Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Group Performance CHPT 13
Group Performance CHPT 13
Uploaded by
Şterbeţ RuxandraOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Group Performance CHPT 13
Group Performance CHPT 13
Uploaded by
Şterbeţ RuxandraCopyright:
Available Formats
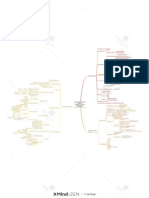
sum of member's performance
additive
e.g. brainstorming
qualitative (maximization) or
quantitative (optimization)
best member's performance
Bias Intensity explanations for failure
Compared to actual unitary or divisible three types
performances occuring when disjunctive
hypothetically working idependently are added group performance (AGP)
e.g. problem solving eureka effect
Potential Group Performance (PGP) Types of Group Tasks
Insufficient all member have to be successful
Discussion biases Discusion Intensity Discussion of information
qualities of members
should fit each other conjuncvtive
solution: equally consider shared and unshared solution: presenting every own point Core Concepts
info avoiding repeated focus on info building (repeating) and avoid to give own weakest member's increased group size =
initial preference - avoid biased shared knowledge opinion (based on own points), motivation specifies certain performance is the result decreased potential
characteristics/knowledge are
distributed within group
hidden profile task Group Composition
info. distributed so that
Insuficcient individuals cannot come up
evaluation biases Processing of Information
Processing intensity with solution with own info
solution: avoid assuming shared info as more solution: processing other member's
sharing info is crucial
accurate, avoid assuming info consistent with info. and integrate in own opinion by Group Performance
own prefernec is more accurate avoid sticking to own preferences
sum of activities aimed at
counters social loafing, maximizing the group specific
dispensability component of group performing AGP= PGP - process
losses + process gains
feedback affecting
continous visibility of optimizing the collaborative generation, Group Performance Management
individual contributes modification and integration of individual Group Process
documenting contributions in a group
three basic principles
techniques Group Synchronization
deviding desicion-making in
phases
specific
debate, devils advocacy dialectical
physical tasks - average
Losses Gains
performance of indivdual ringelmann effect
decreses with group size
solution: nominal group production blocking brainstorming
Coordination
same group size, one idea per time; trust
members work authorities (especially
increased group repeated individual task performance disjunctive tasks)
Individual-to-individual transfer individually
potential results in individual growth
relevant and collective
only if individual
contribution is visible!
strong effect in
additive task importance of group
own contribution not visible social loafing goals
Social competition outperforming each other
stronger members compensate
for weaker members
contributions seem to
increased group repeated collective task performance dispensability Motivation Motivation Social compensation
have little impact
potential results in individual growth Group-to-individual transfer
additive tasks mostly
role induction
task
anticipating other's reduction sucker effect avoid being responsible for weak
of effort, avoid being exploited group performance - effort (work harder)
depends on status Köhler effect
(strong-weak)
Group Learning
conjunctive tasks mostly
learning processes that can only
occur if several people work
interactively on the same task
improved actual repeated collective task performance Group-to-individual-in-group
group performance results in member's improved ability to transfer
perform within groups focus on one idea after being idea mentioned stimulates
Individual Individual
mentiones, at expense of thinking cognitive restriction cognitive stimulation consideration of category
capability capability
about other categories otherwise neglected
Social Influence
improved actual repeated collective task performance
group performance results in group's improved ability to Group-to-group transfer
perform group tasks
You might also like
- DWDM PosterDocument1 pageDWDM Posterapi-3806249100% (1)
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 3: MathRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Code2flow - Online Interactive Code To Flowchart ConverterDocument1 pageCode2flow - Online Interactive Code To Flowchart ConverterFrandi CahyaNo ratings yet
- Reliability Web 5 Sources of Defects SecureDocument1 pageReliability Web 5 Sources of Defects SecureHaitham YoussefNo ratings yet
- Morven Tract HD Final Report With Forms 1209Document147 pagesMorven Tract HD Final Report With Forms 1209Planet PrincetonNo ratings yet
