Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ICU One Pager ECMO Fundamentals
ICU One Pager ECMO Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Nicholas HelmstetterOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ICU One Pager ECMO Fundamentals
ICU One Pager ECMO Fundamentals
Uploaded by
Nicholas HelmstetterCopyright:
Available Formats
onepagericu.
com
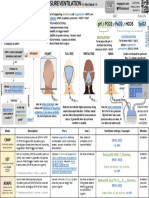
ECMO FUNDAMENTALS by Nick Mark MD & Jonah Rubin MD ONE
Link to the
@nickmmark most current
PURPOSE & DEFINITIONS: INDICATIONS: @JonahRubinMD version →
· ExtraCorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) provides · VV: Refractory hypoxemia/mixed respiratory failure used
as a bridge to recovery or transplant ABG Pulse Ox
prolonged pulmonary and/or circulatory support by removing
venous blood, pumping it across an artificial lung (oxygenator · ECCO2R: Refractory hypercapnia similar to VV but with
lower flow/smaller sized cannula
pH PCO2 PaO2 / HCO3
/ / SpO2
or membrane lung) for gas exchange, & returning it to the pt..
· VV ECMO: artificially oxygenated Venous blood is returned to · VA: Pulmonary & Circulatory support (VA) – cardiac arrest,
the Venous side (right atrium), providing no circulatory overdose, massive PE, cardiogenic shock, etc. Used as a VENTILATION OXYGENATION
support, & adding the artificial lung in series with the native bridge to recovery, transplant, or destination device. To decrease PCO2 or To increase PaO2, increase
lung. increase pH ! increase the RPM / PUMP FLOW RATE or
· VA ECMO: artificially oxygenated Venous blood is returned to SWEEP / GAS FLOW FDO2
the Arterial side (aorta), providing circulatory support, and
adding & artificial lung in parallel with the native lung.
RETURN FDO2
CANNULA
IN R IJ VEIN FDO2 (fractional delivered O2) & AIR & O2
SETTINGS/MANAGEMENT: Different DRAINAGE & RETURN BLOOD FLOW RATE determines BLENDER
· Cannula size/positioning configurations are possible. oxygenation. Initially usually set Flow
(lpm)
· Pump speed (RPM, flow) Choice depends on mode (VV vs at 100% and decreased if PaO2 is 60
· Sweep / Gas flow VA), flow requirements, & patient above goal. SWEEP GAS FLOW 55
· FDO2 determines CO2 removal.
50
anatomy. The configuration here 45
· Alarm settings
is VV ECMO. (R femoral vein 40 FiO2 (%)
· Anticoagulation strategy BUBBLE 35
· Transfusion/fluid goals drainage and R IJ vein return) DETECTOR 30
40 60
· Ventilator settings DRAINAGE SWEEP 21 100
100
CANNULA
(to minimize VILI & prevent atelectasis) IN R FEMORAL VEIN GAS FLOW
ULTRASONIC BUBBLE
CO2 O2 O2
DETECTOR is an SINLETO2 SENSOR
Oxygen saturation of blood OXYGENATOR performs gas
important safety
device that detects entering the circuit exchange (oxygenation, CO2 Air
removal) and regulates blood SOUTLETO2 HEPA
air bubbles in the
FILTER
circuit temperature with a HEAT SENSOR
EXCHANGER. This can be used PPOST-MEMBRANE (also called
PVENOUS for TTM or and it can mask a PARTERIAL) is the positive pressure
Pressure transducer returning to the patient. This is
is the negative suctioning fever.
ports can also be used lower than Ppre-membrane
to sample blood pressure applied to extract
because of resistance in the
blood via the drainage cannula OXYGENATOR OXYGENATOR.
(MEMBRANE LUNG)
The CENTRIFUGAL PUMP
moves blood through the
𝑻𝑴𝑷 = 𝑷𝑷𝒐𝒔𝒕 − 𝑷𝒑𝒓𝒆
ECMO circuit. PUMP RPM
PPRE-MEMBRANE TRANSMEMBRANE PRESSURE (𝞓P
(also called PINTERNAL) is THERMOMETER &
determines the BLOOD or TMP) is the pressure difference
v1.0 (2021-11-13)
PUMP the positive pressure HEAT EXCHANGER
FLOW RATE. Along with across the OXYGENATOR.
propelling blood
CC BY-SA 3.0
FDO2, blood flow determines RPM Trending changes in TPM may
through the oxygenator
PaO2. In VA, the pump RPMs 37 reflect the function of the
also determines CO & MAP oxygenator (e.g. clot burden).
