Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
freehat24Original Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 7
Chapter 7
Uploaded by
freehat24Copyright:
Available Formats
Routing Protocols and Concepts – Chapter 7 2nd extension is the addition of next hop address
Encounter and describe the limitations of RIPv1’s limitations. Enabling and Verifying RIPv2
Apply the basic Routing Information Protocol Version 2 (RIPv2) Configuring RIP on a Cisco router
configuration commands and evaluate RIPv2 classless routing updates. By default it is running RIPv1
Analyze router output to see RIPv2 support for VLSM and CIDR Configuring RIPv2 on a Cisco router
Identify RIPv2 verification commands and common RIPv2 issues. -Requires using the version 2 command
Configure, verify, and troubleshoot RIPv2 in “hands-on” labs -RIPv2 ignores RIPv1 updates
Chapter focus To verify RIPv2 is configured use the
-Difference between RIPv1 & RIPv2 show ip protocols command
RIPv1 Auto-Summary & RIPv2
-A classful distance vector routing protocol RIPv2 will automatically summarize routes at major network boundaries and
-Does not support discontiguous subnets can also summarize routes with a subnet mask that is smaller than the classful
-Does not support VLSM subnet mask
-Does not send subnet mask in routing update Disabling Auto-Summary in RIPv2
-Routing updates are broadcast To disable automatic summarization issue the no auto-summary command
RIPv2 Verifying RIPv2 Updates
-A classless distance vector routing protocol that is an enhancement of When using RIPv2 with automatic summarization turned off
RIPv1’s features. Each subnet and mask has its own specific entry, along with the exit
-Next hop address is included in updates interface and next-hop address to reach that subnet.
-Routing updates are multicast To verify information being sent by RIPv2 use the
-The use of authentication is an option debug ip rip command
Similarities between RIPv1 & RIPv2 VLSM & CIDR
-Use of timers to prevent routing loops RIPv2 and VLSM
-Use of split horizon or split horizon with poison reverse Networks using a VLSM IP addressing scheme
-Use of triggered updates Use classless routing protocols (i.e. RIPv2) to disseminate network addresses
-Maximum hop count of 15 and their subnet masks
RIPv1 Limitations CIDR uses Supernetting
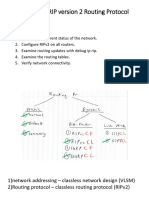
Lab Topology Supernetting is a bunch of contiguous classful networks that is addressed as a
Scenario: single network.
3 router set up To verify that supernets are being sent and received use the following
Topology is discontiguous commands
There exists a static summary route -Show ip route -Debug ip rip
Static route information can be injected into routing table updates using Verifying & Troubleshooting RIPv2
redistribution. Basic Troubleshooting steps
Routers 1 & 3 contain VLSM networks -Check the status of all links
Scenario Continued -Check cabling
VLSM -Check IP address & subnet mask configuration
-Recall this is sub netting the subnet -Remove any unneeded configuration commands
Private IP addresses are on LAN links Commands used to verify proper operation of RIPv2
Public IP addresses are used on WAN links Show ip interfaces brief
Loopback interfaces Show ip protocols
-These are virtual interfaces that can be pinged and added to routing table Debug ip rip
Null Interfaces Show ip route
This is a virtual interface that does not need to be created or configured Common RIPv2 Issues
-Traffic sent to a null interface is discarded When trouble shooting RIPv2 examine the following issues:
-Null interfaces do not send or receive traffic Version
Static routes and null interfaces -Check to make sure you are using version 2
null interfaces will serve as the exit interface for static route Network statements
-Example of configuring a static supernet route with a null interface -Network statements may be incorrectly typed or missing
-R2(config)#ip route 192.168.0.0 255.255.0.0 Null0 Automatic summarization
Route redistribution -If summarized routes are not needed then disable automatic summarization
-Redistribution command is way to disseminate a static route from one router Reasons why it’s good to authenticate routing information