- Exalted 3rd Edition Charm Cascades Legend: Any Five Essence 2+ Performance Charms ???Document1 pageExalted 3rd Edition Charm Cascades Legend: Any Five Essence 2+ Performance Charms ???merashinNo ratings yet
- 1503off SubseaposterDIG PDFDocument1 page1503off SubseaposterDIG PDFHWANG INBUMNo ratings yet
- 1 WSF Risk Management PlanDocument7 pages1 WSF Risk Management PlanYong Kim100% (1)
- Purpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateDocument1 pagePurpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateKrati JainNo ratings yet
- Purpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateDocument1 pagePurpose: IIM Sambalpur Fill RateKrati JainNo ratings yet
- Workload Analysis Form - M. HERNANDEZDocument10 pagesWorkload Analysis Form - M. HERNANDEZMiguel HernandezNo ratings yet
- SwotDocument1 pageSwotMoses KimNo ratings yet
- XB2BD33 DATASHEET AU en-GB PDFDocument1 pageXB2BD33 DATASHEET AU en-GB PDFCaarlosNo ratings yet
- Improving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter Tuning, Regularization and OptimizationDocument1 pageImproving Deep Neural Networks: Hyperparameter Tuning, Regularization and OptimizationSharath Poikayil SatheeshNo ratings yet
- MODEL - FUNCTION Chart W - Step 2.5 Jan09Document1 pageMODEL - FUNCTION Chart W - Step 2.5 Jan09Anthony FelixNo ratings yet
- Amazon Context Map v1 1009182Document1 pageAmazon Context Map v1 1009182Lydia TariganNo ratings yet
- Interview List of HEC Needbased Scholarship FY 2023-2024Document16 pagesInterview List of HEC Needbased Scholarship FY 2023-2024ali03315873No ratings yet
- The Schur Algorithm: Digtal Signal Processing (Et 4235)Document22 pagesThe Schur Algorithm: Digtal Signal Processing (Et 4235)KrishNo ratings yet
- Mind MapDocument1 pageMind Mapsmellypoopy0708No ratings yet
- CRM Foundation ERD PDFDocument1 pageCRM Foundation ERD PDFmamidilkNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Identifying Reasoning Verb Deepen UnderstandingDocument6 pagesModule 5 Identifying Reasoning Verb Deepen Understandingbaronganjennalynpsu.edu.ph psu san carlosNo ratings yet
- MathDocument1 pageMathassal2007faisalNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Math Summary Notes For Some TopicsDocument2 pagesIGCSE Math Summary Notes For Some TopicsskyeNo ratings yet
- Panoma (Council Grove) Geomodel Initial Simulations (Single Well)Document1 pagePanoma (Council Grove) Geomodel Initial Simulations (Single Well)BouregaNo ratings yet
- Ai Anatomy MapDocument1 pageAi Anatomy MapIoan Alexandru FierascuNo ratings yet
- 00702725_Fcontrol & IcontrolDocument2 pages00702725_Fcontrol & IcontrolRHETT BUTLERNo ratings yet
- As App Vs Rev Foot1675404512947Document2 pagesAs App Vs Rev Foot1675404512947Fadi AlatrashNo ratings yet
- Production Report ViosDocument1 pageProduction Report ViosAdam FarishNo ratings yet
- Description / Caractéristiques de Base: ApacitésDocument1 pageDescription / Caractéristiques de Base: ApacitésyukiyurikiNo ratings yet
- WHITEBOARD - AcctgDocument1 pageWHITEBOARD - Acctgkhyla Marie NooraNo ratings yet
- ARKI 2023 Entire Course Cheat SheetDocument1 pageARKI 2023 Entire Course Cheat Sheetbourguibaahmed8No ratings yet
- Appraisal FormDocument8 pagesAppraisal FormSanjukta GanguliNo ratings yet
- Code2floww PDFDocument1 pageCode2floww PDFFrandi CahyaNo ratings yet
- Code2flow - Online Interactive Code To Flowchart Converter PDFDocument1 pageCode2flow - Online Interactive Code To Flowchart Converter PDFFrandi CahyaNo ratings yet
- WTSL Master MapDocument1 pageWTSL Master Mapjoshkek1942No ratings yet
- APEX Cities BrochureDocument7 pagesAPEX Cities Brochureissp.indonesiaNo ratings yet
- 4669 006 Saa DWG 00 FX 5100Document1 page4669 006 Saa DWG 00 FX 5100PKP MECHNo ratings yet
- Appendix 5 MOPO ToucanDocument2 pagesAppendix 5 MOPO ToucanOndo Akwe SergeNo ratings yet
- Masters in Management 2018 PDFDocument1 pageMasters in Management 2018 PDFArnab MaitiNo ratings yet
- Na 172-Ryk-IV Staff DeutyDocument20 pagesNa 172-Ryk-IV Staff DeutyAreej FatimaNo ratings yet
- Illumination Design: Single Dwelling JAJ Sentina JAJ SentinaDocument2 pagesIllumination Design: Single Dwelling JAJ Sentina JAJ SentinaEl Vee Joice HaroNo ratings yet
- Balance Sheet Eng 05-06Document1 pageBalance Sheet Eng 05-06sashdreamNo ratings yet
- FF Service Si-006 Vs Si-029-R1Document12 pagesFF Service Si-006 Vs Si-029-R1Chilo InNo ratings yet
- DWDM Impairments Optical Transport Networks (OTN) : Linear EffectsDocument1 pageDWDM Impairments Optical Transport Networks (OTN) : Linear Effectskapil dev pandeyNo ratings yet
- Performance Manage MenDocument1 pagePerformance Manage MenmariaaltammamNo ratings yet
- To Jersey City: Weekdays Saturdays Sundays HolidaysDocument2 pagesTo Jersey City: Weekdays Saturdays Sundays Holidaysph2020No ratings yet