You might also like
- Tobin Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation 3rd EditionDocument1,585 pagesTobin Principles and Practice of Mechanical Ventilation 3rd EditionLuis Lopez Reveles77% (22)
- @anesthesia Books 2019 Hensley's PDFDocument1,175 pages@anesthesia Books 2019 Hensley's PDFAurora Herrera100% (1)
- Vent Modes ChartDocument1 pageVent Modes Chartladyhavocinc100% (1)
- Pulmonary Catheter Learning Package PDFDocument36 pagesPulmonary Catheter Learning Package PDFnisar khanNo ratings yet
- 2022 Mechanical Ventilation From Pathophysiology To Clinical EvidenceDocument422 pages2022 Mechanical Ventilation From Pathophysiology To Clinical EvidenceJose Castellon75% (4)
- Control of Mechanical VentilationDocument6 pagesControl of Mechanical VentilationMichael Levit100% (1)
- MCU 2021 The Ventilator Book 3rd EditionDocument280 pagesMCU 2021 The Ventilator Book 3rd EditionAlvaro Estupiñan100% (2)
- Cheese Making TechnologyDocument70 pagesCheese Making TechnologynataliatirtaNo ratings yet
- The PCM International Edition v1 Interactive PDFDocument111 pagesThe PCM International Edition v1 Interactive PDFDaniel Augusto Buendia GómezNo ratings yet
- Nurse EcmoDocument124 pagesNurse EcmoSalvatore Cimino100% (5)
- ECMO Cardiac SurgeryDocument54 pagesECMO Cardiac SurgeryMuaath Algoribi100% (3)
- Arterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyFrom EverandArterial Blood Gas Analysis - making it easyRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Haemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideFrom EverandHaemodynamic Monitoring & Manipulation: an easy learning guideNo ratings yet
- ECMO-Extracorporeal+Life+Support+in+Adul (Estudio)Document475 pagesECMO-Extracorporeal+Life+Support+in+Adul (Estudio)Christian Espinoza Silva100% (1)
- Ventilation Cheat SheetDocument1 pageVentilation Cheat Sheetlizzy59683% (6)
- Cardiopulmonary by PassDocument62 pagesCardiopulmonary by PassRezwanul Hoque Bulbul100% (1)
- Basic EcmoDocument62 pagesBasic EcmoBasantkumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Ecmo - Extracorporeal Life Support in AdultsDocument475 pagesEcmo - Extracorporeal Life Support in AdultsMatias Flamm100% (4)
- Ecmo Basic ConceptsDocument37 pagesEcmo Basic Conceptskhoniker bondhuNo ratings yet
- ECMO Management Lecture 5Document39 pagesECMO Management Lecture 5dnafredyNo ratings yet
- Ecmo GuidelineDocument64 pagesEcmo GuidelineDavid Martinez100% (3)
- The Ventilator BookDocument126 pagesThe Ventilator BookAlberto David100% (22)
- ELSO Guidelines For ECMO CentersDocument7 pagesELSO Guidelines For ECMO CentersFernando AlvesNo ratings yet
- Inotropes in Cardiothoracic SurgeryDocument44 pagesInotropes in Cardiothoracic SurgeryMarce8118100% (1)
- Manual EcmoDocument47 pagesManual EcmoBelen NikonNo ratings yet
- Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Support in Critically Ill Adult Patients - Is Its Use Evidence Driven?Document37 pagesExtracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: Support in Critically Ill Adult Patients - Is Its Use Evidence Driven?SNo ratings yet
- ECMO BasicsDocument72 pagesECMO Basicszhelle2100% (2)
- Anaesthesia Management of Patient of PacemakerDocument92 pagesAnaesthesia Management of Patient of PacemakerSiva KrishnaNo ratings yet
- 4 5969910185303475765 PDFDocument116 pages4 5969910185303475765 PDFEdy Tahir MattoreangNo ratings yet
- Mechanical+Ventilation-Basics+for+Beginners (Unlocked by ComDocument49 pagesMechanical+Ventilation-Basics+for+Beginners (Unlocked by Comdokidok100% (14)
- ECMO ExplanationDocument16 pagesECMO Explanationbreaking nurse100% (1)
- Pacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingDocument57 pagesPacemaker Invasive Cardiac PacingAhmad Khalil Ahmad Al-SadiNo ratings yet
- ECMO Learning PackageDocument35 pagesECMO Learning PackageAndrewNo ratings yet
