Cahaya Pada Cermin SatahHEHENo ratings yet
- Tutorial 6.2 A (Concept) Tutorial 6.2 B (Calculation) Tutorial 6.2 C (Problem Solving)Document3 pagesTutorial 6.2 A (Concept) Tutorial 6.2 B (Calculation) Tutorial 6.2 C (Problem Solving)naqibsyazaNo ratings yet
- RAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12Document27 pagesRAY OPTICS Chapter 9 Class 12AkankshaNo ratings yet
- 1 Reflection and RefractionDocument27 pages1 Reflection and RefractionAl John Paz FiedalanNo ratings yet
- PHD Comprehensive Viva by Ayele Ossa LekaDocument151 pagesPHD Comprehensive Viva by Ayele Ossa Lekaayele ossaNo ratings yet
- The Critical AngleDocument8 pagesThe Critical AngleleonNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Learning Plan: General Physics 2Document28 pagesDynamic Learning Plan: General Physics 2lovj melNo ratings yet