to another via a routing protocol -Prevent the possibility of accepting invalid routing updates
-Example :R2(config-router)#redistribute static -Contents of routing updates are encrypted
Verifying and Testing Connectivity Types of routing protocols that can use authentication
Use the following commands: -RIPv2 –EIGRP –OSPF -IS-IS -BGP
show ip interfaces brief, ping, traceroute
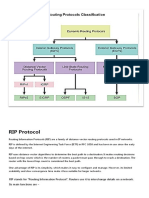
RIPv1 – a classful routing protocol
-Subnet mask are not sent in updates
-Summarizes networks at major network boundaries
-if network is discontiguous and RIPv1 configured convergence will not be
reached
Examining the routing tables
-To examine the contents of routing updates use the debug ip rip command
-If RIPv1 is configured then Subnet masks will not be included with the
network address
RIPv1 does not support VLSM
Reason: RIPv1 does not send subnet mask in routing updates
RIPv1 does summarize routes to the Classful boundary Or uses the Subnet
mask of the outgoing interface to determine which subnets to advertise
No CIDR Support
In the diagram R2 will not include the static route in its update
Reason: Classful routing protocols do not support CIDR routes that are
summarized with a smaller mask than the classful subnet mask
Configuring RIPv2
Comparing RIPv1 & RIPv2 Message Formats
-RIPv2 Message format is similar to RIPv1 but has 2 extensions
1st extension is the subnet mask field
You might also like
- TDMA Vs SCPC Technical NoteDocument13 pagesTDMA Vs SCPC Technical Notevsharma26No ratings yet
- Exploration Routing Chapter 07Document27 pagesExploration Routing Chapter 07lordjebus2000No ratings yet
- RIP Version 1: Routing Protocols and ConceptsDocument28 pagesRIP Version 1: Routing Protocols and ConceptsManjunath KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Rip V1Document29 pagesRip V1SomebodyNo ratings yet
- RIP v1Document1 pageRIP v1virendraNo ratings yet
- Rip Version 1 (Ripv1)Document54 pagesRip Version 1 (Ripv1)AtmanNo ratings yet
- Rip V1 & V2Document6 pagesRip V1 & V2Sujith VSNo ratings yet
- RIP Version 1Document3 pagesRIP Version 1Qila SumadiNo ratings yet
- CA Ex S2M05 RIP Version 1Document36 pagesCA Ex S2M05 RIP Version 1api-3700114No ratings yet
- Networking Concepts - Part 5Document29 pagesNetworking Concepts - Part 5Aayush ShahiNo ratings yet
- Ripv2: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 7Document22 pagesRipv2: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 7api-358658237No ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Ripv2 Protocol in Wired Network Using Cisco Packet TracerDocument6 pagesPerformance Analysis of Ripv2 Protocol in Wired Network Using Cisco Packet TracerAhmed JahaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2: Dynamic Routing: CCNA Routing and Switching Routing and Switching Essentials v6.0Document29 pagesChapter 2: Dynamic Routing: CCNA Routing and Switching Routing and Switching Essentials v6.0Muhammad EmranNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPDocument13 pagesPractical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPkuldeep RajbharNo ratings yet
- Practical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPDocument13 pagesPractical No. 4: Configure IP Routing Using RIPkuldeep RajbharNo ratings yet
- Rahul, Mohd. (2014) A Comparative Evaluation of Classless Routing Protocols (EIGRP) and Classful Routing Protocols (RIP)Document7 pagesRahul, Mohd. (2014) A Comparative Evaluation of Classless Routing Protocols (EIGRP) and Classful Routing Protocols (RIP)Lee HeaverNo ratings yet
- 016 Enabling RIPDocument20 pages016 Enabling RIPBAHRAIN1967No ratings yet
- Lab 10Document5 pagesLab 10Nhat MinhNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 LabDocument6 pagesLecture 6 LabSerin AskecNo ratings yet
- Exercises:: Router # 1 (Ripv1)Document5 pagesExercises:: Router # 1 (Ripv1)Osama FarooquiNo ratings yet