- Retrograde Autologous Priming of Cardiopulmonary Bypass CircuitDocument18 pagesRetrograde Autologous Priming of Cardiopulmonary Bypass CircuitMuhammad Badrushshalih100% (2)
- Cardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsDocument46 pagesCardiac Pacing For The SurgeonsRezwanul Hoque BulbulNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Equipment: By:-Dr. Armaanjeet Singh Moderator: - Dr. Bikram GuptaDocument32 pagesCardiopulmonary Bypass: Equipment: By:-Dr. Armaanjeet Singh Moderator: - Dr. Bikram GuptaJohn Queen100% (2)
- ECMO Protocol AustraliaDocument17 pagesECMO Protocol AustraliaBiswarup Purkayastha100% (1)
- Echmo in Adult PatientDocument169 pagesEchmo in Adult PatientKorash Badiani100% (1)
- Cardiac Pacing Learning Package 2013Document34 pagesCardiac Pacing Learning Package 2013Chetan Amberkar100% (1)
- ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)Document39 pagesECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation)Linto John100% (1)
- Angiographic Views and Nomencluture PDFDocument36 pagesAngiographic Views and Nomencluture PDFZahidNo ratings yet
- Ecmo PDFDocument5 pagesEcmo PDFAarti Dalwani100% (1)
- @anesthesia - Books 2021 Respiratory Critical Care 1st EditionDocument964 pages@anesthesia - Books 2021 Respiratory Critical Care 1st EditionAlex Detick100% (2)
- Myocardial ProtectionDocument77 pagesMyocardial Protectiondrbrdas100% (1)
- Pulmonary Artery CatheterDocument32 pagesPulmonary Artery Catheterwaqas_xs100% (1)
- 37 Pediatric Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument19 pages37 Pediatric Cardiopulmonary BypassDavid Montoya100% (2)
- EKG in IHDDocument349 pagesEKG in IHDDinhLinh100% (1)
- Noninvasive Mechanical Ventilation and Difficult Weaning in Critical CareDocument442 pagesNoninvasive Mechanical Ventilation and Difficult Weaning in Critical CareCritical Group100% (8)
- Adequacy of Perfusion During Cardiopulmonary BypassDocument64 pagesAdequacy of Perfusion During Cardiopulmonary BypassBranka Kurtovic50% (2)
- Respiratory Critical CareDocument323 pagesRespiratory Critical CarePriyadarshini Varadaraj100% (6)
- ECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!From EverandECG & EKG Interpretation: How to interpret ECG & EKG, including rhythms, arrhythmias, and more!No ratings yet
- Ventilator Grafik WeaponDocument6 pagesVentilator Grafik Weaponiqbal100% (1)
- Pilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6e-17-31Document15 pagesPilbeam's Mechanical Ventilation Physiological and Clinical Applications 6e-17-31Lesly Peinado TorresNo ratings yet
- Plante PacemakersDocument57 pagesPlante Pacemakersdragon66100% (1)
- Echocardiography in Hemodynamic MonitoringDocument5 pagesEchocardiography in Hemodynamic MonitoringDr.Biswajit jenaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Resuscitation - Dita AditianingsihDocument48 pagesFluid Resuscitation - Dita AditianingsihGalih Wicaksono100% (1)
- Icu Survival Guide: SUNY Upstate Medical UniversityDocument36 pagesIcu Survival Guide: SUNY Upstate Medical UniversitySAUMOJIT MAJUMDERNo ratings yet
- 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Document7 pages12 Lead EKG Interpretation Part 1Nuru99100% (1)
- ICU One Pager NIPPVDocument1 pageICU One Pager NIPPVNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Massive Hemoptysis v11Document1 pageICU One Pager Massive Hemoptysis v11Nicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager HypoxemiaDocument1 pageICU One Pager HypoxemiaNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Blood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientDocument1 pageBlood Flow Q: The Transmembrane Pressure (TMP) GradientNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Abdominal Compartment SyndromeDocument1 pageICU One Pager Abdominal Compartment SyndromeNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Lactic AcidosisDocument1 pageICU One Pager Lactic AcidosisNicholas Helmstetter100% (1)