- Module 2 AssessmentDocument3 pagesModule 2 AssessmentSheela AliNo ratings yet
- Maintain Safe Work EnvironmentDocument3 pagesMaintain Safe Work EnvironmentSana buttNo ratings yet
- Value TreeDocument1 pageValue TreeMaisaa NajiNo ratings yet
- DR.M Rafat Ka Tassure IlmDocument5 pagesDR.M Rafat Ka Tassure IlmMuhammad GhitreefNo ratings yet
- STR DEX CON WIS CAR: Saving ThrowsDocument2 pagesSTR DEX CON WIS CAR: Saving Throwssemola72No ratings yet
- REKAPGPMB2010BABAKFINALDocument2 pagesREKAPGPMB2010BABAKFINALSang PemimpiNo ratings yet
- Competitor PresentationDocument6 pagesCompetitor PresentationRangarajan SrinivasaNo ratings yet
- JVC ElevationDocument1 pageJVC ElevationSwed F Almahmoud. JVCNo ratings yet
- SCALEXIO IO OverviewDocument1 pageSCALEXIO IO OverviewmanirnaiduNo ratings yet
- (22-03-14) GV350CEU - Supported Car Models and Logistic Parameters (All Vehicles) TableDocument17 pages(22-03-14) GV350CEU - Supported Car Models and Logistic Parameters (All Vehicles) Tablemohamed.khalidNo ratings yet
- PROY AM-Layout4Document1 pagePROY AM-Layout4Cangatron 14No ratings yet
- Instant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: MathFrom EverandInstant Assessments for Data Tracking, Grade 1: MathRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Parenting Styles+ Locus of Control Vs BullyingDocument18 pagesParenting Styles+ Locus of Control Vs BullyingŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- The Utah Marriage HandbookDocument52 pagesThe Utah Marriage HandbookŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Counseling TechniquesDocument369 pagesCounseling TechniquesŞterbeţ Ruxandra100% (6)
- Connect: Engaging in A Positive Social Network of SupportDocument8 pagesConnect: Engaging in A Positive Social Network of SupportŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Using Nurturing, Caring, and Affectionate Behaviors: What Care Looks LikeDocument6 pagesUsing Nurturing, Caring, and Affectionate Behaviors: What Care Looks LikeŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 20: Education: Schooling, Learning Difficulties and High IntelligenceDocument10 pagesModule 20: Education: Schooling, Learning Difficulties and High IntelligenceŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Nermem 04 KnowDocument8 pagesNermem 04 KnowŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 16: Language and Communication: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 16: Language and Communication: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Share: Developing and Maintaining A Couple IdentityDocument8 pagesShare: Developing and Maintaining A Couple IdentityŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 21: Health and Nutrition in A Child's DevelopmentDocument10 pagesModule 21: Health and Nutrition in A Child's DevelopmentŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Care For Self: Maintaining Physical, Sexual, Emotional, and Spiritual WellnessDocument8 pagesCare For Self: Maintaining Physical, Sexual, Emotional, and Spiritual WellnessŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 19: Gender Roles and Differences: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 19: Gender Roles and Differences: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 11: Social Development: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages11: Social Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 14: Attachment and Relationship Building: Student ObjectivesDocument8 pagesModule 14: Attachment and Relationship Building: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 15: The Role of Separation in Child DevelopmentDocument10 pagesModule 15: The Role of Separation in Child DevelopmentŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 18: Behavioral Problems: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 18: Behavioral Problems: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 13: Intellectual Development: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 13: Intellectual Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 10: Physical Development: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pages10: Physical Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 09: The Nature/Nurture Debate: Student ObjectivesDocument8 pages09: The Nature/Nurture Debate: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 04: Cognitive Development in The First Year: Student ObjectivesDocument8 pages04: Cognitive Development in The First Year: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 17: Self-Esteem and Confidence: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 17: Self-Esteem and Confidence: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 02: Child