- Aula 03 - RIPv1&v2Document16 pagesAula 03 - RIPv1&v2MARLON JORGE MEIRELESNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 - Routing TechnologiesDocument88 pagesLesson 4 - Routing TechnologiesPhan Chi BaoNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Configuration Mode Used For?Document10 pagesWhat Is Global Configuration Mode Used For?Abhishek KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Ccna 200-301 - 2Document52 pagesCcna 200-301 - 2Wahyudi YusufNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 All ModulesDocument48 pagesCCNA 3 All ModulesFi3ta100% (1)
- Chapter 3: Dynamic Routing: Instructor MaterialsDocument38 pagesChapter 3: Dynamic Routing: Instructor MaterialsAmjad hassanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Routing: RTTC, ThiruvananthapuramDocument30 pagesDynamic Routing: RTTC, ThiruvananthapuramsenthilnathanNo ratings yet
- NET201 Chapter3 DynamicRoutingDocument34 pagesNET201 Chapter3 DynamicRoutingKenneth LocsonNo ratings yet
- Configuring RIP: RIP Configuration Task ListDocument8 pagesConfiguring RIP: RIP Configuration Task Listsamith1No ratings yet
- Configuring RIP: RIP Configuration Task ListDocument8 pagesConfiguring RIP: RIP Configuration Task Listtare890No ratings yet
- Routing Information ProtocolDocument3 pagesRouting Information ProtocolwertoniwertonisNo ratings yet
- Revision Notes CCNA 3 EasyDocument40 pagesRevision Notes CCNA 3 EasyNur Dinah YeeNo ratings yet
- RIPv2 Part 1Document20 pagesRIPv2 Part 1nurinNo ratings yet
- RIP ProtocolDocument4 pagesRIP ProtocolDion Odessy PaduaNo ratings yet
- Administrative Distances (AD) : Open Shortest Path First Is A Link State and Hierarchical IGP Routing Algorithm. It IsDocument7 pagesAdministrative Distances (AD) : Open Shortest Path First Is A Link State and Hierarchical IGP Routing Algorithm. It IsGebrie BeleteNo ratings yet
- CCNA 3 Study Guide Answers-AllDocument33 pagesCCNA 3 Study Guide Answers-AllgeertvdhNo ratings yet
- 04-RG-S7805C Switch RGOS Configuration Reference, Release 11.0 (4) B19 - IP Routing ConfigurationDocument586 pages04-RG-S7805C Switch RGOS Configuration Reference, Release 11.0 (4) B19 - IP Routing Configurationcindy yudi hermawanNo ratings yet
- RIP Version 1: © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Public ITE I Chapter 6Document36 pagesRIP Version 1: © 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All Rights Reserved. Cisco Public ITE I Chapter 6fauzi endraNo ratings yet
- CCNA RSE Chp3Document36 pagesCCNA RSE Chp3Tayyab AliNo ratings yet
- Laboratorio 12 Configurando RIPv2Document2 pagesLaboratorio 12 Configurando RIPv2Ibeth Amalia MaqueraNo ratings yet
- Rip V2: CCNP S1 (5), Chapter 4Document11 pagesRip V2: CCNP S1 (5), Chapter 4rajahuja411No ratings yet
- Chapter 7 Case Study PDFDocument4 pagesChapter 7 Case Study PDFDaNi AlexisNo ratings yet
- 03 - Dynamic RoutingDocument35 pages03 - Dynamic Routingeztog006No ratings yet
- CCNA 2 R&S - Routing and Switching Essentials Final Exam Answers - CCNA5Document17 pagesCCNA 2 R&S - Routing and Switching Essentials Final Exam Answers - CCNA5albe88aNo ratings yet
- Ccnaexp 5Document77 pagesCcnaexp 5opsssNo ratings yet
- Exploration Routing Chapter 5Document29 pagesExploration Routing Chapter 5Anonymous CRx3B9SNo ratings yet
- Routing Rip PDFDocument19 pagesRouting Rip PDFAxel LwiantoroNo ratings yet
- CCNP SWITCH Chapter 10 Exam Answers (Version 7) - Score 100%Document4 pagesCCNP SWITCH Chapter 10 Exam Answers (Version 7) - Score 100%GC ToolbarNo ratings yet
- CCNA 2 Final Exam TakenDocument25 pagesCCNA 2 Final Exam TakenIslamian_16No ratings yet
- RIP Version 1: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 5Document29 pagesRIP Version 1: Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 5Raheel AslamNo ratings yet
- RIP v1 Routing: CCNA Exploration Semester 2Document35 pagesRIP v1 Routing: CCNA Exploration Semester 2p316jaNo ratings yet
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Document8 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)asdasdasd123456No ratings yet
- Assessment System: Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Document5 pagesAssessment System: Take Assessment - Erouting Chapter 5 - Ccna Exploration: Routing Protocols and Concepts (Version 4.0)Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- 25 CCNA QUESTION by PrinceDocument8 pages25 CCNA QUESTION by PrinceShiv Om Shiv OmNo ratings yet