- ICU One Pager Minnesota TubeDocument1 pageICU One Pager Minnesota TubeNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- 1001 Songs You Must Hear Before You Die 27526Document7 pages1001 Songs You Must Hear Before You Die 27526Nicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Guide Beer Flavor Zymurgy-1987 PDFDocument21 pagesGuide Beer Flavor Zymurgy-1987 PDFNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Movesets)Document158 pagesMovesets)Nicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Flexiflo TankTruckEquipmentsDocument20 pagesFlexiflo TankTruckEquipmentstdecebalus100% (2)
- Parallel Lines Cut by A TransversalDocument2 pagesParallel Lines Cut by A TransversalAnita MeghaniNo ratings yet
- BID2Document2 pagesBID2Inversiones Llanolab, c.a. LlanolabNo ratings yet
- Logic: Evaluation ProjectDocument43 pagesLogic: Evaluation ProjectDC ArkinNo ratings yet
- Notes in Fire Technology & Arson Investigation Evolution of FireDocument41 pagesNotes in Fire Technology & Arson Investigation Evolution of FireYangBedoyaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry: Metall RgyDocument136 pagesChemistry: Metall Rgymukesh kannaNo ratings yet
- A Fully Coupled Hydraulic-Mechanical Solution of A Circular Tunnel in Strain-Softening Rock MassesDocument14 pagesA Fully Coupled Hydraulic-Mechanical Solution of A Circular Tunnel in Strain-Softening Rock MassesqgliangNo ratings yet
- Vin PDFDocument294 pagesVin PDFAnonymous DR7W37SeqNo ratings yet
- National T Esting Agency: GeographyDocument28 pagesNational T Esting Agency: GeographyMahesh B RajputNo ratings yet
- Debug The RPTIME00Document9 pagesDebug The RPTIME00zafer nadeemNo ratings yet
- Exploratory Factor Analysis On Road Accidents in Cagayan de Oro CityDocument23 pagesExploratory Factor Analysis On Road Accidents in Cagayan de Oro CityEino DuldulaoNo ratings yet
- Class Work - 4 - Solutions PDFDocument9 pagesClass Work - 4 - Solutions PDFRaymond LeoNo ratings yet
- 2009 S Pre Exam2 Review 6up PDFDocument9 pages2009 S Pre Exam2 Review 6up PDFLuis MateoNo ratings yet
- Pre CalculusDocument8 pagesPre CalculusBryan SaligaoNo ratings yet
- CMP1401: Introduction To Programming With C: Ece Gelal Soyak Bahc Es Ehir UniversitesiDocument24 pagesCMP1401: Introduction To Programming With C: Ece Gelal Soyak Bahc Es Ehir UniversitesidoaaNo ratings yet
- Use Sqlite002Document4 pagesUse Sqlite002eliseo fuertesNo ratings yet
- VBScript HandoutDocument78 pagesVBScript Handoutaruns2012No ratings yet
- Efficient Test and Commissioning of SIPROTEC 5 CompactDocument13 pagesEfficient Test and Commissioning of SIPROTEC 5 CompactMohamed wahidNo ratings yet
- ThermoDocument12 pagesThermokesiled309No ratings yet
- Understanding Disciplines and School Subjects PDFDocument28 pagesUnderstanding Disciplines and School Subjects PDFSham0% (1)
- DP MassStorage wnt6-x64 1110 Vista-7-X64Document89 pagesDP MassStorage wnt6-x64 1110 Vista-7-X64sonuNo ratings yet
- Bioresource Technology: Mirjana G. Antov, Marina B. ŠC Iban, Nada J. PetrovicDocument3 pagesBioresource Technology: Mirjana G. Antov, Marina B. ŠC Iban, Nada J. PetrovicSulaiman OluwapelumiNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Overview of VibrationsDocument56 pages5.1 Overview of VibrationsAbhishek PandeyNo ratings yet
- New Time Table 2081Document2 pagesNew Time Table 2081shankalprajkhanalNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Amsayu HomeworkDocument1 pageCalculation of Amsayu HomeworkGautamNo ratings yet
- Limitations of Neuropsychological Tests and Remedial MeasuresDocument8 pagesLimitations of Neuropsychological Tests and Remedial MeasuresInternational Journal of Current Research in Science and TechnologyNo ratings yet
- SoltuionsDocument19 pagesSoltuionsBe-fit Be-strongNo ratings yet
- Cash Flow Estimation: Tugas 7 Accounting and FinanceDocument5 pagesCash Flow Estimation: Tugas 7 Accounting and FinanceJessy SeptalistaNo ratings yet
- Apluslift HW 10kbpDocument17 pagesApluslift HW 10kbpGBNo ratings yet