Development Research and Theories: Student ObjectivesDocument7 pagesModule 02: Child Development Research and Theories: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 22: Developing Into Adulthood: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 22: Developing Into Adulthood: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 07: Cognitive Development and The Teenage Years: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages07: Cognitive Development and The Teenage Years: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 06: Cognitive Development in The Middle Years: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages06: Cognitive Development in The Middle Years: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 12: Emotional Development: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pages12: Emotional Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 03: An Overview of Cognitive Development: Student ObjectivesDocument10 pagesModule 03: An Overview of Cognitive Development: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- 05: Cognitive Development in The Toddler and Preschool YearsDocument9 pages05: Cognitive Development in The Toddler and Preschool YearsŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Child Psychology Worksheet Module 17Document6 pagesChild Psychology Worksheet Module 17Şterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- Module 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesDocument9 pagesModule 08: Genetics: Student ObjectivesŞterbeţ RuxandraNo ratings yet
- OJEE 2012 BrochureDocument52 pagesOJEE 2012 BrochureNityabrata DasNo ratings yet
- Differentiated Performance Task TemplateDocument2 pagesDifferentiated Performance Task TemplateMarjorie LescanoNo ratings yet
- La Consolacion College-Arfien DepartmentDocument10 pagesLa Consolacion College-Arfien DepartmentEmilyn Mae SuertoNo ratings yet
- Body Image: Magdalena Razmus, Wiktor RazmusDocument5 pagesBody Image: Magdalena Razmus, Wiktor RazmusEsLu CleomarNo ratings yet
- Pinata Project RubricDocument2 pagesPinata Project Rubricapi-272211615No ratings yet
- Periodic Rating FR Remarks Periodic Rating 1 2 3 4 1 2: Elementary School ProgressDocument8 pagesPeriodic Rating FR Remarks Periodic Rating 1 2 3 4 1 2: Elementary School ProgresstotChingNo ratings yet
- Computer GraphicsDocument5 pagesComputer Graphicsmdharma;No ratings yet
- The NCBTSDocument2 pagesThe NCBTSJesieca BulauanNo ratings yet
- OBE in Technical Writing 2 Police Report Writing (BSCrim)Document4 pagesOBE in Technical Writing 2 Police Report Writing (BSCrim)DJEMC CCJENo ratings yet
- LP Math F3 - Chapter 4Document16 pagesLP Math F3 - Chapter 4ckgfiezahNo ratings yet
- DLP Grade9 Mapeh Q4 Cot2Document3 pagesDLP Grade9 Mapeh Q4 Cot2Jerome PinedaNo ratings yet
- Project Report - An OutlookDocument11 pagesProject Report - An OutlookHamza MudassirNo ratings yet
- SSII JRRG v7 fs12-13Document5 pagesSSII JRRG v7 fs12-13Jan Robert Ramos GoNo ratings yet
- MATH0312 CdoDocument10 pagesMATH0312 CdoNonoyTaclinoNo ratings yet
- FototerapiaDocument137 pagesFototerapiaJ100% (1)
- CLIL Tool Kit WorkshopDocument30 pagesCLIL Tool Kit WorkshopMc BelleNo ratings yet
- Detroit Achievement Academy Founding Teacher Position Information PacketDocument6 pagesDetroit Achievement Academy Founding Teacher Position Information PacketdetroitachievementNo ratings yet
- The Movement #MenaretrashDocument10 pagesThe Movement #MenaretrashFeminists In AfricaNo ratings yet
- Lindsay Helfman: CertificationDocument2 pagesLindsay Helfman: Certificationapi-543834914100% (1)
- 21st Century Education SystemDocument24 pages21st Century Education SystemAmit Phand100% (1)
- Story About Tissues and The TigersDocument6 pagesStory About Tissues and The Tigerswisma saputraNo ratings yet
- PNP Request LetterDocument1 pagePNP Request LetterAnonymous eIuK74dRNo ratings yet
- SW 3010Document21 pagesSW 3010api-312630116No ratings yet
- Form WVSU-OSA-SOI-01-F03 0 West Visayas State University July 10, 2015 OSA Page 1 of 2Document2 pagesForm WVSU-OSA-SOI-01-F03 0 West Visayas State University July 10, 2015 OSA Page 1 of 2Jaimilyn Gabuyo JoseNo ratings yet
- On TargetDocument36 pagesOn TargetCadet LibraryNo ratings yet
- Project R.E.D.O.: (Reach Out and Encourage The Student Not ToDocument5 pagesProject R.E.D.O.: (Reach Out and Encourage The Student Not ToMaricelNo ratings yet
- DirectoryDocument6 pagesDirectoryMaricel ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Syllabus: Life Care PlanningDocument7 pagesSyllabus: Life Care PlanningAnonymous EAhdEfPK0kNo ratings yet
- Ippd Form 1 - Teacher'S Individual Plan For Professional Development (Ippd)Document2 pagesIppd Form 1 - Teacher'S Individual Plan For Professional Development (Ippd)Josephine Manigos100% (1)