- Manually Add The VLAN To The VLAN Database of The VTP Servers.Document16 pagesManually Add The VLAN To The VLAN Database of The VTP Servers.BelNo ratings yet
- Ip Summary Address For Ripv2: Feature OverviewDocument10 pagesIp Summary Address For Ripv2: Feature OverviewAbhijeet NaikNo ratings yet
- ROUTE Final Exam - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)Document28 pagesROUTE Final Exam - CCNP ROUTE (Version 6.0)AS220588% (40)
- CVD IWANDesignGuide FEB16 5Document20 pagesCVD IWANDesignGuide FEB16 5Priscila FloresNo ratings yet
- LEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingFrom EverandLEARN MPLS FROM SCRATCH PART-B: A Beginners guide to next level of networkingNo ratings yet
- ROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONFrom EverandROUTING INFORMATION PROTOCOL: RIP DYNAMIC ROUTING LAB CONFIGURATIONNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Databases: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1Document22 pagesIntroduction To Databases: © Pearson Education Limited, 2004 1hardeepcharmingNo ratings yet
- ٢٠٢٢ ٠٧ ٢٠Document23 pages٢٠٢٢ ٠٧ ٢٠MOUSTAFA KHEDRNo ratings yet
- CCNA Exploration2 - Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 3 ExamDocument6 pagesCCNA Exploration2 - Routing Protocols and Concepts - Chapter 3 Examchocolat4No ratings yet
- Ethics 8 LegardaDocument8 pagesEthics 8 LegardaReychille AbianNo ratings yet
- 02 Huawei Campus Network Products and Solution Pre-Sales TrainingDocument72 pages02 Huawei Campus Network Products and Solution Pre-Sales TrainingMitra SistematikNo ratings yet
- JBC Soldering Iron ManualDocument31 pagesJBC Soldering Iron Manualcisco211No ratings yet
- DB Ip FormatDocument5 pagesDB Ip Formatexplorer2No ratings yet
- HP Ent 500 Color M575 Troubleshooting Manual TOCDocument28 pagesHP Ent 500 Color M575 Troubleshooting Manual TOCJesusLuzardoNo ratings yet
- 821 2418Document304 pages821 2418foru_raghuNo ratings yet
- For Today's Emergency DepartmentsDocument4 pagesFor Today's Emergency DepartmentsdesbestNo ratings yet
- Compuprint Sp40 Service ManualDocument144 pagesCompuprint Sp40 Service Manualaabb_1my372467% (3)
- Paulo AGM v1.4Document19 pagesPaulo AGM v1.4Paulo FilimoneNo ratings yet
- AP Mode Switching - Overview, Configuration Examples, and TroubleshootingDocument43 pagesAP Mode Switching - Overview, Configuration Examples, and Troubleshootingngotuanthanh15a6No ratings yet
- Profienergy Et200s Doku v12 enDocument71 pagesProfienergy Et200s Doku v12 endelciodaminNo ratings yet
- Installation PDFDocument684 pagesInstallation PDF高貳伍No ratings yet
- Am Sat 2008Document11 pagesAm Sat 2008kupybxiypepfNo ratings yet
- ACN - Unit - 1Document46 pagesACN - Unit - 1Shrenik PatilNo ratings yet
- OmniText Data SheetDocument2 pagesOmniText Data SheetRaison MukkathNo ratings yet
- HPE FlexNetwork MSR3000 Router Series-PSN5408895USENDocument4 pagesHPE FlexNetwork MSR3000 Router Series-PSN5408895USENNgoc The NguyenNo ratings yet
- 2MB Mux PDFDocument114 pages2MB Mux PDFRohit Sharma100% (1)
- Dh-Sd5A225Xa-Hnr: 2Mp 25X Starlight Ir Wizsense Network PTZ CameraDocument4 pagesDh-Sd5A225Xa-Hnr: 2Mp 25X Starlight Ir Wizsense Network PTZ CameraJames Will DrinkwaterNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Quiz - Eth Trunk Topic 11Document3 pagesQuiz - Quiz - Eth Trunk Topic 11silas chipondaNo ratings yet
- WCDMA PS Service Optimization GuideDocument215 pagesWCDMA PS Service Optimization GuideEfosa AigbeNo ratings yet
- Using Rac Parallel Instance GroupsDocument6 pagesUsing Rac Parallel Instance GroupsDan Doan DinhNo ratings yet
- D2T3 - Mikko Hypponen - Behind Enemy LinesDocument50 pagesD2T3 - Mikko Hypponen - Behind Enemy LinesErkanNo ratings yet
- How To Subnet in Your HeadDocument67 pagesHow To Subnet in Your Headbaraynavab95% (20)
- Y-Tech Sound Systems 2020-Q3Document17 pagesY-Tech Sound Systems 2020-Q3essamNo ratings yet
- Steps To Install LAMP in A Offline Centos MachineDocument16 pagesSteps To Install LAMP in A Offline Centos MachineRed IeNo ratings yet
- MD06 TVInstruccionesDocument43 pagesMD06 TVInstruccionesDaniel RiberaNo ratings yet